【深度学习】c++部署onnx模型(Yolov5、PP-HumanSeg、GoogLeNet、UNet)
这两天部署了好多模型,记录一下。代码链接。
- onnxruntime在第一张图的推理上比opencv快很多,但在后面的图上略微慢了一点。
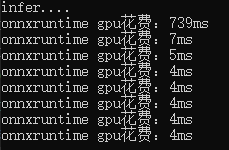

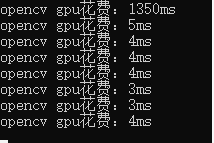
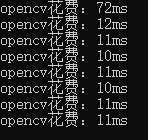
- 不同的模型的部署时的输出不同,处理时需要对输出比较了解,下面分别处理了目标检测、语义分割和分类模型的输出。
onnxruntime模型部署
例1:onnxruntime部署PP-HumanSeg语义分割模型
根据博客的代码做了一点补充:多图并行推理
1. 生成模型时更改inputshape,想要并行推理几张图就写几。
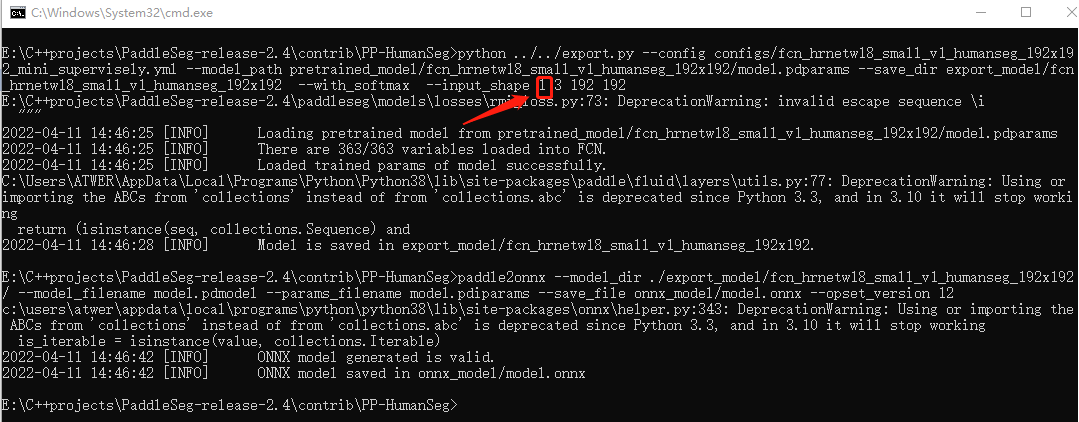
2. 加载模型时选择对应的.onnx
3. 改输入维度
HumanSeg human_seg(model_path, 1, { 3, 3, 192, 192 });//3张 HumanSeg human_seg(model_path, 1, { 8, 3, 192, 192 });//8张
4. 在推理前,将多张图放入vector,后处理时多一层遍历
void HumanSeg::predict_images_together(const std::string& imgpath) { std::vector<std::string> filenames; cv::glob(imgpath, filenames); cv::Mat src, dst; std::vector<cv::Mat> src_images; std::vector<cv::Mat> in_images; int image_count = filenames.size(); clock_t start{ clock() }, end;
//预处理 for (size_t i = 0; i < image_count; ++i) { src = cv::imread(filenames[i]); src_images.push_back(src); dst = preprocess(src); in_images.push_back(dst); } cv::Mat blob = cv::dnn::blobFromImages(in_images, 1, input_size, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), false, true);
//推理 auto memory_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtArenaAllocator, OrtMemTypeDefault); input_tensors_.emplace_back(Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, blob.ptr<float>(), blob.total(), input_node_dims_.data(), input_node_dims_.size())); std::vector<Ort::Value> output_tensors_ = session_.Run( Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr }, input_node_names_.data(), input_tensors_.data(), input_node_names_.size(), out_node_names_.data(), out_node_names_.size() ); int64* floatarr = output_tensors_.front().GetTensorMutableData<int64>(); //后处理 std::vector<cv::Mat> out_images; for(int k=0;k< image_count;k++){ cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(input_size, CV_8UC1); for (int i{ 0 }; i < static_cast<int>(input_node_dims_[2]); i++) { for (int j{ 0 }; j < static_cast<int>(input_node_dims_[3]); ++j) { mask.at<uchar>(i, j) = static_cast<uchar>(floatarr[i * static_cast<int>(input_node_dims_[3]) + j + k * 192 * 192]); } } cv::resize(mask, mask, cv::Size(image_w, image_h)); cv::Mat mask1 = mask * 255; cv::Mat predict_image; cv::bitwise_and(src_images[k], src_images[k], predict_image, mask = mask); out_images.push_back(predict_image); cv::imwrite(imgpath +"\\" +std::to_string(k) + ".jpg", predict_image); } end = clock(); std::cout << (end - start)/ image_count*1.0 << std::endl; input_tensors_.clear(); return; }
例2:onnxruntime部署googlenet 4分类模型
void onnxruntime::predict(cv::Mat& blob) { clock_t start{ clock() }, end; auto memory_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtArenaAllocator, OrtMemTypeDefault); input_tensors_.emplace_back(Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, blob.ptr<float>(), blob.total(), input_node_dims_.data(), input_node_dims_.size())); std::vector<Ort::Value> output_tensors_ = session_.Run( Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr }, input_node_names_.data(), input_tensors_.data(), input_node_names_.size(), out_node_names_.data(), out_node_names_.size()); float* floatarr = output_tensors_[0].GetTensorMutableData<float>(); end = clock(); std::cout << "onnxruntime:" << end - start << "ms" << std::endl; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { std::cout << *floatarr++ << std::endl; } }
结果:(最大数的索引就是类别)

opencv::dnn模型部署
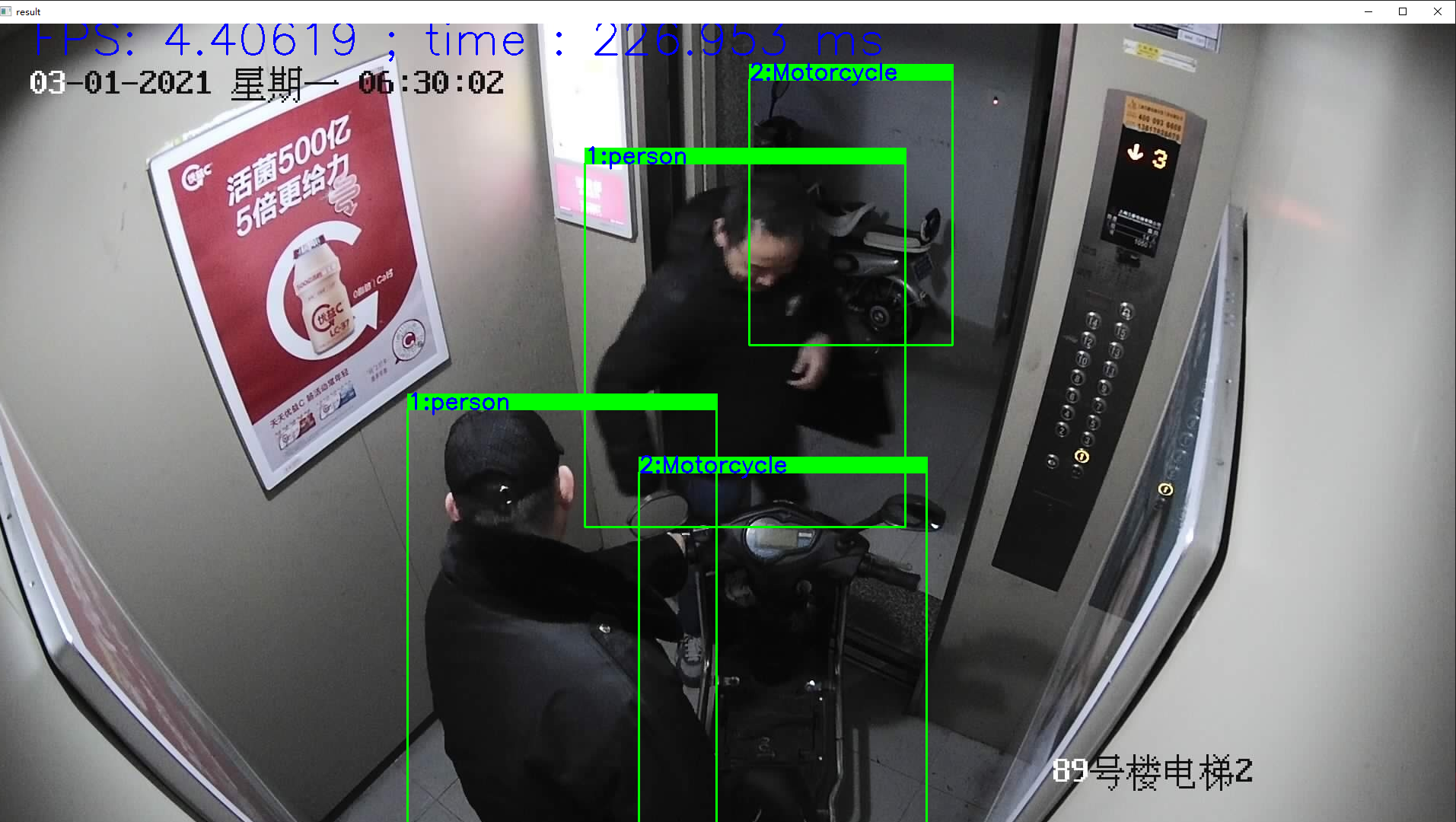
例1:Yolov5 3分类检测模型部署
#include"yolov5_dnn.h" using namespace cv; //初始化网络,classname void YOLOv5Detector::initConfig(std::string onnxpath, string classpath, int iw, int ih, float threshold) { this->input_w = iw; this->input_h = ih; this->threshold_score = threshold; this->net = cv::dnn::readNetFromONNX(onnxpath); this->class_list = readClassNames(classpath); } //检测 void YOLOv5Detector::detect(cv::Mat& frame, std::vector<DetectResult>& results) { //图像预处理 int w = frame.cols; int h = frame.rows; int _max = std::max(h, w); cv::Mat image = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(_max, _max), CV_8UC3); cv::Rect