compilationPrinciple
编译原理
Lexical Analysis
采用NFA,符合一般思维习惯。
Pascal版本
高度封装,尽可能用函数代替重复的部分来减少代码的行数。
源码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdarg.h>
using namespace std;
#define idMax 20
#define keyWordsLen 17
class wordsAnalyzer{
private:
char wd; // 读取字符
int status; // 自动机状态
int len; // 缓存长度
int flag; // 标记分析器是否正常
int wordsLen; // 词元数量
int type; // 种别归类: 0-关键字 1-运算符 2-常数 3-界符 4-标识符 5-注释串
int cag; // 种别码, 保持为可查表位序+1
int srcLen; // 源码长度
int needOF; // 是否需要保存至文件
int p; // 迭代指针
vector<string> strV; // 存储词元
vector<int> typeV; // 存储种别码
string words; // 缓存
string src; // 源码字符串
FILE *oF; // 结果保存文件,默认为fiP
string oFP; // 保存路径
public:
// 词元编码表
vector<string> wordsTable = {
"program", "var", "integer", "bool", // 0-3
"real", "char", "const", "begin", // 4-7
"if", "then", "else", "while", // 8-11
"do", "repeat", "until", "for", // 12-15
"to", "non", "non", "non", // 16(17-19跳过)
"!", "&&", "||", "+", // 20-23
"-", "*", "/", "<", // 24-27
">", "<=", ">=", "=", // 28-31
":=", "id", "intConst", "realConst", // 32-35
"strConst", "boolConst", ";", ",", // 36-39
"'", "\"", "//", "/*", // 40-43
"*/", ":", "(", ")", // 44-47
".", // 48
};
// 空白字符
vector<char> filt = {' ', '\n', '\t', '\0'};
// 单字分隔符,不考虑冒号,点号
vector<char> delm = {';', ',', '(', ')'};
// 布尔常量
vector<string> boolean = {"true", "false"};
wordsAnalyzer(string fiP = "./test.txt", string foP = "./res.txt"){
flag = 1; // 分析器状态ok
words = "";
len = 0;
status = 0; // 自动机起点
wordsLen = 0; // 词元数量
oFP = foP; // 保存路径
p = 0; // 指针初始化为0
ifstream ins;
if(oFP!=""){
needOF = 1;
oF = fopen(oFP.c_str(), "w"); // 覆盖式的写入
if(oF==NULL){
printf("Fail to write in the file: %s", oFP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1);
}
newPrintf("Output file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", oFP.c_str());
}
else needOF = 0; // 不保存文件
ins.open(fiP, ios::in); // 读入模式打开文件
if(!ins.good()){ // 检测文件是否正常打开
printf("Fail to open the file: %s", fiP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1); // 出错, 终止程序
}
newPrintf("Input file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", fiP.c_str()); // 展示读取路径
printSplit("Src"); // 分割线
char _ch;
src = "";
while((_ch = ins.get()) != EOF){ // 存入源码串中
src += _ch;
}
ins.close();
src += '\0'; // 终止符
srcLen = src.length(); // 源码串长度
newPrintf("%s\n", src.c_str()); // 展示源码
}
~wordsAnalyzer(){
fclose(oF); // 关闭FILE文件流
}
void analyze(){ // 词法分析器
while(p < srcLen){
wd = src[p];
switch(status){
case 0: // 自动机起点,words为空
if(isBlank()) blankContinue(); // 跳过空白字符, 并迭代指针
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 转移状态->1 字母开头 大写字母可以用于区分标识符和关键字,但即使全是小写字母也需要单独检查,因此全是字母归为一类
else if(isNumber(0)) newStatus(2); // 转移状态->2 非零数字开头
else if(wd == '0') newStatus(3); // 转移状态->3 0开头
else if(wd == '&') newStatus(4); // 转移状态->4
else if(wd == '|') newStatus(5); // 转移状态->5
else if(wd == ':') newStatus(6); // 转移状态->6
else if(wd == '>') newStatus(7); // 转移状态->7
else if(wd == '<') newStatus(8); // 转移状态->8
else if(wd == '/') newStatus(9); // 转移状态->9
else if(wd == '*') newStatus(10); // 状态转移->10 单字运算符
else if(wd == '=') newStatus(11); // 状态转移->11 单字运算符
else if(wd == '!') newStatus(12); // 状态转移->12 单字运算符
else if(wd == '+' || wd == '-') newStatus(13); // 状态转移->13 加减号(正负号)
else if(wd == '.') newStatus(14); // 状态转移->14 考虑.5 == 0.5 ,此时.后必须有数字
else if(isDelimiter()){ // 单字分界符直接给出结果
newStatus(-1);
typeDelimiter();
output(); // 存储词元、输出、初始化
}
else if(wd == '\'') newStatus(15); // 状态转移->15 单引号
else if(wd == '"') newStatus(16); // 状态转移->16 双引号
else passError(); // 检测到非法字符如"^#$"等
break;
case 1:{ // 字母开头,全字母情况 可终止 -> 标识符或关键字或布尔常量
if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 原地踏步
else if(isNumber() || wd == '_') newStatus(17); // 状态转移->17
else{ // 处理缓存内容
typeWords();
output();
}
break;
}
case 2:{ // 非零数字开头,可终止
if(wd=='.') newStatus(18); // 转移状态->18 十进制实数, 此时.后可以无内容
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E') newStatus(19); // 转移状态->19 科学计数法E
else if(isNumber()) newStatus(2); // 原地踏步
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"') // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
passError(); // 出错处理
else{ // 被视为整常数,重置缓存
typeConst(0); // 整常数->0
output();
}
break;
}
case 3:{ // 0开头数字,可终止
if(wd == 'X' || wd == 'x') newStatus(20); // 状态转移->20 十六进制X
else if(wd == 'b' || wd == 'B') newStatus(21); // 状态转移->21 二进制数b
else if(isNumber(8)) newStatus(22); // 状态转移->22 八进制数
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"') // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
passError(); // 出错处理
else{ // 被视为整常数0
typeConst(0);
output();
}
break;
}
case 4:{ // 检查 & 不可终止
if(wd == '&'){ // 与运算符
newStatus(-1);
typeOperator();
output();
} else passError();
break;
}
case 5:{ // 检查 | 不可终止
if(wd == '|'){ // 或运算符
newStatus(-1);
typeOperator();
output();
} else passError();
break;
}
case 6:{ // 检查 : 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // 赋值号:=
newStatus(-1);
typeOperator();
output();
} else{ // 冒号:
typeDelimiter();
output();
}
break;
}
case 7:{ // 检查 > 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // >=
newStatus(-1);
typeOperator();
output();
} else { // >
typeOperator();
output();
}
break;
}
case 8:{ // 检查 < 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // <=
newStatus(-1);
typeOperator();
output();
} else { // <
typeOperator();
output();
}
break;
}
case 9:{ // 检查 / 可终止
if(wd == '/') newStatus(23); // 状态转移->23 单行注释符//
else if(wd == '*') newStatus(24); // 状态转移->24 多行注释符
else { // 除号/
typeOperator();
output();
}
break;
}
case 10:{ // 检查 * 这样的语法是允许的:3*-5*+5 可终止
// if(wd == '&' || wd == '|' || '*' || '/' || '<' || '>' || '=' || ';' || ',' || '\'' || '"' || ':'){
// i = passError(i);
// } else {
// type = 1;
// output();
// i -= 1;
// }
typeOperator();
output();
break;
}
case 11:{ // 检查 = a = /*2333333*/ 5;
// if(wd == '=' || '&' || '|' || '*' || '<' || '>' || ':' || ';' || ','){
// i = passError(i);
// } else {
// type = 1;
// output();
// i -= 1;
// }
typeOperator();
output();
break;
}
case 12:{ // 检查 ! 先不谈!=, 这样的语法是可以的 !-.5 == !(-0.5) == 0(boolean) 或者 !!"0" == 1(boolean) 可终止
// if(wd == '&' || wd == '|' || wd == '*' || wd == '<' || wd == '>' || wd == ':' || wd == ';' || wd == ',')
typeOperator();
output();
break;
}
case 13:{ // +-号 不完美的DFA 可终止
if(cag >= 34 && cag <= 38 || cag == 48){ // 前面出现操作数则为加减号, '('被视为有效界符, ')' 则被视为操作数
typeOperator();
output();
}
else if(wd == '.') newStatus(14); // 状态转移->14 实数
else if(isNumber(0)) newStatus(2); // 状态转移->2 非0数字
else if(wd == '0') newStatus(3); // 状态转移->3 数字0
else{ // 加减号
typeOperator();
output();
}
break;
}
case 14:{ // . 实数 可终止
if(isNumber()) newStatus(18); // 状态转移->18 正常实数
else {
typeDelimiter();
output();
}
break;
}
case 15:{ // 单引号 条件终止
if(wd == '\''){ // 字符常量
newStatus(-1);
typeConst(2);
output();
} else newStatus(15); // 原地踏步
break;
}
case 16:{ // 双引号 条件终止
if(wd == '"'){ // 字符常量
newStatus(-1);
typeConst(2);
output();
} else newStatus(16); // 原地踏步
break;
}
case 17:{ // 标识符 可终止
if(isNumber() || isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '_') // 原地踏步
newStatus(17);
else { // 获取标识符
typeWords(1);
output();
}
break;
}
case 18:{ // 真 实数 后可不跟数字 可终止
if(isNumber()) newStatus(18); // 原地踏步
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E') // 状态转移->19 科学计数法 允许有: 3.e7 的写法
newStatus(19);
else { // 截取实数
typeConst(1);
output();
}
break;
}
case 19:{ // 科学计数法e 不可终止
if(wd == '+' || wd == '-') newStatus(25); // 状态转移->25 科学计数法+-
else if(isNumber()) newStatus(26); // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
else passError(); // 出错啦
break;
}
case 20:{ // 十六进制x 不可终止
if(isNumber(16)) newStatus(27); // 状态转移->27 十六进制整数后终态
else passError();
break;
}
case 21:{ // 二进制数b 不可终止
if(isNumber(2)) newStatus(28); // 状态转移->28 二进制数后终态
else passError();
break;
}
case 22:{ // 八进制数中态 可终止
if(isNumber(8)) newStatus(22); // 原地踏步
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E') newStatus(19); // 状态转移->19 科学计数法e
else if(wd == '.') newStatus(18); // 状态转移->18 当做十进制数处理的八进制小数(C++中自适应)
else {
typeConst(0);
output();
}
break;
}
case 23:{ // 单行注释符// 条件终止
if(wd == '\n'){ // 截取单行注释串
newStatus(-1);
typeNote();
output();
} else newStatus(23); // 原地踏步
break;
}
case 24:{ // 多行注释符/* 不可终止
if(wd == '*') newStatus(29); // 状态转移->29 检测退出记号*/
else newStatus(24); // 原地踏步
break;
}
case 25:{ // 科学计数法+- 不可终止
if(isNumber()) newStatus(26); // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
else passError();
break;
}
case 26:{ // 十进制整数后终态 可终止
if(isNumber()) newStatus(26); // 原地踏步
else {
typeConst(1);
output();
}
break;
}
case 27:{ // 十六进制整数后终态 十六进制不接受小数点
if(isNumber(16)) newStatus(27); // 原地踏步
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E') newStatus(19); // 状态转移->19
else {
typeConst(0);
output();
}
break;
}
case 28:{ // 二进制数后终态
if(isNumber(2)) newStatus(28);
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E') newStatus(19);
else {
typeConst(0);
output();
}
break;
}
case 29:{ // 检测退出记号 */
if(wd == '/'){
newStatus(-1);
typeNote();
output();
}
else if(wd == '*') newStatus(29); // 原地踏步
else newStatus(24); // 状态转移->24
}
}
}
if(needOF){
printf("==> The output has been saved to the file: %s", oFP.c_str()); // 保存文件
}
return ;
}
int blankContinue(){ // 跳过空白字符,考虑换行对正负加减的影响
if(wd == '\n') cag = 3; // 对于大部分词元而言换行等价于界符
p += 1;
return 1;
}
int passError(){ // 跳过错误部分,不考虑错误部分引号的性质
while(p < srcLen){
wd = src[p];
if(isDelimiter() || isBlank() || wd == '.'){
outError();
return 1;
}
if(wd == ':'){
if(src[p+1]!='='){
outError();
return 1;
}
}
if(wd == '/'){
if(src[p+1]=='/' || src[p+1]=='*'){
outError();
return 1;
}
}
newStatus(-1); // 避免分界符被放入错误输出中
}
return 0; // error?
