结对编程作业
图片华容道
具体分工
队友主要负责原型设计,代码实现,算法设计,写博客;我主要负责游戏的代码实现,算法实现,游戏运行录制,写博客,原型设计。但是有一部分算法代码写崩了,都有相互参与。
一、原型设计
设计说明:要求文字准确、样式清晰、图文并茂(多贴原型图)等。
本次作业的要求是设计一个可玩的华容道小游戏,为了这个目标,我们需要实现以下基本的几项功能:
-
开始界面:简洁的开始界面供用户进行选择,可以根据需求进入其他分支,例如开始游戏,查看规则说明,历史记录等。
-
游戏界面:用wsad字符表示空格图片的移动,可在游戏过程中暂停或查看提示等。
-
结束界面:可以在结束界面查看历史记录或者再挑战一局。
-
历史记录:展示参与本游戏的时间及步数排名。
原型设计及具体分析:
· 开始界面
- 开始游戏
- 规则说明
- 历史记录
分别跳转至相应界面

· 游戏界面
- 撤销
- 提示
- 暂停
分别跳转至相应界面

· 结束界面
- 历史记录
- 重新开始
分别跳转至相应界面

· 暂停界面
- 继续游戏
- 重新开始
- 规则说明

· 提示界面

· 规则说明

· 历史记录

原型模型必须采用专用的原型模型设计工具实现:如Axure Rp、Balsamiq Mockup、Prototype Composer、GUI Design Studio、Adobe设计组件等等。在博文中说明你所采用的原型开发工具。
这次原型设计,我们采用了Axure Rp进行原型模型设计。
描述结对的过程,提供非摆拍的两人在讨论、细化和使用专用原型模型工具时的结对照片。
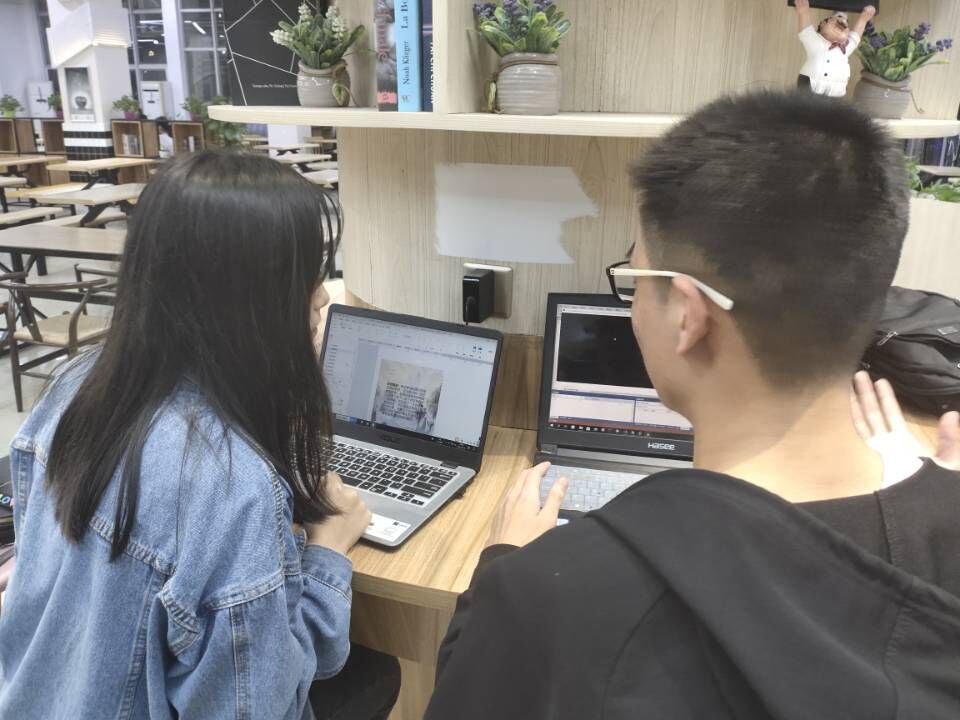

