[MIT 6.S081] Lab: traps
Lab: traps
RISC-V assembly
在这个任务中我们需要观察 call.asm 汇编。
int g(int x) { 0: 1141 addi sp,sp,-16 2: e422 sd s0,8(sp) 4: 0800 addi s0,sp,16 return x+3; } 6: 250d addiw a0,a0,3 8: 6422 ld s0,8(sp) a: 0141 addi sp,sp,16 c: 8082 ret 000000000000000e <f>: int f(int x) { e: 1141 addi sp,sp,-16 10: e422 sd s0,8(sp) 12: 0800 addi s0,sp,16 return g(x); } 14: 250d addiw a0,a0,3 16: 6422 ld s0,8(sp) 18: 0141 addi sp,sp,16 1a: 8082 ret 000000000000001c <main>: void main(void) { 1c: 1141 addi sp,sp,-16 1e: e406 sd ra,8(sp) 20: e022 sd s0,0(sp) 22: 0800 addi s0,sp,16 printf("%d %d\n", f(8)+1, 13); 24: 4635 li a2,13 26: 45b1 li a1,12 28: 00000517 auipc a0,0x0 2c: 7b050513 addi a0,a0,1968 # 7d8 <malloc+0xea> 30: 00000097 auipc ra,0x0 34: 600080e7 jalr 1536(ra) # 630 <printf> exit(0); 38: 4501 li a0,0 3a: 00000097 auipc ra,0x0 3e: 27e080e7 jalr 638(ra) # 2b8 <exit>
Which registers contain arguments to functions? For example, which register holds 13 in main's call to printf?
哪些寄存器包含函数的参数?例如,在 main 对 printf 的调用时,哪个寄存器保存了13?
哪个寄存器保存了 13 ,只需要看一下执行 printf 调用中过程的汇编指令即可。由 24: 4635 li a2,13 可知,13 保存在 a2 寄存器中。
Where is the call to function f in the assembly code for main? Where is the call to g? (Hint: the compiler may inline functions.)
在main中哪里调用了f?对于g呢?
提示已经说的很清楚了,需要注意的是存在内联优化的部分(老实说对于 f 的调优化,更像是 constexpr),观察 main 中对 printf 的调用,可以看到,对于 f 的调用直接优化成了一条语句 li a2, 13 ,在 f 中将对 g 的调用直接优化为一条执行语句了。
At what address is the function printf located?
printf的地址位于哪里?
直接使用编辑器搜 <printf>: ,就可以直接看到地址了,位于 0x630 ,或者要用 gdb 看也可以。
What value is in the register ra just after the jalr to printf in main?
main中jalr到printf之后,寄存器ra中的值是什么?
观察一下两句语句:
30: 00000097 auipc ra,0x0 34: 600080e7 jalr 1536(ra) # 630 <printf>
指令 auipc rd, imm 的作用是 rd = pc + (imm << 12) ,对于 imm << 12 ,左移的位置将会补 0 。对于此处来说,pc = 0x30 ,因此 ra = pc + (0x0 << 12) , 即此处 ra = 0x30 。
指令 jalr 会将接下来要执行的语句地址压入指定的寄存器中,然后跳转到指定的偏移地址,这里也就是将 pc+4 压入 ra 中,即 ra = pc + 4 = 0x34 + 4 = 0x38 。
Run the following code.
unsigned int i = 0x00646c72;
printf("H%x Wo%s", 57616, &i);What is the output? Here's an ASCII table that maps bytes to characters.
The output depends on that fact that the RISC-V is little-endian. If the RISC-V were instead big-endian what would you set i to in order to yield the same output? Would you need to change 57616 to a different value?
运行以下代码,它会输出什么?
如果 RISC-V 不是小端而是大端,那i要怎么样才可以保持输出一致?
57616 的十六进制就是 0xe110 ,也就是这里会输出 E110 。
这里其实就是将 i 作为一个 char 数组输出了,由于小端,按照地址增长的方向读取 i 会得到 72 6c 64 00 ,也就是 rld\0 。如果是大端形式,那么按照地址增长方向,i 的高位字节会被先读,因此要反过来,为 0x726c6400 。
In the following code, what is going to be printed after 'y='? (note: the answer is not a specific value.) Why does this happen?
printf("x=%d y=%d", 3);
在这段代码中,
y会输出什么?为什么会发生这种情况?
