事件高级导读

注册时事件的两种方式:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <button>传统注册事件</button> <button>方法监听注册事件</button> <button>ie9 attachEvent</button> <script> var btns = document.querySelectorAll('button'); // 1. 传统方式注册事件 btns[0].onclick = function() { alert('hi'); } btns[0].onclick = function() { alert('hao a u'); } // 2. 事件侦听注册事件 addEventListener // (1) 里面的事件类型是字符串 必定加引号 而且不带on // (2) 同一个元素 同一个事件可以添加多个侦听器(事件处理程序) btns[1].addEventListener('click', function() { alert(22); }) btns[1].addEventListener('click', function() { alert(33); }) // 3. attachEvent ie9以前的版本支持 btns[2].attachEvent('onclick', function() { alert(11); }) </script> </body> </html>
删除事件:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> div { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div>1</div> <div>2</div> <div>3</div> <script> var divs = document.querySelectorAll('div'); divs[0].onclick = function() { alert(11); // 1. 传统方式删除事件 divs[0].onclick = null; } // 2. removeEventListener 删除事件 divs[1].addEventListener('click', fn) // 里面的fn 不需要调用加小括号 function fn() { alert(22); divs[1].removeEventListener('click', fn); } // 3. detachEvent divs[2].attachEvent('onclick', fn1); function fn1() { alert(33); divs[2].detachEvent('onclick', fn1); } </script> </body> </html>
事件流:
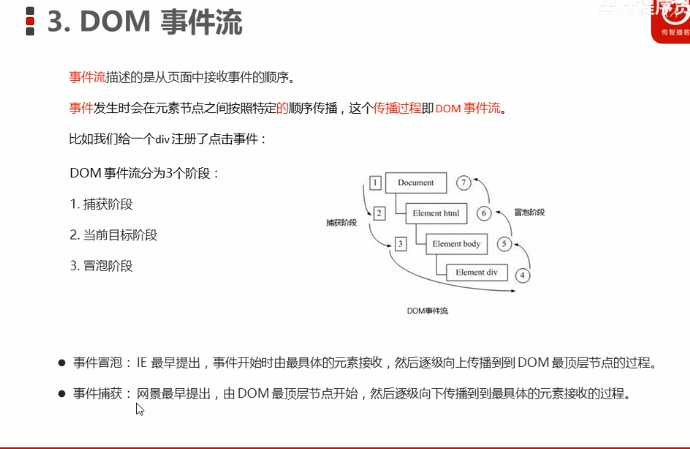
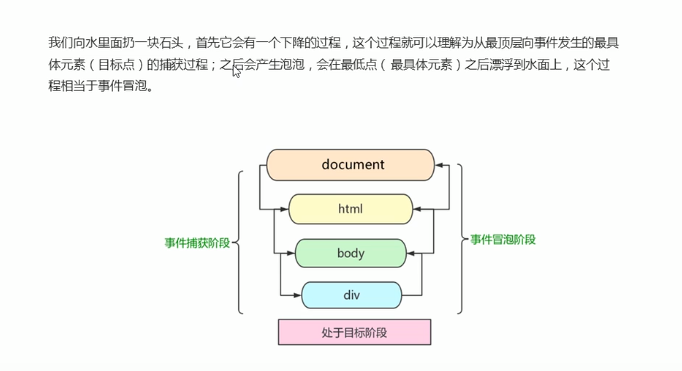

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> .father { overflow: hidden; width: 300px; height: 300px; margin: 100px auto; background-color: pink; text-align: center; } .son { width: 200px; height: 200px; margin: 50px; background-color: purple; line-height: 200px; color: #fff; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="father"> <div class="son">son盒子</div> </div> <script> // dom 事件流 三个阶段 // 1. JS 代码中只能执行捕获或者冒泡其中的一个阶段。 // 2. onclick 和 attachEvent(ie) 只能得到冒泡阶段。 // 3. 捕获阶段 如果addEventListener 第三个参数是 true 那么则处于捕获阶段 document -> html -> body -> father -> son // var son = document.querySelector('.son'); // son.addEventListener('click', function() { // alert('son'); // }, true); // var father = document.querySelector('.father'); // father.addEventListener('click', function() { // alert('father'); // }, true); // 4. 冒泡阶段 如果addEventListener 第三个参数是 false 或者 省略 那么则处于冒泡阶段 son -> father ->body -> html -> document var son = document.querySelector('.son'); son.addEventListener('click', function() { alert('son'); }, false); var father = document.querySelector('.father'); father.addEventListener('click', function() { alert('father'); }, false); document.addEventListener('click', function() { alert('document'); }) </script> </body> </html>
