Python初学
1.1 编程风格
语法要求
缩进同一
[root@k8s-master data]# cat hello.py def main(): print 'hello' print 'world' main() [root@k8s-master data]# python hello.py hello world [root@k8s-master data]# cat hello.py def main(): print 'hello' print 'world' main() [root@k8s-master data]# python hello.py world hello
变量
l 标识符的第一个字符必须是字母表中的字母(大写或小写)或者一个下划线(‘_’)
l 标识符名称的其它部分可以由字母(大写或小写)、下划线(‘_’)或数字(0-9)组成
l 标识符名称是对大小写敏感的。例如 name和Name不是一个标识符。
l 有效标识符:i、_my_name、name_23和a1b2_c3
l 无效标识符:2things、my-name
常量
所谓常量是指不变的变量
[root@k8s-master data]# cat abc.py a=2 b=3 c=a a=4 print a print c [root@k8s-master data]# python abc.py 4 2
1.1.1 数据类型(按特征划分)
数字类型:整形、非整形
整形:布尔型、长整型、标准整形
>>> type(21) <type 'int'>
非整形:双精度浮点型、复数、decimal(不是内建类型)
>>> type(3.14) <type 'float'>
序列类型:字符串(str)、元组(tuple)、列表(list)
>>> name='LL' >>> type(name) <type 'str'> >>> name_list=['alex','real','erion'] >>> type(name_list) <type 'list'>
映像类型:字典(dict)
>>> name={'LL':[28,'IT']}
>>> name['LL']
[28, 'IT']
>>> type(name)
<class 'dict'>
集合类型:可变集合(set)、不可变集合(frozenset)
1.1.2 数据类型(按可变性划分)
可哈希的,不可变数据类型
数字类型
字符串(str)
不可变集合(frozenset)
元组(tuple)
可变数据类型
字典(dict)
列表(list)
可变集合(set)
1.1.3 Python运算符
|
运算符 |
描述 |
实例 |
|
+ |
加 - 两个对象相加 |
a + b 输出结果 30 |
|
- |
减 - 得到负数或是一个数减去另一个数 |
a - b 输出结果 -10 |
|
* |
乘 - 两个数相乘或是返回一个被重复若干次的字符串 |
a * b 输出结果 200 |
|
/ |
除 - x除以y |
b / a 输出结果 2 |
|
% |
取模 - 返回除法的余数 |
b % a 输出结果 0 |
|
** |
幂 - 返回x的y次幂 |
a**b 为10的20次方, 输出结果 100000000000000000000 |
|
// |
取整除 - 返回商的整数部分(向下取整) |
>>> 9//2 4 >>> -9//2 -5 |
a=10 b=20
>>> 1 + 1 * 3/2
2
>>> 1 +1 * 3.0/2
2.5
1.1.4 Python比较符
|
运算符 |
描述 |
实例 |
|
== |
等于 - 比较对象是否相等 |
(a == b) 返回 False。 |
|
!= |
不等于 - 比较两个对象是否不相等 |
(a != b) 返回 true. |
|
<> |
不等于 - 比较两个对象是否不相等 |
(a <> b) 返回 true。这个运算符类似 != 。 |
|
> |
大于 - 返回x是否大于y |
(a > b) 返回 False。 |
|
< |
小于 - 返回x是否小于y。所有比较运算符返回1表示真,返回0表示假。这分别与特殊的变量True和False等价。 |
(a < b) 返回 true。 |
|
>= |
大于等于 - 返回x是否大于等于y。 |
(a >= b) 返回 False。 |
|
<= |
小于等于 - 返回x是否小于等于y。 |
(a <= b) 返回 true。 |
1.1.5 Python逻辑运算
|
运算符 |
逻辑表达式 |
描述 |
实例 |
|
and |
