第1章--基础篇
JS介绍
html 网页的内容;css 网页的样式;javascript 网页的行为
i.e. hello world
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> document.write("hello, world!"); </script> </body> </html>
使用JS的两种方法:
1. <script>...</script>:见上例
2. <script src="url/.js"></script>
JS特性:
运行环境:浏览器 -- 运行在浏览器中的代码
解释型语言:不需编译连接
浏览器中的JS:
ECMAScript:语法规范
DOM (Document Object Model): 文档对象模型,操作文档的规范--见下一章节《DOM编程艺术》
历史:
1995年Netscape Navigator 网景浏览器为了解决表单问题设计了LifeScript,后改名为JavaScript
1997年ECMAScript 1规范诞生
1998年W3C DOM规范诞生
...
2005年Ajax被广泛应用,web2.0时代到来(web应用)
...
JS调试
打开浏览器的调试面板:developor tools - Console面板
如何调试:
alert(var); -- 执行时浏览器弹窗显示
Console.log(var); -- 在Console面板中输出
实际开发:js调试器--Chrome--Developer tools--Source面板
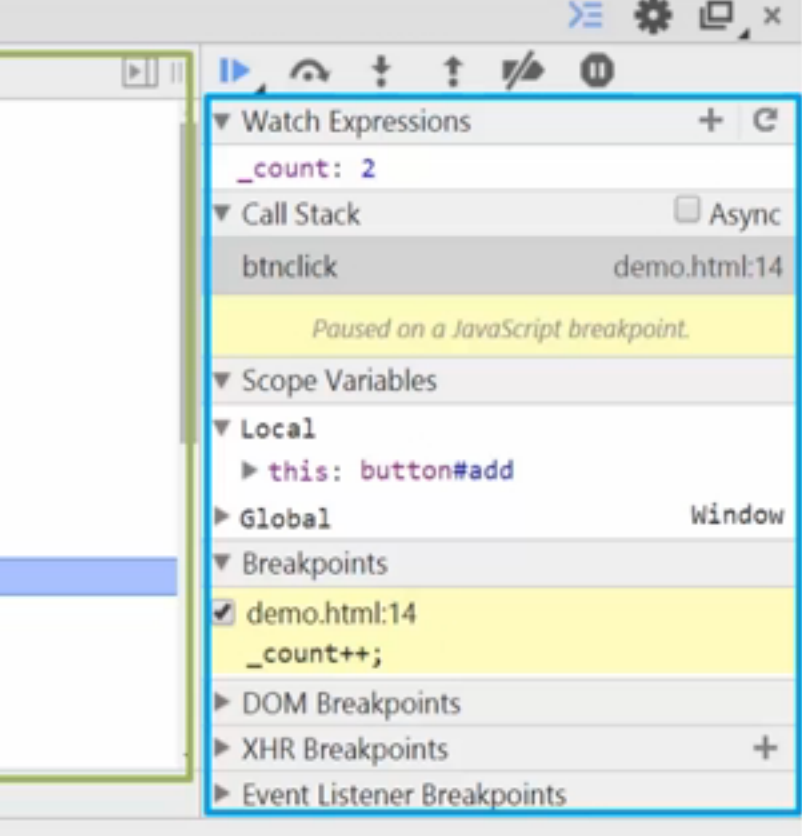
Watch Expressions: 自定义观察某变量
Call Stack:函数调用的堆栈
Scope Variables:局部变量和全局变量
Ctrl + o = 快捷查找文件
Ctrl + Shift + o = 快速查找函数
在正文显示窗口右键选择Evaluate in Console或按esc,可打开Console面板,尝试直接输出/修改某些变量:
在Console中输入变量名即可输出变量值,输入 变量名=值 即可暂时改变变量值
基本语法
直接量: var number = 1/1.2/"hello world"/true/null/[]/{name:'js'}...;
变量:var name; var name1, name2...;
标识符:变量名、函数名、函数参数、对象名等
case-sensitive;以字母、下划线或$开头,以字母、下划线、$和数字组成
关键字和保留字:标识符不能使用关键字或保留字
语句:分号结尾,但分号不是必须的。
赋值语句
条件语句
循环语句
with语句
异常捕获语句
等
注释:
单行注释 //
块级注释 /* */
基本类型
数据类型:
原始类型:
Number:
整数:15, 0377(Oct), 0xff(Hex)
浮点数:1.2,1.4e2,1.4e-2
特殊值:NaN (Not a Number) -- 类型转换时候使用
Infinity (1/0 or -1/0 -- negative infinity)
String:"..." or '...'
