正则表达式
第四章 正则表达式与cut 、sort、uniq、tr
一 正则表达式
概念:正则表达式,又称规则表达式(英语:Regular Expression),在代码中常简写为regex、 regexp或RE),是计算机科学的一个概念。正则表达式通常被用来检索、替换那些符合某个模式(规则)的文本。
正则表达式不只有一种,而且 LINUX中不同的程序可能会使用不同的正则表达式,如:工具: grep sed awk egrep
正则表达式-通常用于判断语句中,用来检查某一字符串是否满足某一格式
正则表达式是由普通字符与元字符组成。
普通字符包括天小写字母、数字、标点符号及一些其他符号
元字符是指在正则表达式中具有特殊意义的专用字符,可以用来规定其前导字符(即位于元字符前面的字符)在目标对象中的出现模式。
LINUX 中常用的有两种正则表达式引擎砖础:正则表达式:BRE 扩展正则表达式:ERE
LINUX 中文本处理工具:grep、egrep、sed、awk

1 基础正则表达式元字符(支持grep、egrep、sed、awk)
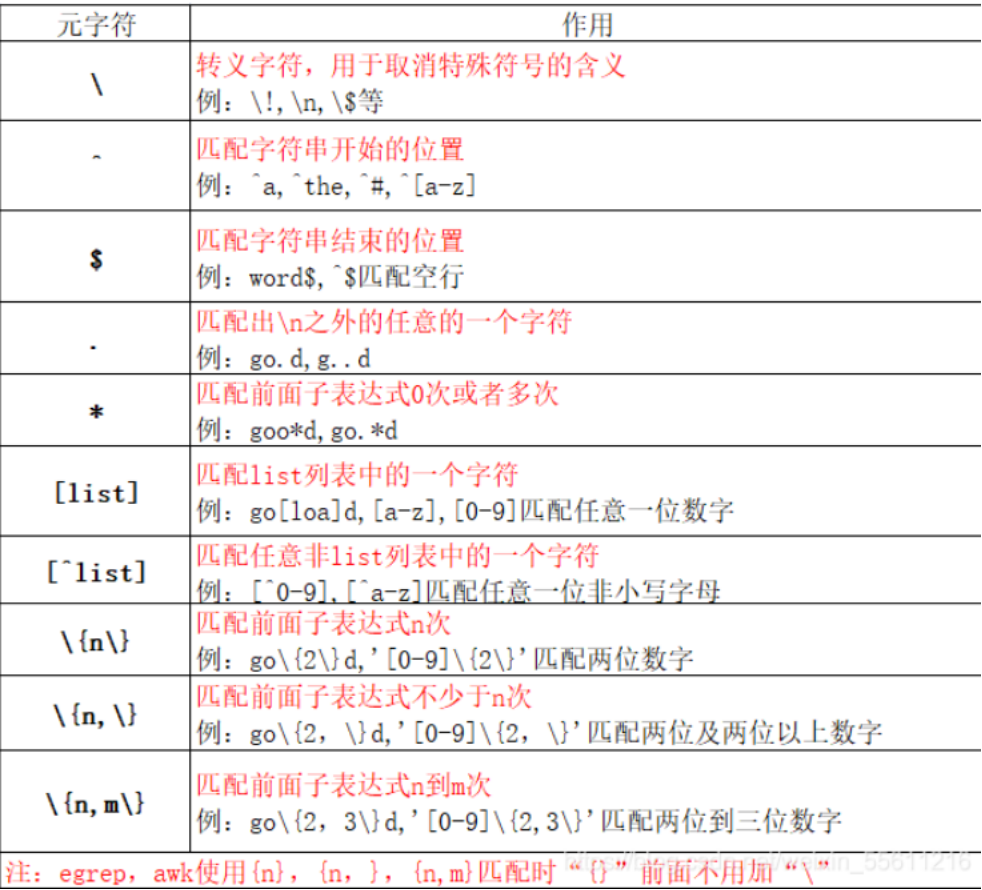
注: egrep、awk使用{n}、{n,}、{n,m}匹配时“}"前不用加"\"
egrep -E -n 'wo{2}d' test.txt1/-E用于显示文件中符合条件的字符
egrep -E -n 'wo{2,3}d' test.txt
2 扩展正则表达式元字符(支持egrep、awk
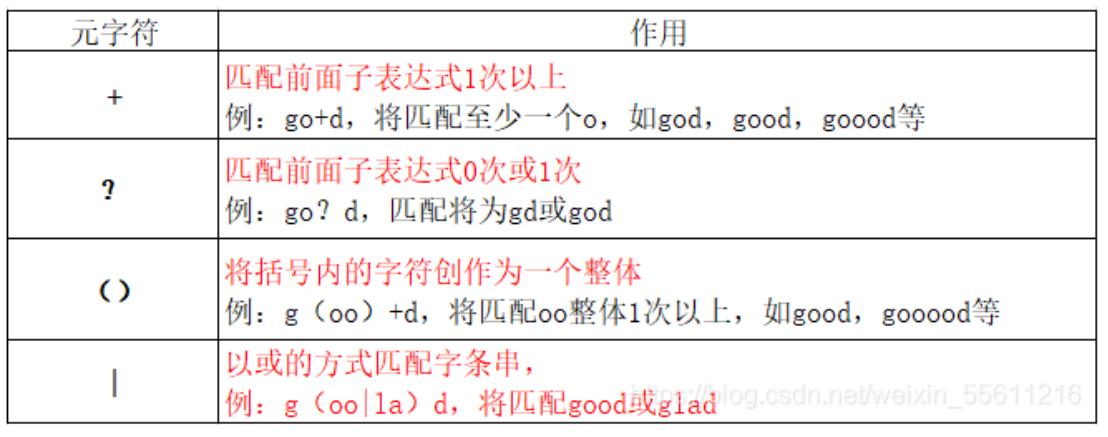
定位符
^ 匹配输入字符串开始的位置
$匹配输入字符串结尾的位置
非打印字符
\n匹配一个换行符
\r匹配一个回车符
\t匹配一个制表符
3 grep命令
grep命令使用正则表达式来搜索文本,并且把匹配的文本打印出来。
格式:grep [options]pattern [file]
option表示选项,pattern表示匹配的模式。file表示一系列文件名。
常用选项:
-c 只打印匹配的文本行的次数,不显示文本内容。
-i 匹配时忽略字母大小写
-h 当搜索多个文件,不显示匹配文件名前缀。
-l 只列出含义匹配的文本行的文件的文件名,不显示其具体匹配的内容。
-n 列出所有匹配的文本行,并显示行号
-s 不显示关于不存在或无法读取文件的错误信息
