C++ Primier Plus(第六版) 第十七章 输入、输出和文件 编程练习答案
1. 编写一个程序计算输入第一个流在留在输入流中。
本题不算难,考查的是peek()方法,即使用peek()查看输入流中的字符而不抽取,注意循环里面应该采用cin.get()与而是cin>>ch,因为cin>>ch会跳过空格,导致程序错误(Ps:笔者遇到的错误)。循环结束后使用cin.get()读取输入流中的字符。程序如下:
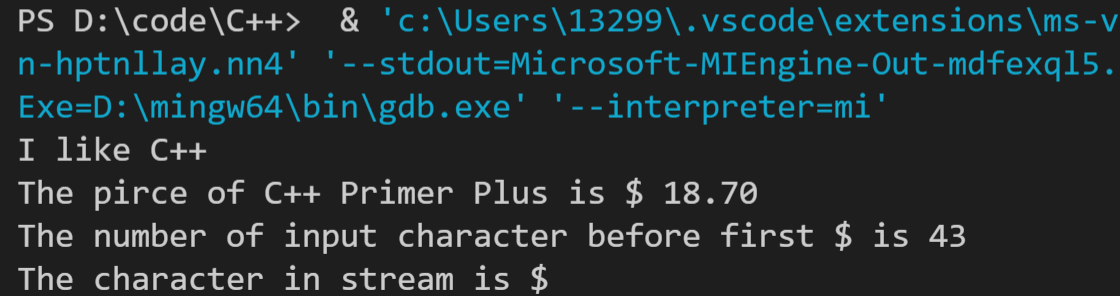
// pe1.cpp -- calculate the number out input character before first $ #include <iostream> int main() { using namespace std; char ch; int ct = 0; while (cin.peek() != '$') { ct++; cin.get(ch); // cin >> ch is wrong } cout << "The number of input character before first $ is " << ct << endl; cin.get(ch); cout << "The character in stream is " << ch << endl; return 0; }
运行结果如下:
2. 编写一个程序,将键盘输入(直到模拟的文件尾)复制通过命令行指定的文件中。
本题考查的是 int main(int argc, char * argv[])的使用,可以使程序在命令行得到要存储的文件名,读取键盘输入,通过ofstream对象存到关联的文件中,注意windows11下的EOF输入必须在行首。程序如下:
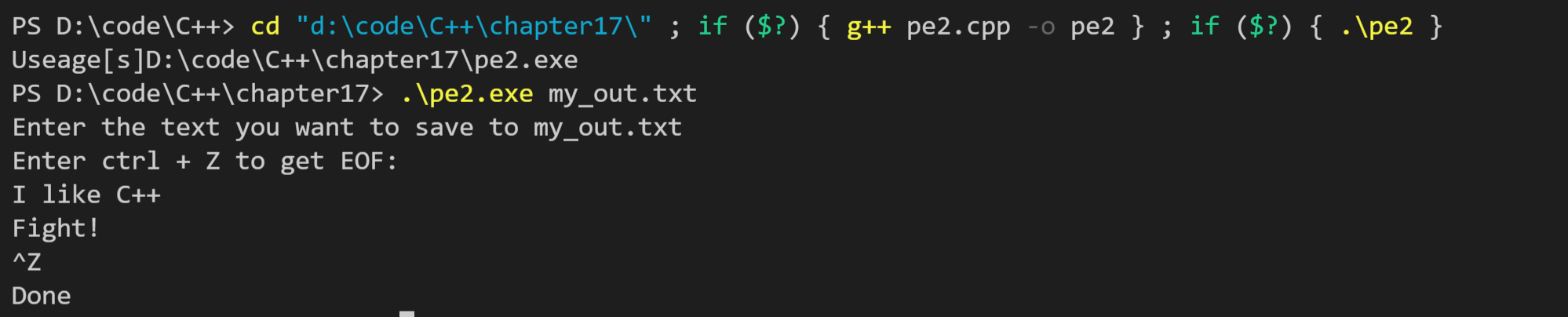
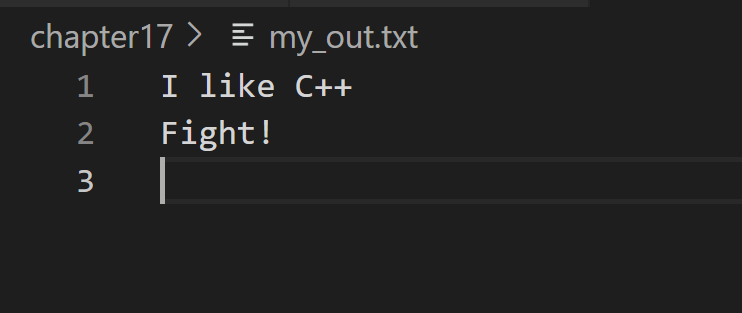
// pe2.cpp -- keyboard input save to file #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { using namespace std; if (argc == 1) { cout << "Useage[s]" << argv[0] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) { cout << "Enter the text you want to save to " << argv[i] << endl; ofstream fout; fout.open(argv[i]); cout << "Enter ctrl + Z to get EOF:\n"; char ch; while (cin.peek() != EOF) { cin.get(ch); // fout << ch; fout.put(ch); } fout.clear(); fout.close(); } return 0; }
运行结果如下(第一幅图是命令行结果,第二幅图是文件结果):
3. 编写一个程序,将一个文件复制到另一个文件中。让程序通过命令行获取文件名。如果文件无法打开,程序将指出这一点。
本题不算难,(Ps:但是笔者刚开始遇到了问题,怎么也找不到哪里错误,找了好久终于找到了。遇到的问题是判断文件是否打开的语句忘了加一个逻辑非,导致文件无法读取,或者文件不进行)首先声明文件输入流和输出流对象,将输入流对象与复制对象关联起来,将存储对象与输出流文件对象关联起来,使用fin.get(ch);读取,使用fout<<ch。
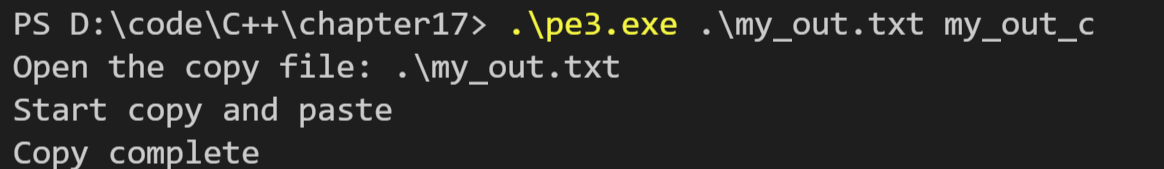
// pe3.cpp -- copy the text from file 1 to file 2 #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { using namespace std; if (argc == 1) { cout << "Useage[s]" << argv[0] << endl; cout << "First file is the original file, and second file is target file\n"; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // prototype fstream object ifstream fin; ofstream fout; // filename interact with stream object fin.open(argv[1]); fout.open(argv[2]); // fin.open() fail if (!fin.is_open()) { cerr << "Can't open the file: " << argv[1] << endl; fin.clear(); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } cout << "Open the copy file: " << argv[1] << endl; char ch; cout << "Start copy and paste\n"; // copy and paste while (fin.get(ch)) { fout << ch; } cout << "Copy complete\n"; fin.clear(); fin.close(); fout.close(); return 0; }
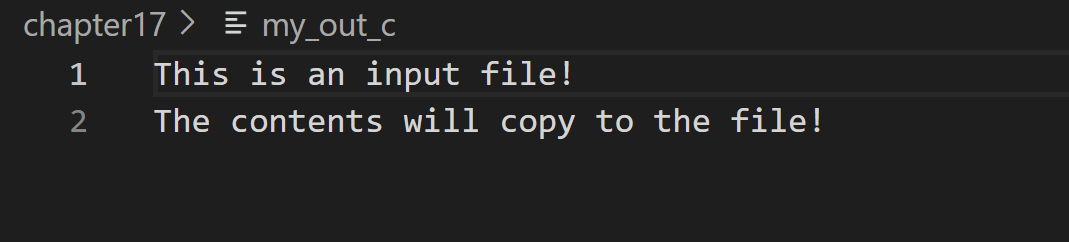
运行结果如下(第一幅图片:复制文件,第二幅图片:运行命令行,第三幅图片:输出文):
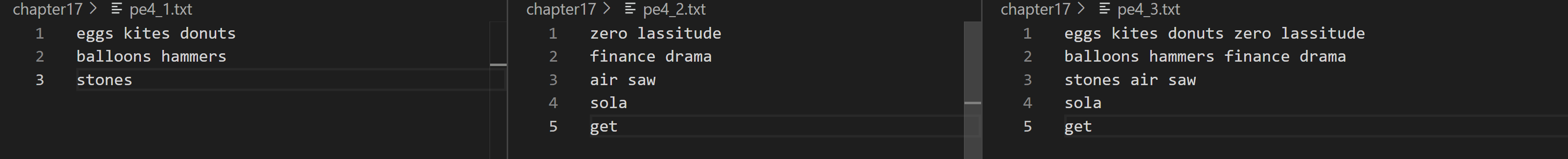
4. 编写一个程序,它打开两个文本文件进行输入,代开一个文本文件进行输出。该程序将两个输入文件中对应的行并接起来,并用空格分隔,然后将结果写入到输出文件中。如果一个文件比另一个短,则将较长文件中余下的几行直接复制到输出文件中。例如,假设第一个文件输入的内容如下:
eggs kites donuts
balloons hammers
stones
而第二个文件的内容如下:
zero lassitude
finace drama
则得到的文件的内容如下:
eggs kites donuts zero lassitude
balloons hammers finance drama
stones
本题由于不知道哪个文本长,哪个文本短,因此有两种解决方法,一种是,分别读取两个文件,获得每个文件的行数。根据行数的实际情况进行读取。程序如下:
