《数据结构-C语言》顺序表
@
顺序表
结构定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define OVERFLOW -1
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
#define MAX_SIZE 100 // 顺序表最大长度
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
/*
顺序表的类型定义
*/
typedef struct
{
ElemType* elem; // 指向数据元素的基地址
int length; // 顺序表的当前长度
}SequenceList;
初始化
/*
初始化顺序表
*/
Status InitList(SequenceList* L)
{
// 为顺序表分配空间
L->elem = (ElemType*)malloc(MAX_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
L->length = 0; // 空表长度为0
return OK;
}
创建表
/*
创建指定大小的顺序表
*/
void CreateSqList(SequenceList* L, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &L->elem[i]);
L->length++;
}
}
求表长
/*
求顺序表L的长度
*/
int GetLength(SequenceList L)
{
return (L.length);
}
判断表是否为空
/*
判断顺序表L是否为空
*/
Status IsEmpty(SequenceList L)
{
if (L.length == 0)
return YES;
else
return NO;
}
取值
/*
获取顺序表中第i个数据元素的内容
*/
Status GetElem(SequenceList L, int i, ElemType* e)
{
if (i < 1 || i > L.length)
return ERROR;
*e = L.elem[i - 1]; // 第i-1个单元存储着第i个数据
return OK;
}
查找
/*
在顺序表中查找值为e的数据元素
*/
int LocateELem(SequenceList L, ElemType e)
{
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
if (L.elem[i] == e) {
return i + 1; // 第i个单元存储着第i+1个数据
}
return 0;
}
插入
/*
插入,将元素插入到指定位序(插在第 i 个元素之前,0<i<=len+1)
*/
Status InsertElem(SequenceList* L, int i, ElemType e)
{
if (i < 1 || i > L->length + 1)
return ERROR; // i值不合法
if (L->length == MAX_SIZE)
return ERROR; // 当前存储空间已满
for (int j = L->length - 1; j >= i - 1; j--) {
L->elem[j + 1] = L->elem[j]; // 插入位置及之后的元素后移
}
L->elem[i - 1] = e; // 将新元素e放入第i个位置
L->length++; //表长增1
return OK;
}
删除
/*
将顺序表中第i个数据元素删除
*/
Status DeleteElem(SequenceList* L, int i, ElemType* e)
{
if ((i < 1) || (i > L->length)) {
return ERROR; // 删除位置不合理
}
*e = L->elem[i - 1];
for (int j = i;j <= L->length - 1;j++) {
L->elem[j - 1] = L->elem[j];
}
L->length--;
return OK;
}
逆置
/*
将顺序表所有元素逆置,空间复杂度为O(1)
*/
void Reverse(SequenceList* L) {
int temp = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < (L->length) / 2; i++) {
temp = L->elem[i];
L->elem[i] = L->elem[(L->length) - i - 1];
L->elem[(L->length) - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
清空
/*
清空顺序表L
*/
void ClearList(SequenceList* L)
{
L->length = 0;
}
销毁
/*
销毁顺序表L
*/
void DestroyList(SequenceList* L)
{
if (L->elem)
free(L->elem);
}
遍历打印
/*
打印顺序表
*/
void PrintSqList(SequenceList L)
{
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
{
printf("%d", L.elem[i]);
if (i < L.length - 1) {
printf(" ");
}
}
}
测试
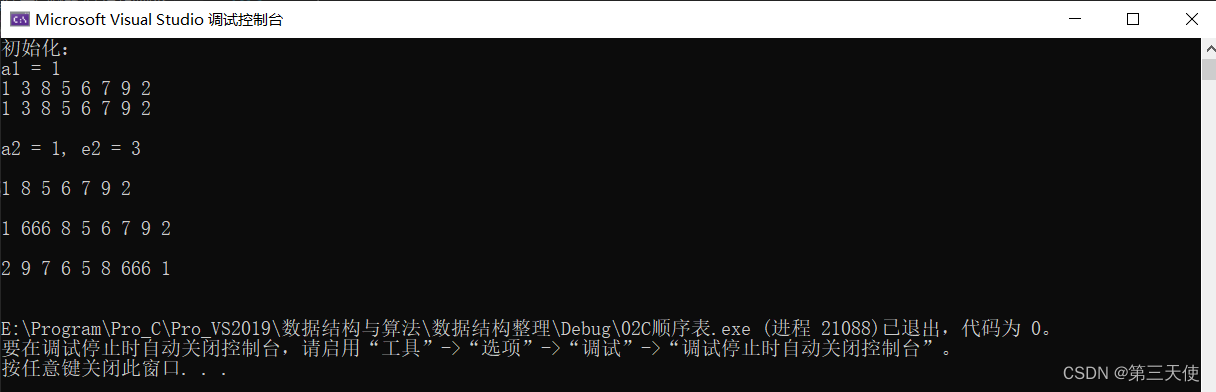
int main() {
// 测试数据:1 3 8 5 6 7 9 2
SequenceList Sq;
Status a1 = InitList(&Sq);
printf("初始化:\na1 = %d\n", a1);
CreateSqList(&Sq, 8);
PrintSqList(Sq);
ElemType e2 = 0;
Status a2 = GetElem(Sq, 2, &e2);
printf("\n\na2 = %d, e2 = %d\n\n", a2, e2);
ElemType e3 = 0;
Status a3 = DeleteElem(&Sq, 2, &e3);
PrintSqList(Sq);
printf("\n\n");
ElemType e4 = 666;
Status a4 = InsertElem(&Sq, 2, e4);
PrintSqList(Sq);
printf("\n\n");
Reverse(&Sq);
PrintSqList(Sq);
printf("\n\n");
ClearList(&Sq);
DestroyList(&Sq);
return 0;
}
测试结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号