python处理excel文件(xls和xlsx)
一、xlrd和xlwt
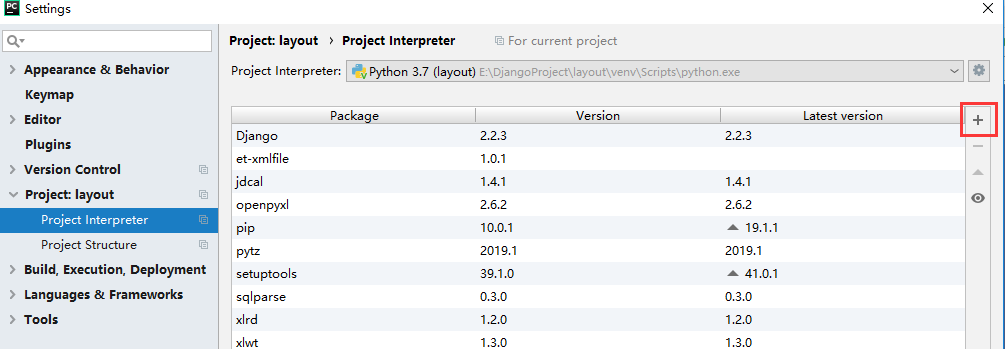
使用之前需要先安装,windows上如果直接在cmd中运行python则需要先执行pip3 install xlrd和pip3 install xlwt,如果使用pycharm则需要在项目的解释器中安装这两个模块,File-Settings-Project:layout-Project Interpreter,点击右侧界面的+号,然后搜索xlrd和xlwt,然后点击Install Package进行安装。
对于excel来说,整个excel文件称为工作簿,工作簿中的每个页称为工作表,工作表又由单元格组成。
对于xlrd和xlwt,行数和列数从0开始,单元格的行和列也从0开始,例如sheet.row_values(2)表示第三行的内容,sheet.cell(1,2).value表示第二行第三列单元格的内容。
1.xlrd模块读取excel文件
使用xlrd模块之前需要先导入import xlrd,xlrd模块既可读取xls文件也可读取xlsx文件。
获取工作簿对象:book = xlrd.open_workbook('excel文件名称')
获取所有工作表名称:names = book.sheet_names(),结果为列表
根据索引获取工作表对象:sheet = book.sheet_by_index(i)
根据名称获取工作表对象:sheet = book.sheet_by_name('工作表名称')
获取工作表行数:rows = sheet.nrows
获取工作表列数:cols = sheet.ncols
获取工作表某一行的内容:row = sheet.row_values(i) ,结果为列表 【sheet.row(i),列表】
获取工作表某一列的内容:col = sheet.col_values(i) 结果为列表 【sheet.col(i),列表】
获取工作表某一单元格的内容:cell = sheet.cell_value(m,n)、 sheet.cell(m,n).value、sheet.row(m)[n].value,sheet.col(n)[m].value,结果为字符串或数值 【sheet.cell(0,0),xlrd.sheet.Cell对象】
示例:假设在py执行文件同层目录下有一fruit.xls文件,有三个sheet页Sheet1、Sheet2、Sheet3,其中Sheet1内容如下:
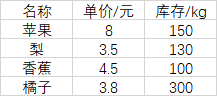