roi(0, 0, w, h); frame.copyTo(image(roi)); float x_factor = image.cols / 640.0f; float y_factor = image.rows / 640.0f; // 推理 cv::Mat blob = cv::dnn::blobFromImage(image, 1 / 255.0, cv::Size(this->input_w, this->input_h), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false); this->net.setInput(blob); cv::Mat preds = this->net.forward(); // 后处理, 1x25200x8 std::cout << "rows: "<< preds.size[1]<< " data: " << preds.size[2] << std::endl; cv::Mat det_output(preds.size[1], preds.size[2], CV_32F, preds.ptr<float>()); float confidence_threshold = 0.5; std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes; std::vector<int> classIds; std::vector<float> confidences; for (int i = 0; i < det_output.rows; i++) { float confidence = det_output.at<float>(i, 4); if (confidence < 0.4) { continue; } cv::Mat classes_scores = det_output.row(i).colRange(5, 8);//此处改动了,因为是三分类,所以输出中先是xywh,confidence,然后是3个类别的分数 cv::Point classIdPoint; double score; minMaxLoc(classes_scores, 0, &score, 0, &classIdPoint); // 置信度 0~1之间 if (score > this->threshold_score) { float cx = det_output.at<float>(i, 0); float cy = det_output.at<float>(i, 1); float ow = det_output.at<float>(i, 2); float oh = det_output.at<float>(i, 3); int x = static_cast<int>((cx - 0.5 * ow) * x_factor); int y = static_cast<int>((cy - 0.5 * oh) * y_factor); int width = static_cast<int>(ow * x_factor); int height = static_cast<int>(oh * y_factor); cv::Rect box; box.x = x; box.y = y; box.width = width; box.height = height; boxes.push_back(box); classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x); confidences.push_back(score); } } // NMS std::vector<int> indexes; cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45, indexes); for (size_t i = 0; i < indexes.size(); i++) { DetectResult dr; int index = indexes[i]; int idx = classIds[index]; dr.box = boxes[index]; dr.classId = idx; dr.score = confidences[index]; cv::rectangle(frame, boxes[index], cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(boxes[index].tl().x, boxes[index].tl().y - 