-v 只显示不匹配的文本行,反向选择,显示与搜索字符串不相符的行。
-w 匹配整个单词
-x 匹配整个文本行
-r 递归搜索,不仅搜索当前目录,还有各级子目录
-E 开启扩展(extend)的正则表达式
--color=auto 可以将找到的关键词部分加上颜色的显示
案列
grep -c root /etc/passwd
//统计root字符总行数;或cat ,letc/passwd / grep root
grep -i "the"web.sh
//不区分大小写查找the所有的行
grep -v root letc/passwd
//查看/etc/passwd,将没有出现root 的行取出来
cat web.sh lgrep -v '^$' >test.txt1
//将非空行写入到test.txt文件
4 元字符操作的案列
(1)查找特定字符
查找特定字符非常简单,如执行以下命令即可从 test.txt 文件中查找出特定字符“the”所在位置。其中“-n”表示显示行号、“-i”表示不区分大小写。命令执行后,符合匹配标准的字符, 字体颜色会变为红色。
grep -n 'the' test.txt
若反向选择,如查找不包含“the”字符的行,则需要通过 grep 命令的“-v”选项实现,并配合“-n”一起使用显示行号。
grep -vn 'the' test.txt
(2)利用中括号“[]”来查找集合字符
想要查找“shirt”与“short”这两个字符串时,可以发现这两个字符串均包含“sh”与“rt”。此时执行以下命令即可同时查找到“shirt”与“short”这两个字符串,其中“[]”中无论有几个字符, 都仅代表一个字符,也就是说“[io]”表示匹配“i”或者“o”。
grep -n 'sh[io]rt' test.txt
若要查找包含重复单个字符“oo”时,只需要执行以下命令即可。
grep -n 'oo' test.txt
若查找“oo”前面不是“w”的字符串,只需要通过集合字符的反向选择“[^]”来实现该目的。例如执行“grep -n‘[^w]oo’test.txt”命令表示在 test.txt 文本中查找“oo”前面不是“w”的字符串。
grep -n '[^w]oo' test.txt
3:The home of Football on BBC Sport online.