事件对象:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> div { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div>123</div> <script> // 事件对象 var div = document.querySelector('div'); div.onclick = function(e) { // console.log(e); // console.log(window.event); // e = e || window.event; console.log(e); } // div.addEventListener('click', function(e) { // console.log(e); // }) // 1. event 就是一个事件对象 写到我们侦听函数的 小括号里面 当形参来看 // 2. 事件对象只有有了事件才会存在,它是系统给我们自动创建的,不需要我们传递参数 // 3. 事件对象 是 我们事件的一系列相关数据的集合 跟事件相关的 比如鼠标点击里面就包含了鼠标的相关信息,鼠标坐标啊,如果是键盘事件里面就包含的键盘事件的信息 比如 判断用户按下了那个键 // 4. 这个事件对象我们可以自己命名 比如 event 、 evt、 e // 5. 事件对象也有兼容性问题 ie678 通过 window.event 兼容性的写法 e = e || window.event; </script> </body> </html>
事件对象常见属性和方法:
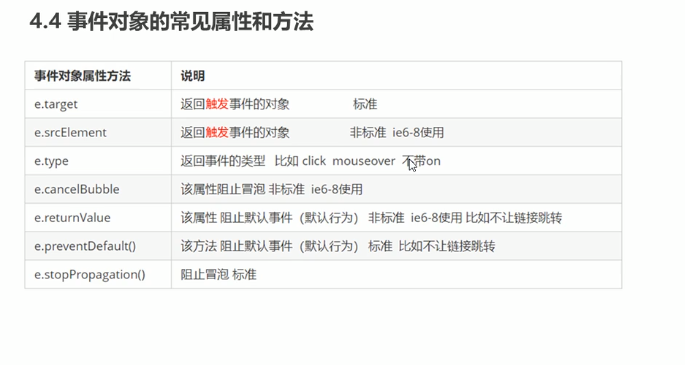
e.target:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> div { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div>123</div> <ul> <li>abc</li> <li>abc</li> <li>abc</li> </ul> <script> // 常见事件对象的属性和方法 // 1. e.target 返回的是触发事件的对象(元素) this 返回的是绑定事件的对象(元素) // 区别 : e.target 点击了那个元素,就返回那个元素 this 那个元素绑定了这个点击事件,那么就返回谁 var div = document.querySelector('div'); div.addEventListener('click', function(e) { console.log(e.target); console.log(this); }) var ul = document.querySelector('ul'); ul.addEventListener('click', function(e) { // 我们给ul 绑定了事件 那么this 就指向ul console.log(this); console.log(e.currentTarget); // e.target 指向我们点击的那个对象 谁触发了这个事件 我们点击的是li e.target 指向的就是li console.log(e.target); }) // 了解兼容性 // div.onclick = function(e) { // e = e || window.event; // var target = e.target || e.srcElement; // console.log(target); // } // 2. 了解 跟 this 有个非常相似的属性 currentTarget ie678不认识 </script> </body> </html>
阻止事件默认行为:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> </style> </head> <body> <div>123</div> <a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度</a> <form action="http://www.baidu.com"> <input type="submit" value="提交" name="sub"> </form> <script> // 常见事件对象的属性和方法 // 1. 返回事件类型 var div = document.querySelector('div'); div.addEventListener('click', fn); div.addEventListener('mouseover', fn); div.addEventListener('mouseout', fn); function fn(e) { console.log(e.type); } // 2. 阻止默认行为(事件) 让链接不跳转 或者让提交按钮不提交 var a = document.querySelector('a'); a.addEventListener('click', function(e) { e.preventDefault(); // dom 标准写法 }) // 3. 传统的注册方式 a.onclick = function(e) { // 普通浏览器 e.preventDefault(); 方法 // e.preventDefault(); // 低版本浏览器 ie678 returnValue 属性 // e.returnValue; // 我们可以利用return false 也能阻止默认行为 没有兼容性问题 特点: return 后面的代码不执行了, 而且只限于传统的注册方式 return false; alert(11); } </script> </body> </html>