}
int outError(){ // 错误报告
newPrintf("Error with: %s\n", words.c_str());
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
int newStatus(int _s){ // 更新状态, 不初始化则迭代指针
switch(_s){
case 0: // 为0则初始化状态
status = 0; // 原始状态
len = 0;
words = "";
break;
case -1: // -1作为一个暂态,处理不需要状态实际转移的情况
len += 1;
words += wd;
p += 1; // 迭代指针
break;
default: // 不为0就更新状态
status = _s;
len += 1;
words += wd;
p += 1;
}
return 1;
}
int output(){ // 存储词元、输出、初始化
switch(type){
case 0: break; // 关键字
case 1: // 运算符
for(int i=20; i<33; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break; // 跳出for循环而非case
}
break;
// 出错啦
case 2: break; // 常数
case 3: // 界符
for(int i=38; i<49; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break;
}
break;
// 出错啦
case 4: // 标识符
cag = 34;
break;
case 5: // 注释 无需输出与存储,初始化后退出
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
wordsLen += 1;
newPrintf("(%d)(%d,%s)\n", wordsLen, cag, words.c_str());
strV.push_back(words); // 存储词元
typeV.push_back(cag); // 存储词元
newStatus(0); // 初始化
return 1;
}
int typeWords(int n = 0){ // 确定全字母词元 关键字 || 标识符 || 布尔常量
if(!n){
cag = isKeywords();
if(cag) type = 0; // 是关键字
else if(isBoolean()){ // 布尔常量
type = 2;
cag = 38;
} else type = 4; // 标识符
} else { // 标识符
type = 4;
}
return 0;
}
int typeOperator(){ // 确定运算符
type = 1; // 常量
return 0;
}
int typeConst(int n){ // 确定常量, 0->整型 1->实数 2->字符串 3->布尔
type = 2; // 常量
switch(n){
case 0:
cag = 35;
return 1;
case 1:
cag = 36;
return 1;
case 2:
cag = 37;
return 1;
case 3:
cag = 38;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int typeDelimiter(){ // 确定界符
type = 4; // 常量
return 0;
}
int typeNote(){ // 确定注释
type = 5; // 常量
return 0;
}
int isBlank()const{ // 检测空白字符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(filt[i] == wd) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isDelimiter()const{ // 判断是否是单字分界符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(wd == delm[i]) return true;
return false;
}
int isBoolean()const{ // 判断布尔常量
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
if(words == boolean[i]) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isKeywords()const{ // 判断关键字,返回种别码或0
for(int i=0; i<keyWordsLen; i++)
if(words == wordsTable[i]) return i+1;
return 0;
}
bool isNumber(int lim = 10)const{ // 判断数字
switch (lim){
case 0: // 除0以外的十进制数字
if(wd >= '1' && wd <= '9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 10: // 十进制
if(wd>='0' && wd<='9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 8:
if(wd >='0' && wd<='7') return 1;
else return 0;
case 2:
if(wd >='2') return 0;
else return 1;
case 16:
if(wd >= '0' && wd <= '9' || wd >= 'a' && wd <= 'f' || wd >= 'A' && wd <= 'F') return 1;
else return 0;
}
return 0;
}
bool isLowerLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='a' && wd<='z') return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isUpperLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='A' && wd<='Z') return 1;
return 0;
}
void printSplit(string text){ // 输出夹带文本的分割线
const int aLen = 60;
int _len = text.length()+2; // 两侧留空
int left = (aLen-_len)/2, right = aLen - left - _len;
for(int i=0; i<left; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf(" %s ", text.c_str());
for(int i=0; i<right; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf("\n");
return ;
}
void newPrintf(const char *fmt, ...){ // 重载自己的printf, 便于保存输出的内容, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51281362/article/details/125445742 | https://blog.csdn.net/wanruiou/article/details/115180466
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, fmt); // 传入地址
vprintf(fmt, arg);
if(needOF) // 需要保存至文件
vfprintf(oF, fmt, arg); // 借助FILE将printf重定向至文件流, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/LuyaoYing001/article/details/79750833
va_end(arg); // 结束可变参数的获取
}
};
int main(){
wordsAnalyzer *wA = new wordsAnalyzer();
wA->printSplit("Lexical Analysis");
wA->analyze();
return 0;
}
Z语言版本
鉴于编译原理老师神奇的吃表操作,而且新的表甚至抛弃了布尔常量和字符串,特地改了一份符合新词元表的词法分析器,总体与上一个版本是一样的。为了后续维护的方便,没有做高度的封装,将一些功能开放出来。
源码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdarg.h>
using namespace std;
#define idMax 20
#define keyWordsLen 14
class wordsAnalyzer{
private:
char wd; // 读取字符
int len, status; // 缓存长度与自动机状态
int flag; // 标记分析器是否正常
int wordsLen; // 词元数量
int type; // 种别归类: 0-关键字 1-运算符 2-常数 3-界符 4-标识符 5-注释串
int cag; // 种别码, 保持为可查表位序+1
int srcLen; // 源码长度
int needOF; // 是否需要保存至文件
vector<string> strV; // 存储词元
vector<int> typeV; // 存储种别码
string words; // 缓存
string src; // 源码字符串
FILE *oF; // 结果保存文件,默认为fiP
string oFP; // 保存路径
public:
// 词元编码表
vector<string> wordsTable = {
"program", "var", "integer", "real", // 0-3
"begin", "end", "if", "then", // 4-7
"else", "while", "do", "repeat", // 8-11
"until", "for", "NaN", "NaN", // 12-15(跳过14, 15)
"NaN", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 16-19(全跳过)
"+", "-", "*", "/", // 20-23
">", ">=", "<", "<=", // 24-27
"=", "<>", ":=", "&&", // 28-31
"||", "!", "NaN", "NaN", // 32-35(跳过34, 35)
"NaN", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 36-39(全跳过)
"integerConst", "doubleConst", "NaN", "NaN", // 40-43(跳过42, 43)
"id", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 44-47(跳过45, 47)
"NaN", "NaN", ";", ".", // 48-51(跳过48, 49)
",", ":", "(", ")", // 52-55
};
// 空白字符
const vector<char> filt = {' ', '\n', '\t', '\0'};
// 单字分隔符,不考虑冒号,点号
const vector<char> delm = {';', ',', '(', ')'};
wordsAnalyzer(string fiP = "./test.txt", string foP = "./res.txt"){
flag = 1; // 分析器状态ok
words = "";
len = 0;
status = 0; // 自动机起点
wordsLen = 0; // 词元数量
oFP = foP; // 保存路径
ifstream ins;
if(oFP!=""){
needOF = 1;
oF = fopen(oFP.c_str(), "w"); // 覆盖式的写入
if(oF==NULL){
printf("Fail to write in the file: %s", oFP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1);
}
newPrintf("Output file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", oFP.c_str());
}
else needOF = 0; // 不保存文件
ins.open(fiP, ios::in); // 读入模式打开文件
if(!ins.good()){ // 检测文件是否正常打开
printf("Fail to open the file: %s", fiP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1); // 出错, 终止程序
}
newPrintf("Input file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", fiP.c_str()); // 展示读取路径
printSplit("Src"); // 分割线
char _ch;
src = "";
while((_ch = ins.get()) != EOF){ // 存入源码串中
src += _ch;
}
ins.close();
src += '\0'; // 添加终止符
srcLen = src.length(); // 源码串长度
newPrintf("%s\n", src.c_str()); // 展示源码
}
~wordsAnalyzer(){
fclose(oF); // 关闭FILE文件流
}
void analyze(){ // 词法分析器
for(int i=0; i<srcLen; i++){
wd = src[i];
switch(status){
case 0: // 自动机起点,words为空
if(isBlank()) blankContinue(); // 跳过空白字符
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 转移状态->1 字母开头 大写字母可以用于区分标识符和关键字,但即使全是小写字母也需要单独检查,因此全是字母归为一类
else if(isNumber(0)) newStatus(2); // 转移状态->2 非零数字开头
else if(wd == '0') newStatus(3); // 转移状态->3 0开头
else if(wd == '&') newStatus(4); // 转移状态->4 多字运算符
else if(wd == '|') newStatus(5); // 转移状态->5
else if(wd == ':') newStatus(6); // 转移状态->6
else if(wd == '>') newStatus(7); // 转移状态->7
else if(wd == '<') newStatus(8); // 转移状态->8
else if(wd == '/') newStatus(9); // 转移状态->9
else if(wd == '*') newStatus(10); // 状态转移->10 单字运算符
else if(wd == '=') newStatus(11); // 状态转移->11
else if(wd == '!') newStatus(12); // 状态转移->12
else if(wd == '+' || wd == '-') newStatus(13); // 状态转移->13 加减号(正负号)
else if(wd == '.') newStatus(14); // 状态转移->14 考虑.5 == 0.5 ,此时.后必须有数字
else if(isDelimiter()){ // 单字分界符直接给出结果
newStatus(-1);
type = 3;
output(); // 存储词元、输出、初始化
}
else i = passError(i); // 检测到非法字符如"^#$"等
break;
case 1:{ // 字母开头,全字母情况 可终止 -> 标识符或关键字
if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 原地踏步
else if(isNumber() || wd == '_'){ // 状态转移->17
newStatus(17);
}
else{ // 处理缓存内容
cag = isKeywords();
if(cag) type = 0; // 是关键字
else type = 4; // 标识符
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 2:{ // 非零数字开头,可终止
if(wd=='.'){ // 转移状态->18 十进制实数, 此时.后可以无内容
newStatus(18);
}
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 转移状态->19 科学计数法E
newStatus(19);
}
else if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(2);
}
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"'){ // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
i = passError(i); // 出错处理
}
else{ // 被视为整常数,重置缓存
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 3:{ // 0开头数字,可终止
if(wd == 'X' || wd == 'x'){ // 状态转移->20 十六进制X
newStatus(20);
}
else if(wd == 'b' || wd == 'B'){ // 状态转移->21 二进制数b
newStatus(21);
}
else if(isNumber(8)){ // 状态转移->22 八进制数
newStatus(22);
}
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"'){ // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
i = passError(i); // 出错处理
}
else{ // 被视为整常数0
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 4:{ // 检查 & 不可终止
if(wd == '&'){ // 与运算符
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 5:{ // 检查 | 不可终止
if(wd == '|'){ // 或运算符
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 6:{ // 检查 : 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // 赋值号:=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else{ // 冒号:
type = 3;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 7:{ // 检查 > 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // >=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else { // >
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 8:{ // 检查 < 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // <=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else if(wd == '>'){ // <>
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
}
else { // <
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 9:{ // 检查 / 可终止
if(wd == '/'){ // 状态转移->23 单行注释符//
newStatus(23);
}
else if(wd == '*'){ // 状态转移->24 多行注释符
newStatus(24);
} else { // 除号/
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 10:{ // 检查 *
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 11:{ // 检查 =
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 12:{ // 检查 !