x and y |
布尔"与" - 如果 x 为 False,x and y 返回 False,否则它返回 y 的计算值。 |
(a and b) 返回 20。 |
|
or |
x or y |
布尔"或" - 如果 x 是非 0,它返回 x 的值,否则它返回 y 的计算值。 |
(a or b) 返回 10。 |
|
not |
not x |
布尔"非" - 如果 x 为 True,返回 False 。如果 x 为 False,它返回 True。 |
not(a and b) 返回 False |
1.1.6 Python赋值运算符
|
运算符 |
描述 |
实例 |
|
= |
简单的赋值运算符 |
c = a + b 将 a + b 的运算结果赋值为 c |
|
+= |
加法赋值运算符 |
c += a 等效于 c = c + a |
|
-= |
减法赋值运算符 |
c -= a 等效于 c = c - a |
|
*= |
乘法赋值运算符 |
c *= a 等效于 c = c * a |
|
/= |
除法赋值运算符 |
c /= a 等效于 c = c / a |
|
%= |
取模赋值运算符 |
c %= a 等效于 c = c % a |
|
**= |
幂赋值运算符 |
c **= a 等效于 c = c ** a |
|
//= |
取整除赋值运算符 |
c //= a 等效于 c = c // a |
1.1.7 Python位运算符
|
运算符 |
描述 |
实例 |
|
& |
按位与运算符:参与运算的两个值,如果两个相应位都为1,则该位的结果为1,否则为0 |
(a & b) 输出结果 12 ,二进制解释: 0000 1100 |
|
| |
按位或运算符:只要对应的二个二进位有一个为1时,结果位就为1。 |
(a | b) 输出结果 61 ,二进制解释: 0011 1101 |
|
^ |
按位异或运算符:当两对应的二进位相异时,结果为1 |
(a ^ b) 输出结果 49 ,二进制解释: 0011 0001 |
|
~ |
按位取反运算符:对数据的每个二进制位取反,即把1变为0,把0变为1 。~x 类似于 -x-1 |
(~a ) 输出结果 -61 ,二进制解释: 1100 0011,在一个有符号二进制数的补码形式。 |
|
<< |
左移动运算符:运算数的各二进位全部左移若干位,由 << 右边的数字指定了移动的位数,高位丢弃,低位补0。 |
a << 2 输出结果 240 ,二进制解释: 1111 0000 |
|
>> |
右移动运算符:把">>"左边的运算数的各二进位全部右移若干位,>> 右边的数字指定了移动的位数 |
a >> 2 输出 |
1.2 注释
单行注释
多行注释
[root@k8s-master data]# python print.py print ddd' print 'dddd' print 'ddddd [root@k8s-master data]# cat print.py #print ddd info='''print ddd' print 'dddd' print 'ddddd''' print info
1.3 字符编码
ASSIC >>> ord('A') 65 >>> ord('a') 97 >>> ord('~') 126 Unicode >>> a = 'alex' >>> type(a) <type 'str'> >>> a = u'alex' >>> type(a) <type 'unicode'> >>> a u'alex' >>> name = u'范特西' >>> name u'\u8303\u7279\u897f' >>> print name 范特西 >>> type (name) <type 'unicode'> UTF-8 >>> name.encode('utf-8') '\xe8\x8c\x83\xe7\x89\xb9\xe8\xa5\xbf' >>> name_utf8=name.encode('utf8') >>> len(name_utf8) 9 >>> len(name) 3 >>> print '\xe8\x8c\x83' 范 >>> print '\xe7\x89\xb9' 特 >>> print '\xe8\xa5\xbf' 西
解码
>>> name = "范特西" >>> name '\xe8\x8c\x83\xe7\x89\xb9\xe8\xa5\xbf' >>> name.decode('utf-8') u'\u8303\u7279\u897f'
1.4 导入模块
l 什么是模块?
