libvlc —— 播放器示例程序[C++代码实现攫取 RGB图像 和 PCM音频 数据功能]
在我以前的实际项目中,曾利用 libvlc 去解码音视频媒体数据(如 RTSP、本地文件 等),通过其提供的回调函数接口,攫取 RGB图像 进行图像分析,如 人脸识别、运动检测 等一类的产品应用。除此之外,只要提供适当的 MRL,配合选项参数,VLC 还可以进行屏幕录制、摄像头图像采集、麦克风音频采集 等功能。
我在网上参看过很多人提供的示例源码,实现流程都很初潜,只适合当作学习的 Demo 来看,与实际的项目应用还有很多问题要解决。为此,在这里公开我封装 libvlc 的 C++ 类,方便TA人吧!
一、获取源码
1. 下载地址
Github: https://github.com/Gaaagaa/MediaGrabber
2. 编译提醒
这个测试程序,是使用 QtCreator 写的 Qt 界面程序,调用我封装好的 vlc_mgrabber_t 类实现了一个简单的播放器。MFC的我也写过相应的测试程序,这里就不重复提供代码了。
因 libvlc 库相关的 dll 文件太多、太大,上传不易,所以在完成编译后,需要另外将 libvlc 的 dll 拷贝至 exe 程序目录中才能运行,我使用的 libvlc 版本是 vlc-3.0.7.1 版,下面是下载地址:
- Win32版本:ftp://ftp.videolan.org/pub/videolan/vlc/3.0.7.1/win32/vlc-3.0.7.1-win32.7z
- Win64版本:ftp://ftp.videolan.org/pub/videolan/vlc/3.0.7.1/win64/vlc-3.0.7.1-win64.7z
拿到下载后的压缩文件,解压出来,将 libvlc.dll、libvlccore.dll 和 plugins 整个目录 这几个拷贝到 exe 程序目录即可。另外,有一点需要特别提醒,压缩包中的 sdk 目录 是我们开发时需要用到的头文件和链接文件。
3. 测试程序截图
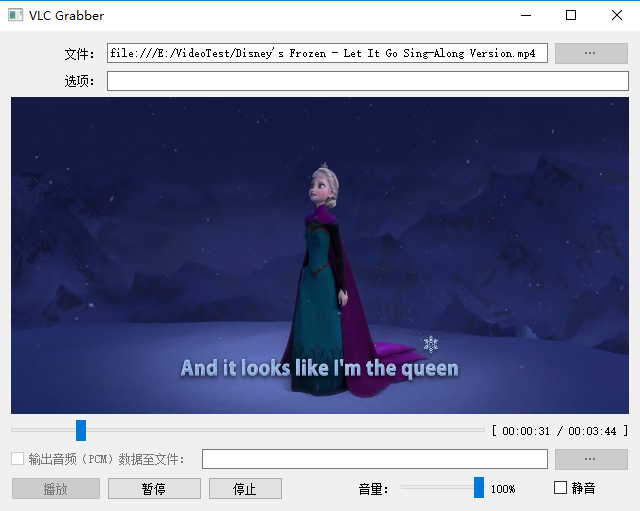
二、如何使用
使用 vlc_mgrabber_t 很简单,我们只需实现主要的 视频回调、音频回调、事件回调 三个接口,然后调用其基本操作接口进行 打开、关闭 操作,就可完成基本的工作流程。下面,我逐个说明这些接口的调用方式。
1. 基本操作流程
主要操作接口的声明如下:
class vlc_mgrabber_t
{
......
public:
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief Startup the libvlc.
*/
static x_int32_t startup(x_int32_t xit_argc, const x_char_t * const * xct_argv;
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief Cleanup the libvlc.
