java线程安全之并发Queue
2019-01-06 23:05 GarfieldEr007 阅读(651) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报java线程安全之并发Queue(十三)
并发Queue
在并发的队列上jdk提供了两套实现,一个是以ConcurrentLinkedQueue为代表的高性能队列,一个是以BlockingQueue接口为代表的阻塞队列,无论在那种都继承自Queue。
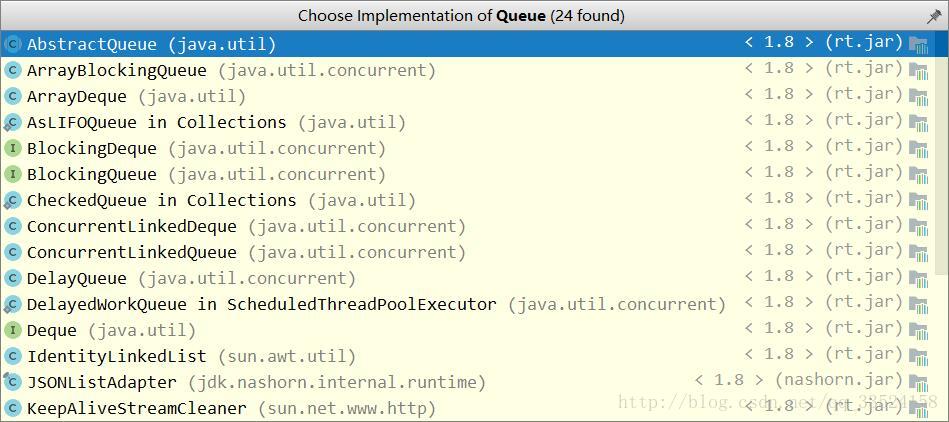
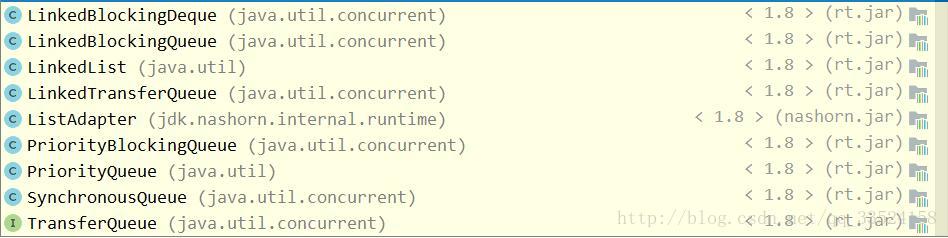
如图继承Queue共有二十四个:
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
概念理解
ConcurrentLinkedQueue:是一个适用于高并发场景下的队列,通过无锁的方式,实现了高并发状态下的高性能,通常ConcurrentLinkedQueue性能好于BlockingQueueo它是一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列。该队列的元素遵循先讲先出的原则。头是最先加入的,尾是最近加入的,该队列不允许null元素。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue重要方法:
Add()和offer()都是加入元素的方法(在ConcurrentLinkedQueue中,这两个方法投有任何区别)
Poll()和peek()都是取头元素节点,区别在于前者会删除元素,后者不会。
案例
public class UseQueue_ConcurrentLinkedQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//高性能无阻塞无界队列:ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>();
q.offer("a");
q.offer("b");
q.offer("c");
q.offer("d");
q.add("e");
System.out.println("从头部取出元素,并从队列里删除 >> "+q.poll()); //a 从头部取出元素,并从队列里删除
System.out.println("删除后的长度 >> "+q.size()); //4
System.out.println("取出头部元素 >> "+q.peek()); //b
System.out.println("长度 >> "+q.size()); //4
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
打印结果:
从头部取出元素,并从队列里删除 >> a
删除后的长度 >> 4
取出头部元素 >> b
长度 >> 4- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
BlockingQueue接口
ArrayBlockingQueue:基于数组的阻塞队列实现,在ArrayBlockingQueue内部,维护了一个定长数组,以便缓存队列中的数据对象,其内部没实现读写分离,也就意味着生产和消费不能完全并行,长度是需要定义的,可以指定先讲先出或者先讲后出,也叫有界队列,在很多场合非常适合使用。
LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表的阻塞队列,同ArrayBlockingQueue类似,其内部也维持着一个数据缓冲队列〈该队列由一个链表构成),LinkedBlockingQueue之所以能够高效的处理并发数据,是因为其内部实现采用分离锁(读写分离两个锁),从而实现生产者和消费者操作的完全并行运行,他是一个无界队列。
SynchronousQueue:一种没有缓冲的队列,生产者产生的数据直接会被消费者获取并消费。
PriorityBlockingQueue:基于优先级的阻塞队列(优先级的判断通过构造函数传入的Compator对象来决定,也就是说传入队列的对象必须实现Comparable接口),在实现PriorityBlockingQueue时,内部控制线程同步的锁采用的是公平锁,他也是一个无界的队列。
DelayQueue:带有延迟时间的Queue,其中的元素只有当其指定的延迟时间到了,才能够从队列中获取到该元素。DelayQueue中的元素必须实现Delayed接口,DelayQueue是一个没有大小限制的队列,应用场景很多,比如对缓存超时的数据进行移除、任务超时处理、空闲连接的关闭等等。
ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue、synchronousQueue案例
public class UseQueue_ConcurrentLinkedQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("--------------- ArrayBlockingQueue --------------");
//阻塞队列 有长度的队列
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> array = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(5);
array.put("a");
array.put("b");
array.add("c");
array.add("d");
array.add("e");
//array.add("f");
//返回一个布尔类型 在3秒之内能不能加入 不能返回false
System.out.println(array.offer("a", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("所有数据 >> " + array.toString());
System.out.println("--------------- LinkedBlockingQueue --------------");
//阻塞队列 无长度限制队列
LinkedBlockingQueue<String> q = new LinkedBlockingQueue<String>();
q.offer("a");
q.offer("b");
q.offer("c");
q.offer("d");
q.offer("e");
q.add("f");
System.out.println("总长度 >> "+q.size());
for (Iterator iterator = q.iterator(); iterator.hasNext(); ) {
String string = (String) iterator.next();
System.out.print(string+" -- ");
}
System.out.println();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
//在 q 的队列中取三个元素放到list 队列里
System.out.println(q.drainTo(list, 3));
System.out.println("取出LinkedBlockingQueue数据放到list列表的长度为 >> "+list.size());
for (String string : list) {
System.out.print(string + " -- ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------------- SynchronousQueue --------------");
final SynchronousQueue<String> q1 = new SynchronousQueue<String>();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取数据 "+ q1.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
q1.add("b");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"加入数据 b");
