《Kali渗透基础》06. 主动信息收集(三)
@
本系列侧重方法论,各工具只是实现目标的载体。
命令与工具只做简单介绍,其使用另见《安全工具录》。
本文以 kali-linux-2022.3-vmware-amd64 为例。
1:服务识别
识别开放端口上运行的应用与服务,可以提高攻击效率。
方法:
- Banner 捕获
- 建立连接后获取 Banner
- 服务指纹识别
- 另类识别方法
- 特征行为
- 可用于识别操作系统
Banner:指目标主机在响应请求时返回的服务标识信息。通常是一个文本字符串,包含了软件开发商、软件名称、服务类型,版本号等。
根据 Banner 抓取的信息有限,且不完全准确。
得到服务版本号可以直接发现已知漏洞和弱点。
1.1:NetCat
基本语法:
nc 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-n |
numeric-only IP addresses, no DNS. |
-v |
verbose [use twice to be more verbose]. |
示例01:尝试连接端口以获取服务信息。
nc -nv 1.1.1.1 22
基于 banner 捕获。
1.2:Socket
在 Python 中,socket 标准库用于网络通信,提供的编程接口用于创建网络套接字(socket)对象,以实现网络连接、数据传输和通信协议。
示例01:banner_grab.py。基于 banner 捕获。
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
import select
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("Usage - ./banner_grab.py <target-ip> <first port> <last port>")
print("Example - ./banner_grab.py 10.1.1.1 1 250")
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
start_ip = int(sys.argv[2])
end_ip = int(sys.argv[3])
for port in range(start_ip, end_ip):
try:
target = (ip, port)
ban_grab = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
ban_grab.connect(target)
ready = select.select([ban_grab], [], [], 1)
if ready[0]:
print("TCP Port " + str(port) + " - " + ban_grab.recv(4096).decode())
ban_grab.close()
except Exception as e:
# print(e)
pass
1.3:dmitry
Deepmagic Information Gathering Tool
"There be some deep magic going on"
基本语法:
dmitry 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-p |
Perform a TCP port scan on a host. |
-b |
Read in the banner received from the scanned port. |
示例01:
dmitry -pb 1.1.1.1
1.4:nmap
Nmap 可以发送一些列复杂的探测,根据响应特征来分析识别服务。
基本语法:
nmap 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM |
TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans. |
-sV |
Probe open ports to determine service/version info. |
示例01:基于 banner 捕获识别。
nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p 1-100 --script=banner
“ banner ” 脚本用于服务识别。基于 banner 捕获。
示例02:基于 nmap 的识别方法。
nmap 1.1.1.1 -p 1-100 -sV
2:操作系统识别
操作系统识别技术种类繁多。好的工具往往采用多种技术组合来识别。
一个简易识别方法,TTL 起始值:
- Windows:128
- Linux:64
- 某些 Unix:256
2.1:Scapy
命令行输入 scapy 进入或作为 python 模块使用。
示例01:ttl_os.py。基于 ttl 的简单验证。
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
from scapy.all import *
from scapy.layers.inet import IP, ICMP
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print('Usage - ./ttl_os.py <IP address>')
print('Example - ./ttl_os.py 10.1.1.1')
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
ans = sr1(IP(dst=str(ip))/ICMP(), timeout=1, verbose=0)
if ans == None:
print('No response')
elif int(ans[IP].ttl) <= 64:
print('Host is Linux/Unix')
else:
print('Host is Windows')
2.2:nmap
Nmap 使用多种技术识别操作系统。
基本语法:
nmap 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-O |
Enable OS detection. |
示例01:
nmap 1.1.1.1 -O
2.3:p0f
p0f(Passive OS Fingerprinting),用于被动操作系统指纹识别。