遇到的困难及解决方法。
-
困难描述:第一次使用原型工具,不知道该怎么操作,有点无从下手,而且平时比较少玩类似华容道的游戏,页面布局不知道怎么构思。
-
解决尝试:利用搜索引擎搜索自己版本对应的软件看视频教程、看对应的功能,跟着一步一步学习。观察一些主流的华容道游戏,总结普遍功能部件,增加页面背景图,使其不那么单调。
-
是否解决:解决了。
-
有何收获:对Axure Rp的一些基本使用方法有所了解,并且这个软件的其他功能还等着我们去探索;第一次有了分工合作的经验,一起讨论,共同实现设计;对原型设计有了初步的认识,尝试美观设计,可能有些细节没有考虑周全,希望在今后的学习中能得到强化。
二、AI与原型设计实现
代码组织与内部实现设计
具体通过 GUI 实现游戏框架和游戏操作。init()函数用于初始化游戏界面,并确保能够随机生成一个可以还原的图片。通过 set_keydown_handler(keyPressEvent) 函数实现按键输入操作,也可以实现鼠标点击。具体代码如下:
class Square:
def __init__(self,coordinage):
self.center = coordinage
def draw(self,canvas,board_pos): #画出随机出来的九宫格图
canvas.draw_image(byamax,self.center,[IMAGE_SIZE,IMAGE_SIZE],
[(board_pos[1]+0.5)*image_size,(board_pos[0]+0.5)*image_size],[image_size,image_size])
def init_board():
global match_array
global match_map
#确保随机生成的华容道可以还原成原来的图片
while(True):
random.shuffle(match_array)
if check_right():
break
for i in range(9):
i1 = (int)(i / 3)
i2 = i % 3
match_map[i1][i2] = match_array[i]
for i in range(ROWS):
for j in range(COLS):
idx = match_map[i][j]
square_center = all_coordinates[idx]
board_coordinates[i][j] = square_center
if square_center is None:
board[i][j] = None
else:
board[i][j] = Square(square_center)
def draw(canvas):
flag = False
for i in range(ROWS):
for j in range(COLS):
if board[i][j] is not None:
flag = True
board[i][j].draw(canvas,[i,j])
if flag is True:
canvas.draw_image(byamax,[WIDTH/2,WIDTH/2],[WIDTH,WIDTH],[52,width+52],[100,100]) #画出原图,便于玩家看着原图还原拼图
canvas.draw_text('步数:'+ str(steps),[400,680],22,'white')
def keyPressEvent(key):
global match_map
global steps
for i in range(ROWS):
for j in range(COLS):
if board[i][j] is None:
xx = i
yy = j
board1 = board[xx][yy]
board2 = match_map[xx][yy]
if(key == Qt.Key_A and yy >= 1):
board[xx][yy] = board[xx][yy - 1]
board[xx][yy - 1] = board1
match_map[xx][yy] = match_map[xx][yy - 1]
match_map[xx][yy - 1] = board2
steps += 1
if(key == Qt.Key_D and yy <= 1):
board[xx][yy] = board[xx][yy + 1]
board[xx][yy + 1] = board1
match_map[xx][yy] = match_map[xx][yy + 1]
match_map[xx][yy + 1] = board2
steps += 1
if(key == Qt.Key_W and xx >= 1):
board[xx][yy] = board[xx - 1][yy]
board[xx - 1][yy] = board1
match_map[xx][yy] = match_map[xx - 1][yy]
match_map[xx - 1][yy] = board2
steps += 1
if(key == Qt.Key_S and xx <= 1):
board[xx][yy] = board[xx + 1][yy]
board[xx + 1][yy] = board1
match_map[xx][yy] = match_map[xx + 1][yy]
match_map[xx + 1][yy] = board2
steps += 1
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
flag = True
last = -1
for i in range(ROWS):
for j in range(COLS):
if last > match_map[i][j]:
flag = False
last = match_map[i][j]
if flag is True:
message = "你过关了,你的通关步数为: " + (str)(steps) + "步"
messagebox.showinfo("提示",message)
frame.set_canvas_background('brown')
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
frame.start()
说明算法的关键与关键实现部分流程图
算法的关键:bfs + hash
贴出你认为重要的/有价值的代码片段,并解释
我认为通关挑战这个功能比较重要,这体现了AI功能,具体实现的算法是bfs + hash,通过 bfs 算法搜索华容道游戏状态,用 hash 来记录已经搜索过的状态,避免多做无用功。
bfs 算法:通过不断存储搜索到的状态,接近正确结果,花费时间较长。
hash 算法:通过将游戏图片分割成九个块,分别进行编号 1-9,然后可以按照 k (可以根据编号数量确定,3*3 图片华容道的可以直接用 10 进制)进制的方式将图片状态 hash 成一个整数,放到集合 set 里面。
但是很遗憾的是,这部分算法的代码出现 bug 了,所以这个功能并没有实现。
class Node(object):
class Struct(object):
def __init__(self,x,y,step,mapp,array):
self.array = array
self.array[0][step] = x
self.array[1][step] = y