// pe4_a.cpp -- combination of two files to third file // first get lines of two files #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { using namespace std; // no other file if (argc == 1) { cout << "Useages(s): " << argv[0] << endl; } if (argc !=4 ) { cerr << "You don't have input correct numbers of file.\n"; cout << "First and second: orginal file, third: output file" << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // prototype file stream object ifstream fin1; ifstream fin2; ofstream fout; // file with stream fin1.open(argv[1]); fin2.open(argv[2]); fout.open(argv[3]); // if file is not open if (!fin1.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << argv[1] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if (!fin2.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << argv[2] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if (!fout.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << argv[3] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // get lines of file1 and lines of file2 string input; // get file input int lines1 = 0; int lines2 = 0; while (getline(fin1, input)) lines1++; while (getline(fin2,input)) lines2++; // close fin1.clear(); fin1.close(); fin2.clear(); fin2.close(); // link restart fin1.open(argv[1]); fin2.open(argv[2]); if (lines1 == lines2) { for(int i = 0; i < lines1 - 1; i++) { getline(fin1, input); fout << input << ' '; getline(fin2, input); fout << input << endl; } getline(fin1, input); fout << input << ' '; getline(fin2, input); fout << input; // last line have not endl } if (lines1 < lines2) { for (int i = 0; i < lines1; i++) { getline(fin1, input); fout << input << ' '; getline(fin2, input); fout << input << endl; } for (int i = 0; i < lines2 - lines1 - 1; i++) { getline(fin2, input); fout << input << endl; } getline(fin2, input); fout << input; } if (lines1 > lines2) { for (int i = 0; i < lines2; i++) { getline(fin1, input); fout << input << ' '; getline(fin2, input); fout << input << endl; } for (int i = 0; i < lines1 - lines2 - 1; i++) { getline(fin1, input); fout << input << endl; } getline(fin1, input); fout << input; } // close all file fstream fin1.clear(); fin1.close(); fin2.clear(); fin2.close(); fout.clear(); fout.close(); cout << "Done\n"; return 0; // }
另一种方法是用if逐级判断,该方法很复杂。需要用if语句对三种情况进行处理,第一个文件比第二个文件短,第一个文件比另一个文件长,两个文件行数相等。程序的设计思路是笔者边调试边设计写成的,比较难以用文字表达出来,因此在关键代码处都做了注释,可以去看代码的注释。程序如下:
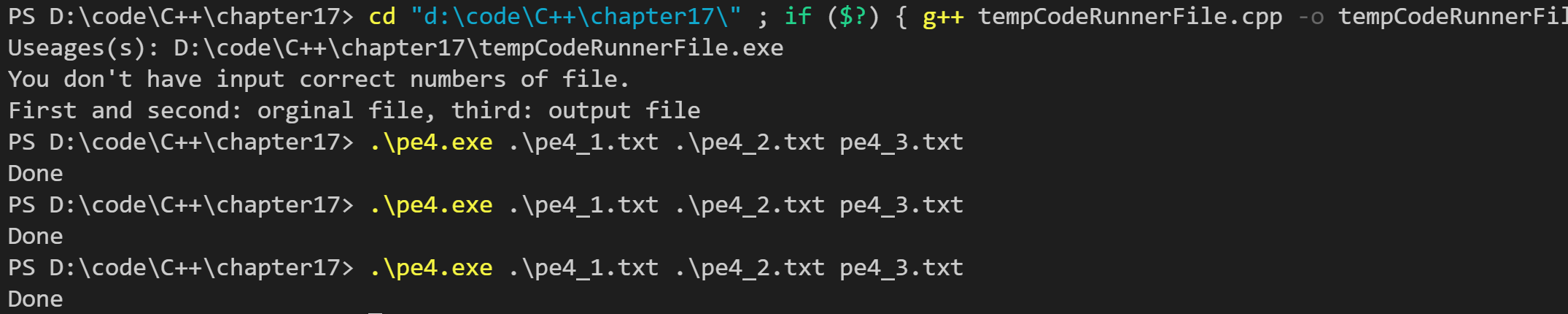
// pe4.cpp -- combination of two files to third file #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { using namespace std; // no other file if (argc == 1) { cout << "Useages(s): " << argv[0] << endl; } if (argc !=4 ) { cerr << "You don't have input correct numbers of file.\n"; cout << "First and second: orginal file, third: output file" << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // prototype file stream object ifstream fin1; ifstream fin2; ofstream fout; // file with stream fin1.open(argv[1]); fin2.open(argv[2]); fout.open(argv[3]); // if file is not open if (!fin1.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << argv[1] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if (!fin2.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << argv[2] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if (!fout.