C++ Primier Plus(第六版) 第十六章 string类和标准模板库 编程练习答案
1.回文指的是顺读和逆读都一样的字符串。例如,“tot”和“otto”都是简单的回文。编写一个程序,让用于输入字符串,并将字符串引用传递给一个bool函数。如果字符串是回文,该函数将返回true,否则返回false。此时不要担心诸如大小写、空格和标点符号这些复杂的问题。即这个简单的版本将拒绝“Otto”和“Madam, I'm Adam”。请查看附录F中的字符串方法列表,以简化这项任务。
本题的难点是将字符串的回文返回出来,在判断是否是回文。返回回文的函数编写过程中遇到了问题,最后一个字符应该是.size()-1而不是size()。
程序如下:
// pe1.cpp -- test palindrome
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
std::string palindrome(const std::string & s);
bool is_palindrome(const std::string & s);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
string input;
cout << "Enter a word(quit to quit): ";
while (cin >> input && input != "quit")
{
if (is_palindrome(input))
cout << input << " is palindrome\n";
else
cout << input << " is not palindrome\n";
cout << "Enter a word(quit to quit): ";
}
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
std::string palindrome(const std::string & s) // get the palindrome of string s
{
std::string result;
int size = s.size();
result = s;
char temp;
for (int i = 0, j = size-1; i < j; i++, j--) // j should be size - 1
{
temp = s[i];
result[i] = result[j];
result[j] = temp;
}
return result;
}
bool is_palindrome(const std::string & s)
{
return palindrome(s) == s;
}
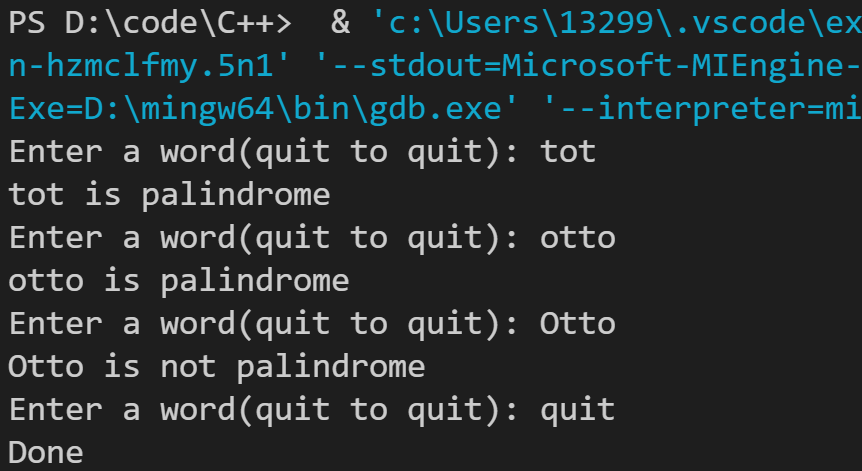
运行结果如下:
2. 与编程练习1中给出的问题相同,但要考虑诸如大小写、空格和标点符号这样的复杂问题。即“Madam, I'm Adam”将作为回文来测试。例如,测试函数可能会将字符串缩略为“madamimadam”,然后测试倒过来是否一样。不要忘了有用的cctype库,您可能从中找到几个有用的STL函数,尽管不一定非要使用它们。
本题使用练习一的代码,再次基础上增加了预处理函数,该函数通过isalpha()函数创建了notalpha()函数,用来找出非字母的字符,使用remove_if(),将非字母字符删除,删除后需要擦除尾部的区间,删除之后进行小写字母转换,利用自己编写的函数进行,通过调用自己的toLower()函数实现,该函数返回tolower()。代码如下:
// pe2.cpp -- test palindrome
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
bool notalpha(char ch) { return !isalpha(ch); } // is not alpha
char toLower(char ch) { return tolower(ch); } // ch to lower