Boolean:true/false (lowercase)
Null:值为null,表示对象不存在
Undefined:值为undefined,表示已声明但未赋值的变量,或当获取对象不存在的属性时
引用类型:存放的为指向数据的的ref
Object:无序的名值对的集合
i.e.
var cat = { name: 'kitty', age: 2, mew: function() { console.log('喵喵喵'); } }
var dog = new Object();
var obj1 = {a:1}; var obj2 = obj1; obj2.a = 3; // obj1.a = ? -- 3
类型识别:typeof
i.e.
var num; typeof num; // Undefined var num = 1; typeof num; // Number typeof '1.1'; // String
运算符与表达式
运算符:
一元操作符: ++ -- + -
算数操作符: + - * / %
关系操作符: > < >= <=
相等操作符: == != === !==
做==相等运算时,类型会自动进行转换
i.e. var num = '4'; num == 4; // true (str 4->num 4)
0 == false; // true (false-->0)
2 == true; // false (true-->1)
'' == 0; // true (''-->0)
全等操作===:不做自动转换
4 === '4'; // false
详见JavaScript中的相等性判断:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Equality_comparisons_and_sameness
逻辑操作符:! && ||
!:
!0; // true
![]; // false
!""; // true
应用:求某变量的布尔值:!![];
&&:若前一个操作数为false,则后一个操作数不会执行
|| :若前一个操作数为true,则后一个操作数不会执行
Q:var a = 0; var b = 0 || ++a; //a和b的值?
A:// a = 1, b = 1
Q:!false && [];
A:// [] (!false为true,&&运算的前一个操作数为true,则返回后一个操作数[] )
赋值操作符: = += -= *= /= %=
条件操作符: __?__ : __;
逗号操作符:在同一个语句中做多个操作 i.e. var num1=5, num2=6;
对象操作符:
new: 获取对象实例 var cat = new Object();
delete:删除对象的一个属性 delete cat.name;
.:获取对象的属性值 cat.name;
[]:获取对象的属性值 cat['name'];
instanceof:判断某个变量是否为某个对象的实例,返回布尔值
in:判断某个属性是否在某个对象中,返回布尔值 'name' in cat; // true
位操作符: ~ & | ^ << >> >>>
i.e. var num = 8; num & 4; // 0 (位操作会先将操作数转化为32位二进制)
var num = 2; num << 2; // 8
操作符优先级:详见https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Operator_Precedence
表达式:
i.e. 5
5 + 4
(5 + 4) || false
语句
条件语句:
if else
switch
循环语句:
while
do-while
for
for in:
for (属性名 in 对象) {...} // 遍历对象中的属性名
循环控制:break; / continue;
with:对同一个对象进行多次操作时,用with将作用域变成该对象
with (表达式) {语句}
var kitty = { age: 3; friend: { name: 'snoopy', age: 2, } } document.write(kitty.friend.name + ":" + kitty.friend.age); // 使用with简化 with(kitty.friend) { document.write(name + ":" + age); }
异常捕获语句:try catch finally
数值
数值:i.e. 163/ 3.14/ 2.5e11/ 0x1ffa/
运算:
+-*/
Math.abs(x)
Math.round(x) // 四舍五入取整
Math.ceil(x) // 向上取整
Math.floor(x) // 向下取整
Math.max/min ( [value1 [, value2 [, ...]]] )
Math.random() // [0, 1)
Math.sin/cos()
Math.exp(x) // ex
Math.log(x)
Math.sqrt(x) // 平方根
Math.pow(x, y) // xy
到数值的转换:
parseInt(String); // 直接取整
parseInt('1.1'); // 1
parseInt('12s1.a'); // 12,忽略非数字以后的所有数值
parseInt('www'); // NaN (Not a Number)
parseFloat(String);
parseFloat('100.1'); // 100.1,其他情况同parseInt()
Number(value);
Number('100.1'); // 100.1
Number('12.1b45); // NaN
number.toFixed(digit); // 保留digit位小数