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 13:{ // +-号 不完美的DFA 可终止
if(cag == 41 || cag == 42 || cag == 45 || cag ==56 ){ // 前面出现操作数则为加减号, '('被视为有效界符, ')' 则被视为操作数
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
else if(wd == '.'){ // 状态转移->14 实数
newStatus(14);
}
else if(isNumber(0)){ // 状态转移->2 非0数字
newStatus(2);
}
else if(wd == '0'){ // 状态转移->3 数字0
newStatus(3);
}
else{ // 加减号
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 14:{ // . 实数 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->18 正常实数
newStatus(18);
} else {
type = 3;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 17:{ // 标识符 可终止
if(isNumber() || isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '_'){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(17);
} else { // 获取标识符
type = 4;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 18:{ // 真 实数 后可不跟数字 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(18);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19 科学计数法 允许有: 3.e7 的写法
newStatus(19);
} else { // 截取实数
type = 2;
cag = 42;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 19:{ // 科学计数法e 不可终止
if(wd == '+' || wd == '-'){ // 状态转移->25 科学计数法+-
newStatus(25);
} else if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
newStatus(26);
} else { // 出错啦
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 20:{ // 十六进制x 不可终止
if(isNumber(16)){ // 状态转移->27 十六进制整数后终态
newStatus(27);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 21:{ // 二进制数b 不可终止
if(isNumber(2)){ // 状态转移->28 二进制数后终态
newStatus(28);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 22:{ // 八进制数中态 可终止
if(isNumber(8)){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(22);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19 科学计数法e
newStatus(19);
} else if(wd == '.'){ // 状态转移->18 当做十进制数处理的八进制小数(C++中自适应)
newStatus(18);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 23:{ // 单行注释符// 条件终止
if(wd == '\n'){ // 截取单行注释串
type = 5;
output();
} else { // 原地踏步
newStatus(23);
}
break;
}
case 24:{ // 多行注释符/* 不可终止
if(wd == '*'){ // 状态转移->29 检测退出记号*/
newStatus(29);
} else { // 原地踏步
newStatus(24);
}
break;
}
case 25:{ // 科学计数法+- 不可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
newStatus(26);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 26:{ // 十进制整数后终态 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(26);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 42;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 27:{ // 十六进制整数后终态 十六进制不接受小数点
if(isNumber(16)){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(27);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19
newStatus(19);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 28:{ // 二进制数后终态
if(isNumber(2)){
newStatus(28);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){
newStatus(19);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 29:{ // 检测退出记号 */
if(wd == '/'){
type = 5;
output();
}
else if(wd == '*'){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(29);
}
else { // 状态转移->24
newStatus(24);
}
}
}
}
if(needOF){
printf("==> The output has been saved to the file: %s", oFP.c_str()); // 保存文件
}
return ;
}
int blankContinue(){ // 跳过空白字符,考虑换行对正负加减的影响
if(wd == '\n') cag = 51; // 对于大部分词元而言换行等价于分号
return 1;
}
int passError(int n){ // 跳过错误部分,不考虑错误部分引号的性质
for(int i=n; i<srcLen; i++){
wd = src[i];
if(isDelimiter() || isBlank() || wd == '.'){
outError();
return i-1;
}
if(wd == ':'){
if(src[i+1]!='='){
outError();
return i-1;
}
}
if(wd == '/'){
if(src[i+1]=='/' || src[i+1]=='*'){
outError();
return i-1;
}
}
newStatus(-1); // 避免分界符被放入错误输出中
}
return srcLen-1;
}
int outError(){ // 错误报告
newPrintf("Error with: %s\n", words.c_str());
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
int newStatus(int _s){ // 更新状态
switch(_s){
case 0: // 为0则初始化状态
status = 0; // 原始状态
len = 0;
words = "";
break;
case -1: // -1作为一个暂态,处理不需要状态实际转移的情况
len += 1;
words += wd;
break;
default: // 不为0就更新状态
status = _s;
len += 1;
words += wd;
}
return 1;
}
int output(){ // 存储词元、输出、初始化
switch(type){
case 0: break; // 关键字
case 1: // 运算符
for(int i=20; i<33; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break; // 跳出for循环而非case
}
// 出错啦
break;
case 2: break; // 常数
case 3: // 界符
for(int i=50; i<56; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break;
}
break;
// 出错啦
case 4: // 标识符
cag = 45;
break;
case 5: // 注释 无需输出与存储,初始化后退出
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
wordsLen += 1;
newPrintf("(%d)(%d,%s)\n", wordsLen, cag, words.c_str());
strV.push_back(words); // 存储词元
typeV.push_back(cag); // 存储词元
newStatus(0); // 初始化
return 1;
}
int isBlank()const{ // 检测空白字符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(filt[i] == wd) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isDelimiter()const{ // 判断是否是单字分界符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(wd == delm[i]) return true;
return false;
}
int isKeywords()const{ // 判断关键字,返回种别码或0
for(int i=0; i<keyWordsLen; i++)
if(words == wordsTable[i]) return i+1;
return 0;
}
bool isNumber(int lim = 10)const{ // 判断数字
switch (lim){
case 0: // 除0以外的十进制数字
if(wd >= '1' && wd <= '9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 10: // 十进制
if(wd>='0' && wd<='9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 8:
if(wd >='0' && wd<='7') return 1;
else return 0;
case 2:
if(wd >='2') return 0;
else return 1;
case 16:
if(wd >= '0' && wd <= '9' || wd >= 'a' && wd <= 'f' || wd >= 'A' && wd <= 'F') return 1;
else return 0;
}
return 0;
}
bool isLowerLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='a' && wd<='z') return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isUpperLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='A' && wd<='Z') return 1;
return 0;
}
void printSplit(string text){ // 输出夹带文本的分割线
const int aLen = 60;
int _len = text.length()+2; // 两侧留空
int left = (aLen-_len)/2, right = aLen - left - _len;
for(int i=0; i<left; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf(" %s ", text.c_str());
for(int i=0; i<right; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf("\n");
return ;
}
void newPrintf(const char *fmt, ...){ // 重载自己的printf, 便于保存输出的内容, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51281362/article/details/125445742 | https://blog.csdn.net/wanruiou/article/details/115180466
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, fmt); // 传入地址
vprintf(fmt, arg);
if(needOF) // 需要保存至文件
vfprintf(oF, fmt, arg); // 借助FILE将printf重定向至文件流, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/LuyaoYing001/article/details/79750833
va_end(arg); // 结束可变参数的获取
}
};
int main(){
wordsAnalyzer *wA = new wordsAnalyzer();
wA->printSplit("Lexical Analysis");
wA->analyze();
return 0;
}
Tips
- 若某些功能需要指向一些常做修改的变量,并且在代码中多次出现,则建议将其封装进函数,如此处的
cag->wordsTable,这样当"wordsTable"发生变化,cag指向需要修改的时候只需要修改一个函数就能解决。
测试源码
++; >=<=:=<>/*sdfsadfasdf23123123sdfsdf*22332376FDD_**/
//
var 32asg,&&&3sdf,sdf123:integer; -*/,;,
a=b+c; a++; a=1234; >= //sdfsadfasdf23123123sdfsdf;
; , /*sdfsadfasdf23123123sdfsdf*22332376FDD_**/ ;4;,,,,,//*sdfsaf*22332376FDD_*
a=b+c; / boolean mod;a div b a<>b 1234.123 sdfddsasdfsdf aaaaasdfsdfsdfsdfsad12123sdfsdfsdfsdf
-5 if -(5+6)+1e25-0x233a+0316/2.5E7 abc123a begin"123++aefb///*"
/* 23123dfsdfsdfdf
++++dsfsdf begin
*/
Grammar Analysis
LL(1)文法
上接Z语言词法分析器
思路
-
处理产生式集合,消除左递归与左因子部分:
<程序> -> program<标识符>;<分程序> <分程序> -> <变量说明>begin<语句表>end. <变量说明> -> var<变量说明表> <变量说明表> -> <变量表>:<类型>;<后变量说明表> <后变量说明表> -> <变量说明表> | <空> <类型> -> integer | real <变量表> -> <变量><后变量表> <后变量表> -> ,<变量表> | <空> <语句表> -> <语句><后语句表> <后语句表> -> ;<语句表> | <空> <语句> -> <赋值语句> | <条件语句> | <WHILE语句> | <复合语句> <赋值语句> -> <变量>:=<算术表达式> <条件语句> -> if<关系表达式>then<语句>else<语句> <WHILE语句> -> while<关系表达式>do<语句> <复合语句> -> begin<语句表>end <算术表达式> -> <项><替算术表达式> <替算术表达式> -> <另算术表达式> | <空> <另算术表达式> -> <后算术表达式><另算术表达式> | <空> <后算术表达式> -> +<项> | -<项> <项> -> <因式><替项> <替项> -> <另项> | <空> <另项> -> <后项><另项> | <空> <后项> -> *<因式> | /<因式> <因式> -> <变量> | <常数> | (<算术表达式>) <关系表达式> -> <算术表达式><关系符><算术表达式> <变量> -> <标识符> <常数> -> <整数> | <浮点数> <关系符> -> < | <= | = | > | >= | <> -
符号的机内表示:将推导式中的字母(1位字母过于有限)替换为数字来标记类型。(为了表示方便,展示推导式时仍保留字母)。将VN从100开始编号:
VN Str int <程序> A 100 <分程序> B 101 <变量说明> C 102 <变量说明表> D 103 <类型> E 104 <变量表> F 105 <语句表> G 106 <语句> H 107 <赋值语句> I 108 <条件语句> J 109 <WHILE语句> K 110 <复合语句> L 111 <算术表达式> M 112 <替算术表达式> N 113 <另算术表达式> O 114 <后算术表达式> P 115 <项> Q 116 <另项> R 117 <后项> S 118 <因式> T 119 <关系表达式> U 120 <变量> V 121 <常数> W 122 <关系符> X 123 <后变量说明表> Y 124 <后变量表> Z 125 <后语句表> A1 126 <替项> B1 127 <空> C1 128 列出VT(不考虑
&&、||、until、for、repeat、!):VT STR INt program a 0 var b 1 integer c 2 real d 3 begin e 4 end f 5 if g 6 then h 7 else i 8 while j 9 do k 10 + l 20 - m 21 * n 22 / o 23 > p 24 >= q 25 < r 26 <= s 27 = t 28 <> u 29 := v 30 <整数> w 40 <浮点数> x 41 <标识符> y 44 ; z 50 . a1 51 , b1 52 : c1 53 ( d1 54 ) e1 55 -
First集与Follow集:
VN 产生式 First follow 产生式(入栈数字) A A->ayzB a # 101, 50, 44, 0 B B->CeGfa1 b # 51, 5, 106, 4, 102 C C->bD b e 103, 1 D D->Fc1EzY y e 124, 50, 104, 53, 105 Y Y->D y e 103 Y-><空> <空> 128 E E->c c z 2 E->d d 3 F F->VZ y c1 125, 121 Z Z->b1F b1 c1 105, 52 Z-><空> <空> 128 G G->HA1 y,g,j,e f 126, 107 A1 A1->zG z f 106, 50 A1-><空> <空> 128 H H->I y z, f, i 108 H->J g 109 H->K j 110 H->L e 111 I I->VvM y z, f, i 112, 30, 121 J J->gUhHiH g z, f, i 107, 8, 107, 7, 120, 6 K K->jUkH j z, f, i 107, 10, 120, 9 L L->eGf e z, f, i 5, 106, 4 M M->QN y,w,x,d1 z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 113, 116 N N->O l,m z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 114 N-><空> <空> 128 O O->PO l,m z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 114, 115 O-><空> <空> 128 P P->lQ l l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 116, 20 P->mQ m 116, 21 Q Q->TB1 y,w,x,d1 l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 127, 119 B1 B1->R n,o l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 117 B1-><空> <空> 128 R R->SR n,o l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 117, 118 R-><空> <空> 128 S S->nT n n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 119, 22 S->oT o 119, 23 T T->V y n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 121 T->W w,x 122 T->d1Me1 d1 55, 112, 54 U U->MXM y,w,x,d1 k, h 112, 123, 112 V V->y y n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, v, b1, c1, h, k, e1 44 W W->w w n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1 40 W->x x 41 X X->p p y,w,x,d1 24 X->q q 25 X->r r 26 X->s s 27 X->t t 28 X->u u 29
预测表
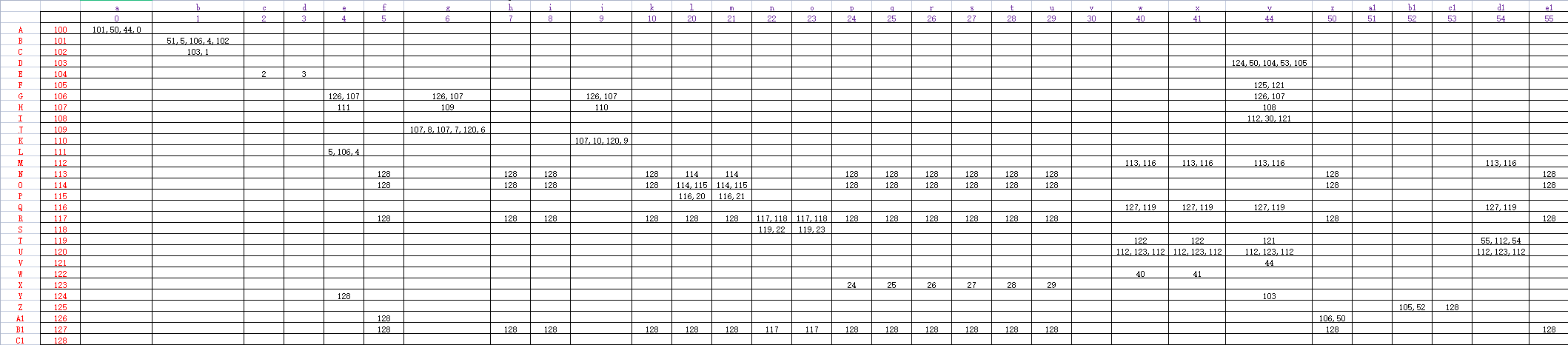
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define idMax 20
#define keyWordsLen 14
class wordsAnalyzer{
private:
char wd; // 读取字符
int silence; // 是否需要输出
int len, status; // 缓存长度与自动机状态
int flag; // 标记分析器是否正常
int wordsLen; // 词元数量
int type; // 种别归类: 0-关键字 1-运算符 2-常数 3-界符 4-标识符 5-注释串
int cag; // 种别码, 保持为可查表位序+1
int srcLen; // 源码长度
int needOF; // 是否需要保存至文件
vector<string> strV; // 存储词元
vector<int> typeV; // 存储种别码
string words; // 缓存
string src; // 源码字符串
FILE *oF; // 结果保存文件,默认为fiP
string oFP; // 保存路径
public:
// 词元编码表
vector<string> wordsTable = {
"program", "var", "integer", "real", // 0-3
"begin", "end", "if", "then", // 4-7
"else", "while", "do", "repeat", // 8-11
"until", "for", "NaN", "NaN", // 12-15(跳过14, 15)
"NaN", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 16-19(全跳过)
"+", "-", "*", "/", // 20-23
">", ">=", "<", "<=", // 24-27
"=", "<>", ":=", "&&", // 28-31
"||", "!", "NaN", "NaN", // 32-35(跳过34, 35)
"NaN", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 36-39(全跳过)
"integerConst", "doubleConst", "NaN", "NaN", // 40-43(跳过42, 43)
"id", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 44-47(跳过45, 47)
"NaN", "NaN", ";", ".", // 48-51(跳过48, 49)
",", ":", "(", ")", // 52-55
};
// 空白字符
const vector<char> filt = {' ', '\n', '\t', '\0'};
// 单字分隔符,不考虑冒号,点号
const vector<char> delm = {';', ',', '(', ')'};
wordsAnalyzer(int sil=0, string fiP = "./test.txt", string foP = "./res.txt"){
silence = sil;
flag = 1; // 分析器状态ok
words = "";
len = 0;
status = 0; // 自动机起点
wordsLen = 0; // 词元数量
oFP = foP; // 保存路径
ifstream ins;
if(oFP!=""){
needOF = 1;
oF = fopen(oFP.c_str(), "w"); // 覆盖式的写入
if(oF==NULL){
printf("Fail to write in the file: %s", oFP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1);
}
newPrintf("Output file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", oFP.c_str());
}
else needOF = 0; // 不保存文件
ins.open(fiP, ios::in); // 读入模式打开文件
if(!ins.good()){ // 检测文件是否正常打开
printf("Fail to open the file: %s", fiP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1); // 出错, 终止程序
}
newPrintf("Input file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", fiP.c_str()); // 展示读取路径
printSplit("Src"); // 分割线
char _ch;
src = "";
while((_ch = ins.get()) != EOF){ // 存入源码串中
src += _ch;
}
ins.close();
src += '\0'; // 添加终止符
srcLen = src.length(); // 源码串长度
newPrintf("%s\n", src.c_str()); // 展示源码
}
~wordsAnalyzer(){
fclose(oF); // 关闭FILE文件流
}
void analyze(){ // 词法分析器
for(int i=0; i<srcLen; i++){
if(i==447){
printf("%d", i);
}
wd = src[i];
switch(status){
case 0: // 自动机起点,words为空
if(isBlank()) blankContinue(); // 跳过空白字符
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 转移状态->1 字母开头 大写字母可以用于区分标识符和关键字,但即使全是小写字母也需要单独检查,因此全是字母归为一类
else if(isNumber(0)) newStatus(2); // 转移状态->2 非零数字开头
else if(wd == '0') newStatus(3); // 转移状态->3 0开头
else if(wd == '&') newStatus(4); // 转移状态->4 多字运算符
else if(wd == '|') newStatus(5); // 转移状态->5
else if(wd == ':') newStatus(6); // 转移状态->6
else if(wd == '>') newStatus(7); // 转移状态->7
else if(wd == '<') newStatus(8); // 转移状态->8
else if(wd == '/') newStatus(9); // 转移状态->9
else if(wd == '*') newStatus(10); // 状态转移->10 单字运算符
else if(wd == '=') newStatus(11); // 状态转移->11
else if(wd == '!') newStatus(12); // 状态转移->12
else if(wd == '+' || wd == '-') newStatus(13); // 状态转移->13 加减号(正负号)
else if(wd == '.') newStatus(14); // 状态转移->14 考虑.5 == 0.5 ,此时.后必须有数字
else if(isDelimiter()){ // 单字分界符直接给出结果
newStatus(-1);
type = 3;
output(); // 存储词元、输出、初始化
}
else i = passError(i); // 检测到非法字符如"^#$"等
break;
case 1:{ // 字母开头,全字母情况 可终止 -> 标识符或关键字
if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 原地踏步
else if(isNumber() || wd == '_'){ // 状态转移->17
newStatus(17);
}
else{ // 处理缓存内容
cag = isKeywords();
if(cag) type = 0; // 是关键字
else type = 4; // 标识符
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 2:{ // 非零数字开头,可终止
if(wd=='.'){ // 转移状态->18 十进制实数, 此时.后可以无内容
newStatus(18);
}
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 转移状态->19 科学计数法E
newStatus(19);
}
else if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(2);
}
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"'){ // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
i = passError(i); // 出错处理
}
else{ // 被视为整常数,重置缓存
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 3:{ // 0开头数字,可终止
if(wd == 'X' || wd == 'x'){ // 状态转移->20 十六进制X
newStatus(20);
}
else if(wd == 'b' || wd == 'B'){ // 状态转移->21 二进制数b
newStatus(21);
}
else if(isNumber(8)){ // 状态转移->22 八进制数
newStatus(22);
}
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"'){ // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
i = passError(i); // 出错处理
}
else{ // 被视为整常数0
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 4:{ // 检查 & 不可终止
if(wd == '&'){ // 与运算符
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 5:{ // 检查 | 不可终止
if(wd == '|'){ // 或运算符
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 6:{ // 检查 : 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // 赋值号:=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else{ // 冒号:
type = 3;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 7:{ // 检查 > 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // >=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else { // >
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 8:{ // 检查 < 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // <=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else if(wd == '>'){ // <>
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
}
else { // <
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 9:{ // 检查 / 可终止
if(wd == '/'){ // 状态转移->23 单行注释符//
newStatus(23);
}
else if(wd == '*'){ // 状态转移->24 多行注释符
newStatus(24);
} else { // 除号/
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 10:{ // 检查 *
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 11:{ // 检查 =
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 12:{ // 检查 !