std::string ToLower(const std::string & s); // string to lower
std::string predeal(const std::string & s); // delete not alpha and ToLower
std::string palindrome(const std::string & s);
bool is_palindrome(const std::string & s);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
string input;
cout << "Enter a line of string (quit to quit): ";
while (getline(cin, input) && input != "quit")
{
string deal_s = predeal(input);
if (is_palindrome(deal_s))
cout << input << " is palindrome\n";
else
cout << input << " is not palindrome\n";
cout << "Enter a line of string (quit to quit): ";
}
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
std::string ToLower(const std::string & s)
{
std::string temp;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
temp[i] = toLower(s[i]);
return temp;
}
std::string predeal(const std::string & s)
{
std::string deal_result;
deal_result = s;
auto end_ir = remove_if(deal_result.begin(), deal_result.end(),notalpha);
deal_result.erase(end_ir, deal_result.end());
return ToLower(deal_result);
}
std::string palindrome(const std::string & s) // get the palindrome of string s
{
std::string result;
int size = s.size();
result = s;
char temp;
for (int i = 0, j = size-1; i < j; i++, j--) // j should be size - 1
{
temp = s[i];
result[i] = result[j];
result[j] = temp;
}
return result;
}
bool is_palindrome(const std::string & s)
{
return palindrome(s) == s;
}
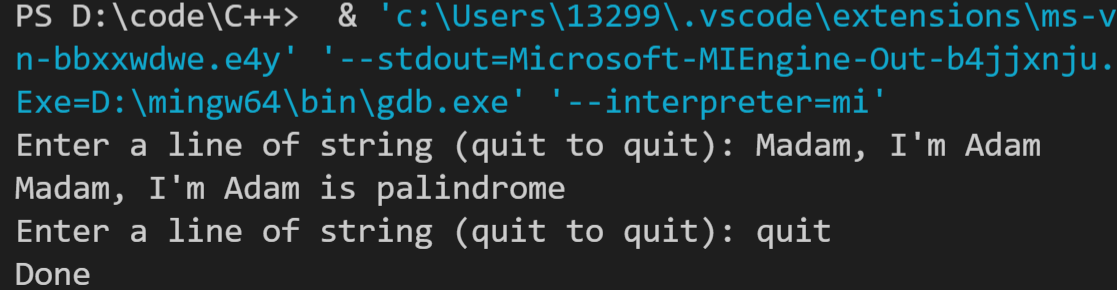
运行结果如下:
// pe3.cpp -- test hangman words form file
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::vector;
using std::ifstream;
vector<string> wordlist;
string word; // record word from file
// input words from files
ifstream inFlie;
inFlie.open("wordlist.txt");
if (!inFlie.is_open())
{
cout << "Can't open the file. Bye.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
while (inFlie >> word)
