20162323周楠 2017-2018-1 《程序设计与数据结构》实验报告二
20162323周楠 2017-2018-1 《程序设计与数据结构》实验报告二
目录预览
实验二 树-1-实现二叉树
实现二叉树

实验结果

实验过程
先补全书上缺少的那部分代码

public LinkedBinaryTree<T> getRight() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (root == null)
throw new EmptyCollectionException ("Get left operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
LinkedBinaryTree<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree<T>();
result.root = root.getRight();
return result;
}
public boolean Contains (T target) {
BTNode<T> node = null;
if (root != null)
node = root.find(target);
if (node == null)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (size() == 0);
}
public String toString() {
String result = "";
ArrayIterator<T> iter = null;
try {
iter = (ArrayIterator<T>) levelorder();
}
catch (EmptyCollectionException e) {
}
result = iter.toString();
return result;
}
public Iterator<T> preorder() {
ArrayIterator<T> iter = new ArrayIterator<T>();
if (root != null)
root.preorder (iter);
return iter;
}
public Iterator<T> postorder() {
ArrayIterator<T> iter = new ArrayIterator<T>();
if (root != null)
root.postorder (iter);
return iter;
}
public
void CreateTree(String[] inorder, String[] preoder) {
}
}
用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的LinkedBinaryTree进行测试
package javafoundations;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
public
class LinkedBinaryTreeTest extends TestCase {
private LinkedBinaryTree<String> tree;
public LinkedBinaryTreeTest() {
String a1 = "What's your name?";
String a2 = "What's your last name?";
String a3 = "What's your first name?";
String a4 = "ZHOU";
String a5 = "WANG";
String a6 = "NAN";
String a7 = "YU";
LinkedBinaryTree <String> n2, n3, n4, n5, n6, n7;
n4 = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a4);
n5 = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a5);
n2 = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a2,n4,n5);
n6 = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a6);
n7 = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a7);
n3 = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a3,n6,n7);
tree = new LinkedBinaryTree <String>(a1,n2,n3);
}
public
LinkedBinaryTreeTest(LinkedBinaryTree <String> tree) {
this.tree = tree;
}
public
void testGetRight() throws Exception, EmptyCollectionException {
assertEquals("What's your first name?","[What's your first name?, NAN, YU]",tree.getRight().toString());
}
public
void testContains() throws Exception {
assertEquals(true, tree.Contains("What's your first name?"));
}
public
void testToString() throws Exception, EmptyCollectionException {
assertEquals("What's your name?, What's your last name?, " +
"What's your first name?, ZHOU, WANG, NAN, " +
"YU","[What's your name?, What's your last name?, Wh" +
"at's your first name?, ZHOU, WANG, NAN, YU]",tree.levelorder().toString() );
}
public
void testPreorder() throws Exception,EmptyCollectionException {
assertEquals("[]","[]",tree.preorder().toString() );
}

实验二 树-2-中序先序序列构造二叉树
中序先序序列构造二叉树

实验结果

实验过程
BTNode root = new BTNode(pre[0]);//定义二叉树的根节点
int i = 0;
while(in[i] != pre[0]){//找到根节点再中序遍历里的位置,
i++;
String[] preLeft = new String[i];//左子树先序遍历
String[] inLeft = new String[i]; //左子树中序遍历
String[] preRight = new String[pre.length - i - 1];//右子树先序遍历
String[] inRight = new String[in.length - i - 1];//右子树中序遍历
for(int j = 0;j<in.length;j++){
if(j < i){
preLeft[j] = pre[j+1];
inLeft[j] = in[j];
}else if(j > i){
preRight[j-i-1] = pre[j];
inRight[j-i-1] = in[j];
}
}
root.left = ConstructBinaryTree(preLeft,inLeft);//递归构建左子树
root.right = ConstructBinaryTree(preRight,inRight);//递归构建右子树
return root;//返回重新构建二叉树
public static void last(BTNode tree){//后序遍历遍历二叉树
if(tree == null){
return ;
}
last(tree.getLeft());
last(tree.getRight());
System.out.print(tree.element+" ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] b = {"H","D","I","B","E","M","J","N","A","F","C","K","G","L"};
String[] a = {"A","B","D","H","I","E","J","M","N","C","F","G","K","L"};
BTNode root = ConstructBinaryTree(a,b);
last(root);