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 13:{ // +-号 不完美的DFA 可终止
if(cag == 41 || cag == 42 || cag == 45 || cag ==56 ){ // 前面出现操作数则为加减号, '('被视为有效界符, ')' 则被视为操作数
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
else if(wd == '.'){ // 状态转移->14 实数
newStatus(14);
}
else if(isNumber(0)){ // 状态转移->2 非0数字
newStatus(2);
}
else if(wd == '0'){ // 状态转移->3 数字0
newStatus(3);
}
else{ // 加减号
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 14:{ // . 实数 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->18 正常实数
newStatus(18);
} else {
type = 3;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 17:{ // 标识符 可终止
if(isNumber() || isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '_'){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(17);
} else { // 获取标识符
type = 4;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 18:{ // 真 实数 后可不跟数字 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(18);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19 科学计数法 允许有: 3.e7 的写法
newStatus(19);
} else { // 截取实数
type = 2;
cag = 42;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 19:{ // 科学计数法e 不可终止
if(wd == '+' || wd == '-'){ // 状态转移->25 科学计数法+-
newStatus(25);
} else if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
newStatus(26);
} else { // 出错啦
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 20:{ // 十六进制x 不可终止
if(isNumber(16)){ // 状态转移->27 十六进制整数后终态
newStatus(27);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 21:{ // 二进制数b 不可终止
if(isNumber(2)){ // 状态转移->28 二进制数后终态
newStatus(28);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 22:{ // 八进制数中态 可终止
if(isNumber(8)){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(22);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19 科学计数法e
newStatus(19);
} else if(wd == '.'){ // 状态转移->18 当做十进制数处理的八进制小数(C++中自适应)
newStatus(18);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 23:{ // 单行注释符// 条件终止
if(wd == '\n'){ // 截取单行注释串
type = 5;
output();
} else { // 原地踏步
newStatus(23);
}
break;
}
case 24:{ // 多行注释符/* 不可终止
if(wd == '*'){ // 状态转移->29 检测退出记号*/
newStatus(29);
} else { // 原地踏步
newStatus(24);
}
break;
}
case 25:{ // 科学计数法+- 不可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
newStatus(26);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 26:{ // 十进制整数后终态 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(26);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 42;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 27:{ // 十六进制整数后终态 十六进制不接受小数点
if(isNumber(16)){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(27);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19
newStatus(19);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 28:{ // 二进制数后终态
if(isNumber(2)){
newStatus(28);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){
newStatus(19);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 29:{ // 检测退出记号 */
if(wd == '/'){
type = 5;
output();
}
else if(wd == '*'){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(29);
}
else { // 状态转移->24
newStatus(24);
}
}
}
}
if(needOF && !silence){
printf("==> The output has been saved to the file: %s", oFP.c_str()); // 保存文件
}
return ;
}
int blankContinue(){ // 跳过空白字符,考虑换行对正负加减的影响
if(wd == '\n') cag = 51; // 对于大部分词元而言换行等价于分号
return 1;
}
int passError(int n){ // 跳过错误部分,不考虑错误部分引号的性质
for(int i=n; i<srcLen; i++){
wd = src[i];
if(isDelimiter() || isBlank() || wd == '.'){
outError();
return i-1;
}
if(wd == ':'){
if(src[i+1]!='='){
outError();
return i-1;
}
}
if(wd == '/'){
if(src[i+1]=='/' || src[i+1]=='*'){
outError();
return i-1;
}
}
newStatus(-1); // 避免分界符被放入错误输出中
}
return srcLen-1;
}
int outError(){ // 错误报告
newPrintf("Error with: %s\n", words.c_str());
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
int newStatus(int _s){ // 更新状态
switch(_s){
case 0: // 为0则初始化状态
status = 0; // 原始状态
len = 0;
words = "";
break;
case -1: // -1作为一个暂态,处理不需要状态实际转移的情况
len += 1;
words += wd;
break;
default: // 不为0就更新状态
status = _s;
len += 1;
words += wd;
}
return 1;
}
int output(){ // 存储词元、输出、初始化
switch(type){
case 0: break; // 关键字
case 1: // 运算符
for(int i=20; i<33; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break; // 跳出for循环而非case
}
// 出错啦
break;
case 2: break; // 常数
case 3: // 界符
for(int i=50; i<56; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break;
}
break;
// 出错啦
case 4: // 标识符
cag = 45;
break;
case 5: // 注释 无需输出与存储,初始化后退出
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
wordsLen += 1;
newPrintf("(%d)(%d,%s)\n", wordsLen, cag, words.c_str());
strV.push_back(words); // 存储词元
typeV.push_back(cag); // 存储词元
newStatus(0); // 初始化
return 1;
}
int isBlank()const{ // 检测空白字符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(filt[i] == wd) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isDelimiter()const{ // 判断是否是单字分界符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(wd == delm[i]) return true;
return false;
}
int isKeywords()const{ // 判断关键字,返回种别码或0
for(int i=0; i<keyWordsLen; i++)
if(words == wordsTable[i]) return i+1;
return 0;
}
bool isNumber(int lim = 10)const{ // 判断数字
switch (lim){
case 0: // 除0以外的十进制数字
if(wd >= '1' && wd <= '9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 10: // 十进制
if(wd>='0' && wd<='9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 8:
if(wd >='0' && wd<='7') return 1;
else return 0;
case 2:
if(wd >='2') return 0;
else return 1;
case 16:
if(wd >= '0' && wd <= '9' || wd >= 'a' && wd <= 'f' || wd >= 'A' && wd <= 'F') return 1;
else return 0;
}
return 0;
}
bool isLowerLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='a' && wd<='z') return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isUpperLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='A' && wd<='Z') return 1;
return 0;
}
void printSplit(string text){ // 输出夹带文本的分割线
if(silence==1) return;
const int aLen = 60;
int _len = text.length()+2; // 两侧留空
int left = (aLen-_len)/2, right = aLen - left - _len;
for(int i=0; i<left; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf(" %s ", text.c_str());
for(int i=0; i<right; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf("\n");
return ;
}
void newPrintf(const char *fmt, ...){ // 重载自己的printf, 便于保存输出的内容, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51281362/article/details/125445742 | https://blog.csdn.net/wanruiou/article/details/115180466
if(silence==1) return;
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, fmt); // 传入地址
vprintf(fmt, arg);
if(needOF) // 需要保存至文件
vfprintf(oF, fmt, arg); // 借助FILE将printf重定向至文件流, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/LuyaoYing001/article/details/79750833
va_end(arg); // 结束可变参数的获取
}
int getVL()const{ return typeV.size(); } // 数组长度
int atTV(int n)const{ return typeV[n]; }
vector<int> getTV()const{ return typeV; }
vector<string> getSV()const{ return strV; }
};
const int threshold=100;
template<class T>
int getLen(T& arr){ // 快速获取数组长度
return sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
}
class grammarAnalyzer{
private:
stack<int> S;
map<pair<int, int>, vector<int>> init; // 预测表
vector<int> typeV;
vector<string> strV;
int flag;
public:
grammarAnalyzer(vector<int> tv, vector<string> sv):typeV(tv), strV(sv){ // 初始化预测表
typeV.push_back(0); // 终止符#外标记为0,内标记为-1
strV.push_back("#"); // 终止符#外标记为0,内标记为-1
int tmp1[]={101,50,44,0};buildMap(100, 0, tmp1, getLen(tmp1));
int tmp2[]={51,5,106,4,102};buildMap(101, 1, tmp2, getLen(tmp2));
int tmp3[]={103,1};buildMap(102, 1, tmp3, getLen(tmp3));
int tmp4[]={124,50,104,53,105};buildMap(103, 44, tmp4, getLen(tmp4));
int tmp5[]={2};buildMap(104, 2, tmp5, getLen(tmp5));
int tmp6[]={3};buildMap(104, 3, tmp6, getLen(tmp6));
int tmp7[]={125,121};buildMap(105, 44, tmp7, getLen(tmp7));
int tmp8[]={126,107};int tmp9[]={4,6,9,44};buildMoreMap(106, tmp8, tmp9, getLen(tmp8), getLen(tmp9));
int tmp10[]={111};buildMap(107, 4, tmp10, getLen(tmp10));
int tmp11[]={109};buildMap(107, 6, tmp11, getLen(tmp11));
int tmp12[]={110};buildMap(107, 9, tmp12, getLen(tmp12));
int tmp13[]={111};buildMap(107, 4, tmp13, getLen(tmp13));
int tmp14[]={108};buildMap(107, 44, tmp14, getLen(tmp14));
int tmp15[]={112,30,121};buildMap(108, 44, tmp15, getLen(tmp15));
int tmp16[]={107,8,107,7,120,6};buildMap(109, 6, tmp16, getLen(tmp16));
int tmp17[]={107,10,120,9};buildMap(110, 9, tmp17, getLen(tmp17));
int tmp18[]={5,106,4};buildMap(111, 4, tmp18, getLen(tmp18));
int tmp19[]={113,116};int tmp20[]={40,41,44};buildMoreMap(112, tmp19, tmp20, getLen(tmp19), getLen(tmp20));