*/
static x_void_t cleanup(void);
public:
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief 设置回调接口。
*
* @param [in ] xfunc_vptr : 视频图像的回调函数接口。
* @param [in ] xfunc_aptr : 音频数据的回调函数接口。
* @param [in ] xfunc_eptr : 操作事件的回调函数接口。
* @param [in ] xpvt_context : 回调的用户上下文描述信息。
*/
inline x_void_t set_callback(xfunc_video_cbk_t xfunc_vptr,
xfunc_audio_cbk_t xfunc_aptr,
xfunc_event_cbk_t xfunc_eptr,
x_pvoid_t xpvt_context)
{
m_xfunc_video_cbk = xfunc_vptr;
m_xfunc_audio_cbk = xfunc_aptr;
m_xfunc_event_cbk = xfunc_eptr;
m_xpvt_xfunc_ctxt = xpvt_context;
}
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief 打开工作流程(操作前请先调用 set_callback() 设置好回调参数)。
*
* @param [in ] xht_instance : 关联的 libvlc 实例句柄(若为 X_NULL,则取全局的实例句柄)。
* @param [in ] xszt_media_file : 音视频文件路径名。
* @param [in ] xszt_options : 附加的参数选项(使用 " :" (空格+':')进行分隔的字符串集,为 X_NULL 时,则忽略)。
* @param [in ] xut_video_nbits : 视频回调操作时的 RGB 图像位数(24 或 32)。
*
* @return x_int32_t
* - 成功,返回 0;
* - 失败,返回 错误码。
*/
x_int32_t open(x_handle_t xht_instance,
x_cstring_t xszt_media_file,
x_cstring_t xszt_options,
x_uint32_t xut_video_nbits);
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief 关闭工作流程。
*/
x_void_t close(void);
......
public:
......
/**
* Set movie position as percentage between 0.0 and 1.0.
* This has no effect if playback is not enabled.
* This might not work depending on the underlying input format and protocol.
*
* \param xft_pos the position
*/
x_void_t set_position(x_float_t xft_pos);
......
/**
* Set mute status.
*
* \param xbt_status If status is X_TRUE then mute, otherwise unmute
* \warning This function does not always work. If there are no active audio
* playback stream, the mute status might not be available. If digital
* pass-through (S/PDIF, HDMI...) is in use, muting may be unapplicable. Also
* some audio output plugins do not support muting at all.
* \note To force silent playback, disable all audio tracks. This is more
* efficient and reliable than mute.
*/
x_void_t audio_set_mute(x_bool_t xbt_status);
......
/**
* Set current software audio volume.
*
* \param xit_volume the volume in percents (0 = mute, 100 = 0dB)
* \return 0 if the volume was set, -1 if it was out of range
*/
x_int32_t audio_set_volume(x_int32_t xit_volume);
......
};
使用的大致流程,如下描述:
- 1 在程序启动时,调用 vlc_mgrabber_t::startup(0, NULL) 初始化 libvlc 库。
- 2 程序执行过程中,开启一个 vlc_mgrabber 对象 object 的工作流程,需要先后调用如下接口:
- 2.1 先使用 object.set_callback(...) 设置回调接口;
- 2.2 然后用 object.open(...) 操作接口打开工作流程;
- 2.3 期间,用 set_position(...) 设置当前播放进度,audio_set_mute(...) 设置静音状态,audio_set_volume(...) 设置播放音量,或者还可以进行其他的操作(详细请查看源码);
- 2.4 另外,libvlc 内部的工作线程,会通过设置的回调函数接口,回调数据(RGB图像 或 PCM 音频数据,以及 通知事件);
- 2.5 最后用 object.close(...) 操作接口关闭工作流程。
- 3 程序在退出前,执行 vlc_mgrabber_t::cleanup() 卸载 libvlc 库。
接下来,继续介绍 数据 和 事件 的回调操作接口要如何实现,以及需要注意的问题。
2. 实现视频回调接口
若需要进行视频帧的图像攫取操作,object.set_callback(...) 时,就必须设置好视频的回调函数接口。下面先看视频回调接口的相关数据声明,如下所示:
class vlc_mgrabber_t
{
......
public:
/**
* @enum x_video_callback_prototype_t
* @brief Callback prototype for video.