(100.123).toFixed(2); // 100.12
字符串
两种形式表达: " " / ' '
字符串长度:str.length // 属性
从html中获得字符串:var userName = input.value; // 详见下例
str.charAt(index); // return the char at index (index starts at 0)
str.indexOf(string [, fromIndex] ); // return the index of the first char found
"micro-major-web".indexOf("-"); // 5
"micro-major-web".indexOf("major"); // 6
"micromajor".indexOf("-"); // -1
str.search(regexp); // return the index of the first char in the first matched string
str.match(regexp); // return string(s) that matched the regexp as an array, null if none matches
"micromajor163".match(/[0-9]/); // ["1"]
"micromajor163".match(/[0-9]/g); // ["1", "6", "3"]
str.replace(regexp | substr, newSubstr | function);
"micromajor163".replace(/[0-9]/, "#"); // "micromajor#63"
"micromajor163".replace(/[0-9]/g, "#"); // "micromajor###"
"micromajor163".replace(/[0-9]/g, ""); // "micromajor"
str.substring(indexA [,indexB]);
"micromajor".substring(5); // "major"
"micromajor".substring(5,7); // "ma", from 5th(inclueded) to 7th(excluded)
str.slice(beginSlice [, endSlice]);
"micromajor".slice(5); // "major"
"micromajor".slice(5,7); // "ma", from 5th(inclueded) to 7th(excluded)
-- what is the diff btw .substring() and .slice()?
"micromajor".slice(1, -1); // "icromajo",-1: 倒数第一个(excluded)
"micromajor".slice(-3); // "jor"
while negative param in .substring() will be considered as 0
str.substr(start [,length]);
"micromajor".substr(5, 2); // "ma"
"micromajor".substr(5); // "major" -- in this case, it is the same as .substring();
str.split( [separator] [,limit] ); // return an array of substrings
// separator can be regular expression
"micro major".split(" "); // ["micro", "major"]
"micro major".split(" ", 1); // ["micro"],need 1 substring only
str.toLowerCase()/ str.toUpperCase();
str1 + str2 --> str1str2
String():和Number()类似--转换成字符串
String(163); // "163"
String(null); // "null"
转义字符:\
"micro\"major"; // "micro"major"
"micro\tmajor"; // "micro major"
对象
创建对象方法:
1. var name = new Ojbect();
2. var name = {...};
对象的属性和方法:
定义
color: "red", // key value pair--属性
run: function() {..}, // 方法
访问:
car.color;
car["color"];
car.run();
car["run"]();
增加:
car.type = "suv";
car.stop = function() {...};
修改:
car.color = "white";
car.run = function() {...};
删除:
delete car.color;
obj.constructor:获取某个对象的构造函数
car.constructor; // Object
var num = new Number(123); num.constructor; // Number
obj.toString():将对象转成字符串
obj.valueOf():获取对象的原始值
var num = new Number(123); num.valueOf(); // 123
obj.hasOwnproperty(property_name):返回是否拥有该属性 (通过继承得到的属性不算,即使可以访问到)
