[MIT 6.S081] Lab: file system
Lab: file system
在这个实现中我们将为 xv6 的文件系统实现二级间接块以支持大文件,与实现文件的软链接。
Large files
在该任务中,我们将为 xv6 的文件系统实现二级间接块,以支持大文件。对于这个功能,我们需要修改 struct inode 中 addr 字段的功能。
在实现功能之前,xv6 的 struct inode 已经预先实现了一级间接块功能了。对于 addr 的前 12 个地址,可以直接指向一个具体的数据,这些数据块被叫作直接块。而对于 addr 的最后一个地址,则指向了一个间接块,这个间接块存放着的,是一个个指向数据块的地址,这样实现了文件的基本存储。经过计算可以知道,目前 xv6 的实现使得一个文件最大只能有
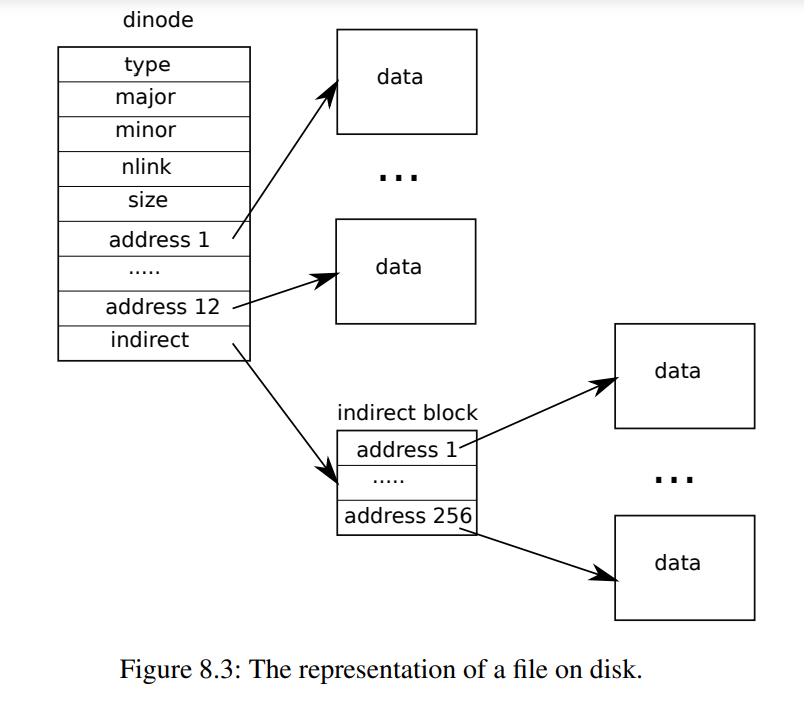
我们的目标就是:以一个直接块的代价,换来一个二级间接块。这样实现后,一个文件最大即可为
首先,我们需要修改一下定义,将原来的 addr 字段的大小,因此还需将其增加一下。由于构建文件涉及到这个宏,因此我们必须修改这个宏的数字大小才可以构建出一个符合的文件系统,否则会报错。
// kernel/fs.h #define NDIRECT 11 #define NINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint)) #define MAXFILE (NDIRECT + NINDIRECT + NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT) struct dinode { short type; // File type short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only) short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only) short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system uint size; // Size of file (bytes) uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // Data block addresses }; // kernel/file.h struct inode { uint dev; // Device number uint inum; // Inode number int ref; // Reference count struct sleeplock lock; // protects everything below here int valid; // inode has been read from disk? short type; // copy of disk inode short major; short minor; short nlink; uint size; uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; };
现在,我们更改一下 bmap 的实现。因为现在增加了一个二级块,那么只需要检查是否需要的数据块位置在这个二级块内就好了,然后就是延迟分配的问题,等到需要被访问到的时候,才分配一块数据块。要注意的是,第一层数据块存放地址,第二层依然存放地址(其实就是重复一次),访问到第三个块的时候才是文件的数据块。
// kernel/fs.c static uint bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn) { ... bn -= NINDIRECT; if (bn < NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT) { if ((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) == 0) { ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = addr = balloc(ip->dev); } bp = bread(ip->dev, addr); a = (uint*)bp->data; uint idx1 = bn / NINDIRECT; if ((addr = a[idx1]) == 0) { a[idx1] = addr = balloc(ip->dev); log_write(bp); } brelse(bp); uint idx2 = bn % NINDIRECT; bp = bread(ip->dev, addr); a = (uint*)bp->data; if ((addr = a[idx2]) == 0) { a[idx2] = addr = balloc(ip->dev); log_write(bp); } brelse(bp); return addr; } panic("bmap: out of range"); }
最后是对这个二级块实现增加一个回收机制,也就是一个二重循环,先将最里面的释放后,才将次层释放。
void itrunc(struct inode *ip) { if (ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) { bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]); a = (uint*)bp->data; for (int j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j ++) { if (a[j]) { struct buf *bp2 = bread(ip->dev, a[j]); uint *ad = (uint*)bp2->data; for (int k = 0; k < NINDIRECT; k ++) { if (ad[k]) bfree(ip->dev, ad[k]); } brelse(bp2); bfree(ip->dev, a[j]); } } brelse(bp); bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]); ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = 0; } ip->size = 0; iupdate(ip); }
Symbolic links
现在我们要增加一个软链接功能,类似于 ln 命令,多个位置的文件都指向一个实际的文件,但在这个当中不能出现链接层数过多或者循环链接的问题。
首先我们依然是要为其添加一下系统调用,就像之前的系统调用添加一样的操作,然后按照实验要求将两个类型定义的宏加上。在读取好 sys_symlink 的参数之后,我们要先为这个链接存放的地址创建一个 inode ,让它作为一个链接文件类型,接着向这个 inode 写入要链接的目标地址。
// kernel/sysfile.c uint64 sys_symlink(void) { char target[MAXPATH], path[MAXPATH]; if (argstr(0, target, sizeof(target)) < 0 || argstr(1, path, sizeof(path)) < 0) { return -1; } begin_op(); struct inode *i_target = create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0); if (i_target == 0) { end_op(); return -1; } if (writei(i_target, 0, (uint64)target, 0, sizeof(target)) < sizeof(target)) { end_op(); return -1; } iunlockput(i_target); end_op(); return 0; }
接着是处理 sys_open 在打开链接文件时候的问题。当打开的文件是一个链接类型的文件时,我们需要找到其真正的文件。但在这里要注意一下,实验要求链接层数不能过多,提供了一个 LINK_LIMIT 宏,作为链接层数的限制。剩下问题就是判断一下这个文件是不是链接文件,是链接文件的话再看看现在的打开模式是不是限制了不能跟踪,如果能跟踪的话,我们再通过迭代尝试找到目标文件,如果找到了就直接退出迭代,出错误了直接
uint64 sys_open(void) { ... if(ip->type == T_DEVICE && (ip->major < 0 || ip->major >= NDEV)){ iunlockput(ip); end_op(); return -1; } if(ip->type == T_SYMLINK && !(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)) { int loop; for (loop = 0; loop < LINK_LIMIT; loop ++) { if (readi(ip, 0, (uint64)path, 0, sizeof(path)) != sizeof(path)) { iunlockput(ip); end_op(); return -1; } iunlockput(ip); if ((ip = namei(path)) == 0) { end_op(); return -1; } ilock(ip); if (ip->type != T_SYMLINK) { break; } } if (loop == LINK_LIMIT) { iunlockput(ip); end_op(); return -1; } } if((f = filealloc()) == 0 || (fd = fdalloc(f)) < 0){ ... }
本文作者:フランドール·スカーレット
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FlandreScarlet/p/18024005
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步