P7745 [COCI2011-2012#3] ROBOT
Description
在一个平面直角坐标系中,有一个点 bot,现有四个指令,分别可以让 bot 向上、下、左、右四个方向中的一个移动一格。同时还有 \(n\) 个固定点,求每次移动后这些点到 bot 的哈曼顿距离之和。
两个点 \((x1, y1)\) 和 \((x2, y2\) 的曼哈顿距离为 \(|x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|\)。
Solution
40 pts
每次移动后暴力求出每个点的哈曼顿距离,相加输出即可。
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 100005
#define int long long
using namespace std;
namespace xycyx {
int n, m;
int hmd[N];
int X[N], Y[N];
char c;
int botx = 0, boty = 0;
int get_hmd(int X1, int Y1) {
return abs(X1 - botx) + abs(Y1 - boty);
}
void solve() {
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> X[i] >> Y[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> c;
if (c == 'S') boty++;
if (c == 'J') boty--;
if (c == 'I') botx++;
if (c == 'Z') botx--;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans += get_hmd(X[i], Y[i]);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
}
signed main() {
xycyx::solve();
return 0;
} //40pts
100 pts
鉴于数据范围,时间复杂度应为 \(O(m)\),故每次查询的时间复杂度都为 \(O(1)\)。
对于两条坐标轴,每次移动后分别二分求出有多少个点小于当前机器人的位置,多少点大于当前机器人的位置,求出当前移动对答案的贡献。直接更新答案并输出即可。
考虑一下每次移动造成的影响:
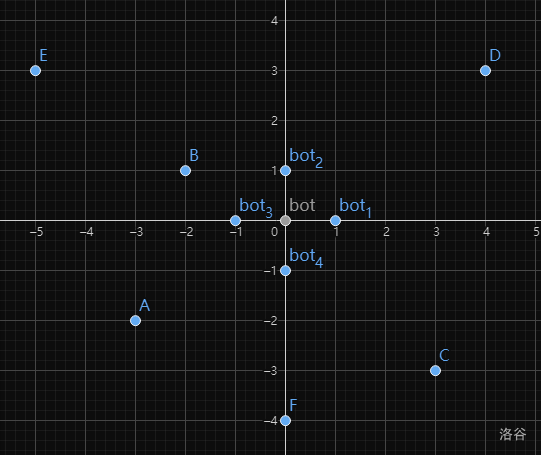
如果执行 S 操作,则意味着 bot 会从 移动到 \((0, 1)\) 的位置,此时明显的,对于 \(y \le y_{bot}\) 的 A、C、F 三点,哈曼顿距离分别加一;而对于 \(y > y_{bot}\) 的 B、D、E 三点而言,哈曼顿距离分别减一。即 \(y_i \le y_{bot}\) 的点在 S 操作时哈曼顿距离会增加,而 \(y_i > y_{bot}\) 的点在 S 操作时哈曼顿距离会减小。此时,答案的更新操作应为:减去移动前 \(y \le y_{bot}\) 的点的数量,加上当前 \(y \le y_{bot}\) 的点的数量。
对于剩余的三种操作同理。
可以使用 upper_bound 和 lower_bound。
code
注意先排序后再二分查找。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 100000
#define M 300000
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
namespace cyxyc {
int n, m;
int X1, Y1, X2, Y2, X = 0, Y = 0;
ll ans = 0;
int x[N + 5], y[N + 5];
char c[M + 5];
int get_hmd(int x, int y) {
return abs(x) + abs(y);
}
void solve() {
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
ans += get_hmd(x[i], y[i]);
}
cin >> c + 1;
sort(x + 1, x + n + 1), sort(y + 1, y + n + 1); //upper_bound 和 lower_bound 都是二分查找
X1 = upper_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, X) - (x + 1); //第一个大于当前位置的点的下标
X2 = lower_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, X) - (x + 1); //第一个大于等于当前位置的点的下标
Y1 = upper_bound(y + 1, y + n + 1, Y) - (y + 1);
Y2 = lower_bound(y + 1, y + n + 1, Y) - (y + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (c[i] == 'S') {
ans += 2 * Y1 - n; //ans = ans - (n - Y1) + Y1
Y++;
Y1 = upper_bound(y + 1, y + n + 1, Y) - (y + 1);
Y2 = lower_bound(y + 1, y + n + 1, Y) - (y + 1);
}
if (c[i] == 'J') {
ans += n - 2 * Y2;
Y--;
Y1 = upper_bound(y + 1, y + n + 1, Y) - (y + 1);
Y2 = lower_bound(y + 1, y + n + 1, Y) - (y + 1);
}
if (c[i] == 'I') {
ans += 2 * X1 - n;
X++;
X1 = upper_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, X) - (x + 1);
X2 = lower_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, X) - (x + 1);
}
if (c[i] == 'Z') {
ans += n - 2 * X2;
X--;
X1 = upper_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, X) - (x + 1);
X2 = lower_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, X) - (x + 1);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
}
}
int main() {
cyxyc::solve();
return 0;
}
Blog by cloud_eve is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号