5:google is the best tools for search keyword.
11:#woood #
12:#woooooood #
14:I bet this place is really spooky late at night!
在上述命令的执行结果中发现“woood”与“wooooood”也符合匹配规则,二者均包含“w”。其实通过执行结果就可以看出,符合匹配标准的字符加粗显示,而上述结果中可以得知, “#woood #”中加粗显示的是“ooo”,而“oo”前面的“o”是符合匹配规则的。同理“#woooooood #”也符合匹配规则。
若不希望“oo”前面存在小写字母,可以使用“grep -n‘[^a-z]oo’test.txt”命令实现,其中“a-z”表示小写字母,大写字母则通过“A-Z”表示。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '[^a-z]oo' test.txt
3:The home of Football on BBC Sport online.
查找包含数字的行可以通过“grep -n ‘[0-9]’ test.txt”命令来实现。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '[0-9]' test.txt
4:the tongue is boneless but it breaks bones.12! 7:PI=3.141592653589793238462643383249901429
(3)查找行首“^”与行尾字符“$”
基础正则表达式包含两个定位元字符:“^”(行首)与“$”(行尾)。在上面的示例中, 查询“the”字符串时出现了很多包含“the”的行,如果想要查询以“the”字符串为行首的行,则可以通过“^”元字符来实现。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '^the' test.txt
4:the tongue is boneless but it breaks bones.12!
查询以小写字母开头的行可以通过“^[a-z]”规则来过滤,查询大写字母开头的行则使用
“^[A-Z]”规则,若查询不以字母开头的行则使用“^[^a-zA-Z]”规则。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '^[a-z]' test.txt
1:he was short and fat.
4:the tongue is boneless but it breaks bones.12! 5:google is the best tools for search keyword.
8:a wood cross!
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '^[A-Z]' test.txt
2:He was wearing a blue polo shirt with black pants. 3:The home of Football on BBC Sport online.
6:The year ahead will test our political establishment to the limit. 7:PI=3.141592653589793238462643383249901429
9:Actions speak louder than words
13:AxyzxyzxyzxyzC
14:I bet this place is really spooky late at night! 15:Misfortunes never come alone/single.
16:I shouldn't have lett so tast.
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '^[^a-zA-Z]' test.txt
11:#woood # 12:#woooooood #
“^”符号在元字符集合“[]”符号内外的作用是不一样的,在“[]”符号内表示反向选择,在“[]” 符号外则代表定位行首。反之,若想查找以某一特定字符结尾的行则可以使用“$”定位符。例如,执行以下命令即可实现查询以小数点(.)结尾的行。因为小数点(.)在正则表达式中也是一个元字符(后面会讲到),所以在这里需要用转义字符“\”将具有特殊意义的字符转化成普通字符。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '\.$' test.txt
1:he was short and fat.
2:He was wearing a blue polo shirt with black pants. 3:The home of Football on BBC Sport online.
5:google is the best tools for search keyword.
6:The year ahead will test our political establishment to the limit. 15:Misfortunes never come alone/single.
16:I shouldn't have lett so tast.
当查询空白行时,执行“grep -n‘^$’test.txt”命令即可。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '^$' test.txt
10:
(4)查找任意一个字符“.”与重复字符“*”
前面提到,在正则表达式中小数点(.)也是一个元字符,代表任意一个字符。例如执行以下命令就可以查找“w??d”的字符串,即共有四个字符,以 w 开头 d 结尾。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'w..d' test.txt
5:google is the best tools for search keyword.
8:a wood cross!