20), cv::Point(boxes[index].br().x, boxes[index].tl().y), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1); cv::putText(frame, class_list[idx], cv::Point(boxes[index].tl().x, boxes[index].tl().y), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0),2); results.push_back(dr); } std::ostringstream ss; std::vector<double> layersTimings; double freq = cv::getTickFrequency() / 1000.0; double time = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimings) / freq; ss << "FPS: " << 1000 / time << " ; time : " << time << " ms"; putText(frame, ss.str(), cv::Point(50, 40), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2.0, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8); imshow("result", frame); waitKey(); } // 读取txt文件 vector<string> YOLOv5Detector::readClassNames(string classpath) { vector<String> classNames; ifstream fp(classpath); if (!fp.is_open()) { printf("could not open file...\n"); exit(-1); } std::string name; while (!fp.eof()) { std::getline(fp, name); if (name.length()) classNames.push_back(name); } fp.close(); return classNames; }
结果:

例2:opencv部署googlenet 4分类模型
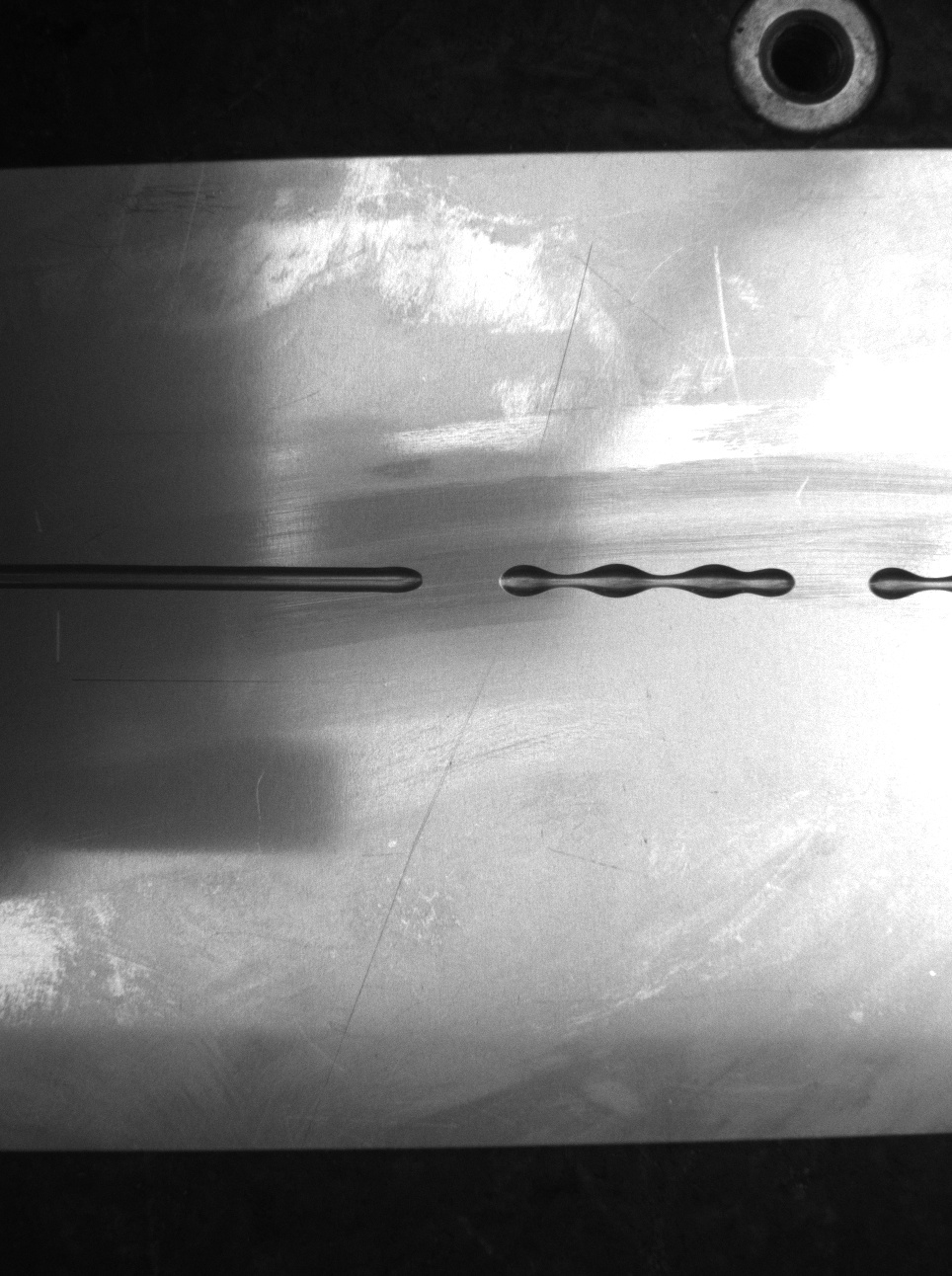




做的是点胶的四分类,用的googlenet,准确率98.6%。
代码:
int main() { string modelpath = "../googlenet.onnx"; try { Mat img = imread("../3.jpg"); resize(img, img, Size(128, 128)); cvtColor(img, img, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB); img.convertTo(img, CV_32F, 1.0 / 255.0); cv::Scalar default_mean(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); cv::Scalar default_std(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); cv::subtract(img, default_mean, img); cv::divide(img, default_std, img); Mat inputBlob = dnn::blobFromImage(img); //opencv Net net = readNetFromONNX(modelpath); clock_t start{ clock() }, end; net.setInput(inputBlob); Mat prob = net.forward(); end = clock(); std::cout << "opencv:"<<end - start<<"ms" << std::endl; float* pData = (float*)prob.data; softmax(prob, prob); Point maxLoc; double maxValue = 0; minMaxLoc(prob, 0, &maxValue, 0, &maxLoc); int labelIndex = maxLoc.x; double probability = maxValue; string cla; switch (labelIndex) { case 0: cla = "断胶"; break; case 1: cla = "多胶"; break; case 2: cla = "少胶"; break; case 3: cla = "正常"; break; } cout << cla << ":" << probability; } catch (exception ex) { } }