car.hasOwnProperty("color"); // true
数组
NB: JS的数组中的元素类型可以不同
创建数组:
var array = new Array();
var array = [];
var array = [1 ,6, 3];
属性和方法:
arr.length
arr[index] 获取数组元素
arr[index] = ... 修改数组元素
arr.indexOf (element [,fromIndex] ) 返回元素所在index,返回-1如没有
arr.forEach (callback [, thisArg] ) traverse the whole array,callback: function, thisArg: replace this in callback)
i.e. 对callback函数的arguments是有要求的:三个值 (元素, 索引, array)
var students = [ {id:1, score:80}, {id:2, score:50}, {id:3, score:70} ]; var editScore = function (item, index, array) { item.score += 5; }; students.forEach (editScore);
arr.reverse(); // 倒序结果覆盖了arr本身
arr.sort( [compareFunction] ) // 排序结果覆盖了arr本身
i.e. 对compareFunction的arguments是有要求的,两个值 (a, b)
对返回值的要求为:若大于0则调换a和b的顺序
var sortingByScore = function (a, b) { return b.score - a.score; }; students.sort(sortingByScore);
compareFunction不传入时,按Unicode编码顺序排序
arr.push( element , ... elementN ) // 在数组最后加入新元素
arr.unshift( element , ... elementN ) // 在数组开头加入新元素
arr.shift() // 获取数组第一个元素并在数组中删除
arr.pop() // 获取数组最后一个元素并在数组中删除
arr.splice( index, howMany [, ele1 [, ...eleN]] ); // 从第index个开始替换howMany个元素为ele1~eleN
若没写element,则为删除
若howMany为0,则为插入
i.e. students.splice(1,1, {id:4, score:90});
NB. reverse/ sort/ push/ unshift/ shift/ pop/ splice 均改变了原来的数组
arr.slice( begin [, end] ) 复制从begin到end(excluded)的元素as a new array
i.e. var newStudents = students.slice(0,2);
arr.concat( value, ... , valueN) 连接多个array (也可以是元素)
var allStudents = students1.concat(students2, students3);
arr.join( [separator] ) 将数组个元素用separator连接起来
若separator不填,则默认用逗号;若separator为"",则无连接符
var emails = [ "111", "222", "333"]; emails.join(";"); // "111;222;333"
实例:修改原数组并保留原数组的备份
var scores = [60, 70, 80, 90]; var newScores = []; var addScore = function(item, index, array) { newScores.push(item+5); } scores.forEach(addScore); newScores; // [65, 75, 85, 95]
→可用arr.map( callback [, thisArg] ); 实现完全相同的效果。
var scores = [60, 70, 80, 90]; var addScore = function(item, index, array) { return item+5; } var newScores = scores.map(addScore); // [65, 75, 85, 95]
arr.reduce( callback, [initialValue] )
i.e. 对callback的arguments是有要求的,四个值 (previousResult, item, index, array).
第一次的previousResult为initialValue
var sum = function(previousResult, item, index, array) { return previousResult + item.score; }; students.reduce(sum, 0); // initial value = 0
NB. slice/ concat/ join/ map/ reduce 没有修改原数组
函数
定义:
方法1:函数声明
function func_name (argument1, argument2, ... ) {
...
}
方法2:函数表达式:将匿名函数赋值给一个变量
var func_name = function (argument1, argument2, ... ) {
...
