链表反转详解
前言:
在上一篇博客实现链表的创建后,我们对其创建的链表进行反转以及任意反转。
分析:
假设我们对链表每三个节点进行一次反转,有如下链表:

若对其反转,则我们想要的结果为:

思路:
我们可以用头插法的方式对其进行反转,头插法的方式:
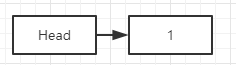
一开始链表只有一个Head头节点,现加入节点1
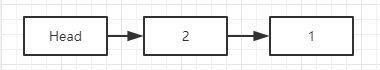
如果此时加入加入节点2那么节点2的next信息为Head头的next信息,即2指向1,Head头的next信息更新为节点2的地址
以此类推,当加入节点4时,我们应该把4接在节点1的后面,这时就应该移动链表的插入位置,在开始时插入位置为头节点,加入节点4时插入位置为节点3,相当于
一个新的目标头节点。
若要实现简单的反转,直接按照头插法插入即可
实现代码:
Node *ReverseList(Node *head) { Node *L = NULL, *tmp = NULL, *newH = NULL; int count = 0; L = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node) ); L -> next = NULL; newH = L; head = head -> next; while(head != NULL) { ++count; // 对节点进行计数, tmp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node) ); // 头插法的实现 tmp -> data = head -> data; // tmp -> next = L -> next; // L->next = tmp; // head = head->next; if(count%3==0) while(L->next!=NULL) L = L -> next; // 移动头节点 } return newH; }
完整代码:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <list> #include <utility> #include <set> #include <algorithm> #include <deque> #include <vector> #define mem(arr,num) memset(arr,0,sizeof(arr)) #define _for(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++) #define __for(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i >=b; i--) #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\ cin.tie(0);\ cout.tie(0); using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef vector<int > vi; const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1e9 + 7; const int N = 5000 + 5; typedef struct node { int data; struct node *next; }Node; Node *CreateList() { Node *L, *head, *tmp; int num; L = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); L -> next = NULL; head = L; while(scanf("%d", &num) && num) { tmp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node) ); tmp -> data = num; tmp -> next = NULL; L -> next = tmp; L = tmp; } return head; } Node *ReverseList(Node *head) { Node *L = NULL, *tmp = NULL, *newH = NULL; int count = 0; L = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node) ); L -> next = NULL; newH = L; head = head -> next; while(head != NULL) { ++count; // 对节点进行计数, tmp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node) ); // 头插法的实现 tmp -> data = head -> data; // tmp -> next = L -> next; // L->next = tmp; // head = head->next; if(count%3==0) while(L->next!=NULL) L = L -> next; // 移动头节点 } return newH; } void ReadList(Node *head) { head = head -> next; while(head != NULL) { printf("%d\n",head -> data); head = head -> next; } } int main() { Node *head = CreateList(); Node *newH = ReverseList(head); ReadList(newH); return 0; }
宝剑锋从磨砺出 梅花香自苦寒来


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号