8、nginx基础
1Nginx基本简述
Nginx是一个开源且高性能、可靠的Http Web服务、代理服务。
开源: 直接获取源代码
高性能: 支持海量并发
可靠: 服务稳定
我们为什么选择 Nginx服务
Nginx非常轻量
功能模块少 (源代码仅保留http与核心模块代码,其余不够核心代码会作为插件来安装)
代码模块化 (易读,便于二次开发,对于开发人员非常友好)
互联网公司都选择Nginx
1.Nginx技术成熟,具备的功能是企业最常使用而且最需要的
2.适合当前主流架构趋势, 微服务、云架构、中间层
3.统一技术栈, 降低维护成本, 降低技术更新成本。
Nginx采用Epool网络模型,Apache采用Select模型
Select: 当用户发起一次请求,select模型就会进行一次遍历扫描,从而导致性能低下。
Epool: 当用户发起请求,epool模型会直接进行处理,效率高效,并无连接限制。
Nginx 典型应用场景

2Nginx快速安装
Nginx软件安装的方式有很多种
1.源码编译=>Nginx (1.版本随意 2.安装复杂 3.升级繁琐)
2.epel仓库=>Nginx (1.版本较低 2.安装简单 3.配置不易读)
3.官方仓库=>Nginx (1.版本较新 2.安装简单 3.配置易读,推荐)
2.1官方仓库
1.安装Nginx软件所需依赖包
[root@web ~]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ autoconf pcre pcre-devel make automake wget httpd-tools vim tree
2.配置nginx官方yum源
[root@web ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
3.安装Nginx服务,启动并加入开机自启
[root@web ~]# yum install nginx -y
[root@web ~]# systemctl enable nginx
[root@web ~]# systemctl start nginx
4.通过浏览器访问该服务器ip或url地址 10.0.0.7
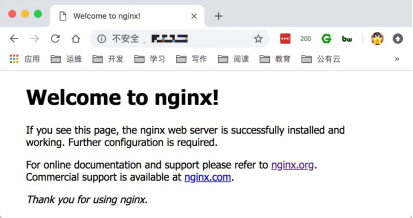
5.检查Nginx软件版本以及编译参数
[root@web ~]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.14.0
[root@web ~]# nginx -V
6.为了让大家更清晰的了解Nginx软件的全貌,可使用rpm -ql nginx查看整体的目录结构及对应的功能,如下表格整理了Nginx比较重要的配置文件
1.Nginx主配置文件
| 路径 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | 配置文件 | nginx主配置文件 |
| /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf | 配置文件 | 默认网站配置文件 |
2.Nginx代理相关参数文件
| 路径 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params | 配置文件 | Fastcgi代理配置文件 |
| /etc/nginx/scgi_params | 配置文件 | scgi代理配置文件 |
| /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params | 配置文件 | uwsgi代理配置文件 |
3.Nginx编码相关配置文件
| 路径 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx/win-utf | 配置文件 | Nginx编码转换映射文件 |
| /etc/nginx/koi-utf | 配置文件 | Nginx编码转换映射文件 |
| /etc/nginx/koi-win | 配置文件 | Nginx编码转换映射文件 |
| /etc/nginx/mime.types | 配置文件 | Content-Type与扩展名 |
4.Nginx管理相关命令
| 路径 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| /usr/sbin/nginx | 命令 | Nginx命令行管理终端工具 |
| /usr/sbin/nginx-debug | 命令 | Nginx命令行与终端调试工具 |
5.Nginx日志相关目录与文件
| 路径 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| /var/log/nginx | 目录 | Nginx默认存放日志目录 |
| /etc/logrotate.d/nginx | 配置文件 | Nginx默认的日志切割 |
2.2源码编译安装
获取官网tar包并解压
[root@web01 ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.2.tar.gz
[root@web01 ~]# tar xf nginx-1.14.2.tar.gz
进入nginx-1.14.2/目录,编译
[root@web01 ~]# cd nginx-1.14.2/
[root@web01 nginx-1.14.2]# ./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx
--modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-compat
--with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module
--with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module
--with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module
--with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module
--with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module
--with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream
--with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module
--with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -fPIC'
--with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie'
[root@web01 nginx-1.14.2]# make && make install
3Nginx默认配置
Nginx主配置文件/etc/nginx/nginx.conf是一个纯文本类型的文件,整个配置文件是以区块的形式组织的。一般,每个区块以一对大括号{}来表示开始与结束。
Nginx主配置文件整体分为三块进行学习,分别是CoreModule(核心模块),EventModule(事件驱动模块),HttpCoreModule(http内核模块)
CoreModule核心模块
user www; #Nginx进程所使用的用户
worker_processes 1; #Nginx运行的work进程数量(建议与CPU数量一致或auto)
error_log /log/nginx/error.log #Nginx错误日志存放路径
pid /var/run/nginx.pid #Nginx服务运行后产生的pid进程号
events事件模块
events {
worker_connections 25535; #每个worker进程支持的最大连接数
use epoll; #事件驱动模型, epoll默认
}
http内核模块
http { #http层开始
...
