语义分割评价指标(Dice coefficient, IoU)
语义分割任务常用的评价指标为Dice coefficient和IoU。Dice和IoU都是用来衡量两个集合之间相似性的度量,对于语义分割任务而言即用来评估网络预测的分割结果与人为标注结果之间的相似度。
1 混淆矩阵
混淆矩阵(confusion matrix)是一种特定的矩阵用来呈现算法性能的可视化效果,其每一列代表预测值,每一行代表的是实际的类别。这个名字来源于它可以非常容易的表明多个类别是否有混淆(也就是一个class被预测成另一个class)。下面是二分类的混淆矩阵:
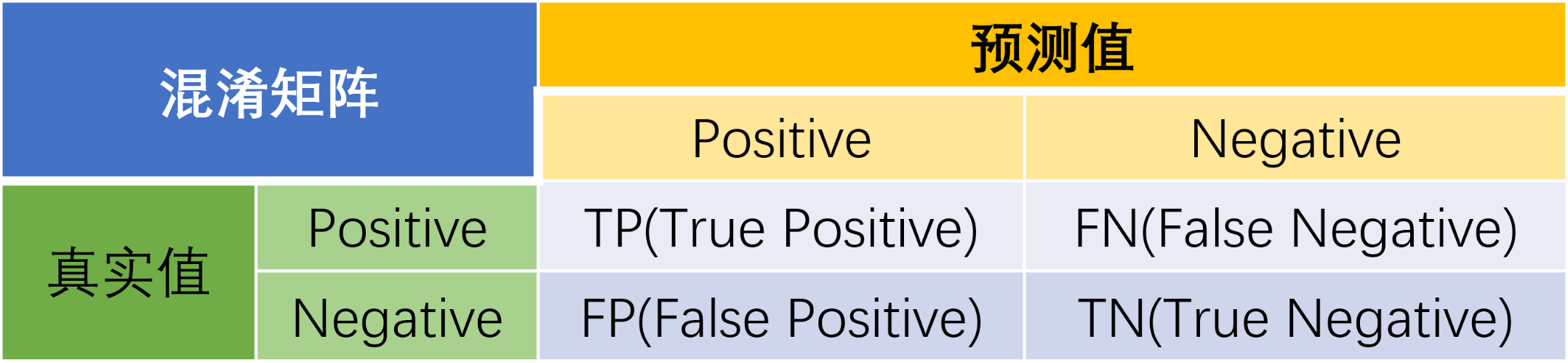
预测值与真实值相同为True,反之则为False。混淆矩阵的对角线是判断正确的,期望TP和TN越大越好,FN和FP越小越好。
-
Accuracy(准确率)
表示预测正确的样本数量占全部样本的百分比,具体表示如下:
![]()
缺点:当数据类别分布不平衡时,不能评价模型的好坏。
-
Precision(查准率)
表示模型预测为正例的所有样本中,预测正确(真实标签为正)样本的占比:
![]()
-
Recall (查全率)
表示所有真实标签为正的样本,有多大百分比被预测出来
![]()
-
F1-score
表示precision和recall的调和平均数,具体公式如下:
![]()
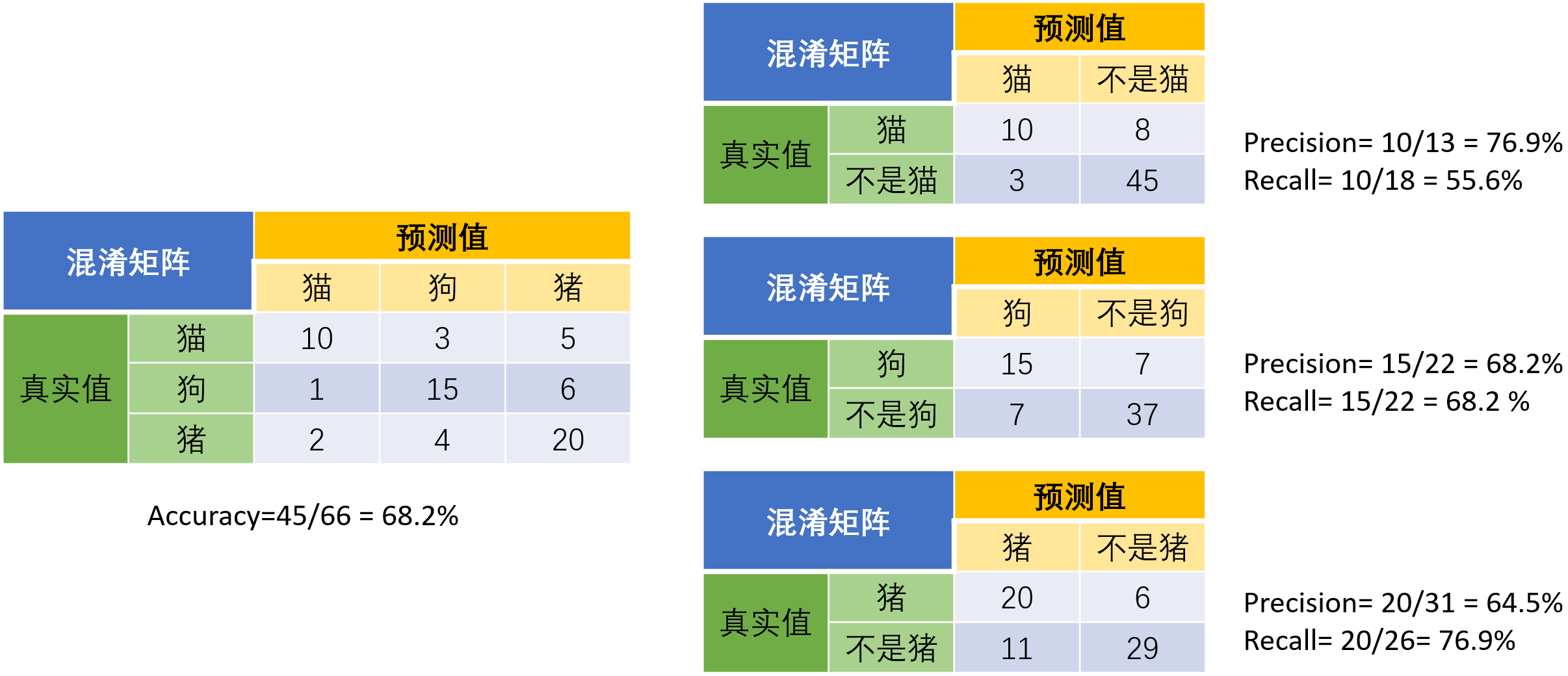
示例 猫狗猪三分类评价指标计算
当分类问题是二分问题时,混淆矩阵可以用上面的方法计算。当分类的结果多于两种的时候,混淆矩阵同时适用。以下面的混淆矩阵为例,我们的模型目的是为了预测样本是什么动物,左边是结果。当分析每个类别时,可以将多分类问题看作是每个类别的二分问题:
2 语义分割的评价指标
语义分割的本质任务是分类任务,常规分类任务的对象是图像中的物体,而语义分割的对象是图像中像素点。
-
Pixel Accuracy(像素准确率)
预测正确的像素值占总像素值的百分比(对应于分类中的准确率)
![]()
-
class Pixel Accuracy(类别像素准确率)
预测正确的像素值占总像素值的百分比(对应于分类中的准确率)
![]()
-
MPA(类别平均像素准确率)
所有类别像素准确率之和的平均。首先求得每个类别的像素准确率,然后对它们求和再平均。