}
});
t2.start();
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
打印结果
--------------- ArrayBlockingQueue --------------
false
所有数据 >> [a, b, c, d, e]
--------------- LinkedBlockingQueue --------------
总长度 >> 6
a -- b -- c -- d -- e -- f --
3
取出LinkedBlockingQueue数据放到list列表的长度为 >> 3
a -- b -- c --
--------------- SynchronousQueue --------------
Thread-1加入数据 b
Thread-0取数据 b- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
PriorityBlockingQueue 案例
Task.java
public class Task implements Comparable<Task>{
private int id ;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Task task) {
return this.id > task.id ? 1 : (this.id < task.id ? -1 : 0);
}
public String toString(){
return this.id + "," + this.name;
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
UsePriorityBlockingQueue.java
public class UsePriorityBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
PriorityBlockingQueue<Task> q2 = new PriorityBlockingQueue<Task>();
Task t1 = new Task();
t1.setId(3);
t1.setName("id为3");
Task t2 = new Task();
t2.setId(4);
t2.setName("id为4");
Task t3 = new Task();
t3.setId(1);
t3.setName("id为1");
Task t4 = new Task();
t4.setId(2);
t4.setName("id为2");
//return this.id > task.id ? 1 : 0;
q2.add(t1); //3
q2.add(t2); //4
q2.add(t3); //1
q2.add(t4);
// 1 3 4
//第一次取值时候是取最小的后面不做排序
System.out.println("容器:" + q2); //[1,id为1, 2,id为2, 3,id为3, 4,id为4]
//拿出一个元素后 又会取一个最小的出来 放在第一个
System.out.println(q2.take().getId());
System.out.println("容器:" + q2); //[2,id为2, 4,id为4, 3,id为3]
System.out.println(q2.take().getId());
System.out.println("容器:" + q2); //[3,id为3, 4,id为4]
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
打印结果
容器:[1,id为1, 2,id为2, 3,id为3, 4,id为4]
1
容器:[2,id为2, 4,id为4, 3,id为3]
2
容器:[3,id为3, 4,id为4]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
DelayQueue 案例
Wangmin.java
public class Wangmin implements Delayed {
private String name;
//身份证
private String id;
//截止时间
private long endTime;
//定义时间工具类
private TimeUnit timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS;
public Wangmin(String name,String id,long endTime){
this.name=name;
this.id=id;
this.endTime = endTime;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getId(){
return this.id;
}
/**
* 用来判断是否到了截止时间
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
//return unit.convert(endTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - unit.convert(System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return endTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* 相互批较排序用
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed delayed) {
Wangmin w = (Wangmin)delayed;
return this.getDelay(this.timeUnit) - w.getDelay(this.timeUnit) > 0 ? 1:0;
}
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
WangBa.java
public class WangBa implements Runnable {
private DelayQueue<Wangmin> queue = new DelayQueue<Wangmin>();
public boolean yinye =true;
public void shangji(String name,String id,int money){
Wangmin man = new Wangmin(name, id, 1000 * money + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("网名"+man.getName()+" 身份证"+man.getId()+"交钱"+money+"块,开始上机...");
this.queue.add(man);
}
public void xiaji(Wangmin man){
System.out.println("网名"+man.getName()+" 身份证"+man.getId()+"时间到下机...");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(yinye){
try {
Wangmin man = queue.take();
xiaji(man);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
System.out.println("网吧开始营业");
WangBa siyu = new WangBa();
Thread shangwang = new Thread(siyu);
shangwang.start();
siyu.shangji("路人甲", "123", 1);
siyu.shangji("路人乙", "234", 10);
siyu.shangji("路人丙", "345", 5);
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
打印结果:
网吧开始营业
网名路人甲 身份证123交钱1块,开始上机...