wordlist.push_back(word);
inFlie.close();
// hangman game
char play;
cout << "Will you play the game? <y/n>";
cin >> play;
play = tolower(play);
while (play == 'y')
{
srand(time(0));
string target = wordlist[rand() % wordlist.size()];
int length = target.size();
string attempt(length, '-');
string badchars;
int guesses = target.size();
cout << "Guess my secret word. It has " << length
<< " letters, and your guess\n"
<< "one letter at a time. You get "<< guesses
<< " wrong guesses.\n";
while (guesses > 0 && attempt != target)
{
char letter;
cout << "Guess a letter: ";
cin >> letter;
if (attempt.find(letter) != string::npos ||
badchars.find(letter) != string::npos)
{
cout << "You have guessed the letter. Try again.\n";
continue;
}
int pos = target.find(letter);
if (pos == string::npos)
{
cout << "Oh, bad guess!\n";
badchars += letter;
guesses--;
}
else
{
cout << "Good guess!\n";
while (pos != string::npos)
{
attempt[pos] = letter;
pos = target.find(letter,pos + 1);
}
}
cout << "Your word: " << attempt << std::endl;
if (attempt != target)
{
if (badchars.size() > 0)
cout << "Bad choices: " << badchars << std::endl;
cout << guesses << " bad guesses left\n";
}
}
if (guesses > 0)
cout << "Congratlations! You guess the word: " << target << std::endl;
else
cout << "Sorry, the word is " << target << std::endl;
cout << "Will you play another? <y/n>";
cin >> play;
}
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
wordlist.txt文件如下:
apiary beetle cereal
danger ensign florid garage health insult
jackal keeper losner manage nonce onset
plaid quilt remote stolid train useful
valid whence xenon yearn zippy
注意wordlist.txt应该与C++文件在同一个目录下,如果不在需要输入文件的绝对路径。运行结果如下:
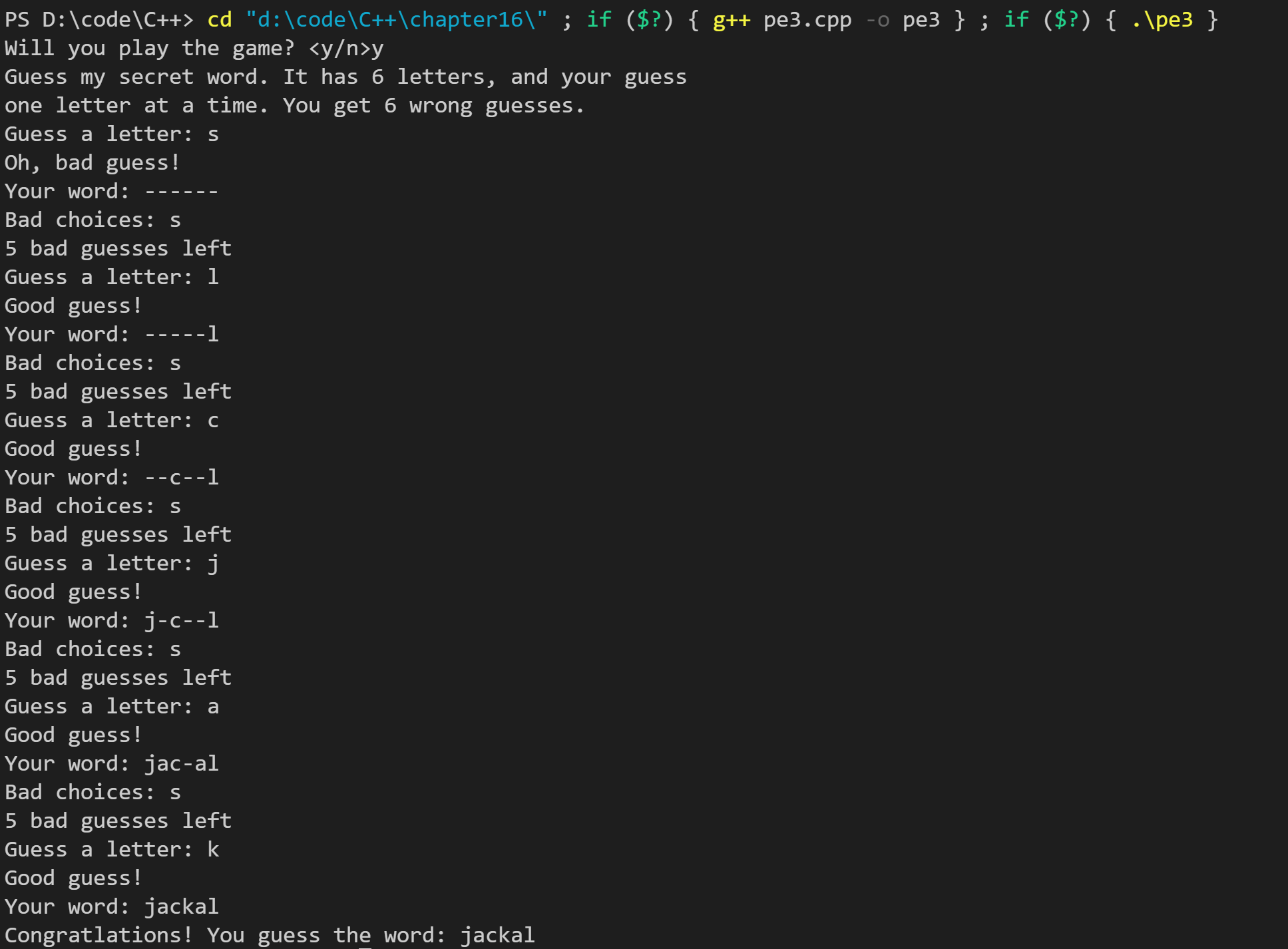

4. 编写一个具有老式风格接口的函数,其原型如下:
int reduce(long ar[], int n);