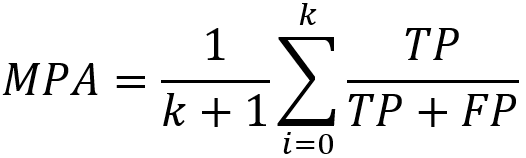
-
IoU(交并比)
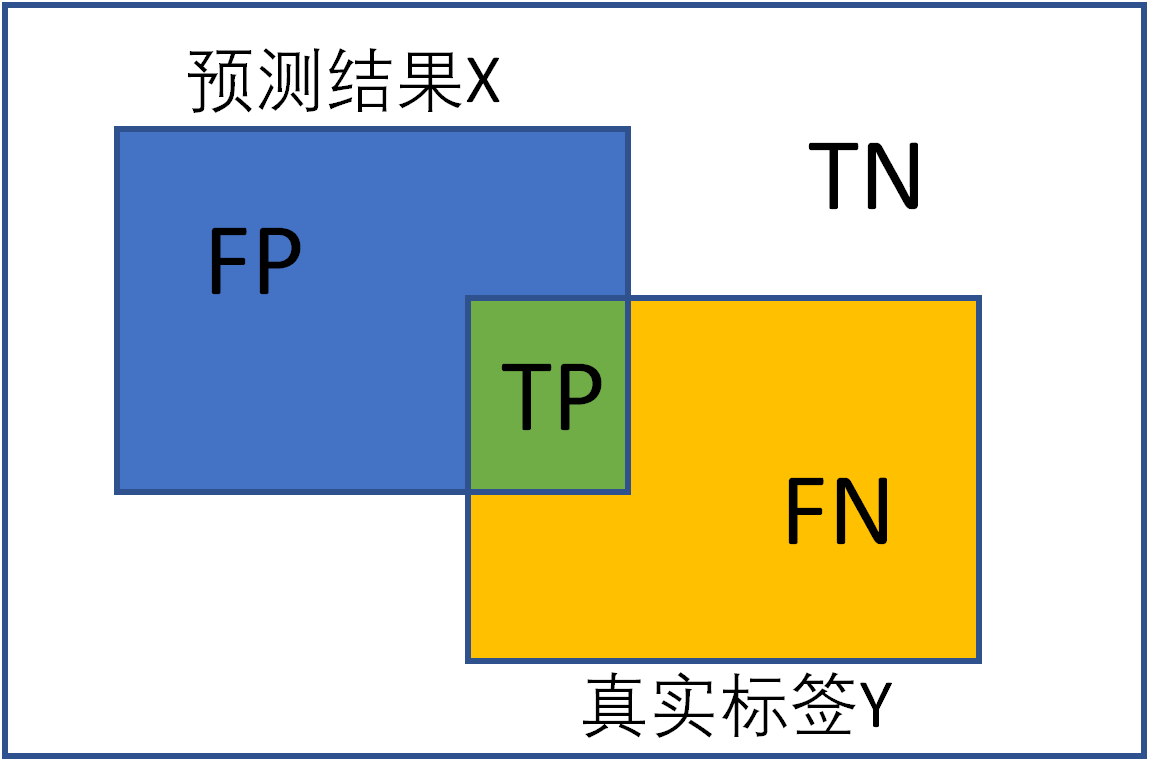
IoU(Intersection-over-Union)即是预测样本和实际样本的交并比,表达式如下:
![]()
-
MIoU(平均交并比)
Mean IoU是在所有类别的IoU上取平均值。

示例 以三分类语义分割为例,使用ConfusionMeter计算混淆矩阵并绘制
假设图片大小为2x2像素,模型输出num_classes=3通道的矩阵,利用torchnet.meter中的ConfusionMeter计算多分类模型的混淆矩阵,acc和iu。
import numpy as np
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torchnet import meter
n_classes = 3 # 分类数
confusion_matrix = meter.ConfusionMeter(3)
score = torch.Tensor([[[[1, 3], [2, 5]], [[2, 2], [3, 7]], [[0, 1], [9, 0]]]]) # torch.Size([1, 3, 2, 2])
target = torch.tensor([[[1, 0], [2, 0]]]) # torch.Size([1, 2, 2])
# 注意2D时,cross_entropy的输入是(N,C,W,H), target是(N,W,H)
loss = torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(score, target) # tensor(0.7366)
# confusion_matrix要求predicted和target维度相同,且num_classes>=predicted,target>=0
predicted = score.argmax(dim=1).reshape(-1) # torch.Size([4])
target = target.reshape(-1) # torch.Size([4])
confusion_matrix.add(predicted, target)