结果:和onnxruntime的一样
例3:dnn部署UNet二分类模型(多图并行推理)
// 加载模型
int UNetInit(string onnx)
{
net = cv::dnn::readNetFromONNX(onnxPath);
// 设置计算后台和计算设备(默认为CPU)
// CPU
//net.setPreferableBackend(cv::dnn::DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
//net.setPreferableTarget(cv::dnn::DNN_TARGET_CPU);
// CUDA
net.setPreferableBackend(cv::dnn::DNN_BACKEND_CUDA);
net.setPreferableTarget(cv::dnn::DNN_TARGET_CUDA);
return 0;
}
// 预处理
void preProcess(vector<Mat>& small_images) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < small_images.size(); i++)
{
Mat image_small = small_images[i];
copyMakeBorder(image_small, image_small, 0, baseSize - image_small.rows, 0, baseSize - image_small.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar(0));
image_small.convertTo(image_small, CV_32FC1, 1.0 / 255);
subtract(image_small, meanVal, image_small);
divide(image_small, stdVal, image_small);
}
}
// 后处理 并行推理
void Segmentation(const cv::Mat& score, vector<Mat>& masks) {
// score.size = batch x 2 x 480 x 480
int bths = score.size[0];
int chns = score.size[1];
int rows = score.size[2];
int cols = score.size[3];
for (int batch = 0; batch < bths; batch++) {
Mat mask = Mat::zeros(rows, cols, CV_8UC1);
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++)
{
const float* bg_score = score.ptr<float>(batch, 0, row);
const float* fg_score = score.ptr<float>(batch, 1, row);
for (int col = 0; col < cols; col++)
{
if ((fg_score[col] > bg_score[col])&& (exp(fg_score[col]) / (exp(fg_score[col]) + exp(bg_score[col])) > 0.95))
mask.at<uchar>(row, col) = 255;
}
}
masks.push_back(mask);
}
}
int main(){
...
UNetInit(onnxPath);//加载模型
vector<Mat> small_images,small_masks;
... //读图
preProcess(small_images);//预处理
Mat blob = dnn::blobFromImages(small_images);
net.setInput(blob);
Mat preds = net.forward();//推理
Segmentation(preds, small_masks);
...
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号