int tmp21[]={128};int tmp22[]={5,7,8,10,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55};buildMoreMap(113, tmp21, tmp22, getLen(tmp21), getLen(tmp22));
int tmp23[]={114};int tmp24[]={20,21};buildMoreMap(113, tmp23, tmp24, getLen(tmp23), getLen(tmp24));
int tmp25[]={128};int tmp26[]={5,7,8,10,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55};buildMoreMap(114, tmp25, tmp26, getLen(tmp25), getLen(tmp26));
int tmp27[]={114,115};int tmp28[]={20,21};buildMoreMap(114, tmp27, tmp28, getLen(tmp27), getLen(tmp28));
int tmp29[]={116,20};buildMap(115, 20, tmp29, getLen(tmp29));
int tmp30[]={116,21};buildMap(115, 21, tmp30, getLen(tmp30));
int tmp31[]={127,119};int tmp32[]={40,41,44,54};buildMoreMap(116, tmp31, tmp32, getLen(tmp31), getLen(tmp32));
int tmp33[]={128};int tmp34[]={5,7,8,10,20,21,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55};buildMoreMap(117, tmp33, tmp34, getLen(tmp33), getLen(tmp34));
int tmp35[]={117,118};int tmp36[]={22,23};buildMoreMap(117, tmp35, tmp36, getLen(tmp35), getLen(tmp36));
int tmp37[]={119,22};buildMap(118, 22, tmp37, getLen(tmp37));
int tmp38[]={119,23};buildMap(118, 23, tmp38, getLen(tmp38));
int tmp39[]={122};int tmp40[]={40,41};buildMoreMap(119, tmp39, tmp40, getLen(tmp39), getLen(tmp40));
int tmp41[]={121};buildMap(119, 44, tmp41, getLen(tmp41));
int tmp42[]={55,112,54};buildMap(119, 54, tmp42, getLen(tmp42));
int tmp43[]={112,123,112};int tmp44[]={40,41,44,54};buildMoreMap(120, tmp43, tmp44, getLen(tmp43), getLen(tmp44));
int tmp45[]={44};buildMap(121, 44, tmp45, getLen(tmp45));
int tmp46[]={40};buildMap(122, 40, tmp46, getLen(tmp46));
int tmp47[]={41};buildMap(122, 41, tmp47, getLen(tmp47));
int tmp48[]={24};buildMap(123, 24, tmp48, getLen(tmp48));
int tmp49[]={25};buildMap(123, 25, tmp49, getLen(tmp49));
int tmp50[]={26};buildMap(123, 26, tmp50, getLen(tmp50));
int tmp51[]={27};buildMap(123, 27, tmp51, getLen(tmp51));
int tmp52[]={28};buildMap(123, 28, tmp52, getLen(tmp52));
int tmp53[]={29};buildMap(123, 29, tmp53, getLen(tmp53));
int tmp54[]={128};buildMap(124, 4, tmp54, getLen(tmp54));
int tmp55[]={105,52};buildMap(125, 52, tmp55, getLen(tmp55));
int tmp56[]={128};buildMap(125, 53, tmp56, getLen(tmp56));
int tmp57[]={128};buildMap(126, 5, tmp57, getLen(tmp57));
int tmp58[]={106,50};buildMap(126, 50, tmp58, getLen(tmp58));
int tmp59[]={128};int tmp60[]={5,7,8,10,20,21,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55};buildMoreMap(127, tmp59, tmp60, getLen(tmp59), getLen(tmp60));
int tmp61[]={117};int tmp62[]={22,23};buildMoreMap(127, tmp61, tmp62, getLen(tmp61), getLen(tmp62));
}
bool buildMoreMap(int a, int V[], int s[], int len, int lens){
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++){
v.push_back(V[i]);
}
for(int j = 0; j<lens; j++){
pair<int, int> p(a, s[j]);
if(init.count(p)) return 0; // 重复定义
init[p]=v;
}
return 1;
}
bool buildMap(int a, int b, int V[], int len){
pair<int, int> p(a, b);
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++){
v.push_back(V[i]);
}
init[p]=v;
return 1;
}
bool isVT(int n){
if(n>=100) return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isEmpty(int n){
if(n==128) return 1;
return 0;
}
bool getPush(vector<int> V){ // 逐个入栈
int len = V.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
S.push(V[i]);
}
return 1;
}
bool analyze(){
S.push(-1); // 终止符
S.push(100); // 起始符A
int len = typeV.size(), c=0;
while(!S.empty() && c<len){
int tmp = S.top();
S.pop();
if(isEmpty(tmp)){ // 空串跳过
continue;
}
if(isVT(tmp)){ // 非终结符
pair<int, int> tmpP(tmp, typeV[c]-1);
if(init.count(tmpP)==0){ // 语法错误
printf("false with unknown: %d (%d,%s)", tmp, typeV[c]-1, strV[c].c_str());
exit(-1);
}
vector<int> tmpV = init[tmpP];
getPush(tmpV);
} else { // 终结符
if(tmp!=typeV[c]-1){ // 语法错误
printf("false with: %d (%d,%s)", tmp, typeV[c]-1, strV[c].c_str());
exit(-1);
} else {
printf("true: (%d,%s)\n", typeV[c]-1, strV[c].c_str());
++c;
}
}
}
if(!S.empty()) printf("stack!");
if(c<len) printf("vector!");
printf("all true!");
return 1;
}
};
int main(){
wordsAnalyzer *wA = new wordsAnalyzer(1);
wA->printSplit("Lexical Analysis");
wA->analyze();
grammarAnalyzer *gA = new grammarAnalyzer(wA->getTV(), wA->getSV());
gA->analyze();
return 0;
}
Semantic Analysis
LL(1)文法
递归下降是语义分析最直观的解决方式,仍然使用LL(1)文法解决
思路
-
产生式集合与语法分析稍有不同,多加了
&&和||,以及if后不一定要跟着else:<程序> -> program<标识符>;<分程序> <分程序> -> <变量说明>begin<语句表>end. <变量说明> -> var<变量说明表> <变量说明表> -> <变量表>:<类型>;<后变量说明表> <后变量说明表> -> <变量说明表> | <空> <类型> -> integer | real <变量表> -> <变量><后变量表> <后变量表> -> ,<变量表> | <空> <语句表> -> <语句><后语句表> <后语句表> -> ;<语句表> | <空> <语句> -> <赋值语句> | <条件语句> | <WHILE语句> | <复合语句> <赋值语句> -> <变量>:=<算术表达式> <条件语句> -> if<关系表达式>then<语句><后条件语句> <后条件语句> -> <空> | else<语句> <WHILE语句> -> while<关系表达式>do<语句> <复合语句> -> begin<语句表>end <算术表达式> -> <项><替算术表达式> <替算术表达式> -> <另算术表达式> | <空> <另算术表达式> -> <后算术表达式><另算术表达式> | <空> <后算术表达式> -> +<项> | -<项> <项> -> <因式><替项> <替项> -> <另项> | <空> <另项> -> <后项><另项> | <空> <后项> -> *<因式> | /<因式> <因式> -> <变量> | <常数> | (<算术表达式>) <关系表达式> -> <子关系表达式><后子关系表达式> <子关系表达式> -> <算术表达式><关系符><算术表达式> <后子关系表达式> -> <逻辑运算符><关系表达式> | <空> <逻辑运算符> -> && | || <变量> -> <标识符> <常数> -> <整数> | <浮点数> <关系符> -> < | <= | = | > | >= | <> -
符号的机内表示:将推导式中的字母(1位字母过于有限)替换为数字来标记类型。(为了表示方便,展示推导式时仍保留字母)。将VN从100开始编号:
VN Str int <程序> A 100 <分程序> B 101 <变量说明> C 102 <变量说明表> D 103 <类型> E 104 <变量表> F 105 <语句表> G 106 <语句> H 107 <赋值语句> I 108 <条件语句> J 109 <WHILE语句> K 110 <复合语句> L 111 <算术表达式> M 112 <替算术表达式> N 113 <另算术表达式> O 114 <后算术表达式> P 115 <项> Q 116 <另项> R 117 <后项> S 118 <因式> T 119 <关系表达式> U 120 <变量> V 121 <常数> W 122 <关系符> X 123 <后变量说明表> Y 124 <后变量表> Z 125 <后语句表> A1 126 <替项> B1 127 <空> C1 128 <后条件语句> D1 129 <子关系表达式> E1 130 <后子关系表达式> F1 131 <逻辑运算符> G1 132 列出VT(不考虑
&&、||、until、for、repeat、!):VT STR INt program a 0 var b 1 integer c 2 real d 3 begin e 4 end f 5 if g 6 then h 7 else i 8 while j 9 do k 10 + l 20 - m 21 * n 22 / o 23 > p 24 >= q 25 < r 26 <= s 27 = t 28 <> u 29 := v 30 <整数> w 40 <浮点数> x 41 <标识符> y 44 ; z 50 . a1 51 , b1 52 : c1 53 ( d1 54 ) e1 55 && f1 31 || g1 32 -
First集与Follow集:
VN 产生式 First follow 产生式(入栈数字) A A->ayzB a # 101, 50, 44, 0 B B->CeGfa1 b # 51, 5, 106, 4, 102 C C->bD b e 103, 1 D D->Fc1EzY y e 124, 50, 104, 53, 105 Y Y->D y e 103 Y-><空> <空> 128 E E->c c z 2 E->d d 3 F F->VZ y c1 125, 121 Z Z->b1F b1 c1 105, 52 Z-><空> <空> 128 G G->HA1 y,g,j,e f 126, 107 A1 A1->zG z f 106, 50 A1-><空> <空> 128 H H->I y z, f, i 108 H->J g 109 H->K j 110 H->L e 111 I I->VvM y z, f, i 112, 30, 121 J J->gUhHD1 g z, f, i 129, 107, 7, 120, 6 D1 D1->iH i z, f, (i) 107, 8 D1-><空> <空> 128 K K->jUkH j z, f, i 107, 10, 120, 9 L L->eGf e z, f, i 5, 106, 4 M M->QN y,w,x,d1 z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 113, 116 N N->O l,m z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 114 N-><空> <空> 128 O O->PO l,m z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 114, 115 O-><空> <空> 128 P P->lQ l l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 116, 20 P->mQ m 116, 21 Q Q->TB1 y,w,x,d1 l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 127, 119 B1 B1->R n,o l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 117 B1-><空> <空> 128 R R->SR n,o l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 117, 118 R-><空> <空> 128 S S->nT n n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 119, 22 S->oT o 119, 23 T T->V y n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 121 T->W w,x 122 T->d1Me1 d1 55, 112, 54 U U->E1F1 y,w,x,d1 k, h 131, 130 E1 E1->MXM y,w,x,d1 k, h, f1 112, 123, 112 F1 F1->G1U f1,g1 k, h 120, 132 F1-><空> <空> 128 G1 G1->f1 f1 y,w,x,d1 31 G1->g1 g1 32 V V->y y n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, v, b1, c1, h, k, e1, f1, g1 44 W W->w w n, o, l, m, z, f, i, p, q, r, s, t, u, h, k, e1, f1, g1 40 W->x x 41 X X->p p y,w,x,d1 24 X->q q 25 X->r r 26 X->s s 27 X->t t 28 X->u u 29 需要注意的是产生式D1->iH,其Follow集合与First集合发生冲突了,按照LL(1)的分析步骤执行这个冲突消除不了,但实际上这个冲突并不成立。
会产生这个冲突,问题在于一个if语句与else的匹配原则。if总是匹配离他最近的else,除非它在复合语句中,if后紧跟end标明复合语句结束,下一个遇到的else才不属于该if,如:
if a>5 then begin if b>5 then b=1; end else a=1;而if的产生式是由<条件语句>开始的,<条件语句>首先是一个<语句>,他可能是then后面的那个<语句>,因此它的后面可能跟有else,对应字母H的Follow集中有i;其次
<条件语句> -> if<关系表达式>then<语句><后条件语句>对于后条件语句而言,他可能产生else,因此碰到else他应该:<后条件语句>->else<语句>,但同时它又可能为<空>,而他为<空>时参考他上级的<条件语句>Follow集,不巧的是这个集合里也有else。也就是说按照LL(1)的基本分析思路,这个Follow集中的else起作用的场景原本是,<后条件语句>为空,然后上一级的<条件语句>匹配到它后面可能跟的else,也就是跟在这整个<语句>后面的属于之前if的else。看似很有道理,但实际上这并不符合if与else的匹配规则,因为if总是匹配离他最近的else!试想如果<后条件语句>为空,那就意味着该式子中的if就是没有else的,那么他后面要么跟其他语句,要么跟end,不可能出现后面跟着一个else,而且这个else还属于别的if!