网名路人乙 身份证234交钱10块,开始上机...
网名路人丙 身份证345交钱5块,开始上机...
网名路人甲 身份证123时间到下机...
网名路人丙 身份证345时间到下机...
网名路人乙 身份证234时间到下机...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
BlockingQueue 接口的重要方法
放入数据:
offer(anObject):表示如果可能的话,将anObject加到BlockingQueue里,即如果BlockingQueue 可以容纳,则返回true,否则返回false.(本方法不阻蹇当前执行方法的线程)
offer(E 0,long timeout, TimeUnit unit),可以设定等待的时间,如果在指定的时间内,还不能往队列中加入BlockingQueue,则返回失败。
put(anObject):把anObject加到BlockingQueue里,如果BlockQueue没有空间,则调用此方法的线程被阻断直到BlokingQue里面有空间再继续,
获取数据:
poll(time):取走BlokingQueue里排在首位的对象,若不能立即取出,则可以等time参数规定的时间,取不到时返回null
poll(long timeout, Timeunit unit):从blockingQueue取出一个队首的对象,如果在指定时间内,队列一旦有数据可取,则立即返回队列中的数据。否则知道时间超时还没有数据可取,返回失败。
take():取走引BlockinQueue里排在首位的对象,若BlockingQueue为空,阻断进入等待状态直到BlckingQueue有新的数据被加入;
drainTo():一次性从BlockingQueue获取所有可用的数据对象(还可以指定获取数据的个数),通过该方法,可以提升获取数据效率:不需要多次分批加锁或释放锁。
Deque 双端队列
Deque允许在队列的头部活尾部进行出队和入队操作。
LinkedBlockingDeque是一个线程安全的双端队列实现,可以说他是最为复杂的一种队列,在内部实现维护了前端和后端节点,但是其没有实现读写分离,因此同一时间只能有一个线程对其讲行操作。在高并发中性能要远低于其他引。BlockingQueue。更要低于ConcurrentLinkedQueue,布jdk早期有一个非线程安全的Deque就是ArryDeque了, java6里添加了LinkBlockingDeque来弥补多线程场景下线程安全的问题。
案例
public class UseDeque {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<String> dq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<String>(10);
dq.addFirst("a");
dq.addFirst("b");
dq.addFirst("c");
dq.addFirst("d");
dq.addFirst("e");
dq.addLast("f");
dq.addLast("g");
dq.addLast("h");
dq.addLast("i");
dq.addLast("j");
//dq.offerFirst("k");
System.out.println("查看头元素:" + dq.peekFirst());
System.out.println("获取尾元素:" + dq.pollLast());
Object [] objs = dq.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {
System.out.print(objs[i] + " -- ");
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
打印结果:
查看头元素:e
获取尾元素:j
e -- d -- c -- b -- a -- f -- g -- h -- i --
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
LinkedBlockingDeque 方法说明
// 创建一个容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingDeque。
LinkedBlockingDeque()
// 创建一个容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingDeque,最初包含给定 collection 的元素,以该 collection 迭代器的遍历顺序添加。
LinkedBlockingDeque(Collection<? extends E> c)
// 创建一个具有给定(固定)容量的 LinkedBlockingDeque。
LinkedBlockingDeque(int capacity)
// 在不违反容量限制的情况下,将指定的元素插入此双端队列的末尾。
boolean add(E e)
// 如果立即可行且不违反容量限制,则将指定的元素插入此双端队列的开头;如果当前没有空间可用,则抛出 IllegalStateException。
void addFirst(E e)
// 如果立即可行且不违反容量限制,则将指定的元素插入此双端队列的末尾;如果当前没有空间可用,则抛出 IllegalStateException。
void addLast(E e)
// 以原子方式 (atomically) 从此双端队列移除所有元素。
void clear()
// 如果此双端队列包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
boolean contains(Object o)
// 返回在此双端队列的元素上以逆向连续顺序进行迭代的迭代器。
Iterator<E> descendingIterator()
// 移除此队列中所有可用的元素,并将它们添加到给定 collection 中。
int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c)
// 最多从此队列中移除给定数量的可用元素,并将这些元素添加到给定 collection 中。
int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements)
// 获取但不移除此双端队列表示的队列的头部。
E element()