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.step = step
self.mapp = mapp #用于hash
self.hash = 0
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
self.hash = self.hash * 10 + mapp[i][j]
self.temp = 0
def swap(self,x1,y1,x2,y2):
self.temp = self.mapp[x1][y1]
self.mapp[x1][y1] = self.mapp[x2][y2]
self.mapp[x2][y2] = self.temp
def make_struct(self,x,y,step,mapp,array):
return self.Struct(x,y,step,mapp,array)
def bfs(sx,sy,mapp):
array = [[],[]]
end = 12345678
QQ = Queue()
S = set()
Q = Queue()
node = Node()
temp = node.make_struct(sx,sy,0,mapp,array)
Q.put(temp)
step = -1
while Q.qsize() > 0:
temp = Q.get()
print(temp.mapp," ",temp.step)
ttx = -1
tty = -1
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if temp.mapp[i][j] == 8:
ttx = i
tty = j
print(temp.mapp[ttx][tty])
i = 0
for i in range(4):
tx = ttx + dx[i]
ty = tty + dy[i]
print(tx," ",ty," ",ttx," ",tty," ",temp.mapp[tx][ty]," ",temp.mapp[ttx][tty])
if tx > 2 or tx < 0 or ty > 2 or ty < 0:
continue
test = node.make_struct(tx , ty , temp.step + 1 , temp.mapp , temp.array)
print(temp.mapp)
test.swap(tx , ty , ttx , tty)
print(test.mapp)
print("HH")
if test.hash == end:
temp = test
array = test.array
step = temp.step
break
if test.hash in S:
continue
else:
S.add(test.hash)
Q.put(test)
if step != -1:
break
print(temp.array)
print(temp.hash)
print(temp.mapp)
print(temp.step)
print(temp.x," ",temp.y)
global steps
global board
steps = 0
temp = QQ.get()
print(temp)
for i in range(step):
#delay()
print(array[0][i]," ",array[1][i])
tp = board[array[i][0]][array[i][1]]
board[array[0][i]][array[1][i]] = board[array[0][i + 1]][array[1][i + 1]]
board[array[0][i + 1]][array[1][i + 1]] = tp
steps += 1
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
return
展示性能分析图和程序中消耗最大的函数
本程序中消耗最大的是 bfs 函数,其中不仅是时间复杂度(不断搜索状态)上消耗最大、空间复杂度(队列 Q 不断放状态进去)也是消耗最大的。
贴出Github的代码签入记录,合理记录commit信息。
遇到的代码模块异常或结对困难及解决方法。
问题描述:在编写游戏框架的时候,不知道怎么编写游戏页面,不知道怎么用 Python 代码编写 STL 和结构体,导致算法一直没办法实现。
解决尝试:查百度,百度上讲述了 GUI 的下载和运用;STL 的用法;结构体的用法。
是否解决:已经解决。
有何收获:学会了一些 GUI 的用法,在 python 上面运用 STL。
评价队友。
- 值得学习的地方:学习态度认真,做事认真细致。
- 需要改进的地方:没有。
提供此次结对作业的PSP和学习进度条
PSP表格
| Pair software process stage | 结对软件过程阶段 | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 100 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 500 | 600 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 100 | 120 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 60 | 60 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 60 | 50 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 90 | 100 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 60 | 100 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 300 | 360 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 60 | 30 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 30 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 30 | 60 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| total | 合计 | 1540 | 1820 |
学习进度条
| 第N周 | 新增代码(行) | 累计代码(行) | 本周学习耗时(小时) | 累计学习耗时(小时) | 重要成长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 200 | 5 | 5 | 思考算法,决定用 bfs + hash 算法来实现 AI 部分 |
| 2 | 300 | 500 | 6 | 11 | 学习了 GUI 的一些函数用法 |
| 3 | 300 | 800 | 8 | 19 | 学习了 STL 、结构体等常在 C++ 上面用的 Python 语言用法 |
| 4 | 500 | 1300 | 10 | 29 | 总和运用所学的内容编写代码 |