9:Actions speak louder than words
在上述结果中,“wood”字符串“w..d”匹配规则。若想要查询 oo、ooo、ooooo 等资料, 则需要使用星号(*)元字符。但需要注意的是,“*”代表的是重复零个或多个前面的单字符。 “o*”表示拥有零个(即为空字符)或大于等于一个“o”的字符,因为允许空字符,所以执行“grep
-n 'o*' test.txt”命令会将文本中所有的内容都输出打印。如果是“oo*”,则第一个 o 必须存在, 第二个 o 则是零个或多个 o,所以凡是包含 o、oo、ooo、ooo,等的资料都符合标准。同理,若查询包含至少两个 o 以上的字符串,则执行“grep -n 'ooo*' test.txt”命令即可。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'ooo*' test.txt
3:The home of Football on BBC Sport online. 5:google is the best tools for search keyword.
8:a wood cross!
11:#woood # 12:#woooooood #
14:I bet this place is really spooky late at night!
查询以 w 开头 d 结尾,中间包含至少一个 o 的字符串,执行以下命令即可实现。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'woo*d' test.txt
8:a wood cross!
11:#woood #
12:#woooooood #
执行以下命令即可查询以 w 开头 d 结尾,中间的字符可有可无的字符串。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'w.*d' test.txt
1:he was short and fat.
5:google is the best tools for search keyword. 8:a wood cross!
9:Actions speak louder than words 11:#woood #
12:#woooooood #
执行以下命令即可查询任意数字所在行。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n '[0-9][0-9]*' test.txt
4:the tongue is boneless but it breaks bones.12! 7:PI=3.141592653589793238462643383249901429
(5)查找连续字符范围“{}”
在上面的示例中,使用了“.”与“*”来设定零个到无限多个重复的字符,如果想要限制一个范围内的重复的字符串该如何实现呢?例如,查找三到五个 o 的连续字符,这个时候就需要使用基础正则表达式中的限定范围的字符“{}”。因为“{}”在 Shell 中具有特殊意义,所以在使用“{}”字符时,需要利用转义字符“\”,将“{}”字符转换成普通字符。“{}”字符的使用方法如下所示。
① 查询两个 o 的字符。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'o\{2\}' test.txt
3:The home of Football on BBC Sport online.
5:google is the best tools for search keyword.
8:a wood cross!
11:#woood # 12:#woooooood #
14:I bet this place is really spooky late at night!
② 查询以 w 开头以 d 结尾,中间包含 2~5 个 o 的字符串。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'wo\{2,5\}d' test.txt
8:a wood cross! 11:#woood #
③ 查询以 w 开头以 d 结尾,中间包含 2 个或 2 个以上 o 的字符串。
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n 'wo\{2,\}d' test.txt
8:a wood cross!
11:#woood # 12:#woooooood #
二 cut、sort、uniq、tr
cut:列截取工具
使用说明:cut 命令从文件的每一行剪切字节、字符和字段并将这些字节、字符和字段写至标准输出。如果不指定 File 参数,cut 命令将读取标准输入。必须指定 -b、-c 或 -f 标志之一
选项:
-b:按字节截取
-c:按字符截取,常用于中文
-d:指定以什么为分隔符截取,默认为制表符
-f:通常和-d一起
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f 1
root
bin
daemon
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f 3
0
1
2
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f1,3
root:0
bin:1
daemon:2
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f1-3
root:x:0
bin:x:1
daemon:x:2
[root@localhost ~]# who | cut -b 3
o
o
o
[root@localhost ~]# who | cut -c 3
o
o
o
[root@localhost ~]# cat name | cut -b 2
[root@localhost ~]# cat name | cut -c 2
刚
春
注意:cut只擅长于处理单个字符为间隔的文本
sort 是一个以行为单位对文件内容进行排序的工具,也可以根据不同的数据类型来排序。例如数据和字符的排序就不一样
语法:
sort [选项] 参数
常用选项
-t:指定分隔符,默认使用[Tab]吧 键或空格分隔
-k:指定排序区域,哪个区间排序
-n:按照数字进行排序,默认是以文字形式排序
-u:等同于 uniq,表示相同的数据仅显示一行,注意:如果行尾有空格去重就不成功
-r:反向排序,默认是升序,-r就是降序
-o:将排序后的结果转存至指定文件
-f: 忽略大小写,会将小写的字母都转换为大写字母来进行比较
-b: 忽略每行前面的空格
sort passwd.txt //不加任何选项默认按第一列升序,字母的话就是从a到z由上而下显示
sort -n -t: -k3 passwd.txt //以冒号为分隔符,以数字大小对第三列排序(升序)
sort -nr -t: -k3 passwd.txt //以冒号为分隔符,以数字大小对第三列排序(降序)
sort -nr -t: -k3 passwd.txt -o passwd.bak //将输结果不在屏幕上输出而是输出到passwd.bak文件