// 获取,但不移除此双端队列的第一个元素。
E getFirst()
// 获取,但不移除此双端队列的最后一个元素。
E getLast()
// 返回在此双端队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器。
Iterator<E> iterator()
// 如果立即可行且不违反容量限制,则将指定的元素插入此双端队列表示的队列中(即此双端队列的尾部),并在成功时返回 true;如果当前没有空间可用,则返回 false。
boolean offer(E e)
// 将指定的元素插入此双端队列表示的队列中(即此双端队列的尾部),必要时将在指定的等待时间内一直等待可用空间。
boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 如果立即可行且不违反容量限制,则将指定的元素插入此双端队列的开头,并在成功时返回 true;如果当前没有空间可用,则返回 false。
boolean offerFirst(E e)
// 将指定的元素插入此双端队列的开头,必要时将在指定的等待时间内等待可用空间。
boolean offerFirst(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 如果立即可行且不违反容量限制,则将指定的元素插入此双端队列的末尾,并在成功时返回 true;如果当前没有空间可用,则返回 false。
boolean offerLast(E e)
// 将指定的元素插入此双端队列的末尾,必要时将在指定的等待时间内等待可用空间。
boolean offerLast(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 获取但不移除此双端队列表示的队列的头部(即此双端队列的第一个元素);如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
E peek()
// 获取,但不移除此双端队列的第一个元素;如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
E peekFirst()
// 获取,但不移除此双端队列的最后一个元素;如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
E peekLast()
// 获取并移除此双端队列表示的队列的头部(即此双端队列的第一个元素);如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
E poll()
// 获取并移除此双端队列表示的队列的头部(即此双端队列的第一个元素),如有必要将在指定的等待时间内等待可用元素。
E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 获取并移除此双端队列的第一个元素;如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
E pollFirst()
// 获取并移除此双端队列的第一个元素,必要时将在指定的等待时间等待可用元素。
E pollFirst(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 获取并移除此双端队列的最后一个元素;如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
E pollLast()
// 获取并移除此双端队列的最后一个元素,必要时将在指定的等待时间内等待可用元素。
E pollLast(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 从此双端队列所表示的堆栈中弹出一个元素。
E pop()
// 将元素推入此双端队列表示的栈。
void push(E e)
// 将指定的元素插入此双端队列表示的队列中(即此双端队列的尾部),必要时将一直等待可用空间。
void put(E e)
// 将指定的元素插入此双端队列的开头,必要时将一直等待可用空间。
void putFirst(E e)
// 将指定的元素插入此双端队列的末尾,必要时将一直等待可用空间。
void putLast(E e)
// 返回理想情况下(没有内存和资源约束)此双端队列可不受阻塞地接受的额外元素数。
int remainingCapacity()
// 获取并移除此双端队列表示的队列的头部。
E remove()
// 从此双端队列移除第一次出现的指定元素。
boolean remove(Object o)
// 获取并移除此双端队列第一个元素。
E removeFirst()
// 从此双端队列移除第一次出现的指定元素。
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)
// 获取并移除此双端队列的最后一个元素。
E removeLast()
// 从此双端队列移除最后一次出现的指定元素。
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o)
// 返回此双端队列中的元素数。
int size()
// 获取并移除此双端队列表示的队列的头部(即此双端队列的第一个元素),必要时将一直等待可用元素。
E take()
// 获取并移除此双端队列的第一个元素,必要时将一直等待可用元素。
E takeFirst()
// 获取并移除此双端队列的最后一个元素,必要时将一直等待可用元素。
E takeLast()
// 返回以恰当顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)包含此双端队列所有元素的数组。
Object[] toArray()
// 返回以恰当顺序包含此双端队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
// 返回此 collection 的字符串表示形式。
String toString()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
源代码:https://github.com/hfbin/Thread_Socket/tree/master/Thread/coll013
from: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33524158/article/details/78578370