}
调用:
func_name (param1, param2, ... );
JS函数注意点:
1. 调用函数时,有一个隐藏变量arguments用于存放实参列表的值,和数量length
实参数量少于形参时,未定义的形参为undefined
实参数量多于形参时,可从arguments中得到多余的实参值。
实例:写一个参数数量不定的求和函数
function add() { var sum = 0; for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) { sum += arguments[i]; } return sum; }
2. 函数参数的类型
函数参数为基本类型时:值传递
函数参数为对象时:对象的引用传递
3. 作用域:
即使函数外定义的变量,函数内也可被使用
<script>
var matt = {
name = "Matt",
gender = 1;
};
function class1 () {
matt.name = "Matthew";
}
class1();
console.log(matt); // "Matthew"
</script>
4. 构造函数(和创建类的思想相似)
function Point(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.move = function(stepX, stepY) { this.x += stepX; this.y += stepY; } } var point = new Point(1,1); // 调用构造函数Point(x, y);
进入构造函数时,构造了一个空对象 {}
this.x = x; // 给该空对象增加属性x,并赋值为实参的值x;
默认返回值 return this;
--> 4中,若创建多个point,每个point中都会有一个move()方法--duplication--solution:原型
5. 原型 prototype -- 公共的给构造对象使用的函数
function Point(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } point.prototype.move = function(stepX, stepY) { this.x += stepX; this.y += stepY; };
此时,若有var point = new Point(1,1); 会创建对象 {x:1, y:1} 不包含move function,
但依然可以使用.move(); 因为Point中有一个隐藏属性是指向prototype.move()的
Date
创建日期:
new Date(); // 当前日期
new Date( year, month [,day [,hour [,minutes [,secondes [,milliseconds]]]]] )
i.e. new Date(1978, 11); // 1978-12-01 00:00:00
i.e. new Date(2012, 11, 5); // 注意:2012年12月5日(月份从0开始)
获取属性:
date.getXXX();
i.e. date.getFullYear(); // year
date.getMonth(); // month: start at 0
date.getDate(); // day
date.getHours();
date.getMinutes();
date.getSeconds();
设置属性:
date.setXXX();
i.e. aaa.setMonth(2); // 3月
注意,自动转化为标准格式
i.e. date.setHours(100); // 会将100h转化为天数并加到Date上。
应用:求某月份天数
hint: new Date(2001, 5, 0); -->2001-05-31
格式化:
var date = new Date(2015, 7, 20, 1, 57, 18);
date.toString(); // Thu Aug 20 2015 14:57:18 GMT+0800(中国标准时间) -- 不是需要的格式
function format(date) { return date.getFullYear() + '-' + padding(date.getMonth() + 1) + '-' + padding(date.getDate()) + ' ' + padding(date.getHours()) + ':' + padding(date.getMinutes()) + ':' + padding(date.getSeconds()); } function padding(number) { return (number<10) ? ('0' + number) : ('' + number); }
Date->Number:
date.getTime(); // 距1970-1-1 00:00:00的毫秒数
Number->Date:
new Date(value);
i.e. new Date(milliseconds);
若已创建Date,则date.setTime(milliseconds);
RegExp
正则表达式:描述字符串规则的表达式
i.e. 网易邮箱正则表达式:/^(.+)@(163|126|188)\.com$/
锚点:匹配一个位置
^ 起始位置:i.e. /^http:/
$ 结尾位置:i.e. /\.jpg$/
\b 单词边界:i.e. /\bis\b/.test('this'); // false
字符类:
i.e. [0-9] 一个数字
[^0-9] 非数字的一个字符
[a-z] 一个小写字母
. 任一字符(换行除外)
元字符:具有特殊意义的字符
刚才的 ^ $ \b
\d [0-9] \D [^\d]
\s 空白符 \S [^\s]
\w [A-Za-z0-9] \W [^\w]
量词:出现的次数
{m, n} 次数m~n
* 次数>=0
+ 次数0/1
? 次数>=1
转义符:需要匹配的字符是元字符时使用转义符
\/ \. \^ \$
多选分支:
( ... | ... )
i.e. /thi(c|n)k/ 或 /thi[cn]k/ -->字符类是每一个分支都是一个字符的多选分支
/\.(png|jpg|jpeg|gif)$/
捕获:保存匹配到的字符串,日后再用
() 捕获
(?:) 不捕获 i.e. /@(?:163|126|188)\.com$/
使用捕获的内容:$1, $2...,或使用str.match(regexp),详见下
创建:
方法1. /pattern/attrs i.e. /123abc/i
方法2. new RegExp(pattern, attrs);
常用方法:
regexObj.text(str); 测试regex与指定字符串是否匹配或包含相同substring,返回boolean
i.e.