#使用Server配置网站, 每个Server{}代表一个网站(简称虚拟主机)
server {
listen 80; #监听端口, 默认80
server_name bgx.com; #提供的域名
access_log access.log; #该网站的访问日志
#控制网站访问路径
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #存放网站源代码的位置
index index.html index.htm; #默认返回网站的文件
}
}
...
#第二个虚拟主机配置
'server' {
...
}
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; #包含/etc/nginx/conf.d/目录下所有以.conf结尾的文件
} #http层结束
http server location扩展了解项
http{}层下允许有多个Server{}层,一个Server{}层下又允许有多个Location
http{} 标签主要用来解决用户的请求与响应。
server{} 标签主要用来响应具体的某一个网站。
location{} 标签主要用于匹配网站具体URL路径。
4Nginx网站配置
4.1.新增nginx配置文件
[root@web01 conf.d]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/game.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name game.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /code;
index index.html;
}
}
4.2.放置游戏源代码文件至nginx配置文件root指定的目录
[root@web01 conf.d]# mkdir /code && cd /code
[root@web01 code]# rz html5.zip
[root@web01 code]# unzip html5.zip
[root@web01 code]# ls
ceshi game html5.zip img index.html readme.txt
4.3.检查nginx的语法是否存在错误
[root@web01 code]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
4.4.重载Nginx [reload|restart]
[root@web01 code]# systemctl reload nginx
5Nginx虚拟主机
通常在企业中可能会有很多业务系统,那么多套业务服务如何使用Nginx配置?
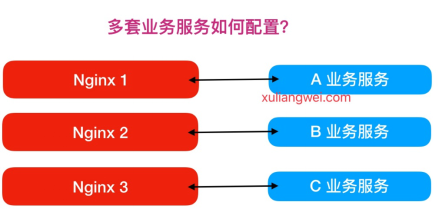
如果使用如上方式部署,则需要多台服务器配置Nginx,但如果使用虚拟主机方式,则在同一个Nginx上运行多套单独服务,这些服务是相互独立的。简单来说,看似多套业务系统,实则可以运行在一台Nginx服务上
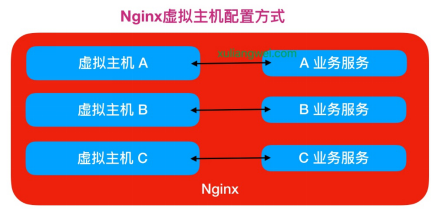
Nginx配置虚拟主机有如下三种方式:
方式一、基于主机多IP方式
方式二、基于端口的配置方式
方式三、基于多个hosts名称方式(多域名方式)
5.1基于多IP的虚拟主机配置实战
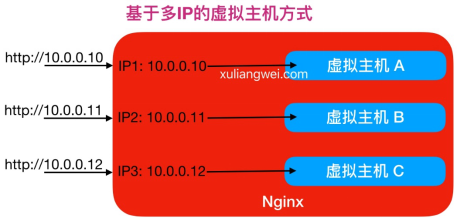
那么基于多IP的方式,有如下两种方式:
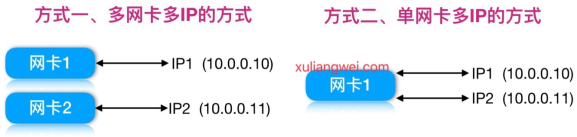
1.配置多网卡多IP的方式
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.10:80;
...
}
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.11:80;
...
}
2.配置单网卡多IP的方式
#添加一个IP
[root@web01 ~]# ip addr add 10.0.0.11/24 dev eth0
# 虚拟机配置方案
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/addr1.conf
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.10:80;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/addr2.conf
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.11:80;
...