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << argv[3] << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } // get file1 and file2 to file3 string input1, input2; int cnt_eof1 = 0; // count times the fin1.peek() == EOF int cnt_eof2 = 0; // count times the fin2.peek() == EOF while (1) { if (fin1.peek() != EOF || fin2.peek() != EOF) { if (getline(fin1, input1)) // get file1 one line { fout << input1; // file1 ont line to output if (fin2.peek() == EOF) cnt_eof2++; // get the times of fin2.peek() == EOF to realize lines of file 1 > lines of file 2 if (cnt_eof2 >= 1 && fin1.peek() != EOF) // make sure this line of file1 is not last line fout << endl; // when lines of file1 > lines of file2, should add endl to file3 } if (getline(fin2,input2)) // get file2 one line { if (fin1.peek() == EOF) cnt_eof1++; // get the times of fin1.peek() == EOF to realize lines of file 1 < lines of file 2 if (cnt_eof1 <= 1) // when lines of file2 > lines of file1 { fout << ' '; // the blank of between file1 line and file2 line fout << input2; if (fin1.peek() != EOF) // make sure the lines of file1 and lines of file2 is equal fout << endl; } else // when the lines of file2 > lines of file1 { fout << endl; fout << input2; } } } else break; } // close all file fstream fin1.clear(); fin1.close(); fin2.clear(); fin2.close(); fout.clear(); fout.close(); cout << "Done\n"; return 0; // }
运行结果如下(4幅图,1:命令行代码;2:文件1<文件2;3:文件1=文件2;4:文件3>文件2):


5. Mat和Pat想邀请它们的朋友来参加派对,就像第16章中的编程练习8那样,但现在他们希望程序使用文件。他们请您编写一个完成下面的任务的程序。
- 从文本文件mat.dat中读取Mat的朋友的姓名清单,其中每一行为一个朋友。姓名将被存储在容器,然后按照顺序显示出来。
- 从文本文件pat.dat中读取Pat的朋友的姓名清单,其中每一行为一个朋友。姓名将被存储在容器,然后按照顺序显示出来。
- 合并两个清单,删除重复的条目,并将结果保存在文件matnpat.dat中,其中每行为一个朋友。
本题不算难,使用两个vector容器来存储mat.dat的姓名和pat.dat的姓名,存储的是文本格式。存储之后,使用set_union()来合并两个清单(注意,使用set_union()之前,需要对两个容器进行排序。),合并之后在将结果存储进一个新的文件中,程序如下:
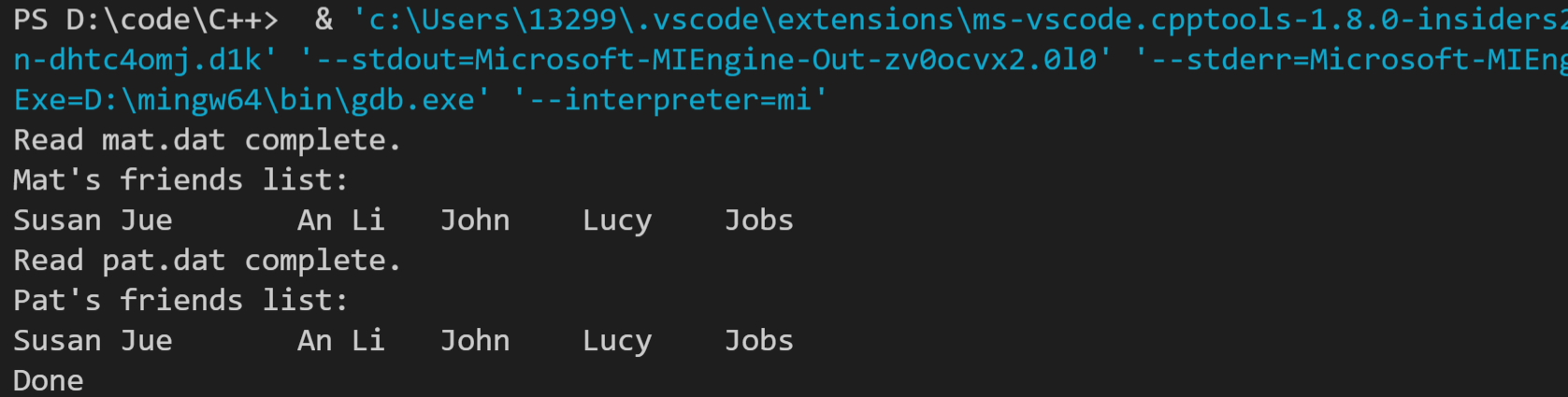
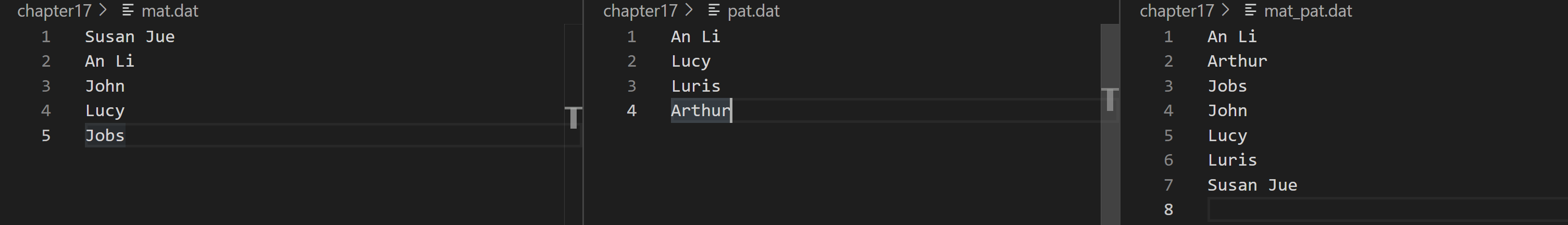
// pe5.cpp -- read name form file and store name to vector #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <iterator> inline void Showname(const std::string & s) { std::cout << s << "\t"; } int main() { using namespace std; // prototype fstream ifstream fin; ofstream fout; // file name string mat_file("mat.dat"); string pat_file("pat.dat"); string mat_pat_file("mat_pat.dat"); // prototype vector vector<string> mat; vector<string> pat; vector<string> mat_pat; // file link with fstream string name; // temp to get a line // get name from mat.dat fin.open(mat_file.c_str()); if (!fin.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << mat_file << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while (getline(fin, name)) { mat.push_back(name); } cout << "Read " << mat_file << " complete.\n"; cout << "Mat's friends list:\n"; for_each(mat.begin(), mat.end(), Showname); cout << endl; fin.clear(); fin.close(); // get name from pat.dat fin.open(pat_file.c_str()); if (!fin.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open " << mat_file << endl; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while (getline(fin, name)) { pat.push_back(name); } cout << "Read " << pat_file << " complete.\n"; cout << "Pat's friends list:\n"; for_each(mat.begin(), mat.end(), Showname); cout << endl; fin.clear(); fin.close(); // set_union(mat and pat) // before use set_union(), need to sort() two contains sort(mat.begin(), mat.end()); sort(pat.begin(), pat.end()); set_union(mat.begin(), mat.end(), pat.begin(), pat.end(), insert_iterator< vector<string> >(mat_pat, mat_pat.begin())); // restore the result to mat_pat.dat fout.open(mat_pat_file.c_str()); for (auto X : mat_pat) { fout << X << endl; } fout.clear(); fout.close(); cout << "Done\n"; return 0; }