实验二 树-3-决策树
决策树

实验结果

实验过程
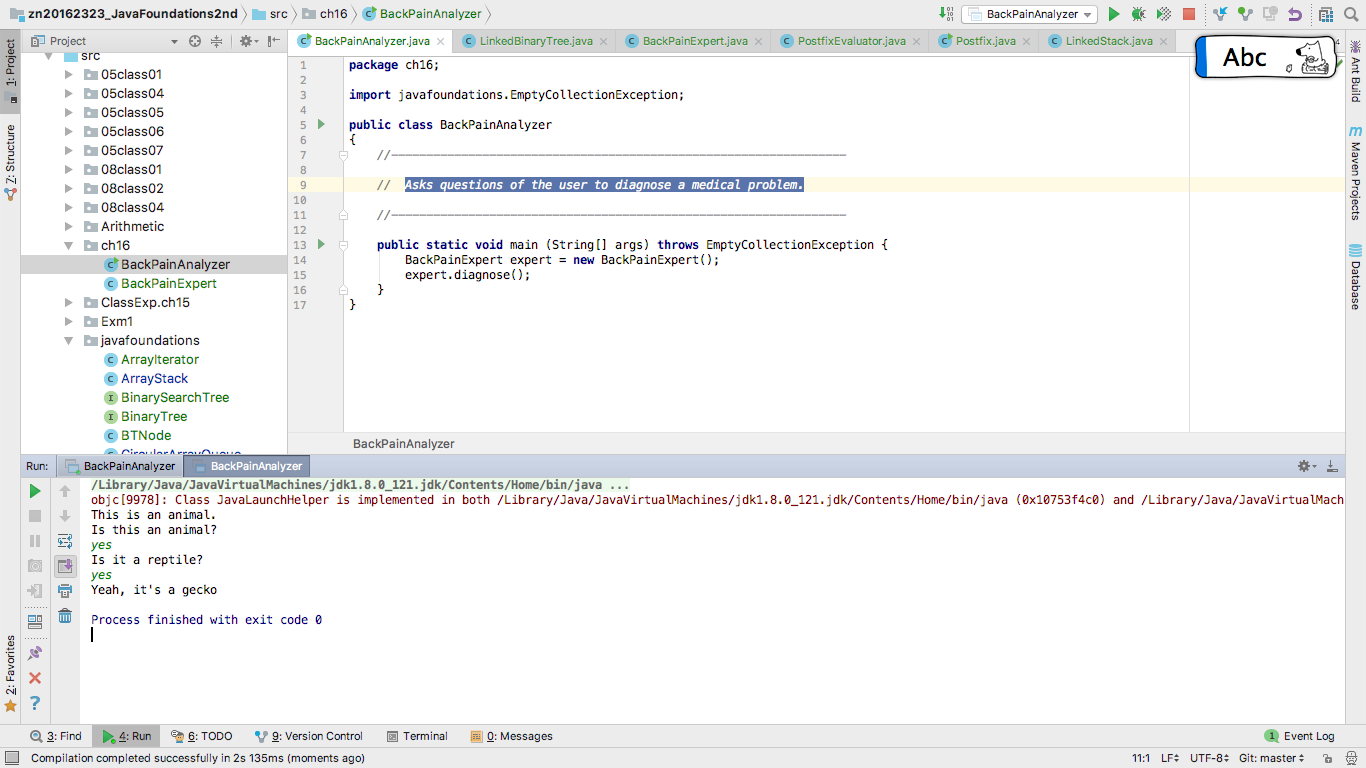
根据书上代码BackPainAnalyzer改写
package ch16;
import javafoundations.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BackPainExpert
{
private LinkedBinaryTree<String> tree;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Sets up the diagnosis question tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public BackPainExpert()
{
String e1 = "Is this an animal?";
String e2 = "Is it big?";
String e3 = "Is it a reptile?";
String e4 = "Is it four legs?";
String e5 = "Is it two legs?";
String e6 = "Is it neck long?";
String e7 = "Yeah, it's a gecko";
String e8 = "Yeah, it's a tiger";
String e9 = "Yeah, it's a kangaroo";
String e10 = "Yeah, it's a kangaroo";
String e11 = "Yeah, it's a tiger";
String e12 = "Yeah, it's a giraffe";
String e13 = "Yeah, it's a tiger";
LinkedBinaryTree<String> n2, n3, n4, n5, n6, n7, n8, n9,
n10, n11, n12, n13;
n8 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e8);
n9 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e9);
n4 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e4, n8, n9);
n10 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e10);
n11 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e11);
n5 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e5, n10, n11);
n12 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e12);
n13 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e13);
n6 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e6, n12, n13);
n7 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e7);
n2 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e2, n4, n5);
n3 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e3, n6, n7);
tree = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e1, n2, n3);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Follows the diagnosis tree based on user responses.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public void diagnose() throws EmptyCollectionException {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedBinaryTree<String> current = tree;
System.out.println ("This is an animal.");
while (current.size() > 1)
{
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
if (scan.nextLine().equalsIgnoreCase("N"))
current = current.getLeft();
else
current = (LinkedBinaryTree <String>) current.getRight();
}
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
}
}