因此这里虽然Follow集合中有i,但是实际制表时只将i放入First集中处理,即匹配到的所有else都采用
<后条件语句> -> else<语句>产生式。 -
递归栈的种类标记:
层数 标记 含义 0 0 始末标记 1 条件语句 2 if后的关系表达式 3 then后的语句 4 else后的语句 5 子关系表达式 6 算术表达式 7 while语句 8 while后的关系表达式 9 do后的语句 10 赋值语句 11 赋值语句后的首个变量
预测表
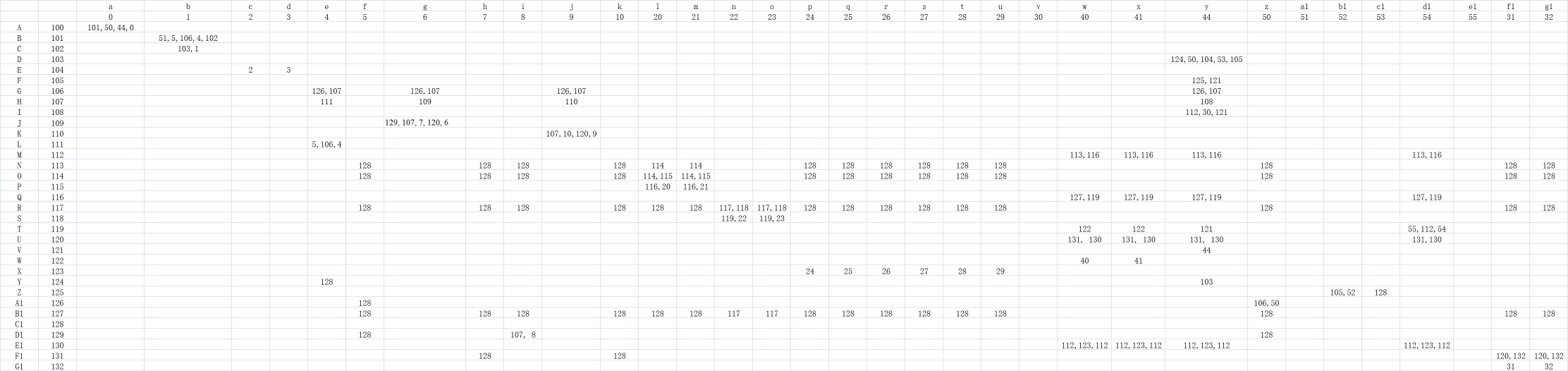
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define idMax 20
#define keyWordsLen 14
class wordsAnalyzer{
private:
char wd; // 读取字符
int silence; // 是否需要输出
int len, status; // 缓存长度与自动机状态
int flag; // 标记分析器是否正常
int wordsLen; // 词元数量
int type; // 种别归类: 0-关键字 1-运算符 2-常数 3-界符 4-标识符 5-注释串
int cag; // 种别码, 保持为可查表位序+1
int srcLen; // 源码长度
int needOF; // 是否需要保存至文件
vector<string> strV; // 存储词元
vector<int> typeV; // 存储种别码
string words; // 缓存
string src; // 源码字符串
FILE *oF; // 结果保存文件,默认为fiP
string oFP; // 保存路径
public:
// 词元编码表
vector<string> wordsTable = {
"program", "var", "integer", "real", // 0-3
"begin", "end", "if", "then", // 4-7
"else", "while", "do", "repeat", // 8-11
"until", "for", "NaN", "NaN", // 12-15(跳过14, 15)
"NaN", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 16-19(全跳过)
"+", "-", "*", "/", // 20-23
">", ">=", "<", "<=", // 24-27
"=", "<>", ":=", "&&", // 28-31
"||", "!", "NaN", "NaN", // 32-35(跳过34, 35)
"NaN", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 36-39(全跳过)
"integerConst", "doubleConst", "NaN", "NaN", // 40-43(跳过42, 43)
"id", "NaN", "NaN", "NaN", // 44-47(跳过45, 47)
"NaN", "NaN", ";", ".", // 48-51(跳过48, 49)
",", ":", "(", ")", // 52-55
};
// 空白字符
const vector<char> filt = {' ', '\n', '\t', '\0'};
// 单字分隔符,不考虑冒号,点号
const vector<char> delm = {';', ',', '(', ')'};
wordsAnalyzer(int sil=0, string fiP = "./test.txt", string foP = "./res.txt"){
silence = sil;
flag = 1; // 分析器状态ok
words = "";
len = 0;
status = 0; // 自动机起点
wordsLen = 0; // 词元数量
oFP = foP; // 保存路径
ifstream ins;
if(oFP!=""){
needOF = 1;
oF = fopen(oFP.c_str(), "w"); // 覆盖式的写入
if(oF==NULL){
printf("Fail to write in the file: %s", oFP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1);
}
newPrintf("Output file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", oFP.c_str());
}
else needOF = 0; // 不保存文件
ins.open(fiP, ios::in); // 读入模式打开文件
if(!ins.good()){ // 检测文件是否正常打开
printf("Fail to open the file: %s", fiP.c_str());
this->flag = 0;
exit(-1); // 出错, 终止程序
}
newPrintf("Input file path: %s -> Succeed!\n", fiP.c_str()); // 展示读取路径
printSplit("Src"); // 分割线
char _ch;
src = "";
while((_ch = ins.get()) != EOF){ // 存入源码串中
src += _ch;
}
ins.close();
src += '\0'; // 添加终止符
srcLen = src.length(); // 源码串长度
newPrintf("%s\n", src.c_str()); // 展示源码
}
~wordsAnalyzer(){
fclose(oF); // 关闭FILE文件流
}
void analyze(){ // 词法分析器
for(int i=0; i<srcLen; i++){
if(i==447){
printf("%d", i);
}
wd = src[i];
switch(status){
case 0: // 自动机起点,words为空
if(isBlank()) blankContinue(); // 跳过空白字符
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 转移状态->1 字母开头 大写字母可以用于区分标识符和关键字,但即使全是小写字母也需要单独检查,因此全是字母归为一类
else if(isNumber(0)) newStatus(2); // 转移状态->2 非零数字开头
else if(wd == '0') newStatus(3); // 转移状态->3 0开头
else if(wd == '&') newStatus(4); // 转移状态->4 多字运算符
else if(wd == '|') newStatus(5); // 转移状态->5
else if(wd == ':') newStatus(6); // 转移状态->6
else if(wd == '>') newStatus(7); // 转移状态->7
else if(wd == '<') newStatus(8); // 转移状态->8
else if(wd == '/') newStatus(9); // 转移状态->9
else if(wd == '*') newStatus(10); // 状态转移->10 单字运算符
else if(wd == '=') newStatus(11); // 状态转移->11
else if(wd == '!') newStatus(12); // 状态转移->12
else if(wd == '+' || wd == '-') newStatus(13); // 状态转移->13 加减号(正负号)
else if(wd == '.') newStatus(14); // 状态转移->14 考虑.5 == 0.5 ,此时.后必须有数字
else if(isDelimiter()){ // 单字分界符直接给出结果
newStatus(-1);
type = 3;
output(); // 存储词元、输出、初始化
}
else i = passError(i); // 检测到非法字符如"^#$"等
break;
case 1:{ // 字母开头,全字母情况 可终止 -> 标识符或关键字
if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter()) newStatus(1); // 原地踏步
else if(isNumber() || wd == '_'){ // 状态转移->17
newStatus(17);
}
else{ // 处理缓存内容
cag = isKeywords();
if(cag) type = 0; // 是关键字
else type = 4; // 标识符
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 2:{ // 非零数字开头,可终止
if(wd=='.'){ // 转移状态->18 十进制实数, 此时.后可以无内容
newStatus(18);
}
else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 转移状态->19 科学计数法E
newStatus(19);
}
else if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(2);
}
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"'){ // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
i = passError(i); // 出错处理
}
else{ // 被视为整常数,重置缓存
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 3:{ // 0开头数字,可终止
if(wd == 'X' || wd == 'x'){ // 状态转移->20 十六进制X
newStatus(20);
}
else if(wd == 'b' || wd == 'B'){ // 状态转移->21 二进制数b
newStatus(21);
}
else if(isNumber(8)){ // 状态转移->22 八进制数
newStatus(22);
}
else if(isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '\'' || wd == '"'){ // 十进制数后跟字母或引号铁铁出错
i = passError(i); // 出错处理
}
else{ // 被视为整常数0
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 4:{ // 检查 & 不可终止
if(wd == '&'){ // 与运算符
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 5:{ // 检查 | 不可终止
if(wd == '|'){ // 或运算符
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 6:{ // 检查 : 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // 赋值号:=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else{ // 冒号:
type = 3;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 7:{ // 检查 > 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // >=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else { // >
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 8:{ // 检查 < 可终止
if(wd == '='){ // <=
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
} else if(wd == '>'){ // <>
newStatus(-1);
type = 1;
output();
}
else { // <
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 9:{ // 检查 / 可终止
if(wd == '/'){ // 状态转移->23 单行注释符//
newStatus(23);
}
else if(wd == '*'){ // 状态转移->24 多行注释符
newStatus(24);
} else { // 除号/
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 10:{ // 检查 *
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 11:{ // 检查 =
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 12:{ // 检查 !
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
break;
}
case 13:{ // +-号 不完美的DFA 可终止
if(cag == 41 || cag == 42 || cag == 45 || cag ==56 ){ // 前面出现操作数则为加减号, '('被视为有效界符, ')' 则被视为操作数
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
else if(wd == '.'){ // 状态转移->14 实数
newStatus(14);
}
else if(isNumber(0)){ // 状态转移->2 非0数字
newStatus(2);
}
else if(wd == '0'){ // 状态转移->3 数字0
newStatus(3);
}
else{ // 加减号
type = 1;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 14:{ // . 实数 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->18 正常实数
newStatus(18);
} else {
type = 3;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 17:{ // 标识符 可终止
if(isNumber() || isLowerLetter() || isUpperLetter() || wd == '_'){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(17);
} else { // 获取标识符
type = 4;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 18:{ // 真 实数 后可不跟数字 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(18);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19 科学计数法 允许有: 3.e7 的写法
newStatus(19);
} else { // 截取实数
type = 2;
cag = 42;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 19:{ // 科学计数法e 不可终止
if(wd == '+' || wd == '-'){ // 状态转移->25 科学计数法+-
newStatus(25);
} else if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
newStatus(26);
} else { // 出错啦
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 20:{ // 十六进制x 不可终止
if(isNumber(16)){ // 状态转移->27 十六进制整数后终态
newStatus(27);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 21:{ // 二进制数b 不可终止
if(isNumber(2)){ // 状态转移->28 二进制数后终态
newStatus(28);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 22:{ // 八进制数中态 可终止
if(isNumber(8)){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(22);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19 科学计数法e
newStatus(19);
} else if(wd == '.'){ // 状态转移->18 当做十进制数处理的八进制小数(C++中自适应)
newStatus(18);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 23:{ // 单行注释符// 条件终止
if(wd == '\n'){ // 截取单行注释串
type = 5;
output();
} else { // 原地踏步
newStatus(23);
}
break;
}
case 24:{ // 多行注释符/* 不可终止
if(wd == '*'){ // 状态转移->29 检测退出记号*/
newStatus(29);
} else { // 原地踏步
newStatus(24);
}
break;
}
case 25:{ // 科学计数法+- 不可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 状态转移->26 十进制整数后终态
newStatus(26);
} else {
i = passError(i);
}
break;
}
case 26:{ // 十进制整数后终态 可终止
if(isNumber()){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(26);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 42;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 27:{ // 十六进制整数后终态 十六进制不接受小数点
if(isNumber(16)){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(27);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){ // 状态转移->19
newStatus(19);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 28:{ // 二进制数后终态
if(isNumber(2)){
newStatus(28);
} else if(wd == 'e' || wd == 'E'){
newStatus(19);
} else {
type = 2;
cag = 41;
output();
i -= 1;
}
break;
}
case 29:{ // 检测退出记号 */
if(wd == '/'){
type = 5;
output();
}
else if(wd == '*'){ // 原地踏步
newStatus(29);
}
else { // 状态转移->24
newStatus(24);
}
}
}
}
if(needOF && !silence){
printf("==> The output has been saved to the file: %s", oFP.c_str()); // 保存文件
}
return ;
}
int blankContinue(){ // 跳过空白字符,考虑换行对正负加减的影响
if(wd == '\n') cag = 51; // 对于大部分词元而言换行等价于分号
return 1;
}
int passError(int n){ // 跳过错误部分,不考虑错误部分引号的性质
for(int i=n; i<srcLen; i++){
wd = src[i];
if(isDelimiter() || isBlank() || wd == '.'){
outError();
return i-1;
}
if(wd == ':'){
if(src[i+1]!='='){
outError();
return i-1;
}
}
if(wd == '/'){
if(src[i+1]=='/' || src[i+1]=='*'){
outError();
return i-1;
}
}
newStatus(-1); // 避免分界符被放入错误输出中
}
return srcLen-1;
}
int outError(){ // 错误报告
newPrintf("Error with: %s\n", words.c_str());
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
int newStatus(int _s){ // 更新状态
switch(_s){
case 0: // 为0则初始化状态
status = 0; // 原始状态
len = 0;
words = "";
break;
case -1: // -1作为一个暂态,处理不需要状态实际转移的情况
len += 1;
words += wd;
break;
default: // 不为0就更新状态
status = _s;
len += 1;
words += wd;
}
return 1;
}
int output(){ // 存储词元、输出、初始化
switch(type){
case 0: break; // 关键字
case 1: // 运算符
for(int i=20; i<33; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break; // 跳出for循环而非case
}
// 出错啦
break;
case 2: break; // 常数
case 3: // 界符
for(int i=50; i<56; i++)
if(wordsTable[i] == words){
cag = i+1;
break;
}
break;
// 出错啦
case 4: // 标识符
cag = 45;
break;