l ImportmoduleName
l From module import sayHi
l Impot module Name as newName
>>> os.system('free -m') total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 14811 2996 7477 755 4336 10680 Swap: 0 0 0 0
保存执行结果
方法一: >>> os.system('pwd') /data 0 >>> a=os.popen('pwd').read() >>> a '/data\n'
方法二: >>> import commands >>> b=commands.getstatusoutput('pwd') >>> b (0, '/data')
1.5 用户交互
l raw_input()
l 程序
查询用户 姓名,年龄,性别,工作,工资
以格式化的方式输出
Information of company staff:
Name:xxx
Age:xxx
Sex:xxx
Job:xxx
#!/usr/bib/env python #_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ name = raw_input ('please input your name: ') sex = raw_input ('sex: ') age = raw_input ('age: ') job = raw_input ('job: ') print ''' Personal information of %s: Name: %s Sex : %s Age : %s job : %s --------------------------- ''' % (name,name,sex,age,job)
1.6 流程控制
1.6.1 If语句
If
elif
else
#!/usr/bib/env python #_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ name = raw_input ('please input your name: ') sex = raw_input ('sex: ') age = raw_input ('age: ') job = raw_input ('job: ') if age >= 40: msg = 'You are too old!' elif age >= 30: masg = 'You are very good!' else: msg = 'You are too young!' print ''' Personal information of %s: Name: %s Sex : %s Age : %s job : %s --------------------------- %s ''' % (name,name,sex,age,job,msg)
1.6.2 For循环
for n in
#!/usr/bib/env python #_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ name = raw_input ('please input your name: ') sex = raw_input ('sex: ') age = raw_input ('age: ') job = raw_input ('job: ') real_age = 29 for i in range(10): if age > 29: print 'too smaller!' elif age = 29: print 'You are very good!' break else: msg = 'too bigger!' print ‘You still got %s shots!’ % (10 – i) print ''' Personal information of %s: Name: %s Sex : %s Age : %s job : %s --------------------------- %s ''' % (name,name,sex,age,job)
1.6.3 While循环
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 print_num= input('which loop do you want it tobr?') count =0 while count < 100000000: if count == print_num: print 'There you got the number:', count choice= raw_input('Do you want to continue the loop?(y/n)') if choice == 'n': break else: while print_num <= count: print_num = input('which loop do you want it to be printed out?') print u'已经过了,sx!' else: print 'loop:', count count +=1 else: print 'loop:', count
练习sx
编写登录接口
- 输入用户名密码
- 认证成功后显示欢迎信息
- 输错三次后锁定