实验一 线性结构-4
表达式树

实验结果

实验二 树-5-二叉查找树
*** ### 二叉查找树 实验结果

实验过程
package javafoundations;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
public
class LinkedBinarySearchTreeTest extends TestCase {
LinkedBinarySearchTree tree = new LinkedBinarySearchTree<Integer>();
public
void testFindMin() throws Exception, ElementNotFoundException {
tree.add("1");
tree.add("2");
tree.add("3");
tree.add("5");
tree.add("6");
assertEquals("1","1",tree.findMin().toString());
}
public
void testFindMax() throws Exception {
tree.add("1");
tree.add("2");
tree.add("3");
tree.add("5");
tree.add("6");
assertEquals("6","6",tree.findMax().toString());
}
}
补充书上代码
public T findMin() {
T min = null;
while (root.getLeft()!=null ){
root = root.getLeft();
}
min = root.getElement();
return min;
}
public T findMax() {
T max = null;
while (root.getRight()!=null ){
root = root.getRight();
}
max = root.getElement();
return max;
}
实验二 树-6-红黑树分析
***红黑树分析

实验过程

- 红黑树的时间复杂度为: O(lgn)
红黑树的基本操作
红黑树的基本操作是添加、删除。在对红黑树进行添加或删除之后,都会用到旋转方法。
1.左旋

对x进行左旋,意味着"将x变成一个左节点"。
- 源代码
LEFT-ROTATE(T, x)
y ← right[x] // 前提:这里假设x的右孩子为y。下面开始正式操作
right[x] ← left[y] // 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”,即 将β设为x的右孩子
p[left[y]] ← x // 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”,即 将β的父亲设为x
p[y] ← p[x] // 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
if p[x] = nil[T]
then root[T] ← y // 情况1:如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
else if x = left[p[x]]
then left[p[x]] ← y // 情况2:如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
else right[p[x]] ← y // 情况3:(x是它父节点的右孩子) 将y设为“x的父节点的右孩子”
left[y] ← x // 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
p[x] ← y // 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”

2.右旋

- 源代码
RIGHT-ROTATE(T, y)
x ← left[y] // 前提:这里假设y的左孩子为x。下面开始正式操作
left[y] ← right[x] // 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”,即 将β设为y的左孩子
p[right[x]] ← y // 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”,即 将β的父亲设为y
p[x] ← p[y] // 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
if p[y] = nil[T]
then root[T] ← x // 情况1:如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
else if y = right[p[y]]
then right[p[y]] ← x // 情况2:如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的左孩子”
else left[p[y]] ← x // 情况3:(y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“y的父节点的左孩子”
right[x] ← y // 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
p[y] ← x // 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”

2.添加
RB-INSERT(T, z)
y ← nil[T] // 新建节点“y”,将y设为空节点。
x ← root[T] // 设“红黑树T”的根节点为“x”
while x ≠ nil[T] // 找出要插入的节点“z”在二叉树T中的位置“y”
do y ← x
if key[z] < key[x]
then x ← left[x]
else x ← right[x]
p[z] ← y // 设置 “z的父亲” 为 “y”
if y = nil[T]
then root[T] ← z // 情况1:若y是空节点,则将z设为根
else if key[z] < key[y]
then left[y] ← z // 情况2:若“z所包含的值” < “y所包含的值”,则将z设为“y的左孩子”
else right[y] ← z // 情况3:(“z所包含的值” >= “y所包含的值”)将z设为“y的右孩子”
left[z] ← nil[T] // z的左孩子设为空
right[z] ← nil[T] // z的右孩子设为空。至此,已经完成将“节点z插入到二叉树”中了。
color[z] ← RED // 将z着色为“红色”
RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T, z) // 通过RB-INSERT-FIXUP对红黑树的节点进行颜色修改以及旋转,让树T仍然是一颗红黑树
资料参考
*** [红黑树](http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3245399.html)代码托管
***PSP(Personal Software Process)时间
| 步骤 | 耗时 | 百分比 |
|---|---|---|
| 需求分析 | 40min | 6% |
| 代码实现 | 500min | 75.8% |
| 测试 | 90min | 13.6% |
| 总结 | 30min | 4.6% |

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号