阻止冒泡:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> .father { overflow: hidden; width: 300px; height: 300px; margin: 100px auto; background-color: pink; text-align: center; } .son { width: 200px; height: 200px; margin: 50px; background-color: purple; line-height: 200px; color: #fff; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="father"> <div class="son">son儿子</div> </div> <script> // 常见事件对象的属性和方法 // 阻止冒泡 dom 推荐的标准 stopPropagation() var son = document.querySelector('.son'); son.addEventListener('click', function(e) { alert('son'); e.stopPropagation(); // stop 停止 Propagation 传播 e.cancelBubble = true; // 非标准 cancel 取消 bubble 泡泡 }, false); var father = document.querySelector('.father'); father.addEventListener('click', function() { alert('father'); }, false); document.addEventListener('click', function() { alert('document'); }) </script> </body> </html>
事件委托:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li>知否知否,点我应有弹框在手!</li> <li>知否知否,点我应有弹框在手!</li> <li>知否知否,点我应有弹框在手!</li> <li>知否知否,点我应有弹框在手!</li> <li>知否知否,点我应有弹框在手!</li> </ul> <script> // 事件委托的核心原理:给父节点添加侦听器, 利用事件冒泡影响每一个子节点 var ul = document.querySelector('ul'); ul.addEventListener('click', function(e) { // alert('知否知否,点我应有弹框在手!'); // e.target 这个可以得到我们点击的对象 e.target.style.backgroundColor = 'pink'; }) </script> </body> </html>
常用的鼠标事件:
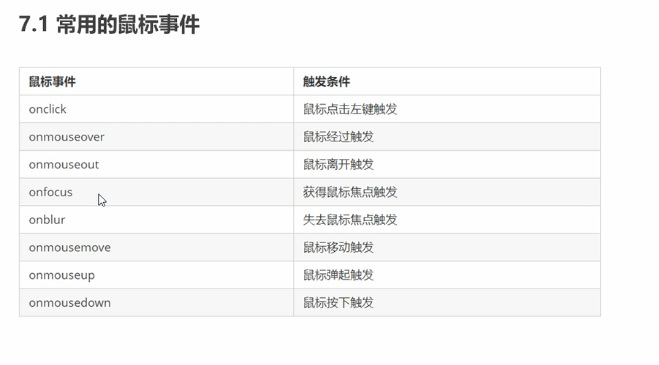
禁用右键,禁用选中文字:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> 我是一段不愿意分享的文字 <script> // 1. contextmenu 我们可以禁用右键菜单 document.addEventListener('contextmenu', function(e) { e.preventDefault(); }) // 2. 禁止选中文字 selectstart document.addEventListener('selectstart', function(e) { e.preventDefault(); }) </script> </body> </html>

跟随鼠标的图片:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> img { position: absolute; top: 2px; } </style> </head> <body> <img src="images/angel.gif" alt=""> <script> var pic = document.querySelector('img'); document.addEventListener('mousemove', function(e) { // 1. mousemove只要我们鼠标移动1px 就会触发这个事件 // console.log(1); // 2.核心原理: 每次鼠标移动,我们都会获得最新的鼠标坐标, 把这个x和y坐标做为图片的top和left 值就可以移动图片 var x = e.pageX; var y = e.pageY; console.log('x坐标是' + x, 'y坐标是' + y); //3 . 千万不要忘记给left 和top 添加px 单位 pic.style.left = x - 50 + 'px'; pic.style.top = y - 40 + 'px'; }); </script> </body> </html>