#!usr/bin/env python #_*_ coding: utf-8 _*_ import sys retry_limit = 3 retry_count = 0 account_file = 'accounts.txt' lock_file = 'account_lock.txt' while retry_count < retry_limit: #只要重试不超过3次就不断循环 username = raw_input('\033[32;1mUsername:\033[0m') lock_check = file(lock_file) #当用户输入用户名后,打开LOCK 文件 以检查是否此用户已经LOCK了 for line in lock_check.readlines(): #循环LOCK文件 line = line.split() if username == line[0]: sys.exit('\033[31;1mUser %s is locked!\033[0m' % username ) #如果LOCK了就直接退出 password = raw_input('\033[32;1mPassword:\033[0m') f = file(account_file,'rb') #打开帐号文件 match_flag = False # 默认为Flase,如果用户match 上了,就设置为 True for line in f.readlines(): user,passwd = line.strip('\n').split() #去掉每行多余的\n并把这一行按空格分成两列,分别赋值为user,passwd两个变量 if username == user and password == passwd: #判断用户名和密码是否都相等 print 'Match!', username match_flag = True #相等就把循环外的match_flag变量改为了True break #然后就不用继续循环了,直接 跳出,因为已经match上了 f.close() if match_flag == False: #如果match_flag还为False,代表上面的循环中跟本就没有match上用户名和密码,所以需要继续循环 print 'User unmatched!' retry_count +=1 else: print "Welcome login OldBoy Learning system!" else: print 'Your account is locked!' f = file(lock_file,'ab') f.write(username) f.close()
1.7 文件处理
r 以只读模式打开文件
w 以只写模式打开文件 (打开已存在文件会将文件覆盖)
a 以追加模式打开文件
r+b 以读写模式打开
w+b 以写读模式打开
a+b 以追加及读模式打开
[root@k8s-master data]# echo 6 >>test.txt [root@k8s-master data]# echo 7 >>test.txt >>> f = open('test.txt','r+') >>> f.read() '1\n2\n3\n4\n5\n' >>> f.read() '6\n7\n'
1.8 字符串处理

1.9 列表
>>> name_list=['1','2','3','4'] >>> name_list[2] '3' >>> del name_list[2] #按索引位置删除值 >>> name_list ['1', '2', '4'] >>> name_list.insert(2,'2.5') #在指定索引位置插入值 >>> name_list ['1', '2', '2.5', '4'] >>> name_list.append('5') #添加一个值 >>> name_list ['1', '2', '2.5', '4', '5'] >>> name_list.remove('2') #删除指定值 >>> name_list ['1', '2.5', '4', '5'] >> name_list.count(2) #统计出现的相同值个数

1.10 元组
l Tuple:元组(即常量数组)
l Tuple = (‘a’,’b’,’c’)
l 可以用list的[],:操作符提取元素
1.11 字典Dict

1.12 列表与字典对比
l dict:
—查找和插入的速度极快,不会随着key的增加而增加;
—需要占用大量内存,内存浪费多;
—KEY不可变;
—默认无序;
l list:
—查找和插入的时间随着元素的增加而增加;
—占用空间小,浪费内存很少;
—通过下标查询;
—有序;
1.13 Set集合
特点:
l 无序
l 元素不重复
功能:
l 关系测试
l 去重
>>> name_set = {1,2,3,4,5}
>>> name_set
set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> name_set = {1,2,1,4}
>>> name_set
set([1, 2, 4])
增加
>>> name_set.add(5)
>>> name_set
set([1, 2, 4, 5])

>>> x = {1,2,3,4}
>>> y = {3,4,5,6}
>>> x & y
set([3, 4])
>>> x | y
set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
>>> x - y
set([1, 2])
>>> x ^ y
set([1, 2, 5, 6])
1.14函数
l Eclipse的使用
l 模块和模块的常用方法
l 函数编程
l Yield
l 三元运算
l Lambda表达式
l 内置函数
l 常用模块
l 装饰器
1.14.1 yield
def foo(): yield 1 yield 2 yield 3 yield 4 yield 5 re = foo() for item in re: print item def Flin(): seek = 0 while True: with open('D:/tmp.txt','r') as f: f.seek(seek) data = f.readline() if data: seek = f.tell() yield data else: return for item in Flin(): print item
1.14.2 Lambda
temp = None if 1>3: temp = 'gt' else: temp = 'lt' print temp result = 'gt' if 1>3 else 'lt' print result def foo(x,y): return x+y print foo(4,10) temp = lambda x,y:x+y print temp(4,2)
1.14.3 内置函数
l help()
l dir()
l vars()
l type()
l import temp
l reload(temp)
l id()
1.15 反射
temp = 'os'
model = __import__(temp)
以字符串的形式导入模块,并以字符串的形式执行函数
1.16 常用模块
