数据结构 -- 链表(LinkedList)
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。
每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
相比于线性表顺序结构,操作复杂。由于不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到O(1)的复杂度,比另一种线性表顺序表快得多,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要O(n)的时间,而线性表和顺序表相应的时间复杂度分别是O(logn)和O(1)。
二、链表种类
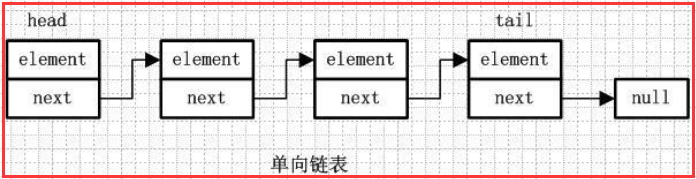
1.1)单向链表:
element:用来存放元素
next:用来指向下一个节点元素
通过每个结点的指针指向下一个结点从而链接起来的结构,最后一个节点的next指向null。
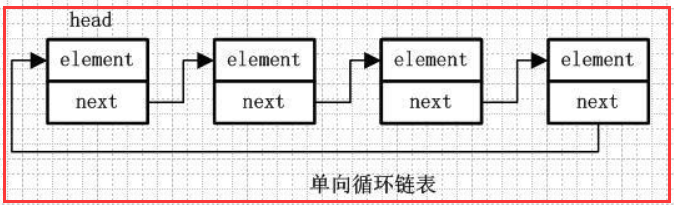
1.2)单向循环链表
element、next 跟前面一样
在单向链表的最后一个节点的next会指向头节点,而不是指向null,这样存成一个环
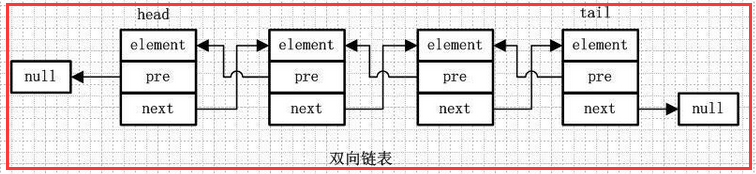
1.3)双向链表
element:存放元素
pre:用来指向前一个元素
next:指向后一个元素
双向链表是包含两个指针的,pre指向前一个节点,next指向后一个节点,但是第一个节点head的pre指向null,最后一个节点的tail指向null。
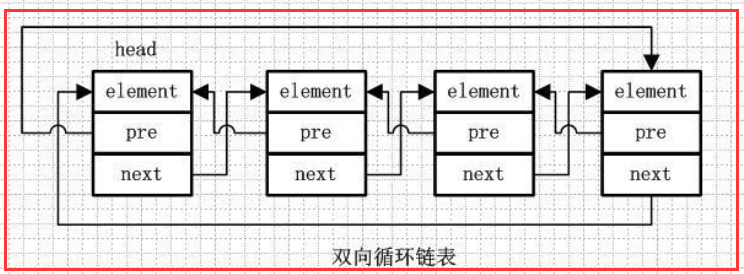
1.4)双向循环链表
element、pre、next 跟前面的一样
第一个节点的pre指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的next指向第一个节点,也形成一个“环”。
时间复杂度
(1)添加操作:O(n)
① addLast(e): O(n) ②addFirst(e): O(1) ③add(index, e): O(n/2)=O(n)
(2)删除操作:O(n)
① removeLast(e): O(n) ②removeFirst(e): O(1) ③remove(index, e): O(n/2)=O(n)
(3)查找操作:O(n)
① get(index): O(n) ②contains(e): O(n)
(4)修改操作:O(n)
① set(index,e): O(n)
三、代码实现
单链表的实现
图解如下:
插入
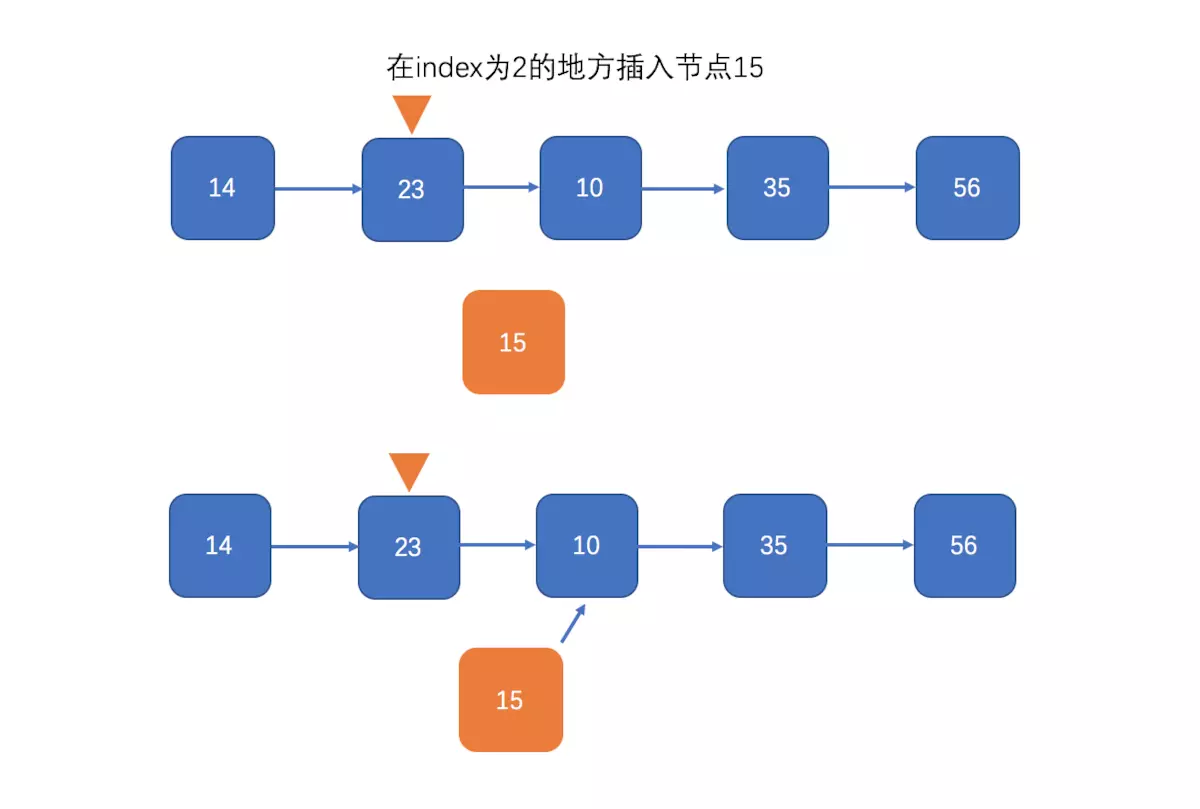
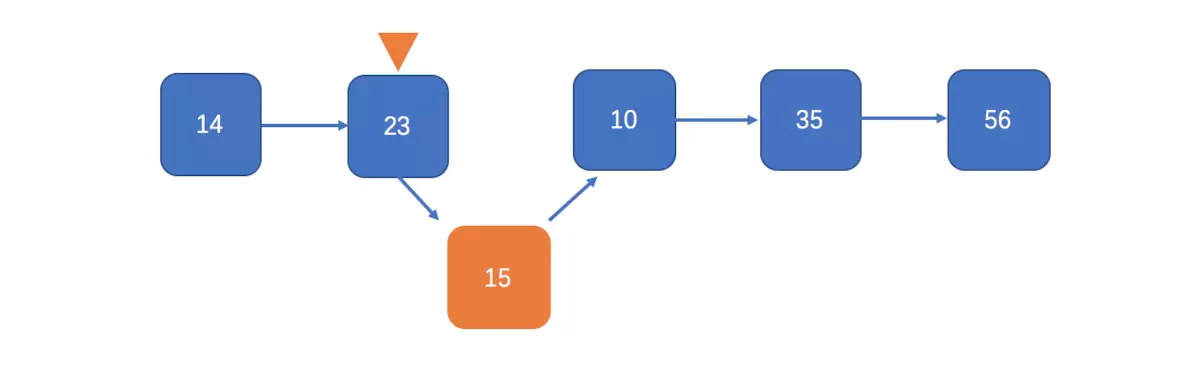
删除
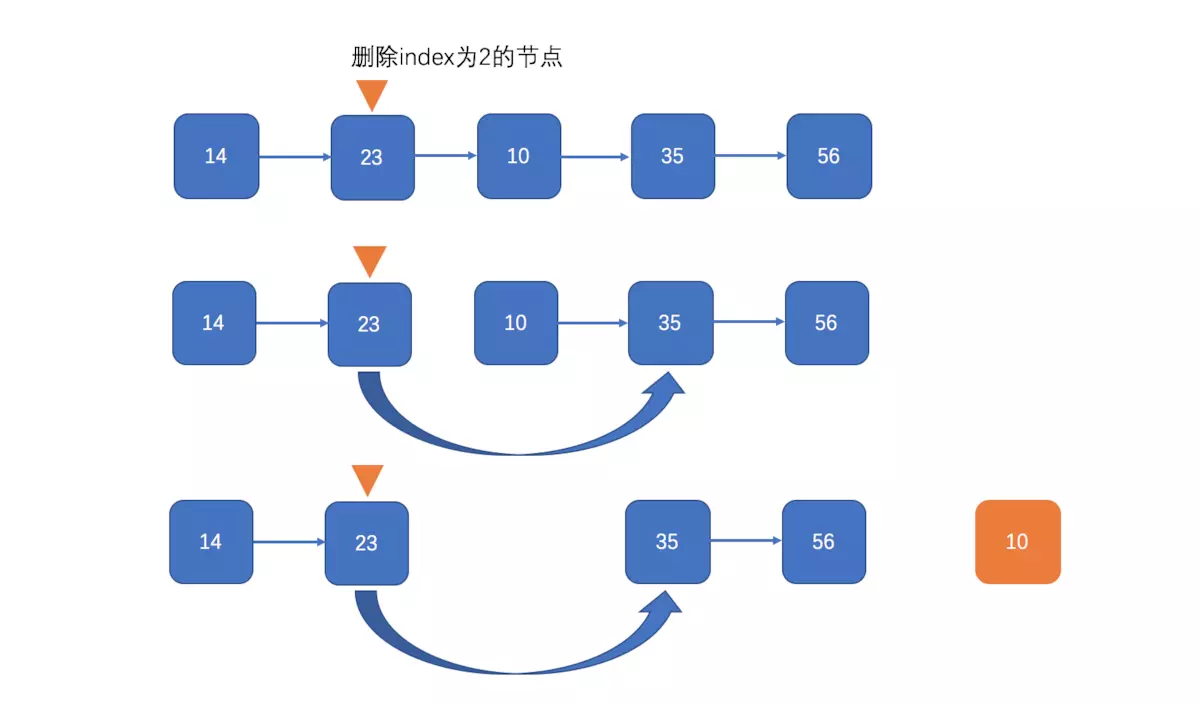
代码
public class LinkedList<E> { //链表节点,使用内部类 private class Node{ public E e; //当前节点内容 public Node next; //指向下一个节点 public Node(E e, Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } public Node(){ this(null,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return e.toString(); } } private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点,位于第一位置的前一个位置 private int size;//链表元素个数 public LinkedList(){ dummyHead = new Node(); size = 0; } public int getSize(){ return size; } //判断是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0; } public void add(int index, E e){ if(index < 0 || index > size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index."); } Node prev = dummyHead; for (int i=0; i<index; i++){ prev = prev.next; } prev.next = new Node(e,prev.next); size ++; } //在链表 表头添加新的元素e public void addFirst(E e){ add(0,e); } //在链表 尾部添加新的元素e public void addList(E e){ add(size,e); } //获得链表的第index位置的元素. 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用 public E get(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >= size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("index Illegal"); } Node cur = dummyHead.next; for (int i =0; i<index; i++){ cur = cur.next; } return cur.e; } public E getLast(){ return get(size - 1); } public E getFirst(){ return get(0); } public void set(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index >= size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("index