这里按照函数参数寄存器来说,"x=%d y=%d" 的指针位于 a0 中,自然 3 位于 a1 中,那么 y 应该是来自于 a2 ,既然没有传递给 a2 ,那么意味着之前调用某个函数时候 a2 中留下来的值将会直接被读取,或者说读了个 a2 寄存器中的脏数据。
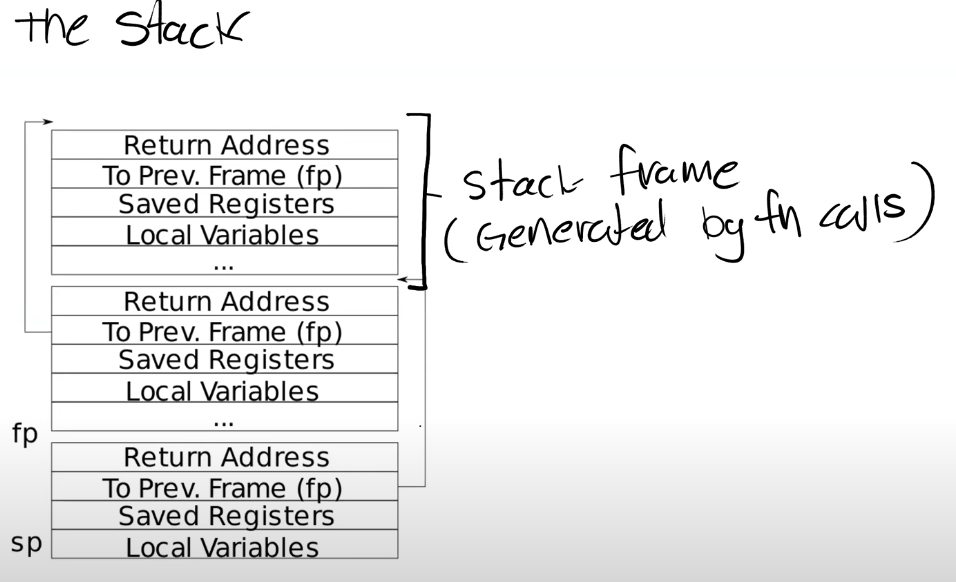
Backtrace
在这个任务中要实现的是:打印函数调用栈内的内容。根据 xv6 中栈的形式,不断循环地址,直到结束即可。
在 xv6 中,内核为每个栈按照内存对齐的格式分配了一个页面,所以只需要判断遍历的时候这个指针是否依然还在一个页面内即可。
接下来就是这个栈的格式,其增长方向是从高地址到低地址的,每一次函数调用,都会产生一个 stack frame ,即栈帧,我们所要做的,就是知道栈顶栈帧的位置,然后通过其中的 fp 遍历,并输出其中的 return address 。对于栈顶栈帧的位置,可以使用所提供的函数 r_fp() 获取到,然后按照地址偏移,返回地址就 -8 ,下一个 fp 就 -16 ,直到遍历到页面结束为止。

void backtrace(void) { printf("backtrace:\n"); uint64 fp = r_fp(); while (PGROUNDUP(fp) - PGROUNDDOWN(fp) == PGSIZE) { uint64 ret_addr = fp - 8; uint64 nex_fp_addr = fp - 16; printf("%p\n", *(pte_t*)ret_addr); fp = *(pte_t*)nex_fp_addr; } }
Alarm
在这个子任务中,所要实现的是一个定时的警报功能,当达到一定时间时,将调用用户指定的函数。
我们需要看一下在 xv6 中一个系统调用大致是什么流程。
- 在用户态下,执行
ecall指令来切换模式,并将pc的值保存在sepc寄存器中,然后再跳转到stvec寄存器指向的指令; - 我们要保证之后回到用户模式的时候,依然是原先的环境,那么就先把 32 个用户寄存器的内容保存在
trapframe page中; - 现在将调用
usertrap,然后将sepc + 4保存在p->trapframe中(这个trapframe也是上面寄存器保存的位置),当恢复到用户模式时将执行下一条语句,而不是继续执行ecall; - 通过
syscall()函数分发到具体的syscall函数中; - 等待系统调用执行完毕后,将执行
usertrapret; - 最后执行
userret,将之前备份的寄存器重新赋值回去,并使用sret返回和切换模式。
我们目前添加的新系统调用涉及到这个过程,需要按照这个过程去构建整个功能。
test0: invoke handler
test0 只需要按部就班实现即可。
首先是添加系统调用的流程,添加 Makefile ,把两个系统调用的函数声明添加到 user/user.h 中,然后修改 user/user.S, 让它能够生成调用系统调用的入口代码。接着转到 kernel 部分,在 kernel/sycall.h 中添加两个系统调用的编号,在 kernel/syscall.c 中让 syscall() 函数能够调用到指定的函数,在 kernel/sysproc.c 中定义以下两个系统调用。
uint64 sys_sigalarm(void) { } uint64 sys_sigreturn(void) { return 0; }
接着我们需要去实现计时的功能,在 kernel/proc.h 中添加这几个成员,作用分别是:记录已经过了几个时钟周期,一次报警所需要的时钟周期,报警所调用的函数指针。
struct proc { ... uint64 alarm_pass_ticks; uint64 alarm_ticks_period; void (*alarm_handler_fn)(); };
接着还是构造和析构的问题,不过这三个并不涉及资源分配,只需要初始化时候清为 0 ,析构的时候也是即可。
static struct proc* allocproc(void) { ... p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; p->alarm_ticks_period = 0; p->alarm_handler_fn = 0; return p; } static void freeproc(struct proc *p) { ... p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; p->alarm_ticks_period = 0; p->alarm_handler_fn = 0; }
这只是构造和析构的问题,我们需要看一下怎样去传递所需要的参数,回到 sys_sigalarm 函数,我们将两个参数传递给两个指定的成员。
uint64 sys_sigalarm(void) { int ticks; uint64 fn_addr; if (argint(0, &ticks) < 0 || argaddr(1, &fn_addr) < 0) return -1; struct proc* cur_proc = myproc(); cur_proc->alarm_ticks_period = ticks; cur_proc->alarm_handler_fn = (void(*)())fn_addr; return 0; }
然后去 kernel/trap.c 中的 usertrap 函数,看向判断时钟中断的位置,即 which_dev == 2 这个地方,我们要在这边处理一下这个如何记时。按照手册提示,每个时钟周期,cpu 都会产生一次时钟中断,将控制权转交给内核,因此在这里,我们只需要判断一下目前是否需要产生警报,需要的话就开始累计 +1 即可。