case 5: // 注释 无需输出与存储,初始化后退出
newStatus(0);
return 1;
}
wordsLen += 1;
newPrintf("(%d)(%d,%s)\n", wordsLen, cag, words.c_str());
strV.push_back(words); // 存储词元
typeV.push_back(cag); // 存储词元
newStatus(0); // 初始化
return 1;
}
int isBlank()const{ // 检测空白字符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(filt[i] == wd) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isDelimiter()const{ // 判断是否是单字分界符
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
if(wd == delm[i]) return true;
return false;
}
int isKeywords()const{ // 判断关键字,返回种别码或0
for(int i=0; i<keyWordsLen; i++)
if(words == wordsTable[i]) return i+1;
return 0;
}
bool isNumber(int lim = 10)const{ // 判断数字
switch (lim){
case 0: // 除0以外的十进制数字
if(wd >= '1' && wd <= '9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 10: // 十进制
if(wd>='0' && wd<='9') return 1;
else return 0;
case 8:
if(wd >='0' && wd<='7') return 1;
else return 0;
case 2:
if(wd >='2') return 0;
else return 1;
case 16:
if(wd >= '0' && wd <= '9' || wd >= 'a' && wd <= 'f' || wd >= 'A' && wd <= 'F') return 1;
else return 0;
}
return 0;
}
bool isLowerLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='a' && wd<='z') return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isUpperLetter()const{ // 判断大写字母
if(wd>='A' && wd<='Z') return 1;
return 0;
}
void printSplit(string text){ // 输出夹带文本的分割线
if(silence==1) return;
const int aLen = 60;
int _len = text.length()+2; // 两侧留空
int left = (aLen-_len)/2, right = aLen - left - _len;
for(int i=0; i<left; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf(" %s ", text.c_str());
for(int i=0; i<right; i++) newPrintf("-");
newPrintf("\n");
return ;
}
void newPrintf(const char *fmt, ...){ // 重载自己的printf, 便于保存输出的内容, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51281362/article/details/125445742 | https://blog.csdn.net/wanruiou/article/details/115180466
if(silence==1) return;
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, fmt); // 传入地址
vprintf(fmt, arg);
if(needOF) // 需要保存至文件
vfprintf(oF, fmt, arg); // 借助FILE将printf重定向至文件流, 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/LuyaoYing001/article/details/79750833
va_end(arg); // 结束可变参数的获取
}
int getVL()const{ return typeV.size(); } // 数组长度
int atTV(int n)const{ return typeV[n]; }
vector<int> getTV()const{ return typeV; }
vector<string> getSV()const{ return strV; }
};
const int threshold=100;
template<class T>
int getLen(T& arr){ // 快速获取数组长度
return sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
}
struct Chain{ // 记录TrueChain指针与FalseChain指针的结构体
int tC; // trueChain
int fC; // falseChain
};
class semanticAnalyzer{
private:
const int opp[7][7]={1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,1,1,1,1,-1,1,1,1,1,1,1,-1,1,1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,0,2,1,1,1,1,2,1,1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,2,0}; //operatorPriority
//运算符顺序:'+','-','*','/','(',')','#' 1表示大于,0等于,-1小于,2非法
/*
+ - * / ( ) #
+ > > < < < > >
- > > < < < > >
* > > > > < > >
/ > > > > < > >
( < < < < < = x
) > > > > x > >
# < < < < < x =
*/
const int opl[5][5]={1, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, -1, -1, -1, 2, 0}; //operatorPriority
//运算符顺序:'&&','||','(',')','#' 1表示大于,0等于,-1小于,2非法
/*
& | ( ) #
& > > < > >
| < > < > >
( < < < = x
) x x x x x
# < < < x =
*/
stack<int> S;
stack<string> calcNS; // 算术表达式操作数栈
stack<int> calcOpS; // 算术表达式运算符栈
stack<int> locNS; // 关系表达式操作数栈
stack<int> locOpS; // 关系表达式运算符栈
stack<string> NS; // 关系运算操作数栈
stack<int> opS; // 关系运算符号栈
stack<Chain> CS; // ChainStack
stack<int> WS; // while首位栈
stack<pair<int, string>> tdS; // 跳转待定栈
stack<vector<int>> cirS; // 递归栈,V[层数(栈中元素个数替代), 标记种类, 特殊位置标记]
map<pair<int, int>, vector<int>> init; // 预测表
vector<int> typeV;
vector<string> strV;
vector<vector<string>> V4; // 四元式存储
int flag;
int ops; // 临时操作数计数
int lFlag; // 排除关系语句的首个关系式
int rFlag; // 寻找赋值语句的首个变量
int tFlag; // 寻找首层算术表达式
public:
semanticAnalyzer(vector<int> tv, vector<string> sv):typeV(tv), strV(sv){ // 初始化预测表
typeV.push_back(0); // 终止符#外标记为0,内标记为-1
strV.push_back("#"); // 终止符#外标记为0,内标记为-1
locOpS.push(0); // 起止符# 0
opS.push(0);
CS.push({0, 0}); // 底层Chain
cirS.push({-1, -1, -1}); // 垫底
tFlag = 1;
// LL(1) 转移表
buildMap(100, 0, {101,50,44,0});
buildMap(101, 1, {51,5,106,4,102});
buildMap(102, 1, {103,1});
buildMap(103, 44, {124,50,104,53,105});
buildMap(104, 2, {2});
buildMap(104, 3, {3});
buildMap(105, 44, {125,121});
buildMap(106, {4,6,9,44}, {126,107});
buildMap(107, 4, {111});
buildMap(107, 6, {109});
buildMap(107, 9, {110});
buildMap(107, 4, {111});
buildMap(107, 44, {108});
buildMap(108, 44, {112,30,121});
buildMap(109, 6, {129,107,7,120,6});
buildMap(110, 9, {107,10,120,9});
buildMap(111, 4, {5,106,4});
buildMap(112, {40,41,44}, {113,116});
buildMap(113, {5,7,8,10,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55,31,32}, {128});
buildMap(113, {20,21}, {114});
buildMap(114, {5,7,8,10,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55,31,32}, {128});
buildMap(114, {20,21}, {114,115});
buildMap(115, 20, {116,20});
buildMap(115, 21, {116,21});
buildMap(116, {40,41,44,54}, {127,119});
buildMap(117, {5,7,8,10,20,21,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55,31,32}, {128});
buildMap(117, {22,23}, {117,118});
buildMap(118, 22, {119,22});
buildMap(118, 23, {119,23});
buildMap(119, {40,41}, {122});
buildMap(119, 44, {121});
buildMap(119, 54, {55,112,54});
buildMap(120, {40,41,44,54}, {131,130});
buildMap(121, 44, {44});
buildMap(122, 40, {40});
buildMap(122, 41, {41});
buildMap(123, 24, {24});
buildMap(123, 25, {25});
buildMap(123, 26, {26});
buildMap(123, 27, {27});
buildMap(123, 28, {28});
buildMap(123, 29, {29});
buildMap(124, 4, {128});
buildMap(125, 52, {105,52});
buildMap(125, 53, {128});
buildMap(126, 5, {128});
buildMap(126, 50, {106,50});
buildMap(127, {5,7,8,10,20,21,24,25,26,27,28,29,50,55,31,32}, {128});
buildMap(127, {22,23}, {117});
buildMap(129, 8, {107,8});
buildMap(129, {50, 5}, {128});
buildMap(130, {40,41,44,54}, {112, 123, 112});
buildMap(131, {31,32}, {120,132});
buildMap(131, {10, 7}, {128});
buildMap(132, 31, {31});
buildMap(132, 32, {32});
}
bool buildMap(int a, vector<int> s, vector<int> V){
vector<int> v;
int len = V.size(), lens = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++){
v.push_back(V[i]);
}
for(int j = 0; j<lens; j++){
pair<int, int> p(a, s[j]);
if(init.count(p)) return 0; // 重复定义
init[p]=v;
}
return 1;
}
bool buildMap(int a, int b, vector<int> V){
int len = V.size();
pair<int, int> p(a, b);
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++){
v.push_back(V[i]);
}
init[p]=v;
return 1;
}
bool isVT(int n){
if(n>=100 && n!=128) return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isEmpty(int n){
if(n==128) return 1;
return 0;
}
bool getPush(vector<int> V){ // 逐个入栈
int len = V.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
S.push(V[i]);
}
return 1;
}
bool analyze(){
V4.resize(0); // 清空四元式存储
ops = 1; // 临时操作数从1开始
S.push(-1); // 终止符
S.push(100); // 起始符A
cirS.push({-1, -1, -1});
V4.push_back({"none", "", "", ""});
int len = typeV.size(), c=0;
while(!S.empty() && c<len){
int tmp = S.top();
string tmpS = strV[c];
S.pop(); // 当前符号出栈
if(isVT(tmp)){ // 非终结符
pair<int, int> tmpP(tmp, getMinus(typeV, c));
if(init.count(tmpP)==0){ // 语法错误
// printf("false with unknown: %d (%d,%s)", tmp, typeV[c]-1, strV[c].c_str());
printf("syntax error.");
exit(-1);
}
vector<int> tmpV = init[tmpP];
if(tmp == 109){ // 条件语句
addChain();
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 1, 0});
}
if(tmp == 120 && getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 6){ // if后面的关系表达式
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 2, 0});
locOpS.push(0); // 起止符标记关系表达式开始
lFlag = 1; // l标记
}
if(tmp == 107 && getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 7){ // 准备进入then后面的语句
linkUpV4(getTC(), to_string(V4.size()));
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 3, 0});
}
if(tmp == 107 && getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 8){ // else后的语句
// FC跳转
upChain(V4.size(), -1);
addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"});
upV4(getFC(), 3, to_string(V4.size())); // 有else则多了一行,FC后移一个
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 4, 0});
}
if(tmp == 130){ // 子关系表达式
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 5, 0});
}
if(tmp == 112 && tFlag == 1){ // 第一层算术表达式
tFlag = 0;
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 6, c});
}
if(tmp == 110){ // while语句
addChain();
WS.push(V4.size());
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 7, 0});
}
if(tmp == 120 && getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 9){ // while后面的关系表达式
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 8, 0});
locOpS.push(0); // 起止符标记关系表达式开始
lFlag = 1; // l标记
}
if(tmp == 107 && getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 10){ // do后的语句
linkUpV4(getTC(), to_string(V4.size()));
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 9, 0});
}
if(tmp == 100){ // 起始符号
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 0, 0}); // 始末标记
}
if(tmp == 108){ // 赋值语句
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 10, 0});
rFlag = 1;
}
if(tmp == 121 && rFlag){ // 赋值语句后的变量
cirS.push({int(S.size()), 11, 0});
rFlag = 0;
}
getPush(tmpV);
} else { // 终结符或空
if(!isEmpty(tmp) && tmp!=getMinus(typeV, c)){ // 不为空才算语法错误
// printf("false with: %d (%d,%s)", tmp, typeV[c]-1, strV[c].c_str());
printf("syntax error.");
exit(-1);
} else {
// printf("true: (%d,%s)\n", typeV[c]-1, strV[c].c_str());
if(!isEmpty(tmp)) // 不为空才迭代
++c;
}
while(1){
vector<int> tmpV = cirS.top(); // 取出顶部标识
if(getMinus(typeV, c-1) >=24 && getMinus(typeV, c-1) <= 29){ // 关系运算符
opS.push(getMinus(typeV, c-1)); // 入栈
}
if(getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 31 || getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 32){ // 逻辑运算符
logicCheck(getMinus(typeV, c-1)); // 逻辑运算
}
if(getMinus(typeV, c-1) == 30){ // 赋值号
opS.push(30); // 赋值号入栈
}
if(S.size() == tmpV[0]){ // 若层数符合要求
switch(tmpV[1]){
case 0:{
addV4({"ret", " ", " ", "0"});
break;
}
case 1:{ // 条件语句
if(!updatedChain(getFC())){ // Falsechain未被连接说明if后没有else
linkUpV4(getFC(), to_string(V4.size()));
}
delChain();
break;
}
case 2:{ // if后的关系表达式整理完毕
logicCheck(0);
break;
}
case 3:{ // then后语句处理完毕
break;
}
case 4:{ // 从else后语句中出来
// 链接TrueChain
linkUpV4(getTC(), to_string(V4.size()));
break;
}