import xlrd book = xlrd.open_workbook('fruit.xls') print('sheet页名称:',book.sheet_names()) sheet = book.sheet_by_index(0) rows = sheet.nrows cols = sheet.ncols print('该工作表有%d行,%d列.'%(rows,cols)) print('第三行内容为:',sheet.row_values(2)) print('第二列内容为%s,数据类型为%s.'%(sheet.col_values(1),type(sheet.col_values(1)))) print('第二列内容为%s,数据类型为%s.'%(sheet.col(1),type(sheet.col(1)))) print('第二行第二列的单元格内容为:',sheet.cell_value(1,1)) print('第三行第二列的单元格内容为:',sheet.cell(2,1).value) print('第五行第三列的单元格内容为:',sheet.row(4)[2].value) print('第五行第三列的单元格内容为%s,数据类型为%s'%(sheet.col(2)[4].value,type(sheet.col(2)[4].value))) print('第五行第三列的单元格内容为%s,数据类型为%s'%(sheet.col(2)[4],type(sheet.col(2)[4]))) # 执行结果 # sheet页名称: ['Sheet1', 'Sheet2', 'Sheet3'] # 该工作表有5行,3列. # 第三行内容为: ['梨', 3.5, 130.0] # 第二列内容为['单价/元', 8.0, 3.5, 4.5, 3.8],数据类型为<class 'list'>. # 第二列内容为[text:'单价/元', number:8.0, number:3.5, number:4.5, number:3.8],数据类型为<class 'list'>. # 第二行第二列的单元格内容为: 8.0 # 第三行第二列的单元格内容为: 3.5 # 第五行第三列的单元格内容为: 300.0 # 第五行第三列的单元格内容为300.0,数据类型为<class 'float'> # 第五行第三列的单元格内容为number:300.0,数据类型为<class 'xlrd.sheet.Cell'>
可以看出通过sheet.row(i)、sheet.col(i)也可获取行或列的内容,并且结果也是一个列表,但是列表中的每一项类似字典的键值对,形式为数据类型:值。
而sheet.cell(0,0)获取单元格内容,结果是一个键值对,并且是一个xlrd.sheet.Cell对象。
2.xlwt写入excel文件
使用xlwt模块之前需要先导入import xlwt,xlwt模块只能写xls文件,不能写xlsx文件(写xlsx程序不会报错,但最后文件无法直接打开,会报错)。
创建工作簿:book = xlwt.Workbook(),如果写入中文为乱码,可添加参数encoding = 'utf-8'
创建工作表:sheet = book.add_sheet('Sheet1')
向单元格写入内容:sheet.write(m,n,'内容1')、sheet.write(x,y,'内容2')
保存工作簿:book.save('excel文件名称'),默认保存在py文件相同路径下,如果该路径下有相同文件,会被新创建的文件覆盖,即xlwt不能修改文件。

import xlwt book = xlwt.Workbook() sheet = book.add_sheet('Sheet1') sheet.write(0,0,'hello') sheet.write(1,0,'你好') book.save('hello.xls')
逐个单元格写入excel比较麻烦,可以按行或者列写入。

import xlwt proj = ['名称','单价/元','库存/kg'] fruit = ['苹果','梨','香蕉','橘子'] price = [8,3.5,4.5,3.8] storage = [150,130,100,300] book = xlwt.Workbook() sheet = book.add_sheet('Sheet1') for i in range(0,len(proj)): sheet.write(0,i,proj[i]) #按行插入行标题 for i in range(0,len(fruit)): sheet.write(i+1,0,fruit[i]) #插入第一列水果名称 for i in range(0,len(price)): sheet.write(i+1,1,price[i]) #插入第二列单价 for i in range(0,len(storage)): sheet.write(i+1,2,storage[i]) #插入第三列库存 book.save('fruit2.xls')
二、openpyxl模块
openpyxl模块可实现对excel文件的读、写和修改,只能处理xlsx文件,不能处理xls文件,使用之前同样需要先安装该模块,再导入 import openpyxl。
对于openpyxl,行数和列数都从1开始,单元格的行和列也从1开始。例如sheet.cell(1,2).value表示第一行第二列单元格的内容
1.openpyxl读取excel文件
获取工作簿对象:book = openpyxl.load_workbook('excel文件名称')
获取所有工作表名称:names = book.sheetnames
获取工作表对象:sheet1 = book.worksheets[n]、sheet2 = book['工作表名称']、sheet3 = book[book.sheetnames[n]]
获取工作表名称:title = sheet1.title
获取工作表行数:rows = sheet1.max_row
获取工作表列数:cols = sheet1.max_column
获取某一单元格内容:cell = sheet.cell(1,2).value、sheet['单元格'].value例如sheet['B1'].value
假设有一fruit2.xlsx,除后缀名其他与上述fruit.xls完全一样