当达到指定的周期数时,我们就需要在返回用户模式的时候执行的是指定的代码,因此将 trapframe->epc 赋值为指定的地址,这样返回时拷贝后,sret 将 sepc 内的内容给 pc ,执行的代码就是它了。
void usertrap(void) { ... if (which_dev == 2) { if (p->alarm_ticks_period != 0) { p->alarm_pass_ticks ++; if (p->alarm_pass_ticks == p->alarm_ticks_period) { p->trapframe->epc = (uint64)p->alarm_handler_fn; p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; } } yield(); } usertrapret(); }
test1/test2(): resume interrupted code
如果注意到的话,在 test0 中其实有一个问题:一旦开始报警,那么是不是没办法返回到原先的环境呢?这个子任务就是要解决这问题的。
首先,我们需要再一次保存寄存器,第一次保存寄存器是为了在内核模式下执行 c 代码而不会将原本的用户模式环境更改,这一次保存寄存器则是要让在之前调用 alarm 的函数环境能得到保留,使得之后返回时候和之前环境一样。因此,我们还需在 struct proc 中添加两个成员,is_alarmed 代表是否已经在警报模式中,alarm_trapframe 则是保存调用 alarm 时候的 trapframe 。
struct proc { int is_alarmed; uint64 alarm_pass_ticks; uint64 alarm_ticks_period; void (*alarm_handler_fn)(); struct trapframe *alarm_trapframe; };
接着还是构造和析构的问题,is_alarmed 直接初始化为 0 即可,alarm_trapframe 像保存模式切换下的 trapframe 一样给一段内存即可。
static struct proc* allocproc(void) { ... if ((p->alarm_trapframe = (struct trapframe*)kalloc()) == 0) { release(&p->lock); return 0; } p->is_alarmed = 0; p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; p->alarm_ticks_period = 0; p->alarm_handler_fn = 0; return p; } static void freeproc(void) { ... if (p->alarm_trapframe) kfree((void *)p->alarm_trapframe); p->is_alarmed = 0; p->alarm_trapframe = 0; p->alarm_handler_fn = 0; p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; ... }
然后因为我们要在被调用的时候就保存 trampframe ,当然是在刚刚的 which_dev == 2 那边,因为那边涉及到寄存器的状态更改了。我们需要在 sepc 更改之前将其保存一下。
void usertrap(void) { ... if(which_dev == 2) { if (p->alarm_ticks_period != 0) { p->alarm_pass_ticks ++; // jump to handler_fn if (!p->is_alarmed && p->alarm_pass_ticks == p->alarm_ticks_period) { p->is_alarmed = 1; p->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; *p->alarm_trapframe = *p->trapframe; p->trapframe->epc = (uint64)p->alarm_handler_fn; } } yield(); } usertrapret(); }
最后,在 sys_sigreturn 中,我们要将代码执行的环境重新回归到之前的函数,也就是直接把这个 alarm_handler_fn 给 trapframe 就好了。
uint64 sys_sigreturn(void) { struct proc* cur_proc = myproc(); if (cur_proc->is_alarmed) { cur_proc->is_alarmed = 0; *cur_proc->trapframe = *cur_proc->alarm_trapframe; cur_proc->alarm_pass_ticks = 0; } return 0; }
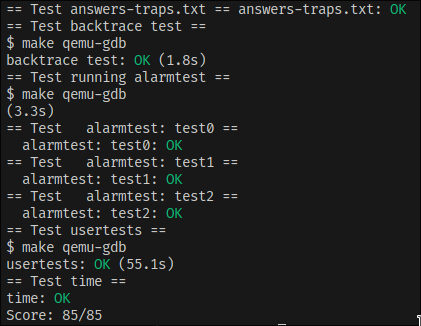
Grade
本文作者:フランドール·スカーレット
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FlandreScarlet/p/17997930
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步