cpp generate random array and then quick sort
#include <algorithm>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <sstream>
#include <thread>
#include <uuid/uuid.h>
#include <vector>
std::string get_time_now()
{
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::high_resolution_clock> now = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
time_t raw_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::to_time_t(now);
tm tm_info = *localtime(&raw_time);
std::stringstream ss;
ss << std::put_time(&tm_info, "%Y%m%d%H%M%S");
auto seconds = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(now.time_since_epoch());
auto mills = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(now.time_since_epoch());
auto micros = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(now.time_since_epoch());
auto nanos = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(now.time_since_epoch());
ss << "_"
<< std::setw(3) << std::setfill('0') << (mills.count() - seconds.count() * 1000)
<< std::setw(3) << std::setfill('0') << (micros.count() - mills.count() * 1000)
<< std::setw(3) << std::setfill('0') << (nanos.count() - micros.count() * 1000);
return ss.str();
}
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937_64 _mt{rd()};
template <typename T>
T gen_rand(T min, T max)
{
std::uniform_int_distribution<T> _uid(min, max);
return _uid(_mt);
}
template <typename T>
void gen_rand_array(T *arr, T min, T max, const int &len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
arr[i] = gen_rand<T>(min, max);
}
}
template <typename T>
void print_t_array(T *arr, const int &len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
std::cout << arr[i] << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
template <typename T>
void gen_print_rand_array(T min, T max, const int &len)
{
T *arr = new T[len];
gen_rand_array(arr, min, max, std::cref(len));
print_t_array(arr, std::cref(len));
delete[] arr;
std::cout << get_time_now() << ",finish in " << __FUNCTION__ << std::endl;
}
template <typename T>
void swap(T *t1, T *t2)
{
if (t1 == t2)
{
return;
}
T temp = *t1;
*t1 = *t2;
*t2 = temp;
}
template <typename T>
int partition(T *arr, int low, int high)
{
T pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j <= high; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i = i + 1;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return i + 1;
}
template <typename T>
void quick_sort_t(T *arr, int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high);
quick_sort_t(arr, low, pivot - 1);
quick_sort_t(arr, pivot + 1, high);
}
}
template <typename T>
void gen_print_quick_sort_t_array(T min, T max, const int &len)
{
T *arr = new T[len];
gen_rand_array(arr, min, max, std::cref(len));
print_t_array(arr, std::cref(len));
// std::cout << "\nAfter quick sort:" << std::endl;
quick_sort_t(arr, 0, len - 1);
print_t_array(arr, std::cref(len));
delete[] arr;
// std::cout << get_time_now() << ",thread id:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << ",finish in " << __FUNCTION__ << std::endl;
}
int main(int args, char **argv)
{
gen_print_quick_sort_t_array<std::uint32_t>(0, UINT32_MAX, atoi(argv[1]));
std::cout << get_time_now() << ",finished in " << __FUNCTION__ << ",thread id:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
}
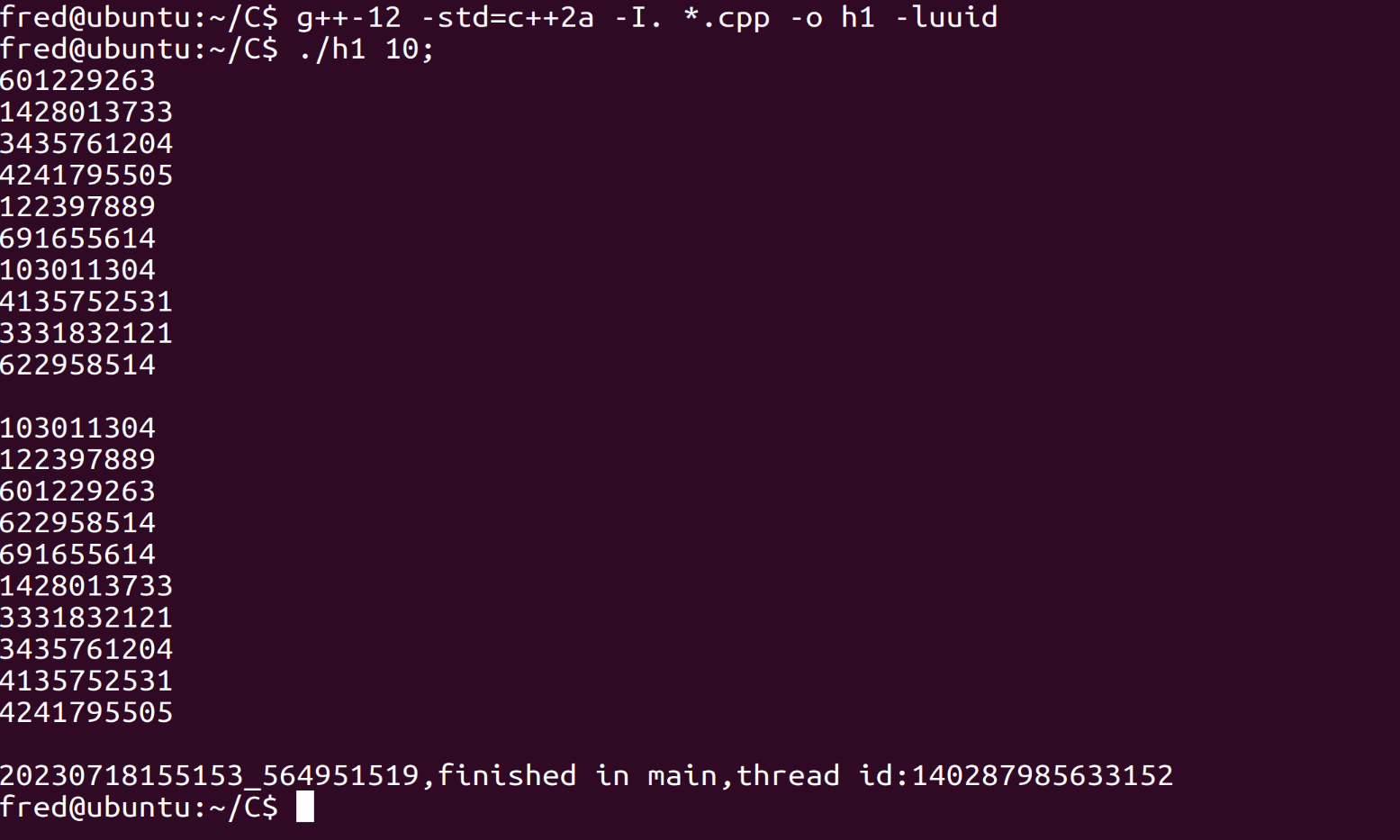
Compile
g++-12 -std=c++2a -I. *.cpp -o h1 -luuid


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号