*/
typedef enum __video_callback_prototype__
{
VIDEO_CALLBACK_FORMAT = 1, ///< Callback prototype to notice the frame's size format.
VIDEO_CALLBACK_LOCK = 2, ///< Callback prototype to allocate and lock a frame buffer.
VIDEO_CALLBACK_UNLOCK = 3, ///< Callback prototype to unlock a frame buffer.
VIDEO_CALLBACK_DISPLAY = 4, ///< Callback prototype to display a frame.
} x_video_callback_prototype_t;
/**
* @struct x_video_callback_data_t
* @brief Callbakc data for video.
*/
typedef struct __video_callback_data__
{
x_handle_t xht_handle; ///< the user-defined handle.
x_byte_t * xbt_bits_ptr; ///< the buffer for video frame output.
x_int32_t xit_pitch; ///< the buffer line stride.
x_int32_t xit_width; ///< the real frame's width.
x_int32_t xit_height; ///< the real frame's height.
} x_video_callback_data_t;
/**
* @brief Callback function type for video.
*
* @param [in ] xit_ptype : callback prototype, @see x_video_callback_prototype_t.
* @param [in,out] xvct_dptr : interactive data for callback operations.
* @param [in ] xpvt_ctxt : the user context description.
*/
typedef x_void_t (* xfunc_video_cbk_t)(x_int32_t xit_ptype,
x_video_callback_data_t * xvct_dptr,
x_pvoid_t xpvt_ctxt);
......
};
视频的回调,有四个类型,描述如下:
- VIDEO_CALLBACK_FORMAT: 帧信息的通知操作,借此可知道后续回调的图像基本描述信息(x_video_callback_data_t 的字段中有描述);这个只在打开工作流程后,进行几次回调通知,之后就再没有了。在我的测试中,不大理解的是,libvlc 竟然回调了 3 次该类型。
- VIDEO_CALLBACK_LOCK: 帧图像的输出缓存申请操作,通过回写设置 x_video_callback_data_t 的 xbt_bits_ptr 字段实现;注意,申请的缓存必须足够大,且不能为 NULL。
- VIDEO_CALLBACK_UNLOCK:帧图像完成解码后的通知操作。
- VIDEO_CALLBACK_DISPLAY:帧图像的显示通知操作;其实可以忽略该回调操作,在 UNLOCK 回调时一并完成显示操作即可。
注意:视频的回调过程中,每一帧都会经历:LOCK、UNLOCK、DISPLAY 三个步骤,所以期间这三个类型的回调是多次发生的。同时,我们要学会利用好 x_video_callback_data_t 的 xht_handle 字段进行操作标识。
下面请看我的测试程序中,是这样实现回调流程的:
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief Callback function for video.
*
* @param [in ] xit_ptype : callback prototype.
* @param [in,out] xvct_dptr : interactive data for callback operations.
*/
x_void_t Widget::real_video_cbk(x_int32_t xit_ptype, x_vcbk_data_t * xvct_dptr)
{
switch (xit_ptype)
{
// FORMAT 回调时,初始化图像渲染的显示控件,
// 要注意的是,以 xvct_dptr->xit_height + 16 保证开辟的图像输出缓存足够大
case vlc_mgrabber_t::VIDEO_CALLBACK_FORMAT:
if (!ui->widget_render->isStart())
{
#if 0
ui->widget_render->startRender(xvct_dptr->xit_width,
xvct_dptr->xit_height + 16,
32);
#else
emit real_start_render(xvct_dptr->xit_width,
xvct_dptr->xit_height + 16,
32);
#endif
}
else if ((xvct_dptr->xit_width > ui->widget_render->cxImage()) ||
(xvct_dptr->xit_height > ui->widget_render->cyImage()))
{
#if 0
ui->widget_render->stopRender();
ui->widget_render->startRender(xvct_dptr->xit_width,
xvct_dptr->xit_height + 16,
32);
#else
emit real_stop_render();
emit real_start_render(xvct_dptr->xit_width,
xvct_dptr->xit_height + 16,
32);
#endif
}
break;
// LOCK 回调时,申请图像输出缓存,回写 x_video_callback_data_t 的 xbt_bits_ptr 字段,