实参应是数组名和数组中的元素个数。该函数对数组进行排序,删除重复的值,返回缩减后数组中的元素数目。请使用STL函数编写该函数(如果决定使用通用的unqiue()函数,请注意它将返回结果区间的结尾)。请使用一个小程序测试该函数。
本题有两种实现方法,一种是使用set容器,只需要完成将ar的元素插入到set容器中,然后再将set容器的内容复制进ar数组里就完成了,数组的新长度可以用set容器的.size()方法,程序如下:
// pe4.cpp -- definition of int reduce(long ar[], int n) and use STL
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
int reduce(long ar[], int n);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
srand(time(0));
const int LIM = 20;
long testar[LIM];
for (int i = 0; i < LIM; i++)
testar[i] = rand() % 10;
cout << "Before using reduce() function, the test array:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < LIM; i++)
{
cout << testar[i] << " ";
if (i % 10 == 9)
cout << "\n";
}
if (LIM % 10 != 0)
cout << endl;
int len = reduce(testar, LIM);
cout << "After using reduce() function, the test array:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << testar[i] << " ";
if (i % 10 == 9)
cout << "\n";
}
if (len % 10 != 0)
cout << endl;
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
int reduce(long ar[], int n)
{
std::set<long> temp;
// std::vector<long> temp(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
temp.insert(ar[i]);
int len = temp.size();
int i;
copy(temp.begin(), temp.end(), ar);
return len;
}
另一种方法使用sort()对数组进行排序,排序完成之后使用unique完成删除相同的元素,之后用返回的超尾迭代器减去ar首端的地址即为ar的新长度,程序如下:
// version use sort and unique
int reduce(long ar[], int n)
{
std::sort(ar, ar + n);
auto air = std::unique(ar, ar + n);
return (air - ar) ;
}
运行结果如下:
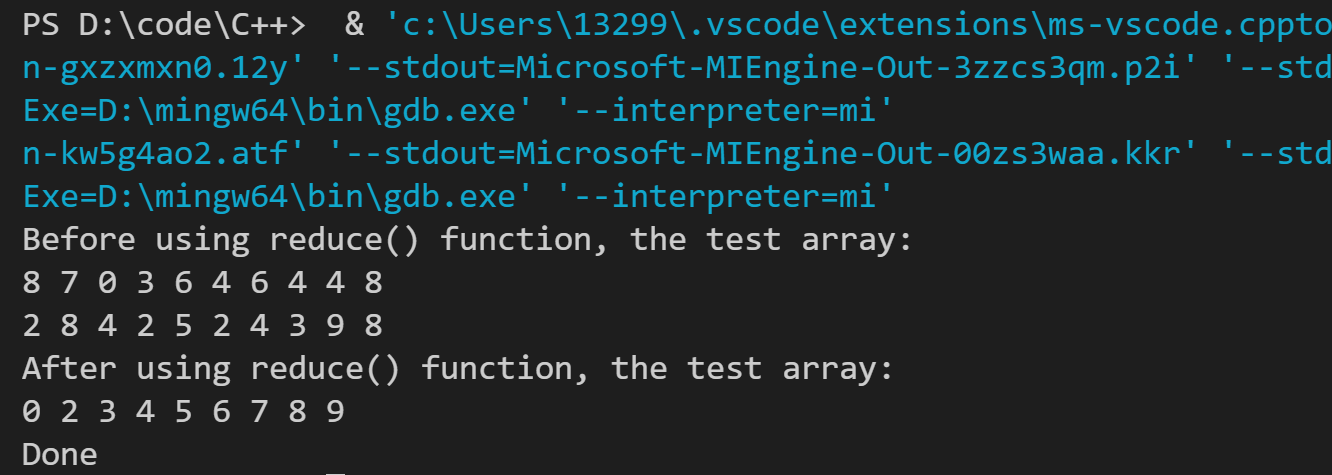
5. 问题与编程练习四相同,但要编写一个模板函数:
template<class T>
int reduce(long ar[], int n);
在使用一个long实例和string实例的小程序中测试该函数。
本题很简单,要修改的地方不多,对于sort()、unique()版本,只需要修改函数参数的声明就可以了,而se版本在此基础上修改了set声明就可以了,程序如下:
// pe5.cpp -- template definition of int reduce(long ar[], int n) and use STL
// pe4.cpp -- definition of int reduce(long ar[], int n) and use STL