sort -u passwd.txt //去掉文件中重复的行(重复的行可以是不连续的)
zhangsan
gggggg
lisi
uniq
主要用于去除连续的重复行
注意:是连续的行,所以通常和sort结合使用先排序使之变成连续的行再执行去重操作,否则不连续的重复行他不能去重
(1)语法
uniq [选项] 参数
(2)常用选项
-c:对重复的行进行计数;
-d:仅显示重复行;
-u:仅显示出现一次的行
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit //创建一个水果类型的文件,一共9行内容
apple
apple
peache
pear
banana
cherry
cherry
banana
orange
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | uniq -c //统计重复行的次数,不连续的重复行他不算做重复行
2 apple
1 peache
1 pear
1 banana
2 cherry
1 banana
1 orange
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | sort | uniq -c //结合sort使用就是我们想要的效果
2 apple
2 banana
2 cherry
1 orange
1 peache
1 pear
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | sort | uniq -d //结合sort使用,过滤出重复行
apple
banana
cherry
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | sort | uniq -u //结合sort使用,过滤出不重复的行
orange
peache
pear
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | sort | uniq //结合sort使用,去重
apple
banana
cherry
orange
peache
pear
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | sort -u //也可以直接用sort -u
apple
banana
cherry
orange
peache
pear
实例1:查看登陆用户
[root@localhost ~]# who
root :0 2021-04-29 00:09 (:0)
root pts/0 2021-04-29 00:09 (:0)
root pts/1 2021-06-10 01:32 (192.168.245.1)
[root@localhost ~]# who | awk '{print $1}'
root
root
root
[root@localhost ~]# who | awk '{print $1}'| uniq
root
实例2:查看登陆过系统的用户
[root@localhost ~]# last | awk '{print $1}' | sort | uniq | grep -v "^$" | grep -v wtmp
reboot
root
shengjie
tr:它可以用一个字符来替换另一个字符,或者可以完全除去一些字符,也可以用它来除去重复字符
语法
用法:tr [选项]… SET1 [SET2]
从标准输入中替换、缩减和/或删除字符,并将结果写到标准输出。
常用选项
-d 删除字符
-s 删除所有重复出现的字符,只保留第一个
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
APPLE
APPLE
PEACHE
PEAR
BANANA
CHERRY
CHERRY
BANANA
ORANGE
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr 'apple' 'APPLE' //替换是一一对应的字母的替换
APPLE
APPLE
PEAchE
PEAr
bAnAnA
chErry
chErry
bAnAnA
orAngE
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr 'a' ' ' //把替换的字符用单引号引起来,包括特殊字符
pple
pple
pe che
pe r
b n n
cherry
cherry
b n n
or nge
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr 'a' '/'
/pple
/pple
pe/che
pe/r
b/n/n/
cherry
cherry
b/n/n/
or/nge
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr 'ap' '/' //多个字符替换成一个
///le
///le
/e/che
/e/r
b/n/n/
cherry
cherry
b/n/n/
or/nge
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr "'" '/' //如果想替换单引号则需要用双引号把单引号引起来,反斜杠转义也不行
apple
apple
peache
pear
banana
cherry
cherry
banana
/orange/
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr -d 'a' //删除所有a
pple
pple
peche
per
bnn
cherry
cherry
bnn
'ornge'
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr -d 'apple' //把所有含有这5个字母的都删除
ch
r
bnn
chrry
chrry
bnn
'orng'
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr -d '\n' //删除换行符
appleapplepeachepearbananacherrycherrybanana'orange'[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr -s 'p' //对p字符去重,只保留第一个
aple
aple
peache
pear
banana
cherry
cherry
banana
'orange'
[root@localhost ~]# cat fruit | tr -s '\n' //遇到多个回车只保留一个回车,相当于去除空行
apple
apple
peache
pear
banana
cherry
cherry
banana
'orange'




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律