1.16.1 Random生成随机数
import random print random.random() #生成随机数 print random.randit(1,5) #生成固定区间内的整数 print random.randrange(1,3) #生成大于等于1小于等于3 生成六位随机验证码 import random code = [] for i in range(6): if i == random.randint(1,5): code.append(str(random.randint(1,5))) else: temp = random.randint(65,90) code.append(chr(temp)) print ''.join(code)
1.16.2 MD5加密
import hashlib hash = hashlib.md5() hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest()
1.17 序列化和json
序列化反序列化
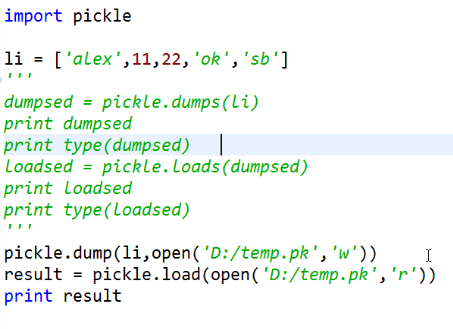
import pickle li = ['LL',11,22,'XX','cc'] dumpsed = pickle.dumps(li) print dumpsed print type(dumpsed) loadsed = pickle.loads(dumpsed) print loadsed print type(loadsed)

序列化之后存储到文件,再从文件内读取进行反序列化
1.18 Re
l compile
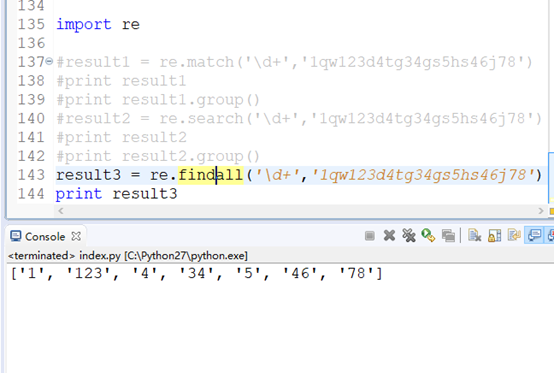
l match search findall
l group groups

import re result1 = re.match('\d+','1qw123d4tg34gs5hs46j78') print result1 print result1.group() result2 = re.search('\d+','1qw123d4tg34gs5hs46j78') print result2 print result2.group()
1.19 time

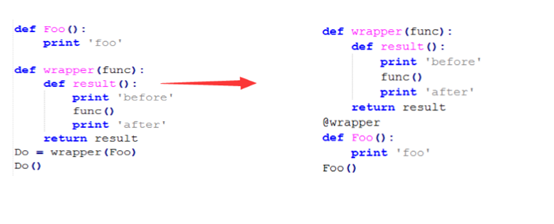
1.20 装饰器
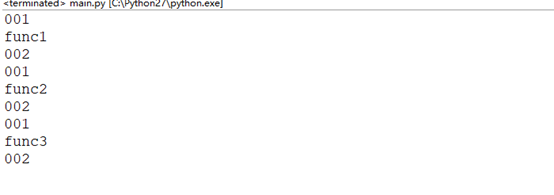
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 def outer(fun): def wrapper(): print '001' fun() print '002' return wrapper @outer def Func1(): print 'func1' Func1() @outer def Func2(): print 'func2' Func2() @outer def Func3(): print 'func3' Func3()
1.21 类和对象
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 class Province: #静态字段 memo = '中国23个省之一' def __init__(self,name,capital,leader): #动态字段 self.Name = name self.Capital = capital self.Leader = leader self.__Thailand = flag def show(self): print self.__Thailand def _sha(self): print 'alex' def Foo2(self): self._sha() @property def Thailand(self): return self.__Thailand hebei = Province('河北','石家庄','LL') shanxi = Province('陕西','西安','KK') japan.show() #对象可以访问动态字段 print hebei.Capital #类可以访问静态字段 print Province.memo #类不能访问动态字段 #print Province.Name #对象可以访问静态字段 print hebei.memo
1.22 面向对象和函数式编程
class FOO: def __init__(self): pass def __del__(self): print '121212124124563' def Go(self): print 'Go' def __call__(self): print 'call' f1 = FOO() f1.Go() f1() l 类的继承 l 类的多继承 class year: def __init__(self): self.year = '年' def data(self): print '2019' class month(year): def __init__(self): self.month = '月' def data(self): print '10' f1=month() f1.data() 新式类和经典类的区别:Python2.2之后采用新式类 经典类存在多类继承的问题(根据类的前后顺序决定)
1.22.1 抽象类
抽象类+抽象方法 = 接口 from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod class Bar: __metaclass__ = ABCMeta @abstractmethod def Fun(self):pass class Foo(Bar): def __init__(self): print '__init__' Foo()
1.23 异常处理
AttributeError 试图访问一个对象没有的树形,比如foo.x,但是foo没有属性x
IOError 输入/输出异常;基本上是无法打开文件
ImportError 无法引入模块或包;基本上是路径问题或名称错误
IndentationError 语法错误(的子类) ;代码没有正确对齐 IndexError 下标索引超出序列边界,比如当x只有三个元素,却试图访问x[5]
KeyError 试图访问字典里不存在的键