// 同时设置 xht_handle 字段,是为了在 UNLOCK 回调时,知道原来 bits 缓存关联的对象。
case vlc_mgrabber_t::VIDEO_CALLBACK_LOCK:
if (ui->widget_render->isStart())
{
QImage * ximage_ptr = ui->widget_render->pull();
xvct_dptr->xht_handle = (x_handle_t)ximage_ptr;
xvct_dptr->xbt_bits_ptr = ximage_ptr->bits();
}
break;
// UNLOCK 回调后,将完成解码后得到的图像帧放入渲染控件,通知其刷新显示
case vlc_mgrabber_t::VIDEO_CALLBACK_UNLOCK:
if (ui->widget_render->isStart())
{
QImage * ximage_ptr = (QImage *)xvct_dptr->xht_handle;
ui->widget_render->push(ximage_ptr, xvct_dptr->xit_width, xvct_dptr->xit_height);
}
break;
case vlc_mgrabber_t::VIDEO_CALLBACK_DISPLAY:
{
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
3. 实现音频回调接口
要进行音频数据的攫取操作,object.set_callback(...) 时,设置了音频的回调函数接口即可。但与此同时,播放过程就会出现无声状态,毕竟此时的所有音频数据都已经流向了用户的回调接口,音频输出设备未能接收到数据。音频回调接口的相关数据声明,如下所示:
class vlc_mgrabber_t
{
......
public:
......
/**
* @enum x_audio_callback_prototype_t
* @brief Callback prototype for audio.
*/
typedef enum __audio_callback_prototype__
{
AUDIO_CALLBACK_FORMAT = 1, ///< Callback prototype for audio format.
AUDIO_CALLBACK_PLAYBACK = 2, ///< Callback prototype for audio playback.
AUDIO_CALLBACK_PAUSE = 3, ///< Callback prototype for audio pause.
AUDIO_CALLBACK_RESUMPTION = 4, ///< Callback prototype for audio resumption (i.e. restart from pause).
AUDIO_CALLBACK_BUFFER_FLUSH = 5, ///< Callback prototype for audio buffer flush.
AUDIO_CALLBACK_BUFFER_DRAIN = 6, ///< Callback prototype for audio buffer drain.
AUDIO_CALLBACK_VOLUME_CHANGE = 7, ///< Callback prototype for audio volume change.
} x_audio_callback_prototype_t;
/**
* @brief Callback function type for audio.
* xit_ptype:
* 1, Callback prototype for audio format.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 2, Callback prototype for audio playback.
* xpvt_dptr == pointer to the first audio sample to play back.
* 3, Callback prototype for audio pause.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 4, Callback prototype for audio resumption (i.e. restart from pause).
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 5, Callback prototype for audio buffer flush.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 6, Callback prototype for audio buffer drain.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 7, Callback prototype for audio volume change.
* xpvt_dptr == { x_float_t : volume software volume (1. = nominal, 0. = mute),
* x_uint32_t : muted flag. }.
* xut_size == sizeof(x_float_t) + sizeof(x_uint32_t) .
*
* @param [in ] xit_ptype : the callback type, @see x_audio_callback_prototype_t.
* @param [in ] xpvt_dptr : the callback data.
* @param [in ] xut_size : the callback data's size.
* @param [in ] xit_pts : time stamp.
* @param [in ] xpvt_ctxt : the user context description.
*/
typedef x_void_t (* xfunc_audio_cbk_t)(x_int32_t xit_ptype,
x_pvoid_t xpvt_dptr,
x_uint32_t xut_size,
x_int64_t xit_pts,
x_pvoid_t xpvt_ctxt);
......