运行结果如下(图1:程序输出结果,图2:各个文件内容):
6. 考虑14章的编程练习5中的类定义。如果还没有完成这个练习,请现在就做,然后完成下面的任务。
编写一个程序,它使用标准C++I/O、文件I/O以及14章的编程练习5中的定义employee、manager、fink和highfink类型的数据。该程序应包含程序清单17.17中的代码行,即允许用户将新数据添加到文件中。该程序首次被运行时,将要求用户输入数据,然后显示数据,并将这些信息保存到一个文件中。当该程序再次被运行时,将首先读取并显示文件中的数据,然后让用户添加数据,并显示所有的数据。差别之一是,应该通过一个指向employee类型的指针数组来处理数据。这样,指针可以指向employee对象,也可以指向从employee派生出来的其他三种对象的任何一种。使数组较小有助于检查程序,例如,您可能将数组限定为最多包含10个元素:
const int MAX = 10; ... employee * pc[MAX];
通过键盘输入,程序应使用一个菜单,让用户选择要创建的对象类型。菜单将使用一个switch,以便使用new来创建指定类型的对象,并将它的地址赋给pc数组中的一个指针。然后该对象可以使用虚函数setall()来提示用户输入相应的数据:
pc[i]->setall(); // invokes function corresponding to type of object
为将数据保存到文件中,应设计一个虚函数writeall():
for (i = 0; i < index; i++) pc[i]->writeall(fout);// fout ofstream connected to output file
注意:对于这个练习,应使用文本I/O,而不是二进制I/O(遗憾的是,虚对象包含指向虚函数指针表的指针,而write()将把这种信息复制到文件中。使用read()读取文件的内容,以填充对象时,函数指针值将为乱码,这将扰乱虚函数的行为)。可使用换行符将字段分隔开,这样在输入时将很容易识别各个字段,也可以使用二进制I/O,但不能将对象作为一个整体写入,而应该提供分别对每个类成员应用write()和read()的类方法。这样,程序将只把所需的数据保存到文件中。
比较难处理的部分是使用文件恢复数据。问题在于:程序如何才能直到接下来要恢复的项目是employee对象、manager对象、fink对象还是highfink对象?一种方法是,在对象的数据写入文件时,在数据前面添加上一个指示对象类型的整数。这样,在文件输入时,程序便可以读取该整数,并使用switch语句创建一个适当的对象来接受数据:
enum classkind{Employee, Manager, Fink, Highfink}; // in class header ... int classtype; while ((fin>>classtype).get(ch)){ // newline separates int from data switch(classtype){ case Employee : pc[i] = new employee; : break; } }
然后便可以使用指针调用虚函数getall()来读取信息:
pc[i++]->getall();
本题不算难,但是实现上比较复杂,之前笔者第14章练习5是使用一个虚基类作为虚拟继承的基类,employee类也是从该类派生出来,笔者先修改了每个类的定义,使employee类作为虚拟继承的基类,然后分别实现题目中的功能;第一步实现了输入选择的功能,该功能在Menu()函数中实现,接着实现第一次运行程序时,输入对象并存储对象到文件的功能,这通过给类增加writeall()函数,在Menu创建对象完成后调用该函数完成;接下来实现第二次从文件读取的功能,这里采用首次运行时文件是fin是否可以打开实现,如过不可以打开文件,说明第一次创建,应该执行写入功能,如果可以打开,说明不是第一次运行,首先fin读取文件中的内容进行输出,接着提醒用户进行增加用户;最后需要实现代码17_17的命令行使用文件的功能,这里将前面的三个功能写成一个DealWith()函数,将主函数稍微修改一下,就得到了最终程序。(运行过程中存在一个问题,是由Menu函数时,并没有给分配内存导致输出显示时失败,没有找到好的解决办法,输出时,通过读取文件输出。Ps:找到了解决方法,将Menu函数的功能拓展成了输入一组雇员数据而不是一个雇员数据解决。)程序如下:
// emp.h -- header file for abstr_emp class and children #ifndef EMP_H_ #define EMP_H_ #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <iomanip> const int MAX = 10; // the number of employees // function prototype void ShowMenu(); void ListHeader(); // display the list first line // enum classkind enum classkind { Employee, Manager, Fink, Highfink }; // in class header // class prototype class employee { private: std::string fname; // employee's first name std::string lname; // employee's last name std::string job; protected: void Get(); void Data() const; void Write(std::ofstream & fo) const; void Read(std::ifstream & fi); // read from file public: employee(); employee(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j); virtual void ShowAll() const; virtual void SetAll(); virtual void writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const; virtual void readall(std::ifstream & fi); friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, employee & e); virtual ~employee(); }; class manager : virtual public employee { private: int inchargeof; protected: void Get(); void Data() const; void Write(std::ofstream & fo) const; void Read(std::ifstream & fi); // read from file