<body> <input type="text" onblur="check(this)" onfocus="reset(this)"> <script> function check(mobileInput) { var value = mobileInput.value; if (!/[0-9]{11}/.text(value)) { mobileInput.style.borderColor = 'red'; } } function reset(mobileInput) { mobileInput.style.borderColor = ''; } </script> </body>
str.match(regexp); 获取匹配的字符串
i.e. 路径 http ://blog.163.com /album ?id=1 #comment
protocol host pathname search hash
var url = 'http://blog.163.com/album?id=1#comment'; var reg = /^(https?:)\/\/([^\/]+)(\/[^\?]*)?(\?[^#]*)?(#.*)?$/; var arr = url.match(reg); var protocol = arr[1]; var host = arr[2]; var pathname = arr[3]; var search = arr[4]; var hash = arr[5];
arr[0] 为 整个url
str.replace(regexp/substr, replacement)
替换一个子串
i.e. "The price of tomato is 5." --> "The price of tomato is 5.00."
var str = "The price of tomato is 5, the price of apple is 10."; str.replace(/(\d+)/g, '$1.00'); // The price of tomato is 5.00, the price of apple is 10.00.
i.e. replacement可以是函数
题目:在网页中显示源代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>replace</title> </head> <body> <div id="container"></div> <script type="text/javascript"> var container = document.getElementById('container'); var html = '<label>网址:</label><input placeholder="以http://起始">'; html = html.replace(/[<>]/g, function(m0) { switch(m0) { case "<": return "<"; case ">": return ">"; } }); container.innerHTML = html; </script> </body> </html>
regexpObj.exec(str) 更强大的检索功能(很少用)
更详尽的结果,包括index
过程的状态,lastIndex
i.e.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>exec</title> </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> var reg = /(.)(/d+)/g; var scores = "Tom $88, Nicholas ¥234, jack $38."; var result; while(result = reg.exec(scores)) { console.log(result); console.log(reg.lastIndex); } </script> </body> </html>
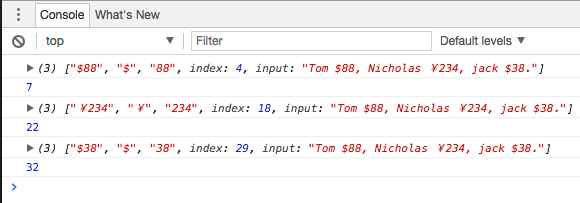
匹配的部分 匹配的每个捕获分别显示 从第几个index开始匹配(该例中为'$', index=4)
lastIndex表示下一个搜索开始的位置(该例中为 ',' index=7)
每次循环后,可以将lastIndex手动修改,即修改了下一次搜索开始的位置
JSON
问题:如何将var jerry = { name:"jerry", age:1 }; 转化成字符串呢
答:通过"" + jerry; 或通过jerry.toString(); 吗?
不行,结果为 '[object Object]'
那怎么做呢? JSON.
JSON: JavaScript Object Notation
JS对象: ;JSON表示
;JSON表示
i.e. 在浏览器中打开网易云音乐的页面,打开审查元素,Network,选中XHR,左边选中comment的csrf_token...选择Response,显示出的即为JSON格式的数据。将数据拷贝到sublime中,为很长的一行数据,使用命令HTMLPrettify如没有请安装该plugin,即可查看该JSON数据。
常用方法:
JSON.parse(text [,reviver])
JSON数据 -> JS数据
<script type="text/javascript">
var userJson = '{\
"id":1,\
"nick":"春鸟秋虫",\
"avatar":"1.jpg",\
"tags":null,\
"authed":false\
}'; // JSON string
var user = JSON.parse(userJson);
debugger
</script>
进入浏览器调试,Watch -- user: Object, 属性跟JSON文件描述的相同
function reviver的用法:
<script type="text/javascript">
var userJson = '{\
"id":1,\
"nick":"春鸟秋虫",\
"avatar":"1.jpg",\
"tags":null,\
"authed":false\
}'; // JSON string
var user = JSON.parse(userJson, function(k, v) {
if (k === 'avatar') {
// 给avatar加了前缀
return 'http://music.163.com/img/' + v;
}
return v;
});
debugger;
</script>
IE6、IE7不支持parse方法:自己在JSON中创建parse()
<script type="text/javascript">
if (window.JSON) {