Illegal"); } Node cur = dummyHead.next; for (int i=0; i<index; i++){ cur =cur.next; } cur.e = e; } //查找链表中是否包含元素e public boolean contains(E e){ Node cur = dummyHead.next; while (cur != null){ if (cur.e.equals(e)) return true; cur = cur.next; } return false; } // 从链表中删除index(0-based)位置的元素, 返回删除的元素 // 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:) public E remove(int index){ if (index < 0 || index >= size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal."); } Node prev = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++){ prev = prev.next; } Node retNode = prev.next; prev.next = retNode.next; //删除retNode节点,则它的下一个节点指引就不需要了,设置null,让GC干活 retNode.next = null; size --; return retNode.e; } public E removeFirst(){ return remove(0); } public E removeLast(){ return remove(size - 1); } public void removeElement(E e){ Node prev = dummyHead; while (prev != null){ if (prev.next.e.equals(e)){ break; } prev = prev.next; } if (prev.next != null){ Node delNode = prev.next; prev.next = delNode.next; delNode.next = null; size --; } } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); Node cur = dummyHead.next; while( cur != null){ stringBuilder.append(cur + "- >"); cur = cur.next; } stringBuilder.append("null"); return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
测试代码
public class LinkedListTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(); for (int i=0; i< 10; i++){ linkedList.add(i,i*10); System.out.println(linkedList); } linkedList.remove(1); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeElement(50); System.out.println(linkedList); } }
//测试结果
0- >null 0- >10- >null 0- >10- >20- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >80- >null 0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >80- >90- >null 0- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >80- >90- >null //删除第二个位置的10 0- >20- >30- >40- >60- >70- >80- >90- >null //删除指定元素50
链表实现队列
import com.wj.queue.Queue; //Queue连接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11808221.html public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e, Node next){ this.e=e; this.next = next; } public Node(){ this(null,null); } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } @Override public String toString() { return e.toString(); } } private Node head, tail; //指针队首和队尾 private int size; //数据个数 public LinkedListQueue(){ head = null; tail = null; size = 0; } @Override public int getSize() { return size; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } //入队 @Override public void enqueue(Object o) { if (tail == null){ tail = new Node((E) o); head = tail; }else { tail.next = new Node((E) o); tail = tail.next; } size++; } //出队 @Override public E dequeue() { if (isEmpty()){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue."); } Node retNode = head; head = head.next; retNode.next = null; if (head == null){ tail = null; } size--; return retNode.e; } //返回队首元素 @Override public E getFront() { if (isEmpty()){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue."); } return head.e; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append("Queue: front "); Node cur = head; while (cur != null){ stringBuilder.append(cur + "- >"); cur = cur.next; } stringBuilder.append("NULL tail"); return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
测试类
public class LinkedListQueueTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedListQueue linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue(); for (int i=0; i<10; i++){ linkedListQueue.enqueue(i); //入队 System.out.println(linkedListQueue); if (i % 3 ==0){ linkedListQueue.dequeue(); //符合条件,出队 } } } }
//测试结果 Queue: front 0- >NULL tail Queue: front 1- >NULL tail Queue: front 1- >2- >NULL tail Queue: front 1- >2- >3- >NULL tail Queue: front 2- >3- >4- >NULL tail Queue: front 2- >3- >4- >5- >NULL tail Queue: front 2- >3- >4- >5- >6- >NULL tail Queue: front 3- >4- >5- >6- >7- >NULL tail Queue: front 3- >4- >5- >6- >7- >8- >NULL tail Queue: front 3- >4- >5- >6- >7- >8- >9- >NULL tail
链表实现栈
import com.wj.stack.Stack; //详情连接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11809042.html public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private LinkedList<E> linkedList; public LinkedListStack(){ linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); } @Override public int getSize() { return linkedList.getSize(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return linkedList.isEmpty(); } //压入 public void push(Object o) { linkedList.addFirst((E) o); } //移除 @Override public E pop() { return linkedList.removeFirst(); } //返回栈首元素 @Override public E peek() { return linkedList.getFirst(); } public String toString(){ StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append("Stack: top "); stringBuilder.append(linkedList); return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
测试类
public class LinkedListStackTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedListStack stack = new LinkedListStack(); for (int i =0; i< 10; i++){ stack.push(i); //压入 System.out.println(stack); } System.out.println("============="); stack.pop(); //移除 System.out.println(stack); } }
//测试结果 Stack: top 0- >null Stack: top 1- >0- >null Stack: top 2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 3- >2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 8- >7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null Stack: top 9- >8- >7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null //将第一个移除 ============= Stack: top 8- >7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
