C++11 单例类实现
单例类:
(1) 单例类保证全局只有一个唯一的实例对象。
(2) 单例类保证只有唯一的接口获取这唯一实例。
非线程安全的单例类举例:
1 class CSingleton 2 { 3 public: 4 ~CSingleton(){} 5 static CSingleton * getInstance() 6 { 7 if (m_instance == nullptr) 8 { 9 m_instance = new CSingleton; 10 } 11 return m_instance; 12 } 13 static void delInstance() 14 { 15 if (m_instance) 16 { 17 delete m_instance; 18 m_instance = nullptr; 19 } 20 } 21 void print() 22 { 23 std::cout << "print test" << std::endl; 24 } 25 private: 26 CSingleton(){} 27 CSingleton & operator=(const CSingleton & ) = delete; 28 CSingleton(const CSingleton &) = delete; 29 private: 30 static CSingleton * m_instance; 31 }; 32 33 CSingleton * CSingleton::m_instance = nullptr;
上述单例类面对多线程并发访问时会出错。
看如下线程安全的单例类(非C++11实现)
1 class CSingleton
2 {
3 public:
4 ~CSingleton() {}
5 static CSingleton * getInstance()
6 {
7 if (m_instance == nullptr)
8 {
9 std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lgd(m_mt);
10 if (m_instance == nullptr)
11 {
12 m_instance = new CSingleton;
13 }
14 }
15 return m_instance;
16 }
17 static void delInstance()
18 {
19 std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lgd(m_mt);
20 if (m_instance)
21 {
22 delete m_instance;
23 m_instance = nullptr;
24 }
25 }
26 void print()
27 {
28 std::cout << "print test" << std::endl;
29 }
30 private:
31 CSingleton() {}
32 CSingleton & operator=(const CSingleton & ) = delete;
33 CSingleton(const CSingleton &) = delete;
34 private:
35 static CSingleton * m_instance;
36 static std::mutex m_mt;
37 };
38
39 CSingleton * CSingleton::m_instance = nullptr;
40 std::mutex CSingleton::m_mt;
当然绝对的线程安全还是有问题,因为C++创建对象时,会执行1、分配内存,2 调用构造,3 赋值操作三步操作,然而现代CPU和编译器高并发下可能
会进行乱序重排操作,因而创建对象new CSingleton的第2步可能会晚于第3步进行指令调用,因而导致出现未定义的的行为。
举例:
线程A : getInstance 判断 instance是否为空,为空则
线程A : 分配内存 此时CPU乱序指令重排,赋值操作提前
线程B : getInsnace 判断instance是否为空,非空,则返回
线程B : 使用了未初始化的instacne 出现未定义行为。
线程A : 调用构造函数对instance初始化。
因此要解决上述问题需要引入内存栅栏来确保指令运行的同步性。在CPU指令重排的前提下保持数据的一致性。
C++11支持线程安全的单例类:
C++11的单例模式的实现
1 class CSingleton
2 {
3 public:
4 ~CSingleton() {}
5 static CSingleton & getInstance()
6 {
7 static CSingleton m_instance;
8 return m_instance;
9 }
10 void print()
11 {
12 std::cout << "print test" << std::endl;
13 }
14 };
返回静态局部对象的引用,C++11中是线程安全的。
验证一下:
1 class CStatic
2 {
3 public:
4 CStatic()
5 {
6 std::cout << "construct begin" << std::endl;
7 Sleep(5000);
8 std::cout << "construct end" << std::endl;
9 }
10 void print()
11 {
12 std::cout << "print" << std::endl;
13 std::cout << s_num++ << std::endl;
14 }
15 static int s_num;
16 static std::mutex s_mt;
17 };
1 int CStatic::s_num = 0;
2 std::mutex CStatic::s_mt;
3
4 //
5 void thread_func()
6 {
7 static CStatic st;
8 st.print();
9 }
10
11 int main()
12 {
13 std::vector<std::thread> vecThread;
14 for (auto i = 0; i< 8; i++)
15 {
16 vecThread.push_back(std::thread(thread_func));
17 }
18 for (auto i = 0; i< 8; i++)
19 {
20 vecThread[i].join();
21 }
22 //
23 system("pause");
24 return 0;
25 }
首先我们创建一个CStatic类,然后创建8个线程来启动thread_func(),thread_func()初始化了一个静态CStatic对象,(静态局部变量仅被初始化一次)
然后接着运行。我们发现,当首个线程初始化CStatic时,其他线程都是被阻塞的,从构造函数的begin和end中可以看到,我们故意让其停留5s,
如下图,其他线程都是在st被初始化之后才运行。
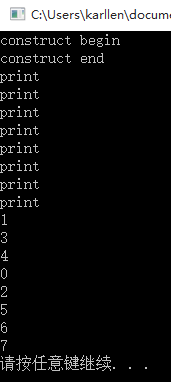
所以CStatic静态局部对象被构造的过程中是线程安全的,但是其拥有的成员变量则不是线程安全的。
因此我们增加个简单的锁,
1 class CStatic
2 {
3 public:
4 CStatic()
5 {
6 std::cout << "construct begin" << std::endl;
7 Sleep(5000);
8 std::cout << "construct end" << std::endl;
9 }
10 void print()
11 {
12 std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lgd(s_mt);
13 std::cout << "print" << std::endl;
14 std::cout << s_num++ << std::endl;
15 }
16 static int s_num;
17 static std::mutex s_mt;
18 };




