Keras 之 多层感知机(MLP)
这里以 mnist 数据集为例,代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
# 设置GPU使用方式
# 获取GPU列表
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices('GPU')
if gpus:
try:
for gpu in gpus:
# 设置GPU为增长式占用
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
except RuntimeError as e:
# 打印异常
print(e)
# 导入数据
(x_train, y_train),(x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
print('datasets:', x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_train.min(), x_train.max())
# 将样本属性转换为张量
x_train = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_train, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
x_val = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_val, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
# 每批次的样本个数
batch_size = 512
# 模型迭代次数
epochs = 100
# 序列模型 Sequential 适用于每层只有一个输入张量和一个输出张量的简单层堆栈
model = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10)])
# input_shape 为输入层的形状参数 None 代表任意批次 28* 28 代表输入参数维度
model.build(input_shape=(None, 28*28))
# 序列模型信息打印
model.summary()
# Keras 中的一种训练方式
x_train = tf.reshape(x_train, (-1, 28*28))
x_val = tf.reshape(x_val, (-1, 28*28))
y_train = tf.one_hot(y_train, depth=10)
y_val = tf.one_hot(y_val, depth=10)
model.compile(
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01),
loss = tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.CategoricalAccuracy()])
history = model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size,epochs,validation_data = (x_val, y_val))
x = [i for i in range(0, epochs)]
plt.figure()
plt.plot(x, history.history["categorical_accuracy"], color='blue', label='vaildation')
plt.plot(x, history.history["val_categorical_accuracy"], color='red', label='training')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.close()
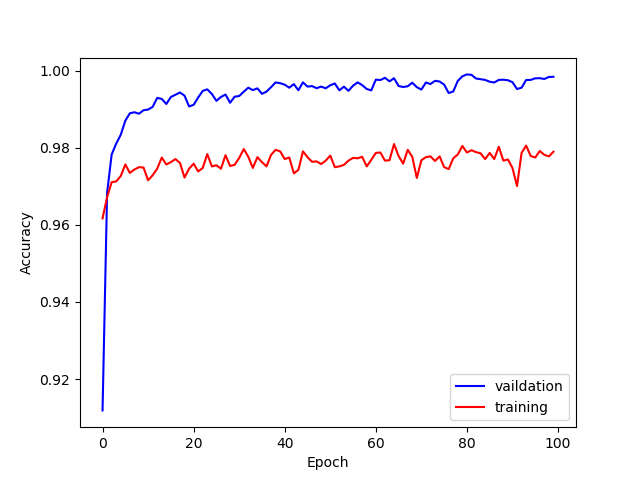
训练曲线如下:
任世事无常,勿忘初心



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号