C++ pass function via <functional> function and invoke via function address
#include <iostream> #include <functional> int callFunction55(int x, int y, function<int(int, int)> func); void invokeCall56(int x, int y); int sum57(int x, int y); int multiply58(int x, int y); int main(int args, char **argv) { invokeCall56(atoi(argv[1]), atoi(argv[2])); } void invokeCall56(int x, int y) { cout << "The sum of x and y is " << callFunction55(x, y, &sum57)<<endl; cout << "The prod of x and y is " << callFunction55(x, y, &multiply58)<<endl; } int callFunction55(int x, int y, function<int(int, int)> func) { return func(x, y); } int multiply58(int x, int y) { return x * y; } int sum57(int x, int y) { return x + y; }
The point located at two aspects, first declare #include <functional>,second declare the function as below via function key word
int callFunc55(int x,int y,function<int(int,int)> func)
Then define it which seems common as general function.
int callFunction55(int x, int y, function<int(int, int)> func) { return func(x, y); }
Be cautious,it's not pass function address but function keyword with angle bracket.
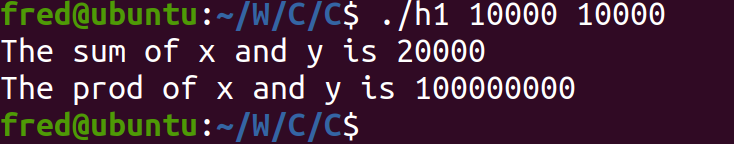
Compile via g++ and its standard is -std=c++2a, and run as below ./h1 10000 10000


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号