case 5:{ // 子关系表达式结束
// 处理关系运算
handleLogic();
break;
}
case 6:{ // 算术表达式结束
handleCalc(tmpV[2], c); // 处理算术表达式
tFlag = 1;
break;
}
case 7:{ // while语句
delChain();
break;
}
case 8:{ // while后的关系表达式结束
logicCheck(0);
break;
}
case 9:{ // do后语句结束
int wBeg = WS.top();
WS.pop();
addV4({"j", " ", " ", to_string(wBeg)});
linkUpV4(getFC(), to_string(V4.size()));
break;
}
case 10:{ // 赋值语句
string a, b;
int tmpTp = opS.top();
opS.pop();
b = NS.top();
NS.pop();
a = NS.top();
NS.pop();
handleGive(a, b, tmpTp);
break;
}
case 11:{ // 赋值语句后的首个变量
NS.push(strV[c-1]);
break;
}
}
cirS.pop();
continue;
}
if(S.size() < tmpV[0]){ // 预留给内层的已失效,如对应if的else
cirS.pop();
}
break;
}
}
//
}
// if(!S.empty()) printf("stack error");
// if(c<len) printf("vector error.");
// printf("true");
return 1;
}
int getMinus(vector<int> V, int index){
return V[index] - 1;
}
void getOut(){ // 输出结果
int len = V4.size();
for(int i=1; i<len; i++){
vector<string> tmp = V4[i];
printf("%d.(%s, %s, %s, %s)\n", i, tmp[0].c_str(), tmp[1].c_str(), tmp[2].c_str(), tmp[3].c_str());
}
return ;
}
int updatedChain(int idx){ // 检查if的FalseChain是否被连接过
string tmp = V4[idx][3];
int tmpN = stoi(tmp);
if(tmpN == -1 || tmpN == lastJ(idx)){ // 指向空-1或前一个结点则认为未被连接
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void logicCheck(int k){ // 进行逻辑运算
int k1, k2 = opl2Int(k);
int tmpVar;
while(1){ // 执行前面的运算
k1 = opl2Int(locOpS.top());
if(opl[k1][k2] != 1)
break;
k1 = locOpS.top();
tmpVar = locNS.top();
locNS.pop();
logicCalc(tmpVar, k1); // 根据运算生成四元式
locOpS.pop();
}
if(opp[k1][k2] == 0){ // 等级相消
locOpS.pop();
} else if(opp[k1][k2] == -1){
locOpS.push(k);
}
return ;
}
int lastJ(int k){ // 关系表达式内的J跳转搜索
int p = k-1;
string tmp = V4[p][0];
while(1){
if(tmp.substr(0, 1) == "j"){ // 检测到跳转语句
return p-1;
}
p -= 1;
tmp = V4[p][0];
}
return -1; // error
}
void logicCalc(int loc, int op){ // 逻辑运算
int pre = lastJ(loc), cur = loc;
switch(op){
case 31:{ // and
backV4(cur+1);
linkUpV4(pre, to_string(cur));
break;
}
case 32:{ // or
backV4(cur);
linkUpV4(pre+1, to_string(cur));
}
}
return ;
}
void handleGive(string a, string b, int op){
addV4({"=", b, " ", a}); // 赋值语句
}
void handleLogic(){ // 处理关系运算式
string a, b;
int tmpTp = opS.top();
opS.pop();
b = NS.top();
NS.pop();
a = NS.top();
NS.pop();
opLogic(a, b, tmpTp);
};
string newOps(){ // 迭代临时操作数
string tmp = "T";
tmp = tmp+to_string(ops);
ops++;
return tmp;
}
int op2Int(int c){ // 算术运算符转对应矩阵编号,-1表示异常
switch(c){
case 20:return 0;
case 21:return 1;
case 22:return 2;
case 23:return 3;
case 54:return 4;
case 55:return 5;
case 0:return 6;
}
return -1;
}
int opl2Int(int c){ // 逻辑运算符转对应矩阵编号,-1表示异常
switch(c){
case 31:return 0;
case 32:return 1;
case 54:return 2;
case 55:return 3;
case 0:return 4;
}
return -1;
}
void upChain(int tC, int fC){ // 更新最顶层的TC与FC,-1表示不更新
Chain tmp = CS.top();
CS.pop();
if(tC != -1){ // TC
tmp.tC = tC;
}
if(fC != -1){ // FC
tmp.fC = fC;
}
CS.push(tmp);
return ;
}
void addChain(){ // 添加一层FC与TC
CS.push({0, 0});
return ;
}
void delChain(){ // 删除一层FC与TC
CS.pop();
return ;
}
int getTC(){ // 获取顶层TC
return CS.top().tC;
}
int getFC(){ // 获取顶层FC
return CS.top().fC;
}
void opCalc(string a,string b,int c){ // 发生运算,记录四元式
string _ops = newOps();
switch(c){
case 20:{
addV4({"+", a, b, _ops});
calcNS.push(_ops);
return ;
}
case 21:{
addV4({"-", a, b, _ops});
calcNS.push(_ops);
return ;
}
case 22:{
addV4({"*", a, b, _ops});
calcNS.push(_ops);
return ;
}
case 23:{
addV4({"/", a, b, _ops});
calcNS.push(_ops);
return ;
}
}
return ;
}
void opLogic(string a,string b,int c){ // 存在逻辑运算,记录四元式
int tC, fC;
switch(c){
case 24:{
tC = addV4({"j>", a, b, "-1"}); // true指针
fC = addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"}); // false指针
break;
}
case 25:{
tC = addV4({"j>=", a, b, "-1"}); // true指针
fC = addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"}); // false指针
break;
}
case 26:{
tC = addV4({"j<", a, b, "-1"}); // true指针
fC = addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"}); // false指针
break;
}
case 27:{
tC = addV4({"j<=", a, b, "-1"}); // true指针
fC = addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"}); // false指针
break;
}
case 28:{
tC = addV4({"j=", a, b, "-1"}); // true指针
fC = addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"}); // false指针
break;
}
case 29:{
tC = addV4({"j<>", a, b, "-1"}); // true指针
fC = addV4({"j", " ", " ", "-1"}); // false指针
}
}
upChain(tC, fC); // 更新Chain
if(lFlag == 1){ // 首个不成对,不入栈
lFlag = 0;
} else { // 入栈逻辑关系对: tC与tC-2
locNS.push(tC);
}
return ;
}
void handleCalc(int beg, int end){ // 处理算术表达式
string _beg = strV[beg], _end = strV[end];
int tmpTp;
string tmpStr;
calcOpS.push(0); // 起止符
for(int i=beg; i<end; i++){
tmpTp = getMinus(typeV, i);
if(tmpTp == 50) continue; // 跳过分号
tmpStr = strV[i];
switch(tmpTp){
case 40:{ // 整数
calcNS.push(tmpStr); // 推入操作数
break;
}
case 41:{ // 浮点数
calcNS.push(tmpStr);
break;
}
case 44:{ // 标识符
calcNS.push(tmpStr);
break;
}
case 20:
case 21:
case 22:
case 23:
case 54:
case 55:{
int k1, k2 = op2Int(tmpTp);
string a, b;
while(1){ // 执行前面的运算
k1 = op2Int(calcOpS.top());
if(opp[k1][k2] != 1)
break;
k1 = calcOpS.top();
b = calcNS.top(); // 后运算符
calcNS.pop();
a = calcNS.top(); // 前
calcNS.pop();
opCalc(a, b, k1); // 根据运算生成四元式
calcOpS.pop();
}
if(opp[k1][k2] == 0){ // 等级相消
calcOpS.pop();
} else if(opp[k1][k2] == -1){
calcOpS.push(tmpTp);
}
}
}
}
tmpTp = 0;
tmpStr = "#";
int k1, k2 = op2Int(tmpTp);
string a, b;
while(1){ // 执行前面的运算
k1 = op2Int(calcOpS.top());
if(opp[k1][k2] != 1)
break;
k1 = calcOpS.top();
b = calcNS.top(); // 后运算符
calcNS.pop();
a = calcNS.top(); // 前
calcNS.pop();
opCalc(a, b, k1); // 根据运算生成四元式
calcOpS.pop();
}
if(opp[k1][k2] == 0){ // 等级相消
calcOpS.pop();
} else if(opp[k1][k2] == -1){
calcOpS.push(tmpTp);
}
tmpStr = calcNS.top();
calcNS.pop();
NS.push(tmpStr); // 入关系运算操作数栈
return ;
}
int addV4(vector<string> V){
V4.push_back(V);
if(V[0] == "j"){ // 新添加语句是无条件跳转语句
while(!tdS.empty()){ // 待语句出现再回填
pair<int, string> tmp = tdS.top();
tdS.pop();
linkUpV4(tmp.first, V[3]);
}
} else { // 无用语句
while(!tdS.empty()){ // 待语句出现再回填
pair<int, string> tmp = tdS.top();
tdS.pop();
linkUpV4(tmp.first, tmp.second);
}
}
return V4.size()-1;
}
void linkUpV4(int idx, string dst){ // 按链条回填
string tmps = V4[idx][0].substr(0, 1);
if(tmps == "j" && stoi(dst) >= int(V4.size())){ // 无条件跳转 且 跳转目标尚未确定 ——这种情况一般是下一条即将填写的语句就是目标语句
tdS.push({idx, dst});
return ;
}
string s = V4[idx][3], nul = "-1";
while(s != nul){
upV4(idx, 3, dst);
idx = lastJ(idx);
s = V4[idx][3];
}
upV4(idx, 3, dst);
return ;
}
void upV4(int idx1, int idx2, string dst){ // 单个修改
V4[idx1][idx2] = dst;
return ;
}
void backV4(int idx){
string s = V4[idx][3], nul = "-1";
int tmp;
if(s == nul){ // 值为空
tmp = lastJ(idx);
upV4(idx, 3, to_string(tmp));
} else {
linkUpV4(lastJ(idx), s);
}
return ;
}
};
int main(){
wordsAnalyzer *wA = new wordsAnalyzer(1);
wA->printSplit("Lexical Analysis");
wA->analyze();
semanticAnalyzer *sA = new semanticAnalyzer(wA->getTV(), wA->getSV());
sA->analyze();
sA->getOut();
return 0;
}
问题解决
VSC C++环境配置
重新配置C++环境时,忘记配置编译器的环境变量,捣鼓了VSC的配置文件好久,发现了一些有意思的事。
编译连接C++的编译器是"g++.exe",用于调试链接生成的可执行文件的是"gdb.exe",在VSC中想要使用C++,一般需要先配置环境。
-
Ctrl+Shift+P打开控制台,输入 "C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI)",进入配置页面,选择编译器路径为下载的MinGW中的"MinGW/bin/g++.exe",选择IntelliSense模式为"windows-gcc-x64"。点击输入框外的地方vsc就会自动保存设置,并在当前文件夹下生成一个".vscode"文件夹,里面会有一个"c_cpp_properties.json"文件,包含了C++的编译器配置。 -
".vscode"下,"tasks.json"文件提供了编译链接CPP文件的设置,demo:
{ "tasks": [ { "type": "cppbuild", "label": "C/C++: g++.exe build active file", // tasks的链接标签 "command": "F:\\CPP\\MinGW\\bin\\g++.exe", // 输入g++的路径 "args": [ "-fdiagnostics-color=always", "-g", "${file}", "-o", "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe" // 链接所得的exe文件的位置 ], "options": { "cwd": "${fileDirname}" // 设置工作目录,它决定了代码中相对路径的起始路径 }, // 即"./"所代表的位置 "problemMatcher": ["$gcc"], "group": { "kind": "build", "isDefault": true }, "detail": "Task generated by Debugger." } ], "version": "2.0.0" }${fileDirname}表示源码所在文件夹的文件夹名称,带"/";${fileBasenameNoExtension}表示源码文件名,不带扩展名。有该文件的情况下,配置了编译器的环境变量,则已经可以编译调试运行C++程序了。如果没有配置环境变量,将"cwd"设置为编译器所在文件夹,也能编译,因为这样vsc也能访问到g++来链接程序,但相对路径的起始位置将被捆绑为该文件夹,源码中将无法使用正确的相对路径,只能采用绝对路径。
-
"launch.json"文件提供了调试运行链接生成的可执行文件的设置,demo:
{ "configurations": [ { "name": "(gdb) 启动", "type": "cppdbg", "request": "launch", "program": "${workspaceFolder}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe", // exe位置 "args": [], "stopAtEntry": false, "cwd": "${fileDirname}", // 设置工作目录,即相对路径起始位置 "environment": [], "externalConsole": false, // 弹出外部shell——不便于看到历史调试记录 "MIMode": "gdb", // 虽然vsc的内部终端也会吞输出就是了 "miDebuggerPath": "F:/CPP/MinGW/bin/gdb.exe", // 调试器gdb所在位置 "setupCommands": [ { "description": "为 gdb 启用整齐打印", "text": "-enable-pretty-printing", "ignoreFailures": true }, { "description": "将反汇编风格设置为 Intel", "text": "-gdb-set disassembly-flavor intel", "ignoreFailures": true } ], "preLaunchTask": "C/C++: g++.exe build active file", // 要与tasks.json的 } // label相对应,该配置才能正确被采用 ] }该文件不是必要的,但它提供了更丰富的调试配置,通过"label"与"preLaunchTask"将链接与调试操作连接起来,依据配置文件依次执行。若某份源码在之前的编译中已经生成了exe文件,但在某次调试中编译出现问题,此时如果设置了弹出外部终端,则该源码的旧exe文件将会被执行,输出在shell中的部分由于闪退将不可得,但文件操作的留下痕迹的行为将正常保留。
当两个配置文件"cwd"冲突时,以"launch.json"的cwd为主。
C++数组操作
数组长度快速获取
测试源码1:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int getLen(int *p){
cout<<"sizeof(p) = "<<sizeof(p)<<endl;
cout<<"sizeof(p[0]) = "<<sizeof(p[0])<<endl;
cout<<"p = "<<p<<endl;
cout<<"p[0] = "<<p[0]<<endl;
return sizeof(p)/sizeof(p[0]);
}
int main(){
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int lenth = getLen(a);
cout<<"len = "<<lenth;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
sizeof(p) = 8
sizeof(p[0]) = 4
p = 0x61fe00
p[0] = 1
len = 2
int类型的指针(或数组)长度结果默认为8,该结果固定。
测试源码2:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
int getLen(T &p){
cout<<"sizeof(p) = "<<sizeof(p)<<endl;
cout<<"sizeof(p[0]) = "<<sizeof(p[0])<<endl;
cout<<"p = "<<p<<endl;
cout<<"p[0] = "<<p[0]<<endl;
return sizeof(p)/sizeof(p[0]);
}
int main(){
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int lenth = getLen(a);
cout<<"len = "<<lenth;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
sizeof(p) = 24
sizeof(p[0]) = 4
p = 0x61fe00
p[0] = 1
len = 6
可以成功获取到正确的长度,传入为引用时必须要设置为模板,否则不过编译。
当将a设置为指针时:
int *a = new int[5];
运行结果:
sizeof(p) = 8
sizeof(p[0]) = 4
p = 0x744150
p[0] = 1
len = 2
也不能获取到正确的长度
数组快速构造
初始化数组时:
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具