KeyboardInterrupt Ctrl+C被按下
NameError 使用一个还未被赋予对象的变量
SyntaxError Python代码非法,代码不能编译(个人认为这是语法错误,写错了)
TypeError 传入对象类型与要求的不符合
UnboundLocalError 试图访问一个还未被设置的局部变量,基本上是由于另有一个同名的全局变量, 导致你以为正在访问它
ValueError 传入一个调用者不期望的值,即使值的类型是正确的
data = raw_input('请输入地址:') array = data.split('/') #array[0] = account try: userspance = __import__('backend.'+array[0]) model = getattr(userspance, array[0]) func =getattr(model, array[1]) func() except ImportError,e: print 1,e print '跳转到自定义的404' except AttributeError,e: print 2,e print '跳转到自定义的404' except Exception,e: print 3,e print '跳转到自定义的404' else: print '么有出错' finally: print '无论异常与否,都会执行!'. class MyError(Exception): def __init__(self,msg): self.Message = msg def __str__(self): return self.Message try: a = 1 raise MyError(' 卧槽 ') except Exception,e: print e
1.24 socket网络编程
服务端
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 import socket #创建对象 server = socket.socket() #绑定IP和端口 server.bind(('192.168.1.160',8000)) #可等待数量 server.listen(5) ''' #等待客户端连接,如果没有连接将阻塞 #conn是客户端和服务端连接的介质,服务端以后通过该介质和客户端进行数据传输 #addr是客户端的地址信息 conn,addr = server.accept() #1024:服务端通过连接介质获取数据时,一次性最多1024字节 data = conn.recv(1024) print (data) #服务端通过介质给客户端发送一条消息 conn.send(b'stop') #与客户端断开时,释放介质 conn.close() #关闭服务端 server.close() ''' while True: conn,addr = server.accept() # data = conn.recv(1024) response = data +b'LL' conn.send(response) server.close()
客户端
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 import socket client = socket.socket() #如果连接地址无法通信将进行阻塞 直到地址可以通信 client.connect(('192.168.1.160',8000)) ''' #连接成功后向服务器发送信息 client.send(b'hello') #客户端等待服务端回复消息 data = client.recv(1024) print(data) #关闭客户端服务 client.close() ''' name = input('请输入姓名:') client.send(name.encode('utf-8')) response_ = client.recv(1024) client.close()
阻塞的原因:
服务端:
l accept 等待客户端来连接
l recv 等待客户端发来数据
客户端
l connect 一直连接,直到连接成功才往下运行其他代码
l recv 等待服务端发来消息
模拟ssh
服务端
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 import socket import subprocess sock = socket.socket() sock.bind(('127.0.0.1',8000)) sock.listen(5) while True: print("server is working") conn,addr = sock.accept() while True: try: cmd = conn.recv(1024).decode('utf8') if cmd ==b'exit': break res=subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, ) #print('stdout',res,stdout.read()) #print('stdeer',res.stdeer.read().decode('gbk')) out=res.stdout.read() err=res.stdeer.read() print('响应长度',len(out)) if err: conn.send(err) else: conn.send(out) except Exception as e: break conn.close()
客户端
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 import socket sk=socket.socket() sk.connect(('127.0.0.1',8000)) while True: cmd=raw_input('请输入命令:') sk.send(cmd.encode('utf8')) if cmd=="": continue if cmd==b'exit': break response = sk.recv(1024) print(response.decode('gbk')) sk.close()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号