};
音频回调,主要关心 AUDIO_CALLBACK_FORMAT 和 AUDIO_CALLBACK_PLAYBACK 这两个回调即可:
- AUDIO_CALLBACK_FORMAT:格式信息的回调通知,可确定后续音频(PCM)数据的 通道数量、采样率、每采样位数 这些信息。
- AUDIO_CALLBACK_PLAYBACK:音频数据输出的回调通知,回调的数据即为 每个采样点 PCM音频数据。
在我的测试程序中,是如下代码实现的,为此,还写了个 WAV 格式的文件输出工具类(wave_file.h 里面的 x_wave_file_writer_t 类)。
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief Callback function type for audio.
* xit_ptype:
* 1, Callback prototype for audio format.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 2, Callback prototype for audio playback.
* xpvt_dptr == pointer to the first audio sample to play back.
* 3, Callback prototype for audio pause.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 4, Callback prototype for audio resumption (i.e. restart from pause).
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 5, Callback prototype for audio buffer flush.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 6, Callback prototype for audio buffer drain.
* xpvt_dptr == X_NULL.
* 7, Callback prototype for audio volume change.
* xpvt_dptr == { x_float_t : volume software volume (1. = nominal, 0. = mute),
* x_int32_t : muted flag. }.
*
* @param [in ] xit_ptype : the callback type, @see x_audio_callback_prototype_t.
* @param [in ] xpvt_dptr : the callback data.
* @param [in ] xut_size : the callback data's size.
* @param [in ] xit_pts : time stamp.
*/
x_void_t Widget::real_audio_cbk(x_int32_t xit_ptype,
x_pvoid_t xpvt_dptr,
x_uint32_t xut_size,
x_int64_t xit_pts)
{
switch (xit_ptype)
{
// FORMAT 回调,是在 open() 操作后进行的格式通知,
// 借此,可以知道后续回调的 PCM 音频数据的 通道数量、采样率、每个采样位数 这些信息
case vlc_mgrabber_t::AUDIO_CALLBACK_FORMAT:
if (!m_wfile_writer.is_open())
{
QByteArray text_file = ui->lineEdit_audioFile->text().toUtf8();
std::string xstr_file = text_file.data();
m_wfile_writer.open(xstr_file.c_str(),
(x_uint16_t)m_xvlc_mgrabber.get_audio_channels(),
m_xvlc_mgrabber.get_audio_rate(),
(x_uint16_t)m_xvlc_mgrabber.get_audio_bits_per_sample());
}
break;
// PLAYBACK 回调,这是回调 PCM 音频数据的
case vlc_mgrabber_t::AUDIO_CALLBACK_PLAYBACK:
if (m_wfile_writer.is_open())
{
m_wfile_writer.write((x_uchar_t *)xpvt_dptr, xut_size);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
4. 实现事件回调接口
最后,是工作流程中的事件回调接口,先看相关的数据声明:
class vlc_mgrabber_t
{
......
public:
......
/**
* @enum x_event_callback_prototype_t
* @brief Callback prototype for event.
*/
typedef enum __event_callback_prototype__
{
EVENT_CALLBACK_END_REACHED = 265, ///< media player end reached.
EVENT_CALLBACK_TIME_CHANGED = 267, ///< media player time changed.
EVENT_CALLBACK_POSITION_CHANGED = 268, ///< media player position changed.
EVENT_CALLBACK_LENGTH_CHANGED = 273, ///< media player length changed.
} x_event_callback_prototype_t;
/**
* @brief Callback function type for event.
*
* @param [in ] xit_event : the callback event code, @see x_event_callback_prototype_t.
* @param [in ] xlpt_param1 : reserved parameter.
* @param [in ] xlpt_param2 : reserved parameter.
* @param [in ] xpvt_ctxt : the user context description.
*/
typedef x_void_t (* xfunc_event_cbk_t)(x_int32_t xit_event,
x_lptr_t xlpt_param1,
x_lptr_t xlpt_param2,
x_pvoid_t xpvt_ctxt);
......