四、效率对比
栈的对比
import com.wj.stack.ArrayStack; //详情连接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11809042.html import com.wj.stack.Stack; import java.util.Random; public class StackEfficiency { private static double testStack(Stack<Integer> stack, int opCount){ long startTime = System.nanoTime(); Random random = new Random(); for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){ stack.push(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); } for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){ stack.pop(); } long endTime = System.nanoTime(); return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0; } public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 100000; ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack(); double time1 = testStack(arrayStack,opCount); System.out.println("ArrayStack - time1: " + time1); LinkedListStack<Integer> linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack(); double time2 = testStack(linkedListStack,opCount); System.out.println("LinkedListStack - time2: " + time2); } }
//测试结果,添加和删除 ArrayStack - time1: 7.071363002 LinkedListStack - time2: 0.006395025
//说明数组的增删 效率要低于 链表。
//对于增删数组的时间复杂度是O(n),而链表是O(1)
队列的对比
import com.wj.queue.ArrayQueue;//详情:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11808221.html import com.wj.queue.LoopQueue; import com.wj.queue.Queue; import java.util.Random; public class MainQueue { private static double testStack(Queue<Integer> queue, int opCount){ long startTime = System.nanoTime(); Random random = new Random(); for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){ queue.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); } for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){ queue.dequeue(); } long endTime = System.nanoTime(); return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0; } public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 1000000; ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue(); double time1 = testStack(arrayQueue,opCount); System.out.println("ArrayStack - time1: " + time1); LinkedListQueue<Integer> linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue(); double time2 = testStack(linkedListQueue,opCount); System.out.println("LinkedListStack - time2: " + time2); LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue(); double time3 = testStack(loopQueue,opCount); System.out.println("LoopQueue - time3: " + time3); } }
//测试结果 ArrayQueue - time1: 368.014648575 LinkedListQueue - time2: 0.395344446 LoopQueue - time3: 0.045756219
//对于增删操作,数组(O(n))的时间复杂度高于链表队列和循环队列,所以数组最慢。
//链表和队列。队列增删只在队首和队尾,时间复杂度低于链表,所以循环队列要高于链表队列。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号