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
template <class T>
int reduce(T ar[], int n);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
srand(time(0));
// test long numbers
const int LIM = 20;
long testar[LIM];
for (int i = 0; i < LIM; i++)
testar[i] = rand() % 10;
cout << "Before using reduce() function, the test array:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < LIM; i++)
{
cout << testar[i] << " ";
if (i % 10 == 9)
cout << "\n";
}
if (LIM % 10 != 0)
cout << endl;
int len = reduce<long>(testar, LIM);
cout << "After using reduce() function, the test array:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << testar[i] << " ";
if (i % 10 == 9)
cout << "\n";
}
if (len % 10 != 0)
cout << endl;
// test string
std::string test_sar[LIM] = {"Union", "for", "cat", "dog", "for", "why", "how", "what", "want", "cat",
"white", "can", "air", "dog", "for", "why", "how", "what", "want", "cat"};
cout << "Before using reduce() function, the test array:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < LIM; i++)
{
cout << test_sar[i] << " ";
if (i % 10 == 9)
cout << "\n";
}
if (LIM % 10 != 0)
cout << endl;
len = reduce<std::string>(test_sar, LIM);
cout << "After using reduce() function, the test array:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << test_sar[i] << " ";
if (i % 10 == 9)
cout << "\n";
}
if (len % 10 != 0)
cout << endl;
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
// version use set
template <class T>
int reduce(T ar[], int n)
{
std::set<T> temp;
// std::vector<long> temp(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
temp.insert(ar[i]);
int len = temp.size();
int i;
copy(temp.begin(), temp.end(), ar);
return len;
}
// // version use sort and unique
// template <class T>
// int reduce(T ar[], int n)
// {
// std::sort(ar, ar + n);