};
vlc_mgrabber_t 在 open(...) 操作中,只注册了 4 个事件(x_event_callback_prototype_t 的四个),若实际应用中,仍不够,就请参考 libvlc 中 libvlc_event_e 所枚举的事件,照猫画虎的在 vlc_mgrabber_t.open(...) 增加代码了。
通常,我们只需要关心 EVENT_CALLBACK_END_REACHED (播放结束)事件就可以了。需要特别注意的是,事件回调接口中的代码,是由 libvlc 内部开启的线程执行的,所以在我们在收到 EVENT_CALLBACK_END_REACHED 事件通知后,必须以 异步通知的方式 执行 object.close() 关闭操作,例如我的示例程序中是这样实现的:
......
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
......
connect(this, SIGNAL(real_end_reached()),
this, SLOT(on_pushButton_stop_clicked()),
Qt::QueuedConnection);
......
}
......
/**********************************************************/
/**
* @brief Callback function for event.
*
* @param [in ] xit_event : the callback event code.
* @param [in ] xlpt_param1 : param1.
* @param [in ] xlpt_param2 : param2.
*/
x_void_t Widget::real_event_cbk(x_int32_t xit_event,
x_lptr_t xlpt_param1,
x_lptr_t xlpt_param2)
{
switch (xit_event)
{
case vlc_mgrabber_t::EVENT_CALLBACK_END_REACHED:
{
// 异步方式,通知播放结束事件
emit real_end_reached();
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void Widget::on_pushButton_stop_clicked()
{
m_xvlc_mgrabber.close();
......
}
三、几个关键的 libvlc API
集中在 vlc_mgrabber_t.open(...) 的实现流程中,使用到的几个关键 API:
LIBVLC_API libvlc_media_t *libvlc_media_new_location(
libvlc_instance_t *p_instance,
const char * psz_mrl );
LIBVLC_API
void libvlc_video_set_callbacks( libvlc_media_player_t *mp,
libvlc_video_lock_cb lock,
libvlc_video_unlock_cb unlock,
libvlc_video_display_cb display,
void *opaque );
LIBVLC_API
void libvlc_video_set_format_callbacks( libvlc_media_player_t *mp,
libvlc_video_format_cb setup,
libvlc_video_cleanup_cb cleanup );
LIBVLC_API
void libvlc_audio_set_callbacks( libvlc_media_player_t *mp,
libvlc_audio_play_cb play,
libvlc_audio_pause_cb pause,
libvlc_audio_resume_cb resume,
libvlc_audio_flush_cb flush,
libvlc_audio_drain_cb drain,
void *opaque );
LIBVLC_API
void libvlc_audio_set_volume_callback( libvlc_media_player_t *mp,
libvlc_audio_set_volume_cb set_volume );
LIBVLC_API
void libvlc_audio_set_format_callbacks( libvlc_media_player_t *mp,
libvlc_audio_setup_cb setup,
libvlc_audio_cleanup_cb cleanup );
LIBVLC_API libvlc_event_manager_t * libvlc_media_player_event_manager ( libvlc_media_player_t *p_mi );
LIBVLC_API int libvlc_event_attach( libvlc_event_manager_t *p_event_manager,
libvlc_event_type_t i_event_type,
libvlc_callback_t f_callback,
void *user_data );
LIBVLC_API int libvlc_media_player_play ( libvlc_media_player_t *p_mi );
四、总结
libvlc 的回调操作,对于视频图像来说,并不仅限于 RGB 格式,YUV 格式也是可以的,但这方面我并未去尝试,毕竟接触到的应用场景使用 RGB 格式的图像使用更广泛。至少,对于很多进行图像算法分析的工作,使用 RGB 格式的更多一些。若是需要进行其他格式的图像回调,就需要另行调整代码了。
对于音频的回调格式,我也曾尝试过按照指定格式进行数据回调(比如,回调 8 位采样点、单通道的 PCM),并未成功。就我目前的工作而言,攫取音频数据的场景不多,这问题也就没过多纠结。
而字幕流的回调,在 vlc_mgrabber_t 更是没有去实现,libvlc 中是有这些接口的,感兴趣的朋友可以自行研究。
最后,要是上面的代码在使用过程中,有任何问题或建议,欢迎请在评论区留言联系我 🙂