parse: function(sJSON) {
return eval ('(' + sJSON + ')');
}
}
</script>
JSON.stringify(value [, replacer [, space]])
JS --> JSON
<script type="text/javascript">
var user = {
id:1,
nick:"春鸟秋虫",
avatar:"1.jpg",
tags:null,
authed:false
}; // Object
var userJson = JSON.stringify(user);
</script>
得到的userJson为JSON类型数据
replacer--预处理(少用)
例:只选择部分属性做转化
<script type="text/javascript">
var user = {
id:1,
nick:"春鸟秋虫",
avatar:"1.jpg",
tags:null,
authed:false
}; // Object
var userJson = JSON.stringify(user, ['id', 'nick', 'avatar']);
</script>
IE6、IE7不支持stringify()方法。解决方法与parse相同
if(!window.JSON) { window.JSON = { stringify: function() {...}}; }
ref:http://www.jianshu.com/p/7fdad7005957
基础篇课堂交流区问题汇总
1. 获取随机整数
2. 字符串第一个字符的删除
3. 数组求和的各种方法
4. 正则表达式的贪婪模式/惰性模式
5. JSON.stringify()兼容问题
http://blog.csdn.net/lovejulyer/article/details/51438515
基础篇的单元测验
以下表达式 1&&0 返回结果是
- A.1
- B.true
- C.NaN
- D.0
以下表达式 !0?1:2 返回结果是
- A.false
- B.true
- C.1
- D.2
以下代码执行后的结果为typeof (1>0)
- A."object"
- B."number"
- C."boolean"
- D."string"
以下不是Number类型的是
- A.10
- B."4"
- C.Infinity
- D.056
以下代码执行后,total的值为
var total = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < 5; i++){
if(i == 3){continue;}
total += i;
}
- A.6
- B.7
- C.8
- D.16
以下代码执行后,total的值为
var total = 0,
i = 5;
do{
total += i++;
}while(i < 7)
- A.7
- B.18
- C.11
- D.6
以下代码执行后,total的值为
var num1 = 10;
var num2 = 5;
var obj = {
num1:30,
num2:20
}
var total = 0;
with(obj){
total = num1 + num2;
}
- A.40
- B.0
- C.15
- D.50
以下代码执行后a的值为:
function increment(x){
x + 1;
}
var a = increment(3);
- A.2
- B.4
- C.5
- D.undefined
以下代码执行后a的值为:
var a = JSON.stringify({name: "jerry", age: 1, nick: undefined, tags: null});
- A.'{"name":"jerry","age":1,"nick":undefined,"tags":null }'
- B.'{"name":"jerry","age":"1","nick":"undefined","tags":"null" }'
- C.'{"name":"jerry","age":1 }'
- D.'{"name":"jerry","age":1,"tags":null}'
以下代码执行后circle的值为:
var circle = {x: 1, y: 0, r: 5};
function move(shape, stepX, stepY){
shape.x = shape.x + stepX;
shape.y = shape.y + stepY;
return shape
}
move(circle, -2, 3);
- A.{x: 1, y: 3, r: 5}
- B.{x: 4, y: -2, r: 5}
- C.{x: 1, y: -3, r: 5}
- D.{x: -1, y: 3, r: 5}
以下表达式中返回当前时间的有:
- A.new Date(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY)
- B.new Date(Date.now())
- C.Date.getNow()
- D.new Date()
Number("1.6a")的值为__________
Math.ceil("1.6")的值为
new Date(2015, 10, 0).getDate() 的值为_____________
/[a-z][^a-z]/.test("jerry") 的值为____________
基础篇的单元作业
函数random用于生成0-999之间的随机整数。
语法如下:
var number = random();
number是0-999之间的整数。
<script type="text/javascript">
var number = random();
function random () {
return Math.floor((Math.random() * 1000));
}
console.log(number);
</script>
函数parseQuery用于解析url查询参数。
语法如下:
var obj = parseQuery(query)
query是被解析的查询参数,函数返回解析后的对象。
使用范例如下:
var jerry = parseQuery("name=jerry&age=1");
jerry; 返回值:{name: " jerry ", age: "1"}
var tom = parseQuery("name= tom &age=12&gender&");
tom; 返回值:{name: "tom", age: "12", gender: ""}
请写出函数parseQuery的实现代码。
<script type="text/javascript">
var jerry = parseQuery("name=jerry&age=1");