// auto air = std::unique(ar, ar + n);
// return (air - ar) ;
// }
运行结果如下:
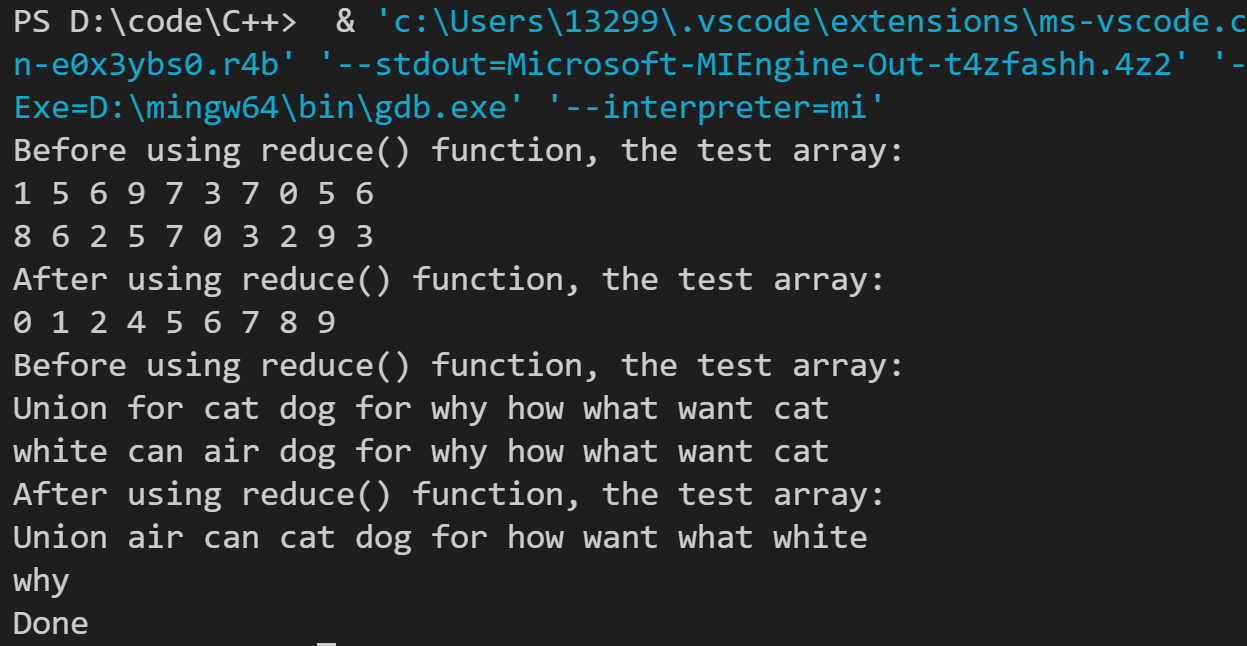
6.使用STL queue模板类而不是第12章的Queue类,重新编写程序清单12.12所示的示例。
本题不算难,首先添加queue头文件,然后添加顾客类的定义,方法实现,修改生成的队列line,不限制长度,在判断队列是否满处修改代码为if(line.size() == qs),入队改用方法push,出队用方法pop,出对之前,用line.front()方法读取队首的类。程序如下:
// pe6.cpp use queue to realize bank
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // for rand() and srand()
#include <ctime> // for time()
#include <queue>
const int MIN_PER_HR = 60;
// Custormer items
class Customer
{
private:
long arrive; // arrive time for customer
int processtime; // processing time for customer
public:
Customer() { arrive = processtime = 0; }
void set(long when);
long When() const { return arrive; }
int Ptime() const { return processtime; }
};
typedef Customer Item;
// time set to a random value in the range 1 - 3
void Customer::set(long when)
{
processtime = std::rand() % 3 + 1;
arrive = when;
}
bool newcustomer(double x); // is there a new customer
int main()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::ios_base;
using std::queue;
// setting things up
std::srand(std::time(0)); // random intializing of rand
cout << "Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\n";
cout << "Enter the maximum size of queue: ";
int qs;
cin >> qs;
queue<Item> line; // line queue holds up to qs people
cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: ";
int hours;
cin >> hours;
// simulation will run 1 cycle per minute
long cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours; // # of cycles
cout << "Enter the average number of customers per hour: ";
double perhour;
cin >> perhour;
double min_per_cust;
min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour;
Item temp; // new customer data
long turnaways = 0; // turn away by full queue
long customers = 0; // joined the queue
