【macOS】xattr命令简介
✨扩展文件属性
扩展文件属性是文件系统功能,使用户能够将计算机文件与文件系统不解释的元数据相关联,而常规属性具有由文件系统严格定义的目的(例如权限或创建和修改时间的记录)。与通常可以与最大文件大小一样大的forks不同,扩展属性的大小通常被限制为明显小于最大文件大小的值。典型用途包括存储文档的作者、纯文本文档的字符编码或校验和、加密哈希或数字证书和自主访问控制信息。
在类 Unix系统中,扩展属性通常缩写为xattr。
Mac OS X 10.4及更高版本通过使用HFS+文件系统属性文件B* 树功能支持扩展属性,该功能允许命名分叉。尽管 HFS+ 中的命名分叉通过扩展区支持任意大量数据,但操作系统对扩展属性的支持仅支持内联属性,将它们的大小限制在单个 B* 树节点中可以容纳的大小。[需要引用]任何常规文件都可能有一个扩展属性列表。HFS+ 支持任意数量的命名分叉,不知道macOS是否对扩展属性的数量施加任何限制。
每个属性都包含名称和相关数据。该名称是一个以 null 结尾的 Unicode字符串。不存在名称空间限制(使其成为一个开放的 xattr系统),并且约定是使用反向 DNS 字符串(类似于Uniform Type Identifiers)作为属性名称。
macOS 支持使用类似 Linux 的 API 从文件或目录中列出、 获取、设置、和删除扩展属性。在命令行中,这些能力通过xattr实用程序公开。
从 macOS 10.5 开始,来自网络的文件被标记为com.apple.quarantinevia 扩展文件属性。在某些旧版本的 macOS(例如Mac OS X 10.6)中,用户空间扩展属性不会在保存在常见的Cocoa应用程序(TextEdit、Preview 等)中时保留。
✨xattr命令简介
✨命令手册
macOS使用xattr命令来管理扩展文件属性
使用man xattr即可查看xattr命令手册
Last login: Fri Feb 24 21:19:49 on ttys000
➜ ~ xattr /Applications/iTerm.app
com.apple.quarantine
➜ ~ xattr -l /Applications/iTerm.app
com.apple.quarantine: 01c1;63f0c653;Homebrew\x20Cask;0D2B9537-08B4-4AC7-ABD1-8D6E3BFA078C
➜ ~ clear
XATTR(1) General Commands Manual XATTR(1)
NAME
xattr – display and manipulate extended attributes
SYNOPSIS
xattr [-lrsvx] file ...
xattr -p [-lrsvx] attr_name file ...
xattr -w [-rsx] attr_name attr_value file ...
xattr -d [-rsv] attr_name file ...
xattr -c [-rsv] file ...
xattr -h | --help
DESCRIPTION
The xattr command can be used to display, modify or remove the extended
attributes of one or more files, including directories and symbolic links.
Extended attributes are arbitrary metadata stored with a file, but separate
from the filesystem attributes (such as modification time or file size).
The metadata is often a null-terminated UTF-8 string, but can also be
arbitrary binary data.
One or more files may be specified on the command line. For the first two
forms of the command, when there are more than one file, the file name is
displayed along with the actual results. When only one file is specified,
the display of the file name is usually suppressed (unless the -v option
described below, is also specified).
In the first form of the command (without any other mode option specified),
the names of all extended attributes are listed. Attribute names can also
be displayed using “ls -l@”.
In the second form, using the -p option (“print”), the value associated
with the given attribute name is displayed. Attribute values are usually
displayed as strings. However, if nils are detected in the data, the value
is displayed in a hexadecimal representation.
The third form, with the -w option (“write”), causes the given attribute
name to be assigned the given value.
The fourth form, with the -d option (“delete”), causes the given attribute
name (and associated value), to be removed.
In the fifth form, with the -c option (“clear”), causes all attributes
(including their associated values), to be removed.
Finally, the last form, with either the -h or --help option, displays a
short help message and exits immediately.
OPTIONS
-l By default, the first two command forms either displays just the
attribute names or values, respectively. The -l option causes both the
attribute names and corresponding values to be displayed. For
hexadecimal display of values, the output is preceeded with the
hexadecimal offset values and followed by ASCII display, enclosed by
“|”.
-r If a file argument is a directory, act as if the entire contents of the
directory recursively were also specified (so that every file in the
directory tree is acted upon).
-s If a file argument is a symbolic link, act on the symbolic link itself,
rather than the file that the symbolic link points at.
-v Force the file name to be displayed, even for a single file.
-x Force the attribute value to be displayed in the hexadecimal
representation.
The -w option normally assumes the input attribute value is a string.
Specifying the -x option causes xattr to expect the input in
hexadecimal (whitespace is ignored). The xxd(1) command can be used to
create hexadecimal representations from exising binary data, to pass to
xattr.
EXIT STATUS
The xattr command exits with zero status on success. On error, non-zero is
returned, and an error message is printed to the standard error. For
system call errors, both the error code and error string are printed (see
getxattr(2), listxattr(2), removexattr(2) and setxattr(2) for a complete
list of possible error codes).
Some attribute data may have a fixed length that is enforced by the system.
For example,
% xattr -w com.apple.FinderInfo 0 foo
xattr: [Errno 34] Result too large: 'foo'
The com.apple.FinderInfo attribute must be 32 bytes in length.