var tom = parseQuery("name= tom &age=12&gender&");
function parseQuery(query) {
// delete spaces in url and overwrite the url itself
query = query.replace(/\s/g, "");
var splitedQueries = query.split("&");
// divides each piece of url into key-value pair
var reg = /^(\w+)=?([^\&]*)/;
var resultStr = "{"; // final result with type of String
for (var i = 0; i < splitedQueries.length; i++) {
if (splitedQueries[i] !== "") {
if (i != 0) {
resultStr += ",";
}
var arr = splitedQueries[i].match(reg);
resultStr += ("\"" + arr[1] + "\":\"" + arr[2] + "\"");
}
}
resultStr += "}";
return JSON.parse(resultStr);
}
</script>
函数multiply用于计算多个数字的乘积。
语法如下:
var product = multiply (number0, number1[, number2, ….]);
使用范例如下:
multiply(2, 3); 返回值: 6
multiply(-1, 3, 4); 返回值: -12
multiply(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); 返回值: 120
请写出函数multiply的实现代码。
<script type="text/javascript">
var product1 = multiply(2, 3);
var product2 = multiply(-1, 3, 4);
var product3 = multiply(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
console.log("product1: " + product1);
console.log("product2: " + product2);
console.log("product3: " + product3);
function multiply() {
var multiplication = 1;
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
multiplication *= arguments[i];
}
return multiplication;
}
</script>
构造函数Person用于构造人,语法如下:
function Person(name, age){
// 函数体
}
使用范例如下:
var jerry = new Person("Jerry", 2);
jerry.introduce(); 返回值: "I am Jerry, I am 2 years old! "
var tom = new Person("Tom", 12);
tom.introduce(); 返回值: "I am Tom, I am 12 years old! "
请写出构造函数Person的实现代码。
<script type="text/javascript">
var jerry = new Person("Jerry", 2);
jerry.introduce();
var tom = new Person("Tom", 12);
tom.introduce();
// print part for test
console.log(jerry.introduce());
console.log(tom.introduce());
function Person(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.introduce = function () {
if (this.age != 1) { // plural none
return "I am " + this.name + ", I am " + this.age + " years old!";
} else { // singular none
return "I am " + this.name + ", I am " + this.age + " year old!";
}
}
}
</script>
函数escapeHTML用于转义html字符串中的特殊字符(<>"&)。
语法如下:
var escapedStr = escapeHTML(htmlStr);
使用范例如下:
escapeHTML('<div>Tom&Jerry</div> ');
返回值:
'<div>Tom&Jerry</div> '
escapeHTML('<input type="text" name="mobile"> ');
返回值:
'<inputtype="text" name="mobile"> '
请写出函数escapeHTML的实现代码。
<script type="text/javascript">
var escapedStr1 = escapeHTML('<div>Tom&Jerry</div> ');
var escapedStr2 = escapeHTML('<input type="text" name="mobile"> ');
console.log(escapedStr1);
console.log(escapedStr2);
document.write(escapedStr1);
document.write(escapedStr2);
function escapeHTML(str) {
var escapedStr = ""; // initialization
escapedStr = str.replace(/[<>"&"]/g, function (char) {
switch(char) {
case '<':
return '<';
case '>':
return '>';
case '\"':
return '"';
default:
return '&';
}
});
return escapedStr;
}
</script>
other's ref: http://www.jianshu.com/p/4f74f0726abb

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号