long served = 0; // served during the simulation
long sum_line = 0; // cmulative line length
long wait_time = 0; // time untile autoteller is free
long line_wait = 0; // cumulative time in line
// running the simulation
for (int cycle = 0; cycle < cyclelimit; cycle++)
{
if(newcustomer(min_per_cust)) // have newcomer
{
if(line.size() == qs)
turnaways++;
else
{
customers++;
temp.set(cycle); // cycle = time of arrival
line.push(temp);
// line.enqueue(temp); // add newcomer to line
}
}
if(wait_time <= 0 && !line.empty())
{
temp = line.front();
line.pop(); // attend next customer
wait_time = temp.Ptime(); // for wait_time minuetes
line_wait += cycle - temp.When();
served++;
}
if(wait_time > 0)
wait_time--;
sum_line += line.size();
}
// reporting results
if(customers > 0)
{
cout << "customers accepted: " << customers << endl;
cout << " customers served: " << served << endl;
cout << " turnaways: " << turnaways << endl;
cout << "average queue size: ";
cout.precision(2);
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
cout << (double) sum_line / cyclelimit << endl;
cout << " avergae wait time: "
<< (double) line_wait / served << "minutes\n";
}
else
cout << "No customerr!\n";
cout << "Done!\n";
return 0;
}
// x = average time in minutes, between customers
// return value is true if customer shows up this minute
bool newcustomer(double x)
{
return (std::rand() * x / RAND_MAX < 1);
}
运行结果如下:
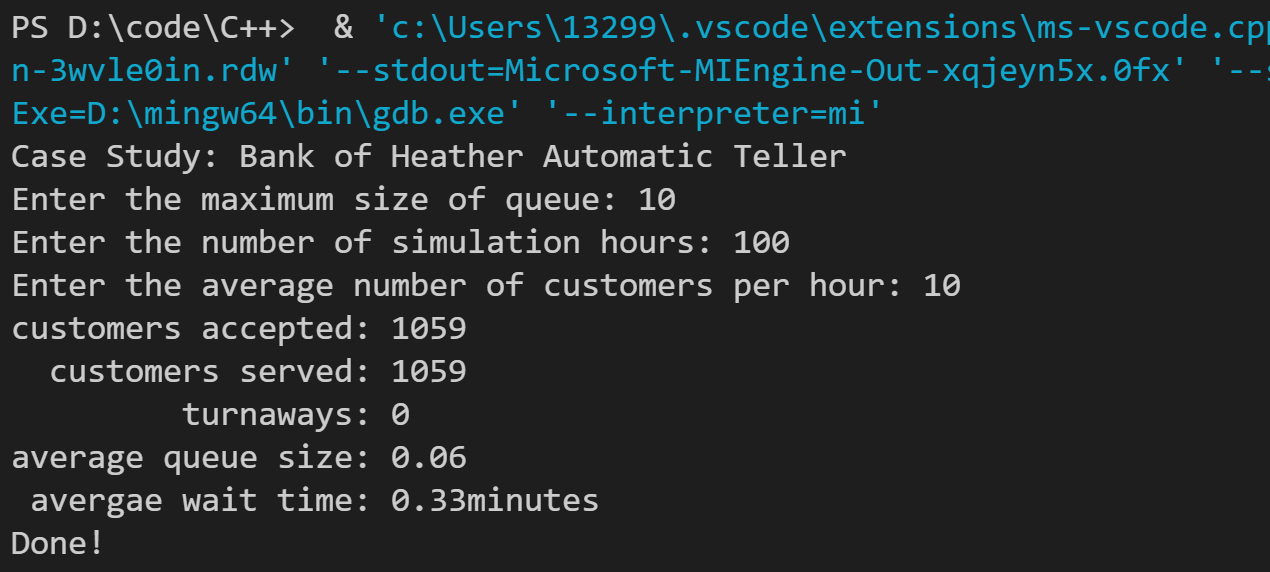
7. 彩票卡是一个常见的游戏。卡片上是带编号的圆点,其中一些圆点被随机选中。编写一个lotto()函数,它接受两个参数。第一个参数是彩票卡上圆点的个数,第二个参数是随机选择的圆点的个数。该函数返回一个vector<int>对象,其中包含(按排列后的顺序)随机选择的号码。例如,可以这样使用该函数:
vector<int>winners;
winners = Lotto(51,6);
这样将一个矢量赋给winner,该矢量包含1~51随机选定的6个数字。注意,仅仅使用rand()无法完成这项任务,因为它会生成重复的值。提示:让函数创建一个包含所有可能值的矢量,使用random_shuffle(),然后通过打乱后的矢量的第一个值来获取值。