通过监控网络流量中的数据包并分析其特征,来确定操作系统类型和版本。
被动操作系统识别在有 IDS(Intrusion Detection System,入侵检测系统)时能派上用场。
基本语法:
p0f [选项]
示例01:开始流量监控并分析。
p0f
3:SNMP 扫描
信息的金矿。
经常被错误配置。
SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol)是一种用于网络设备管理和监控的协议,提供了一种标准的方式来收集、组织和传输网络设备的信息。
- SNMP 常使用 161 端口。
SNMP 允许网络管理员监视和管理网络中的设备,例如路由器、交换机、服务器和打印机等。
SNMP 基本工作原理:
管理器发送请求(Get、Set、Trap 等)到目标设备,目标设备响应请求并提供所需的信息。包括设备状态、性能指标、配置参数、事件通知等。
MIB(Management Information Base)是 SNMP 协议定义的一种树形网络设备管理功能数据库,用于描述网络设备中可管理的对象和属性。
每个网络设备都有一个特定的 MIB,其中包含了可查询和操作的对象。通过 SNMP 协议,管理器可以使用 OID(对象标识符)来访问和操作 MIB 中的信息。
3.1:onesixtyone
onesixtyone 用于 SNMP 字典攻击。
主要原理是尝试使用不同的社区字符串(community string)对目标设备执行 SNMP 查询,以发现设备的 MIB 数据。
Community String 是用于访问和管理网络设备的一种凭证或密码。SNMP 中,Community String 被用作一种简单的身份验证机制,用于控制对设备的访问权限。
基本语法:
onesixtyone 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Community String |
指定社区字符串。 |
-c <communityfile> |
file with community names to try. |
-o <outputfile> |
output log. |
-w n |
wait n milliseconds (1/1000 of a second) between sending packets (default 10). |
示例01:使用 public 作为社区字符串。
onesixtyone 1.1.1.1 public
示例02:
onesixtyone -c /usr/share/doc/onesixtyone/dict.txt 1.1.1.1 -o my.log -w 100
3.2:snmpwalk
snmpwalk 用于执行 SNMP Walk 操作,用于获取网络设备的管理信息。
SNMP Walk 操作:
是一种遍历 SNMP 设备的 MIB 树的过程,以收集设备上可用的 SNMP 对象和相关信息。
基本语法:
snmpwalk 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-c COMMUNITY |
set the community string. |
-v 1/2c/3 |
specifies SNMP version to use. |
示例01:
snmpwalk 1.1.1.1 -c public -v 2c
3.3:snmpcheck
snmpcheck 通过执行一系列 SNMP 查询和测试,检查目标设备的 SNMP 实现和配置,并提供相关的信息和报告。
基本语法:
snmpcheck 选项
4:SMB 扫描
SMB(Server Message Block)是一种用于在计算机网络上共享文件、打印机和其他资源的协议。最初由微软开发,已成为主流网络操作系统中常见的文件和打印共享协议之一。
- SMP 常使用 139 或 445 端口。
SMB 协议允许客户端通过网络与服务器通信,并请求对文件和资源的访问、读取、写入和管理。通过 SMB,用户可以在局域网或广域网上共享文件夹、打印机和其他网络资源。
- 微软历史上出现安全问题最多的协议
- 实现复杂
- 默认开放
- 文件共享
4.1:nmap
基本语法:
nmap 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
--script=<Lua scripts> |
Lua scripts is a comma separated list of directories, script-files or script-categories. |
--script-args=<n1=v1,[n2=v2,...]> |
provide arguments to scripts. |
可以到 /usr/share/nmap/scripts/ 目录下查看所有 nmap 脚本。
可以查看某个脚本内容以了解其功能与参数使用。
示例01:简单扫描 139,445 端口。
nmap -v -p 139,445 1.1.1.1-20
示例02:
nmap 1.1.1.1 -p 139,445 --script=smb-os-discovery.nse
smb-os-discovery.nse 脚本用于通过 SMB 协议进行信息发现和识别。
4.2:nbtscan
nbtscan 用于扫描局域网中的 NetBIOS(Network Basic Input/Output System)信息。
NetBIOS 是一种在早期 Windows 网络中广泛使用的协议,用于在局域网上识别和通信。
鉴于现在的发展,nbtscan 在对付古老的系统时可能会起到作用,现在可能用处已经不大。
基本语法:
nbtscan 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-r |
use local port 137 for scans. Win95 boxes respond to this only. |
示例01:
nbtscan -r 192.168.60.0/24
4.3:enum4linux
enum4linux 用于枚举和收集信息。通过与目标系统的 SMB 协议交互获取信息。
基本语法:
enum4linux 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-a |
Do all simple enumeration (-U -S -G -P -r -o -n -i). |
示例01:
enum4linux -a 192.168.60.10
5:SMTP 扫描
SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)是一种用于电子邮件传输的标准协议。
SMTP 本身没有提供任何身份验证或加密机制,需要结合其他安全机制确保邮件传输的安全性。
SMTP 扫描主要用来发现邮件账号。
5.1:NetCat
基本语法:
nc 选项
示例01:
nc -nv 1.1.1.1 25
5.2:nmap
基本语法:
nmap 选项
示例01:
nmap smtp.163.com -p 25 --script=smtp-enum-users.nse --script-args=smtp-enumusers.methods={VRFY}
smtp-enum-users.nse 用于枚举SMTP服务器上存在的有效用户。
smtp-enumusers.methods={VRFY} 指定脚本使用 VRFY 方法进行用户枚举。
示例02:
nmap smtp.163.com -p 25 --script=smtp-open-relay.nse
smtp-open-relay.nse 用于检测 SMTP 服务器是否开放了中继(Open Relay)功能。
中继是指允许未经身份验证的第三方通过 SMTP 服务器发送电子邮件的功能。
5.3:smtp-user-enum
smtp-user-enum 用于枚举 SMTP 服务器上存在的有效用户。
基本语法:
smtp-user-enum 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-M mode |
Method to use for username guessing EXPN, VRFY or RCPT (default: VRFY). |
-U file |
File of usernames to check via smtp service. |
-t host |
Server host running smtp service. |
示例01:
smtp-user-enum -M VRFY -U users.txt -t 10.0.0.1
6:防火墙识别
通过发送数据包并检查回包,可能识别端口是否经过防火墙过滤。
主要情况有以下四种:
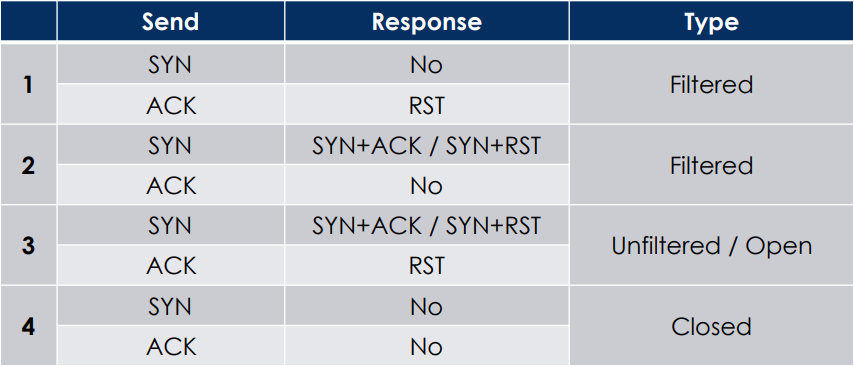
由于设备的不同,结果存在一定误差。
6.1:Scapy
示例01:FW.py。基于发送包并检查回包。
#!/usr/bin/python
import logging
import sys
from scapy.all import *
from scapy.layers.inet import IP, TCP
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print('Usage - ./FW.py <IP address> <Port>')
print('Example - ./FW.py 10.1.1.1 443')
sys.exit()
ip = sys.argv[1]
port = int(sys.argv[2])
ACK_response = sr1(IP(dst=str(ip))/TCP(dport=port, flags='A'), timeout=1, verbose=0)
SYN_response = sr1(IP(dst=str(ip))/TCP(dport=port, flags='S'), timeout=1, verbose=0)
if (ACK_response == None) and (SYN_response == None):
print('Port is either unstatefully filtered or host is down')
elif ((ACK_response == None) or (SYN_response == None)) and not ((ACK_response == None) and (SYN_response == None)):
print('Stateful filtering in place')
elif int(SYN_response[TCP].flags == 18):
print('Port is unfiltered and open')
elif int(SYN_response[TCP].flags == 20):
print('Port is unfiltered and closed')
else:
print('Unable to determine if the port is filtered')
6.2:nmap
nmap 带有一系列防火墙过滤检测功能。
基本语法:
nmap 选项
示例01:
nmap -sA 1.1.1.1 -p 22
7:负载均衡识别
负载均衡器是一种网络设备或软件,用于在多个服务器之间平衡传入流量,以提高性能和可靠性。
- DNS-Loadbalancing:DNS 轮巡,智能 DNS。
- HTTP-Loadbalancing。
7.1:lbd
LBD 用于查询和检测负载均衡。
lbd - load balancing detector.
基本语法:
lbd 选项
示例01:
lbd www.baidu.com
8:WAF 识别
WAF(Web Application Firewall,Web 应用防火墙)用于保护 Web 应用程序免受常见的网络攻击。
8.1:wafw00f
wafw00f 用于识别 WAF。通过分析 HTTP 响应头、页面内容和错误消息等信息,来识别是否存在 WAF 及可能的 WAF 类型。
The Web Application Firewall Fingerprinting Toolkit.
基本语法:
wafw00f 选项
部分选项:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
url |
要探测的网站 url。 |
-l, --list |
List all WAFs that WAFW00F is able to detect. |
示例01:
wafw00f http://www.baidu.com
8.2:nmap
基本语法:
nmap 选项
示例01:
nmap www.baidu.com --script=http-waf-detect.nse
http-waf-detect.nse 脚本用于检测 WAF 的存在。
人世几回伤往事,山形依旧枕寒流。
——《西塞山怀古》(唐)刘禹锡


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号