public: manager(); manager(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j, int ico = 0); manager(const employee & e, int ico); manager(const manager & m); virtual void ShowAll() const; virtual void SetAll(); virtual void writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const; virtual void readall(std::ifstream & fi); }; class fink : virtual public employee { private: std::string reportsto; // to whom fink reports protected: void Get(); void Data() const; void Write(std::ofstream & fo) const; void Read(std::ifstream & fi); // read from file public: fink(); fink(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j, const std::string & rpo); fink(const employee & e, const std::string & rpo); fink(const fink & f); virtual void ShowAll() const; virtual void SetAll(); virtual void writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const; virtual void readall(std::ifstream & fi); }; class highfink : public manager, public fink { public: highfink(); highfink(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j, const std::string & rpo, int ico); highfink(const employee & e, const std::string & rpo, int ico); highfink(const fink & f, int ico); highfink(const manager & m, const std::string & rpo); highfink(const highfink & h); virtual void ShowAll() const; virtual void SetAll(); virtual void writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const; virtual void readall(std::ifstream & fi); }; // function protype // choice a object to create and save to filename void Menu(employee * e, std::ofstream & fout, char choice); // show the list of employee ar[] void ShowList(employee *ar[], int n); // Read employee from file int Readfile(std::ifstream & fin, employee * pc[], int n); // dealwith filename void DealWith(std::string & filename); #endif
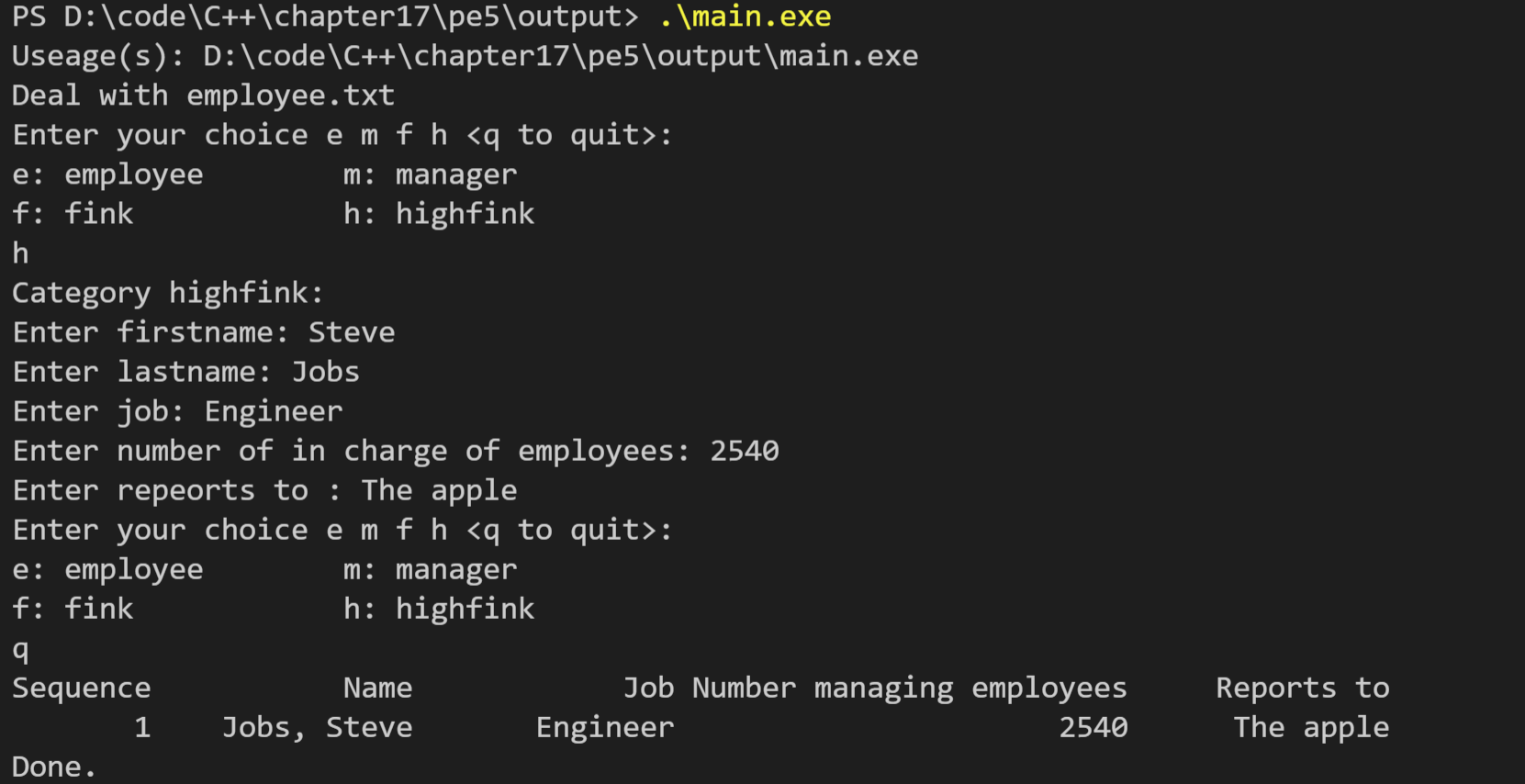
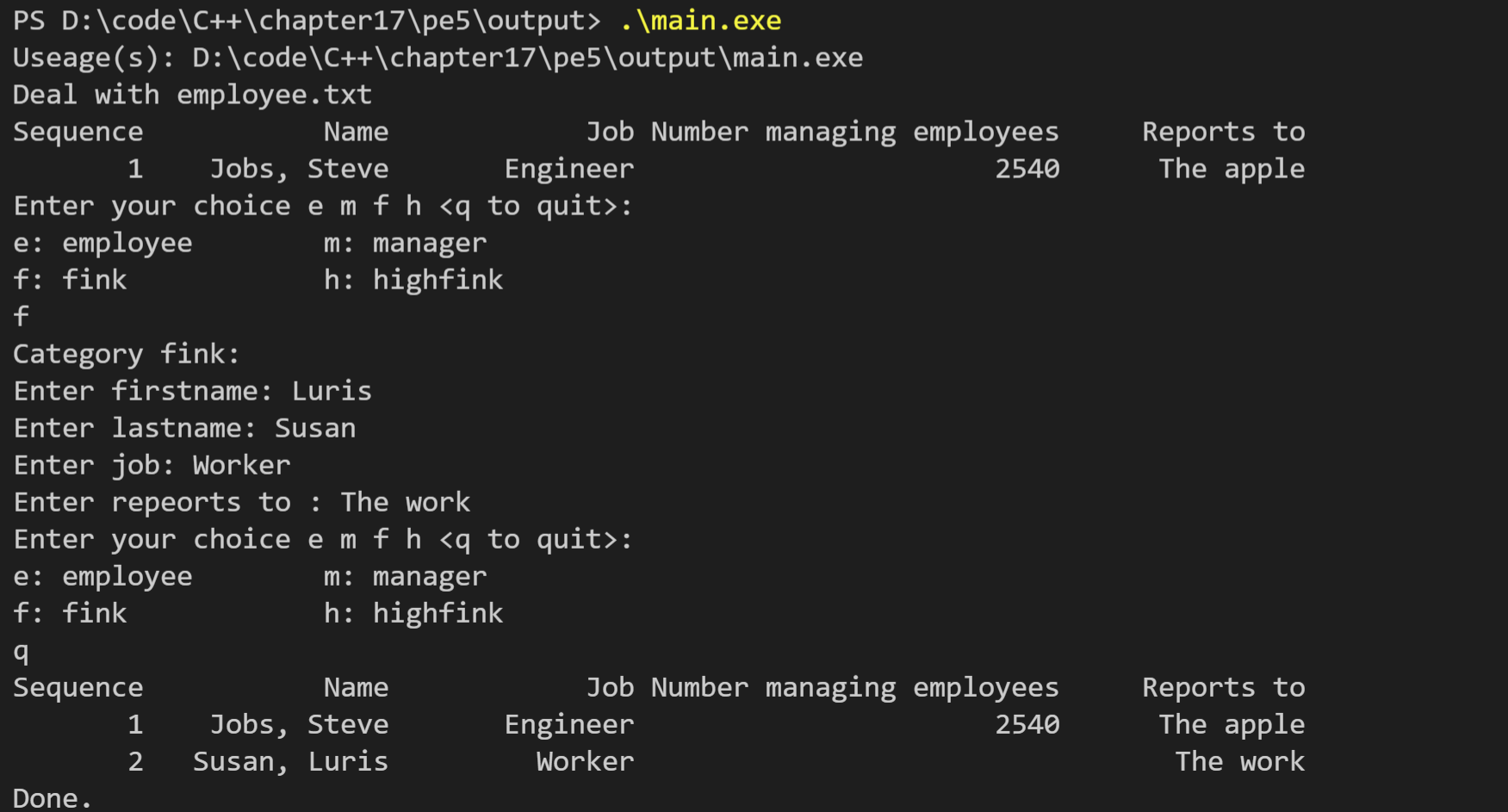
// emp.cpp -- methods for mi #include "emp.h" using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; using std::string; using std::setw; // function definition void ShowMenu() { cout << "Enter your choice e m f h <q to quit>:\n" << "e: employee m: manager\n" << "f: fink h: highfink\n"; } void ListHeader() { cout << std::right << setw(8) << "Sequence" << setw(15) << "Name" << setw(15) << "Job" << setw(26) << "Number managing employees" << setw(15) << "Reports to" << endl;; } // methods for employee_class // protected mothod void employee::Data() const { string name = lname + ", " + fname; cout << setw(15) << name << setw(15) << job; } void employee::Get() { cout << "Enter firstname: "; cin >> fname; cout << "Enter lastname: "; cin >> lname; while (cin.get() != '\n') continue; cout << "Enter job: "; getline(cin, job); } void employee::Write(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << fname << endl; fo << lname << endl; fo << job << endl; } void employee::Read(std::ifstream & fi) { getline(fi, fname); getline(fi, lname); getline(fi, job); } // public method employee::employee() { } employee::employee(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j) : fname(fn), lname(ln), job(j) { } void employee::ShowAll() const { employee::Data(); cout << endl; } void employee::SetAll() { cout << "Category employee:\n"; employee::Get(); } void