键盘事件:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1NK4y1e7nh?p=815
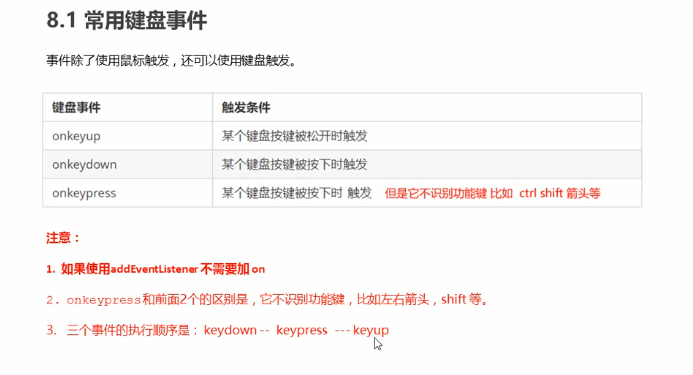

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> // 常用的键盘事件 //1. keyup 按键弹起的时候触发 // document.onkeyup = function() { // console.log('我弹起了'); // } document.addEventListener('keyup', function() { console.log('我弹起了'); }) //3. keypress 按键按下的时候触发 不能识别功能键 比如 ctrl shift 左右箭头啊 document.addEventListener('keypress', function() { console.log('我按下了press'); }) //2. keydown 按键按下的时候触发 能识别功能键 比如 ctrl shift 左右箭头啊 document.addEventListener('keydown', function() { console.log('我按下了down'); }) // 4. 三个事件的执行顺序 keydown -- keypress -- keyup </script> </body> </html>
模拟京东按键输入内容:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <input type="text"> <script> // 核心思路: 检测用户是否按下了s 键,如果按下s 键,就把光标定位到搜索框里面 // 使用键盘事件对象里面的keyCode 判断用户按下的是否是s键 // 搜索框获得焦点: 使用 js 里面的 focus() 方法 var search = document.querySelector('input'); document.addEventListener('keyup', function(e) { // console.log(e.keyCode); if (e.keyCode === 83) { search.focus(); } }) </script> </body> </html>
模拟京东快递单号查询:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .search { position: relative; width: 178px; margin: 100px; } .con { display: none; position: absolute; top: -40px; width: 171px; border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, .2); box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, .2); padding: 5px 0; font-size: 18px; line-height: 20px; color: #333; } .con::before { content: ''; width: 0; height: 0; position: absolute; top: 28px; left: 18px; border: 8px solid #000; border-style: solid dashed dashed; border-color: #fff transparent transparent; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="search"> <div class="con">123</div> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入您的快递单号" class="jd"> </div> <script> // 快递单号输入内容时, 上面的大号字体盒子(con)显示(这里面的字号更大) // 表单检测用户输入: 给表单添加键盘事件 // 同时把快递单号里面的值(value)获取过来赋值给 con盒子(innerText)做为内容 // 如果快递单号里面内容为空,则隐藏大号字体盒子(con)盒子 var con = document.querySelector('.con'); var jd_input = document.querySelector('.jd'); jd_input.addEventListener('keyup', function() { // console.log('输入内容啦'); if (this.value == '') { con.style.display = 'none'; } else { con.style.display = 'block'; con.innerText = this.value; } }) // 当我们失去焦点,就隐藏这个con盒子 jd_input.addEventListener('blur', function() { con.style.display = 'none'; }) // 当我们获得焦点,就显示这个con盒子 jd_input.addEventListener('focus', function() { if (this.value !== '') { con.style.display = 'block'; } }) </script> </body>


