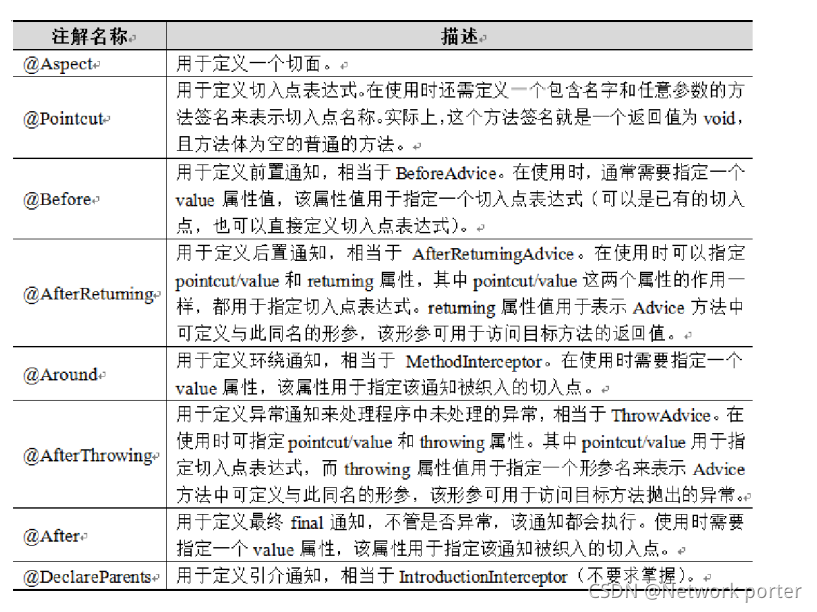
SpringAOP动态代理的实现和原理
官方点这AOP
一、常见面试题
- 说下你对Spring AOP理解
- 基于Java的AOP实现有哪些?AspectJ,Spring AOP,JBoss AOP
- AOP的使用场景: 权限,错误处理,记录跟踪 优化 校准,同步,事务
SpringAOP:就是对AOP设计模式的一种实现。SpringAOP基于动态代理的——运行时产生代理对
象。
JDK CGlib
是spring 项目用CGlib
二、怎么实现AOP
SpringAOP基于AspectJ实现AOP有三种形式:
基于XML的声明式AspectJ——配置
基于注解的声明式AspectJ。——注解,开启注解就行
JAVA的AspectJ
基于XML声明式AspectJ 切入点 切面 配置通知 配置织入
public class MyAdivce {
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("---------beforeMethod-------------");
}
//最终通知
public void afterMethod(){
System.out.println("======================== 方法执行完毕的最终");
}
public void arterReturnMethod(){
System.out.println("-------------------方法执行·完毕 之后 必须 正常方法就是");
}
public void ExceptionMethod(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println("================= 出现异常 异常");
}
/* 环绕通知*/
public Object arrroudMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==================环绕通知2");
Object[] objects= joinPoint.getArgs();
if (objects!=null){
for (Object obj:objects){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
System.out.println("开启事务");
Object obj=null;
try {
obj=joinPoint.proceed(objects);
System.out.println("事务提交");
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("回滚");
throw new Exception("操作异常");
}
System.out.println(obj);
return obj;
}
}

<bean id="tongzhi" class="com.advice.MyAdivce"/>
<aop:config><!-- 通知类型-->
<aop:pointcut id="qie" expression="execution(* com.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect id="qiemian" ref="tongzhi">
<!--前缀-->
<aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="qie"/>
<!-- 最终-->
<aop:after method="afterMethod" pointcut-ref="qie"/>
<!-- 后置-->
<aop:after-returning method="arterReturnMethod" pointcut-ref="qie"/>
<!-- 异常-->
<aop:after-throwing method="ExceptionMethod" pointcut-ref="qie" throwing="e"/>
<aop:around method="arrroudMethod" pointcut-ref="qie"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
注解配置
@Component//声明成bean
@Aspect//声明成切面
public class MyAdivce2 {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.service.*.*(..))")/* 定义切入点*/
public void qie(){
}
@Before("execution(* com.service.*.*(..))")