employee::writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << Employee << endl; employee::Write(fo); } void employee::readall(std::ifstream & fi) { employee::Read(fi); } std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, employee & e) { os << e.lname << ", " << e.fname; return os; } employee::~employee() { } // is necessary // methods for manager class // protected method void manager::Get() { cout << "Enter number of in charge of employees: "; cin >> inchargeof; while (cin.get() != '\n') continue; } void manager::Data() const { cout << setw(26) << inchargeof; } void manager::Write(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << inchargeof << endl; } void manager::Read(std::ifstream & fi) { fi >> inchargeof; fi.get(); // } // public method manager::manager() { } manager::manager(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j, int ico) : employee(fn, ln, j), inchargeof(ico) { } manager::manager(const employee & e, int ico) : employee(e), inchargeof(ico) { } manager::manager(const manager & m) : employee(m) { inchargeof = m.inchargeof; } void manager::ShowAll() const { employee::Data(); manager::Data(); cout << endl; } void manager::SetAll() { cout << "Category manager:\n"; employee::Get(); manager::Get(); } void manager::writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << Manager << endl; employee::Write(fo); manager::Write(fo); } void manager::readall(std::ifstream & fi) { employee::Read(fi); manager::Read(fi); } // methods for fink class // protected method void fink::Get() { cout << "Enter repeorts to : "; getline(cin, reportsto); } void fink::Data() const { cout << setw(15)<< reportsto; } void fink::Write(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << reportsto << endl; } void fink::Read(std::ifstream & fi) { getline(fi, reportsto); } // public method fink::fink() { } fink::fink(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j, const std::string & rpo) : employee(fn, ln, j), reportsto(rpo) { } fink::fink(const employee & e, const std::string & rpo) : employee(e), reportsto(rpo) { } fink::fink(const fink & f) : employee(f) { reportsto = f.reportsto; } void fink::ShowAll() const { employee::Data(); cout << setw(26) << " "; fink::Data(); cout << endl; } void fink::SetAll() { cout << "Category fink:\n"; employee::Get(); fink::Get(); } void fink::writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << Fink << endl; employee::Write(fo); fink::Write(fo); } void fink::readall(std::ifstream & fi) { employee::Read(fi); fink::Read(fi); } // methods for highfink class highfink::highfink() { } highfink::highfink(const std::string & fn, const std::string & ln, const std::string & j, const std::string & rpo, int ico) : employee(fn, ln, j), manager(fn, ln, j, ico), fink(fn, ln, j, rpo) { } highfink::highfink(const employee & e, const std::string & rpo, int ico) : employee(e), manager(e, ico), fink(e, rpo) { } highfink::highfink(const manager & m, const std::string & rpo) : employee(m), manager(m), fink(m,rpo) { } highfink::highfink(const fink & f, int ico) : employee(f), manager(f, ico), fink(f) { } highfink::highfink(const highfink & h) : employee(h), manager(h), fink(h) { } void highfink::ShowAll() const { employee::Data(); manager::Data(); fink::Data(); cout << endl; } void highfink::SetAll() { cout << "Category highfink:\n"; employee::Get(); manager::Get(); fink::Get(); } void highfink::writeall(std::ofstream & fo) const { fo << Highfink << endl; employee::Write(fo); manager::Write(fo); fink::Write(fo); } void highfink::readall(std::ifstream & fi) { employee::Read(fi); manager::Read(fi); fink::Read(fi); } // function definition void Menu(employee * e, std::ofstream & fout, char choice) { while (!strchr("emfh",choice)) { cout << "Please enter e m f h\n"; cin >> choice; } switch (choice) { case 'e': e = new employee; e->SetAll(); e->writeall(fout); break; case 'm': e = new manager; e->SetAll(); e->writeall(fout); break; case 'f': e = new fink; e->SetAll(); e->writeall(fout); break; case 'h': e = new highfink; e->SetAll(); e->writeall(fout); break; } } void ShowList(employee *ar[], int n) { ListHeader(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << setw(8) << i + 1; ar[i]->ShowAll(); } } int Readfile(std::ifstream & fin, employee * pc[], int n) { int i = 0; int classtype; while (fin >> classtype) { fin.get(); switch(classtype) { case Employee : pc[i] = new employee; pc[i]->readall(fin); break; case Manager : pc[i] = new manager; pc[i]->readall(fin); break; case Fink : pc[i] = new fink; pc[i]->readall(fin); break; case Highfink : pc[i] = new highfink; pc[i]->readall(fin); break; default : break; } i++; if (i == n) break; } return i; } void DealWith(std::string & filename) { // fstream prototype std::ofstream fout; std::ifstream fin; // variable prototype char choice; employee * pc[MAX]; // prototype a pointer array to employee // link file with ofstream; fin.open(filename.c_str()); if (!fin.is_open()) { fout.open(filename.c_str()); int i; for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { ShowMenu(); cin >> choice; if (choice == 'q') break; Menu(pc[i], fout, choice); // input an employee data } fout.clear(); fout.close(); // close file fin.open(filename.c_str()); int cnt = Readfile(fin, pc, MAX); ShowList(pc, cnt); // show the data fin.clear(); fin.close(); } else { int cnt = Readfile(fin, pc, MAX); ShowList(pc, cnt); fin.clear(); fin.close(); // break link fout.open(filename.c_str(), std::ios_base::out|std::ios_base::app); int i; for (i = cnt; i < MAX; i++) { ShowMenu(); cin >> choice; if (choice == 'q') break; Menu(pc[i], fout, choice); } fout.clear(); fout.close(); fin.open(filename.c_str()); cnt = Readfile(fin, pc, MAX); ShowList(pc, cnt); } }
#include <iostream> #include "emp.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { using namespace std; string filename("employee.txt"); if (argc == 1) { cout << "Useage(s): " << argv[0] << endl; cout << "Deal with " << filename << endl; DealWith(filename);// link file with ofstream; } else { for (int a = 1; a < argc; a++) { filename = argv[a]; DealWith(filename); } } cout << "Done.\n"; return 0; }
运行结果如下(图1:首次运行,图2:运行第二次):
7. 下面是某个程序的部分代码。该程序将键盘输入读取到一个有string对象组成的vector中,将字符串内容(而不是string对象)存储到一个文件中,然后该文件的内容复制到另一个由string对象组成的vector中。