cm_value = confusion_matrix.value()
# 计算全局预测准确率(混淆矩阵的对角线为预测正确的个数)
mpa = np.diag(cm_value).sum() / cm_value.sum()
# 计算每个类别的准确率
cpa = np.diag(cm_value) / cm_value.sum(1)
# 计算每个类别预测与真实目标的iou
iu = np.diag(cm_value) / (cm_value.sum(1) + cm_value.sum(0) - np.diag(cm_value))
# 绘制混淆矩阵
labels = ['cat', 'dog', 'pig'] # 每种类别的标签
# 显示数据
plt.imshow(cm_value, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
# 在图中标注数量/概率信息
thresh = cm_value.max() / 2 # 数值颜色阈值,如果数值超过这个,就颜色加深。
for x in range(n_classes):
for y in range(n_classes):
# 注意这里的matrix[y, x]不是matrix[x, y]
info = int(cm_value[y, x])
plt.text(x, y, info,
verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',
color="white" if info > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout() # 保证图不重叠
plt.yticks(range(n_classes), labels)
plt.xticks(range(n_classes), labels, rotation=45) # X轴字体倾斜45°
plt.show()
plt.close()
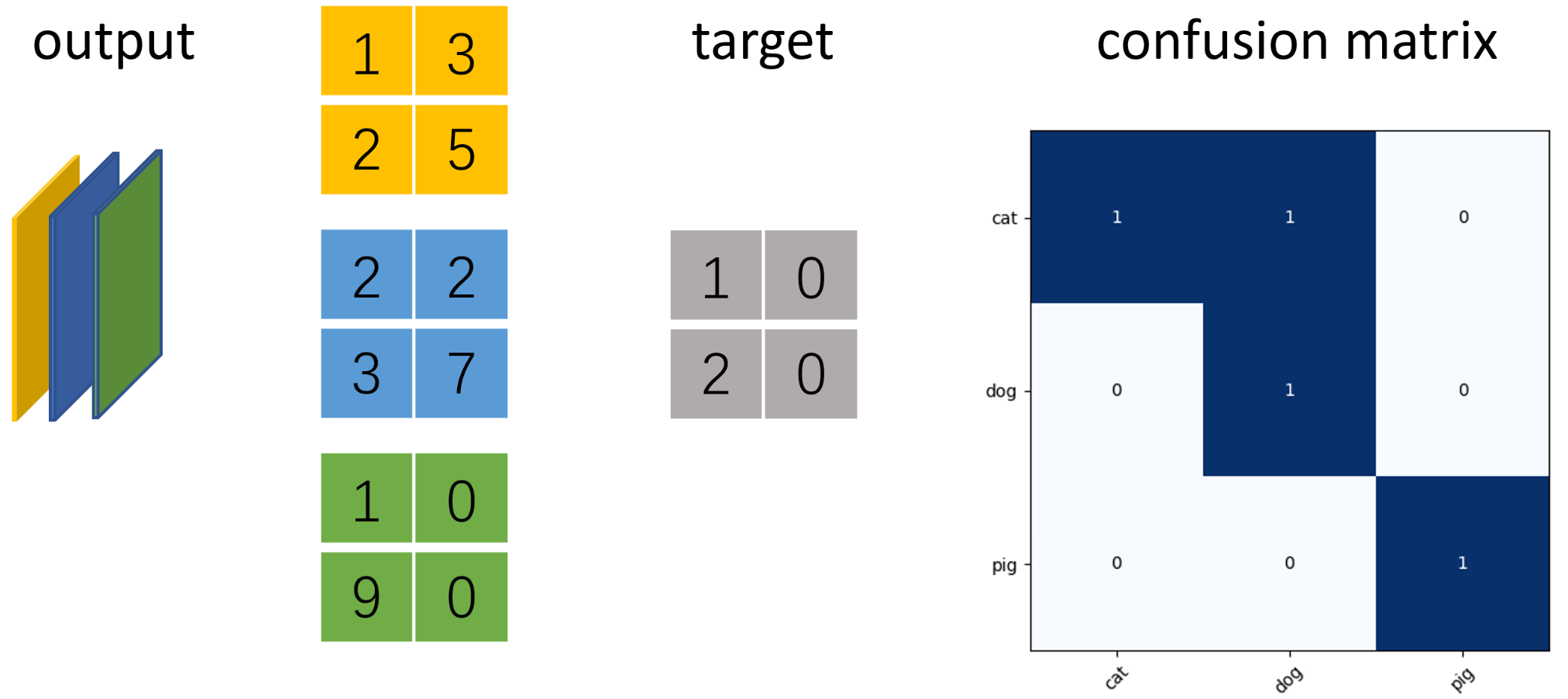
-
Dice Coefficient
Dice coefficient是医学影像分割中最常用的指标,是用于评估两个样本的相似性的度量函数,取值范围在0到1之间,取值越大表示越相似。假设ground true为X,预测结果为Y,dice coefficient定义如下:
![]()
其中|x|和|y|分别表示X和Y的元素的个数,分子乘2为了保证分母重复计算后取值范围在[0,1]之间。可见dice coefficient等同于F1-score。
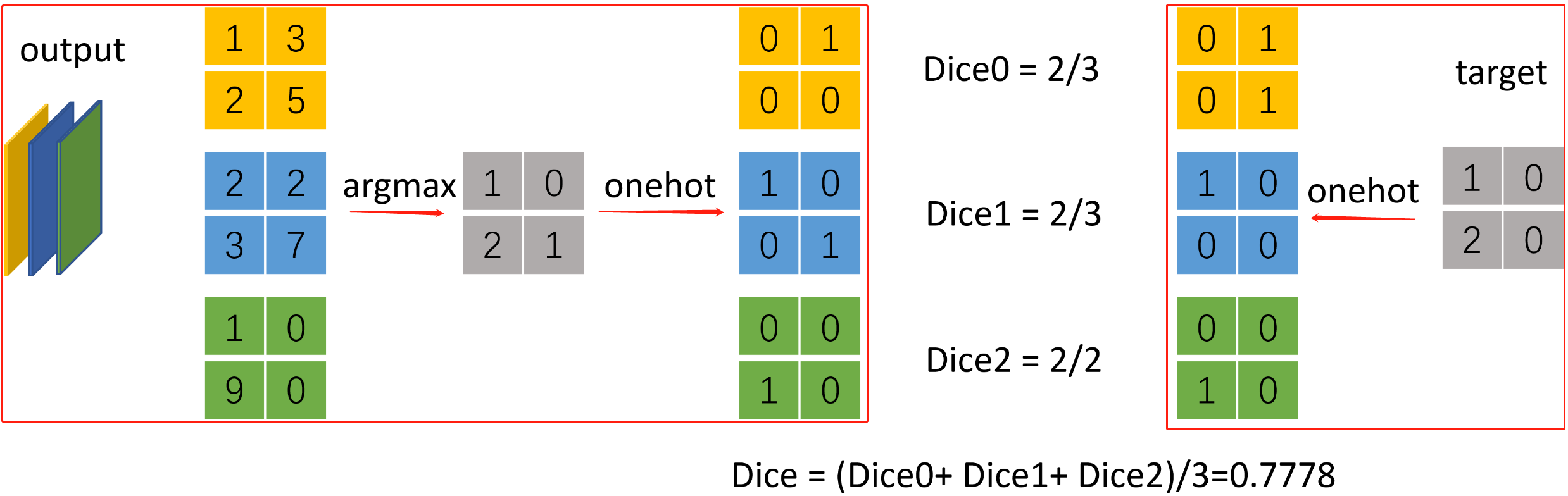
示例 三分类语义分割计算dice
import torch
from torchnet import meter
def dice_coeff(x: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, ignore_index: int = -100, epsilon=1e-6):
# Average of Dice coefficient for all batches, or for a single mask
# 计算一个batch中所有图片某个类别的dice_coefficient
d = 0.
batch_size = x.shape[0]
for i in range(batch_size):
x_i = x[i].reshape(-1)
t_i = target[i].reshape(-1)
if ignore_index >= 0:
# 找出mask中不为ignore_index的区域
roi_mask = torch.ne(t_i, ignore_index)
x_i = x_i[roi_mask]
t_i = t_i[roi_mask]
inter = torch.dot(x_i, t_i)
sets_sum = torch.sum(x_i) + torch.sum(t_i)
if sets_sum == 0:
sets_sum = 2 * inter
d += (2 * inter + epsilon) / (sets_sum + epsilon)
return d / batch_size
def multiclass_dice_coeff(x: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, ignore_index: int = -100, epsilon=1e-6):
"""Average of Dice coefficient for all classes"""
dice = 0.
for channel in range(x.shape[1]):
dice += dice_coeff(x[:, channel, ...], target[:, channel, ...], ignore_index, epsilon)
return dice / x.shape[1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
n_classes = 3 # 分类数
confusion_matrix = meter.ConfusionMeter(3)
output = torch.Tensor([[[[1, 3], [2, 5]], [[2, 2], [3, 7]], [[0, 1], [9, 0]]]]) # torch.Size([1, 3, 2, 2])
target = torch.tensor([[[1, 0], [2, 0]]]) # torch.Size([1, 2, 2])
# [1, 3, 2, 2] -> [1, 2, 2] -> [1, 2, 2, 3] -> [1, 3, 2, 2]
pred = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(output.argmax(dim=1), n_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float()
# [1, 2, 2] -> [1, 2, 2, 3] -> [1, 3, 2, 2]
dice_target = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(target, n_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float()
dice = multiclass_dice_coeff(pred, dice_target)
print(dice) # tensor(0.7778)
参考
2. 语义分割的评价指标


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号