import openpyxl book = openpyxl.load_workbook('fruit2.xlsx') print('所有sheet页名称:',book.sheetnames) sheet = book.worksheets[0] sheet2 = book['Sheet1'] sheet3 = book[book.sheetnames[0]] print('工作表名称:',sheet3.title) rows = sheet.max_row cols = sheet.max_column print('该工作表有%d行,%d列.'%(rows,cols)) # 执行结果 # 所有sheet页名称: ['Sheet1', 'Sheet2', 'Sheet3'] # 工作表名称: Sheet1 # 该工作表有5行,3列.
2.行和列生成器
对于xlrd模块来说,可直接通过sheet.row[i]和sheet.col[i]获取行和列的内容,但是对于openpyxl模块来说,无法直接获取某一行或列的内容,openpyxl模块的sheet.rows和sheet.columns表示行和列的生成器,即generator object,需要通过循环或转换成列表、元组的形式得到行或列的值。

print(sheet.rows,sheet.columns) for col in sheet.columns: print(col) for row in sheet.rows: for i in row: print(i.value,end=' ') print() # 执行结果 # <generator object Worksheet._cells_by_row at 0x00000230E011A2A0> <generator object Worksheet._cells_by_col at 0x00000230E102FC00> # (<Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A5>) # (<Cell 'Sheet1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B5>) # (<Cell 'Sheet1'.C1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C5>) # 名称 单价/元 库存/kg # 苹果 8 150 # 梨 3.5 130 # 香蕉 4.5 100 # 橘子 3.8 300
如果要获取某一行或者列的内容,可将行、列生成器对象转换成列表或者元组,再循环列表或者元组得到内容。
前面说过openpyxl模块的行和列都从1开始,但是由于将生成器转化成了列表list(sheet.rows),而列表的索引从0开始,因此list(sheet.rows)[1]还是表示第二行的内容,不是第一行的内容。

for i in list(sheet.rows)[1]: print(i.value,end=' ') print() for i in list(sheet.columns)[0]: print(i.value,end=' ') # 执行结果 # 苹果 8 150 # 名称 苹果 梨 香蕉 橘子
获取单元格的内容
print(sheet.cell(1,2).value) #第一行第二列单元格的内容 print(sheet['a2'].value) #使用excel单元格的表示法,字母不区分大小写
3.openpyxl写excel文件
创建工作簿:book = openpyxl.Workbook(),如果写入中文为乱码,可添加参数encoding = 'utf-8'
创建工作表:sheet = book.create_sheet('工作表名称',0),0表示创建的工作表在工作薄最前面
向单元格写入内容:sheet.cell(m,n,'内容1')、sheet.cell(x,y,'内容2')
保存工作簿:book.save('excel文件名称'),默认保存在py文件相同路径下,如果该路径下有相同文件,会被新创建的文件覆盖。

book = openpyxl.Workbook() sheet = book.create_sheet('Sheet1',0) proj = ['名称','单价/元','库存/kg'] fruit = ['苹果','香蕉','梨','橘子'] price = [8,3.5,4.5,3.8] storage = [150,130,300,100] for i in range(len(proj)): sheet.cell(1,i+1,proj[i]) for i in range(len(fruit)): sheet.cell(i+2,1,fruit[i]) for i in range(len(price)): sheet.cell(i+2,2,price[i]) for i in range(len(storage)): sheet.cell(i+2,3,storage[i]) book.save('fruit2.xlsx')
4.openpyxl修改excel文件
sheet.insert_rows(m)和sheet.insert_cols(n)分别表示在第m行、第n列前面插入行、列
sheet.delete_rows(m)和sheet.delete_cols(n)分别表示删除第m行、第n列

rows = sheet.max_row sheet.insert_rows(rows+2) cherry = ['樱桃',17,80] for j in cherry: sheet.cell(rows+1,cherry.index(j)+1,j) book.save('fruit2.xlsx')
修改单元格内容:sheet.cell(m,n) = '内容1'或者sheet['B3'] = '内容2'

sheet.cell(3,2,4) sheet['B3'] = 5 book.save('fruit2.xlsx')
在最后追加行:sheet.append(可迭代对象)

straberry = ['草莓',20,50] sheet.append(straberry) book.save('fruit2.xlsx')
xlrd、xlwt和openpyxl处理excel文件,在写入文件的时候不如pandas简单,pandas处理excel文件见另外一篇博客https://www.cnblogs.com/Forever77/p/11298173.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号