int main() { using namespace std; vector<string> vostr; string temp; // acquire strings cout << "Enter strings (empty line to quit):\n"; while (getline(cin, temp) && temp[0] != '\0') vostr.push_back(temp); cout << "Here is your input.\n"; for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(). ShowStr); // stroe in a file ofstream fout("string.dat", ios_base::out | ios_base::binary); for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), Store(fout)); fout.close(); // recover file contents vector<string> vistr; ifstream fin("string.dat", ios_base::in | ios_base::binary); if (!fin.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open file for input.\n"; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } GetStrs(fin, vistr); cout << "\nHere are the strings read from the file:\n"; for_each(vistr.begin(), vistr.end(), ShowStr); return 0; }
该程序以二进制格式打开文件,并想使用read()和write()来完成I/O。余下工作如下所述。
- 编写函数void ShowStr(const string & ),它显示一个string对象,并在显示完后换行
- 编写函数符Store,它将字符串信息写入到文件中。Store的构造函数应接受一个指定ifstream对象的参数,重载的operator(const string & )应指出要写入到文件中的字符串。一种可行的计划是,首先将字符串的长度写入到文件中,然后将字符串的内容写入到文件中。例如,如果len存储了字符串的长度,则可以这样做:
os.write((char *)& len, sizeof(std::size_t)); // store length os.write(s.data(), len); // store characters
成员函数data()返回一个指针,该指针指向一个其中存储了字符串中字符的数组。它类似于成员函数c_str(),指示后者在末尾加上了一个空字符。
- 编写函数GetStrs(),他根据文件恢复信息。该函数可以使用read来获得字符串的长度,然后使用一个循环从文件中读取相应数量的字符,并将它们附加到一个原来为空的临时string末尾。由于string的数据是私有的,因此必须使用string类的方法将数据存储到string对象中,而不能直接存储。
本题考查的是简单二进制文件的写入和读取,第一个显示函数很简单;第二个写入函数按照题目的方法,首先得到字符串的长度,然后将长度写入二进制文件,接着将字符数据写入二进制文件。注意由于第二个函数实际上是两个参数,因此可以使用类函数符,第二个参数作为()运算符重载;第三个读取函数使用while()来首先获取字符串的长度,接下来一个字符一个字符读取,读取完毕之后使添加一个空字符'\0',然后使用string构造函数将字符转换为string对象,使用容器的pushback方法将该字符串对象插入容器中。程序如下:
// pe7.cpp #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <algorithm> class Store { private: std::ofstream & os; public: Store(std::ofstream & fo) : os(fo){ } void operator()(const std::string & s); }; void Store::operator()(const std::string & s) { auto len = s.size(); // get length of string os.write((char *)&len, sizeof(std::size_t)); // write len os.write(s.data(), len); // write string data } int GetStrs(std::ifstream & is, std::vector<std::string> & vs) { size_t len; // to store the length of string int j = 0; while (is.read((char *)&len, sizeof(std::size_t))) { char temp[len + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { is.read(&temp[i], 1); // get every char } temp[len] = '\0'; vs.push_back(std::string(temp)); // add string to vector j++; } return j; // return the number of strings } void ShowStr(const std::string & s) { std::cout << s << std::endl;}; int main() { using namespace std; vector<string> vostr; string temp; // acquire strings cout << "Enter strings (empty line to quit):\n"; while (getline(cin, temp) && temp[0] != '\0') vostr.push_back(temp); cout << "Here is your input.\n"; for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), ShowStr); // stroe in a file ofstream fout("string.dat", ios_base::out | ios_base::binary); for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), Store(fout)); fout.close(); // recover file contents vector<string> vistr; ifstream fin("string.dat", ios_base::in | ios_base::binary); if (!fin.is_open()) { cerr << "Could not open file for input.\n"; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } GetStrs(fin, vistr); cout << "\nHere are the strings read from the file:\n"; for_each(vistr.begin(), vistr.end(), ShowStr); return 0; }
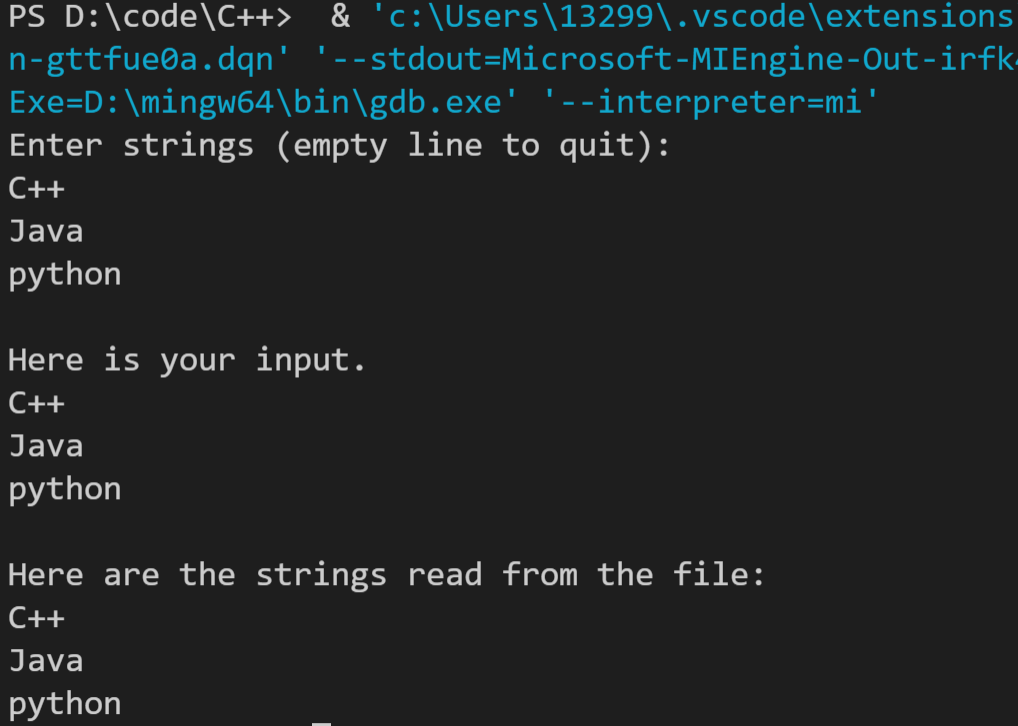
运行结果如下:



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· Vue3状态管理终极指南:Pinia保姆级教程