}
5.2基于端口虚拟主机配置实战
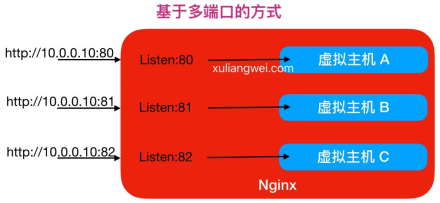
Nginx多端口虚拟主机方式,具体配置如下
#仅修改listen监听端口即可, 但不能和系统端口出现冲突
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/port1.conf
server {
...
listen 80;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/port2.conf
server {
...
listen 81;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/port3.conf
server {
...
listen 82;
...
}
5.3基于host名称的虚拟主机方式配置实战
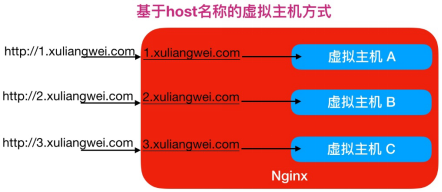
1.创建对应的web站点目录以及程序代码
[root@web01 ~]# mkdir /soft/code/{server1,server2}
[root@web01 ~]# echo "server1" > /code/server1/index.html
[root@web01 ~]# echo "server2" > /code/server2/index.html
2.配置不同域名的虚拟主机
[root@web02 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/server1.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name 1.xuliangwei.com;
root /code/server1;
index index.html;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/server2.conf
server {
...
listen 80;
server_name 2.xuliangwei.com;
root /code/server2;
index index.html;
}
6Nginx日志管理
Nginx有非常灵活的日志记录模式,每个级别的配置可以有各自独立的访问日志。日志格式通过log_format命令定义格式。
6.3.1.log_format定义日志格式语法
# 配置语法: 包括: error.log access.log
Syntax: log_format name [escape=default|json] string ...;
Default: log_format combined "...";
Context: http
6.3.2.默认Nginx定义语法格式如下
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
6.3.3.Nginx日志格式允许包含的内置变量
$remote_addr # 记录客户端IP地址
$remote_user # 记录客户端用户名
$time_local # 记录通用的本地时间
$time_iso8601 # 记录ISO8601标准格式下的本地时间
$request # 记录请求的方法以及请求的http协议
$status # 记录请求状态码(用于定位错误信息)
$body_bytes_sent # 发送给客户端的资源字节数,不包括响应头的大小
$bytes_sent # 发送给客户端的总字节数
$msec # 日志写入时间。单位为秒,精度是毫秒。
$http_referer # 记录从哪个页面链接访问过来的
$http_user_agent # 记录客户端浏览器相关信息
$http_x_forwarded_for #记录客户端IP地址
$request_length # 请求的长度(包括请求行, 请求头和请求正文)。
$request_time # 请求花费的时间,单位为秒,精度毫秒
# 注:如果Nginx位于负载均衡器,nginx反向代理之后, web服务器无法直接获取到客 户端真实的IP地址。
# $remote_addr获取的是反向代理的IP地址。 反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,
# 增加X-Forwarded-For信息,用来记录客户端IP地址和客户端请求的服务器地址。
6.3.4.access_log日志配置语法
Syntax: access_log path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] [flush=time] [if=condition]];
access_log off;
Default: access_log logs/access.log combined;
Context: http, server, location, if in location, limit_except
6.3.5.Nginx Access日志配置实践
server {
listen 80;
server_name code.oldboy.com;
#将当前的server网站的访问日志记录至对应的目录,使用main格式
access_log /var/log/nginx/code.oldboy.com.log main;
location / {
root /code;
}
#当有人请求改favicon.ico时,不记录日志
location /favicon.ico {
access_log off;
return 200;
}
}
6.3.6.日志切割logrotate
[root@nginx conf.d]# cat /etc/logrotate.d/nginx
/var/log/nginx/*.log {
daily # 每天切割日志
missingok # 日志丢失忽略
rotate 52 # 日志保留52天
compress # 日志文件压缩
delaycompress # 延迟压缩日志
notifempty # 不切割空文件
create 640 nginx adm # 日志文件权限
sharedscripts
postrotate # 切割日志执行的命令
if [ -f /var/run/nginx.pid ]; then
kill -USR1 `cat /var/run/nginx.pid`
fi
endscript
}
6.3.7.日志切割后的效果
[root@bgx ~]# ll /var/log/nginx/
total 4044
-rw-r----- 1 www adm 54438 Oct 12 03:28 access.log-20181012.gz
-rw-r----- 1 www adm 28657 Oct 13 03:48 access.log-20181013.gz
-rw-r----- 1 www adm 10135 Oct 12 03:28 error.log-20181130.gz
-rw-r----- 1 www adm 7452 Oct 13 03:48 error.log-20181201.gz


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号