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("---------beforeMethod-------------");
}
//最终通知
@After("qie()")
public void afterMethod(){
System.out.println("======================== 方法执行完毕的最终");
}
@AfterReturning("qie()")
public void arterReturnMethod(){
System.out.println("-------------------方法执行·完毕 之后 必须 正常方法就是");
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "qie()",throwing = "e")
public void ExceptionMethod(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println("================= 出现异常 异常");
}
/* 环绕通知*/
@Around("qie()")
public Object arrroudMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==================环绕通知2");
Object[] objects= joinPoint.getArgs();
if (objects!=null){
for (Object obj:objects){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
System.out.println("开启事务");
Object obj=null;
try {
obj=joinPoint.proceed(objects);
System.out.println("事务提交");
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("回滚");
throw new Exception("操作异常");
}
System.out.println(obj);
return obj;
}
}
<!-- 声明注解配置1AOP-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
基于java 配置的AOP
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author zhangyifan
* @version 8.0
* @description:
* @date 2021/11/26 9:52
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class PeiZhi {
}
三、原理动态代理
动态代理有以下特点:
1.代理对象:必须实现接口
2.代理对象的生成,是利用JDK的API,动态的在内存中构建代理对象(需要我们指定创建代理对
象/目标对象实现的接口的类型)
相关的类和接口:
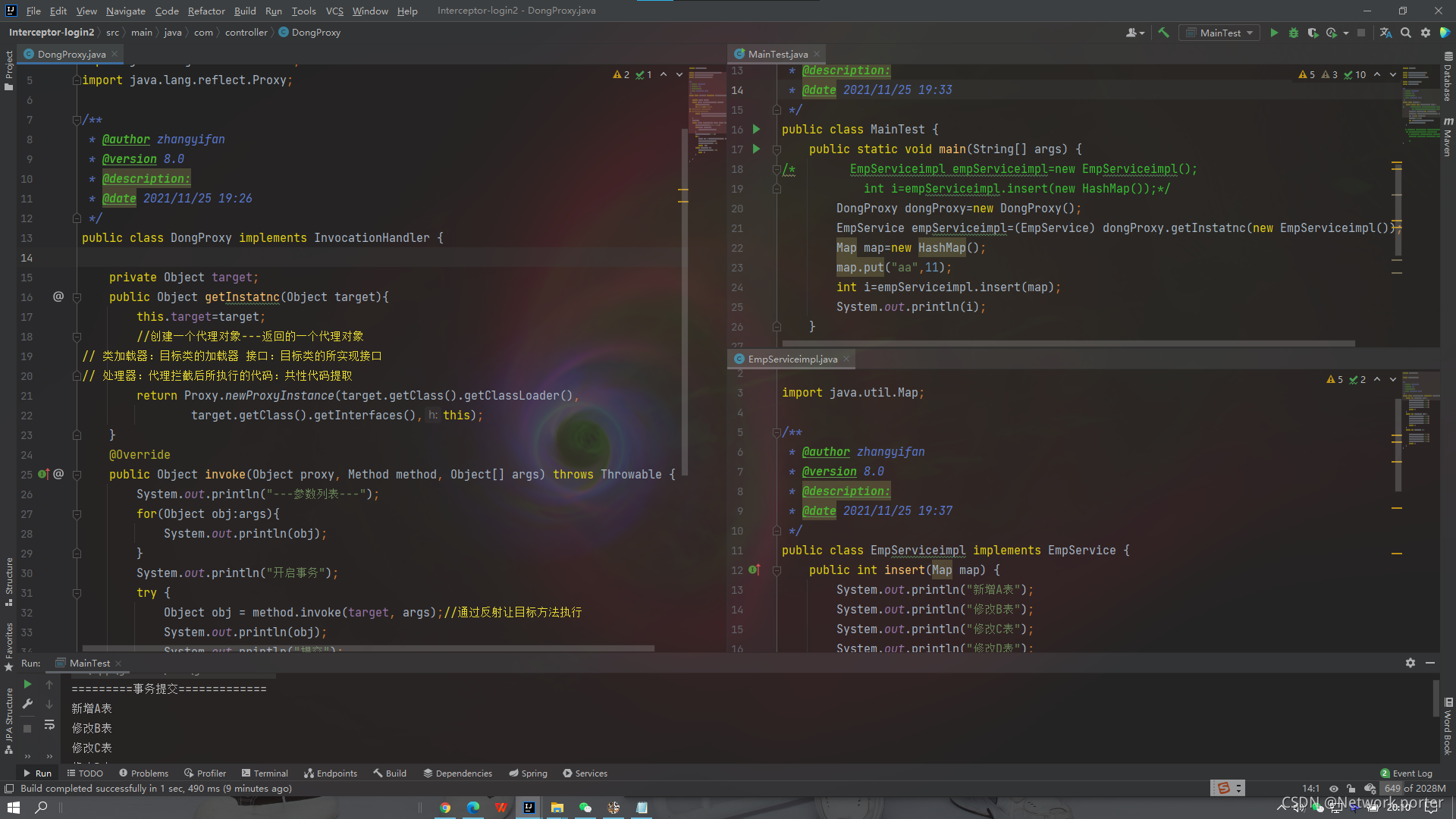
- java.lang.reflect.Proxy:这是 Java 动态代理机制的主类,它提供了一组静态方法来为一组接口动态地生成代理类及其对象
- java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler:这是调用处理器接口,它自定义了一个invoke方法,用于集中处理在动态代理类对象上的方法调用。通常在该方法中实现对委托类的代理访问。即用来指明产生的这个代理对象要做什么事情。
创建JDK动态代实现需要使用Proxy的newProxyInstance方法,该方法用来生成动态代理对
象,需要接收三个参数,完整的写法是:
static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h ) 注意该方法是在Proxy类中是静态方法,且接收的三个参数依次为: Ø ClassLoader loader:类加载器,定义了由哪个ClassLoader对象来对生成的代理对象进行加载 Ø Class<?>[] interfaces:代理类要实现的全部接口(需要代理的接口)
Ø InvocationHandler h:事件处理,执行目标对象的方法时,会触发事件处理器的方法,会把当前执行目标对象的方法作
为参数传入
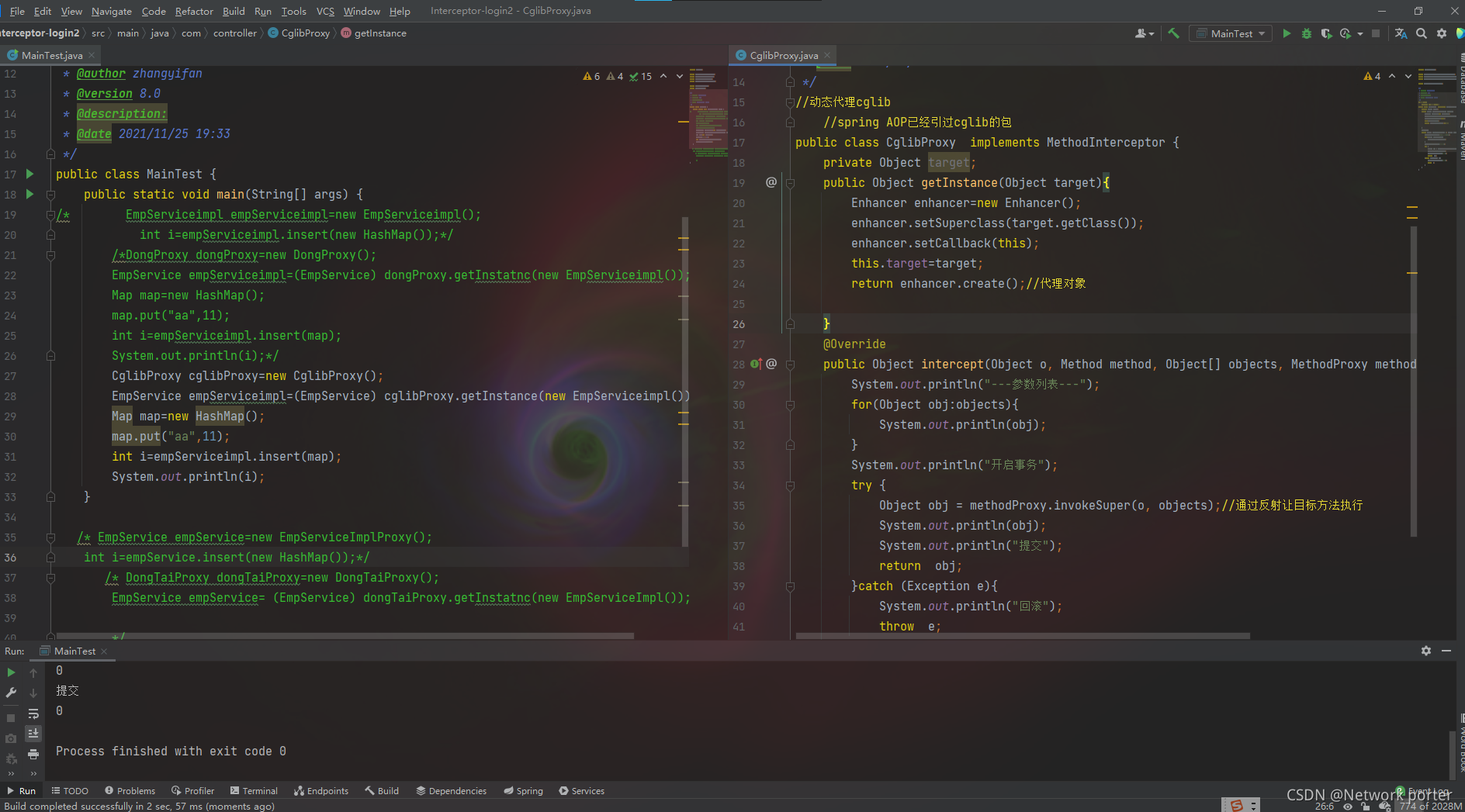
主要有两种方式,JDK 动态代理和 CGLIB 动态代理
- JDK 动态代理只提供接口代理,不支持类代理,核心 InvocationHandler 接口和Proxy 类,InvocationHandler 通过 invoke()方法反射来调用目标类中的代码,动态地将横切逻辑和业务编织在一起,Proxy 利用 InvocationHandler 动态创建一个符合某一接口的的实例, 生成目标类的代理对象。
- 如果代理类没有实现 InvocationHandler 接口,那么 Spring AOP 会选择使用
CGLIB 来动态代理目标类。CGLIB(Code Generation Library),是一个代码生成的类库,
可以在运行时动态的生成指定类的一个子类对象,并覆盖其中特定方法并添加增强代码,从
而实现 AOP。CGLIB 是通过继承的方式做的动态代理,因此如果某个类被标记为 final,
那么它是无法使用 CGLIB 做动态代理的
3.1、JDK动态代理(jdk自带的不需要在引jar包)
3.2、动态代理cglib
四、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
类关系
- 待更新




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号