EXAMPLES
This example copies the com.apple.FinderInfo attribute from the /usr
directory to the MyDir directory:
% xattr -px com.apple.FinderInfo /usr
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
% xattr -l MyDir
% xattr -wx com.apple.FinderInfo \
"`xattr -px com.apple.FinderInfo /usr`" MyDir
% xattr -l MyDir
com.apple.FinderInfo:
00000000 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |........@
.......|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.........
.......|
00000020
SEE ALSO
ls(1), xxd(1), getxattr(2), listxattr(2), removexattr(2), setxattr(2)
macOS 12.6 November 29, 2010 macOS 12.6
(END)
✨命令行选项
-
-l 默认情况下,前两个命令形式要么只显示属性名称或值,分别。 -l 选项会同时导致要显示的属性名称和相应的值。
-
-r 如果文件参数是目录,就好像目录的全部内容一样还指定了递归目录(以便目录中的每个文件目录树被执行)。
-
-s 如果文件参数是符号链接,则对符号链接本身进行操作,而不是符号链接指向的文件。
-
-v 强制显示文件名,即使是单个文件。
-
-x 强制属性值以十六进制显示表示。
-
-w 选项通常假定输入属性值是一个字符串。
✨常用xattr命令
显示扩展文件属性
xattr ${file}
显示所有扩展文件属性
xattr -l ${file}
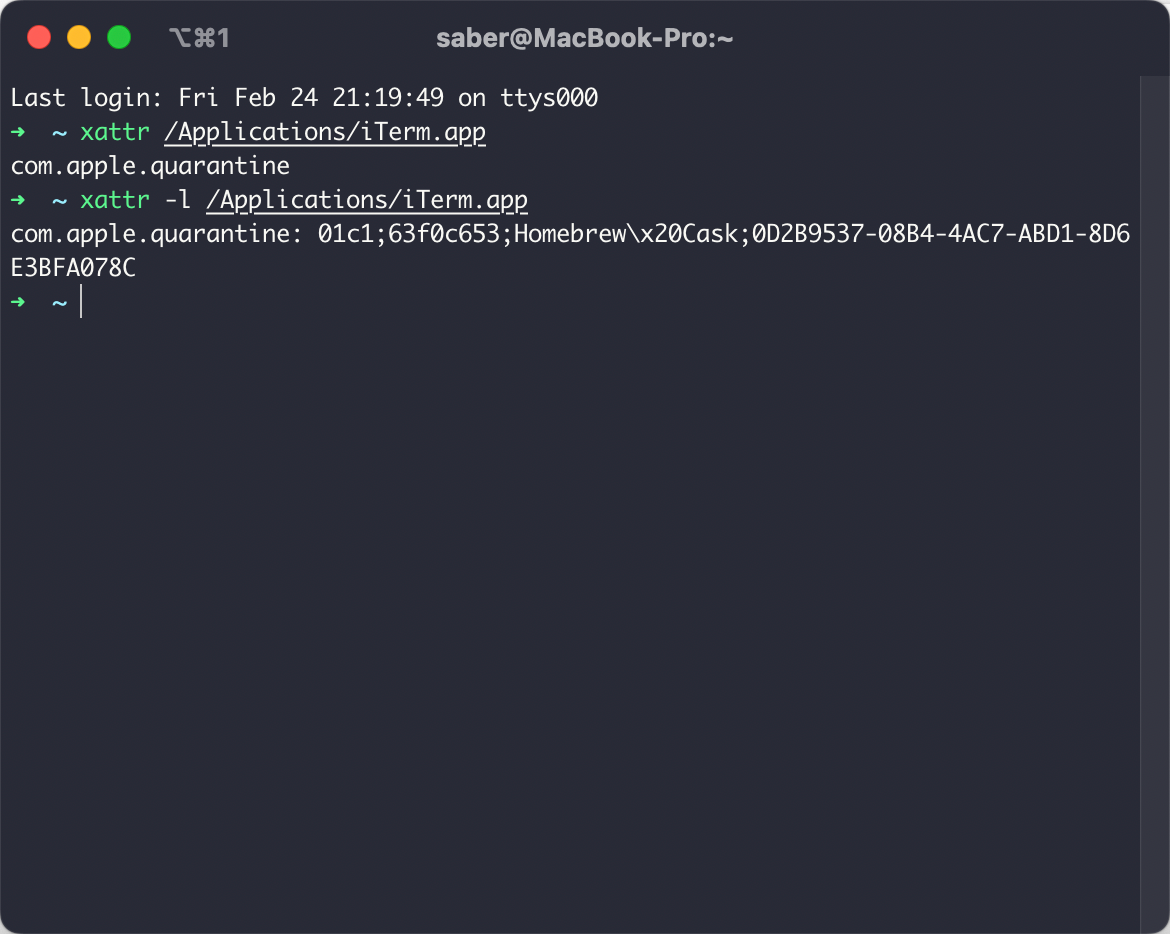
其中com.apple.quarantine为隔离扩展属性
可以使用xattr -p com.apple.quarantine ${file}来查看隔离扩展属性具体信息
删除隔离扩展属性
sudo xattr -r -d com.apple.quarantine ${file}
如上命令可以用来解决某些应用程序出现提示无法打开时的情况:
无法打开“xxx”,因为无法验证开发者。
macos无法验证此 App 是否包含恶意软件。
✨参考及引用
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_file_attributes
⭐转载请注明出处
本文作者:双份浓缩馥芮白
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Flat-White/p/17040381.html
版权所有,如需转载请注明出处。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号