本题采用了题里提示的思路,使用随机打乱后的第一个值来获取值,测试时发现值也有可能重复,因此加了一个while循环,判断第一个值在不在结果里,若在,重新随机生成一个顺序,直到第一个值不在结果容器里,取第一个值;还有一种方法是生成一个随机顺序,在这个随机顺序里随机取6个值,如果重复,不添加,直到不重复位置。这里采用第一种方法,程序如下:
// pe7.cpp -- simulation of lottery card
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using std::vector;
vector<int> Lotto(int numbers, int num_choices);
void show(int x) { std::cout << x << ' ';}
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int numebrs, num_choices;
cout << "Enter the numbers of point and the numebr of chooses <q to quit>: ";
while (cin >> numebrs >> num_choices)
{
auto winner = Lotto(numebrs,num_choices);
cout << "The winner's numbers is ";
std::for_each(winner.begin(), winner.end(), show);
cout << endl;
cout << "Enter next two numbers <q to quit>: ";
}
return 0;
}
vector<int> Lotto(int numbers, int num_choices)
{
vector<int> temp;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 1; i <= numbers; i++)
temp.push_back(i);
for (int i = 0; i < num_choices; i++)
{
std::random_shuffle(temp.begin(), temp.end());
// make sure the value not repeat
while (find(result.begin(), result.end(),temp[0]) != result.end())
std::random_shuffle(temp.begin(), temp.end());
result.push_back(temp[0]);
}
return result;
}
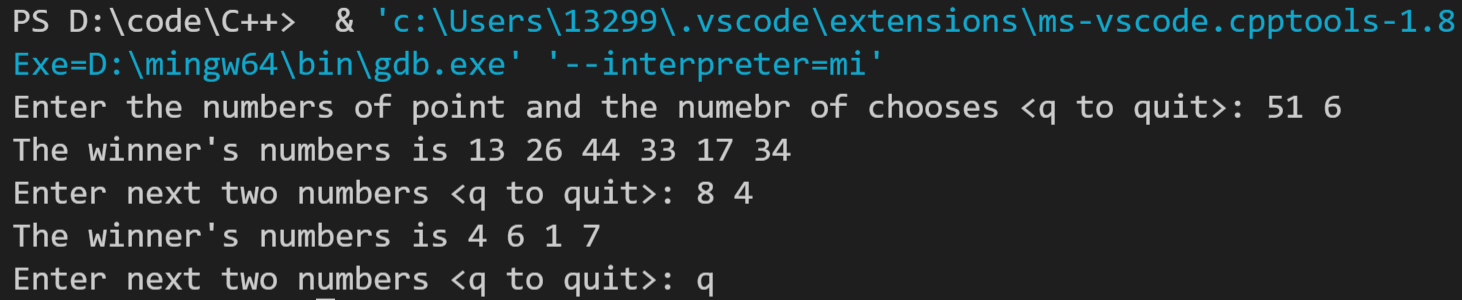
运行结果如下:
8. Mat和Pat希望邀请他们的朋友来参加派对。它们要编写一个程序完成下面的任务。
- 让Mat输入他朋友的姓名列表。姓名存储在一个容器中,然后按排列顺序显式出来。
- 让Pat输入她的朋友的姓名列表。姓名存储在另一个容器中,然后按排列后的顺序显式出来。
- 创建第三个容器,将两个列表合并,删除重复的部分,并显示这个容器的内容。
本题不算难,使用set容器来解决该问题,编写程序时,在set_union()函数的使用上出现了问题,第五个迭代器应该是一个输出迭代器,而pm_union.begin()是一个输入迭代器,因此编译时引发了错误,添加insert_iterator迭代器之后,程序正确,程序如下:
// pe8.cpp -- use set and set_union
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
void show(const std::string & s) { std::cout << s << "; "; }
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::set;
using std::string;
using std::for_each;
// mat
set<string> mat;
string name;
cout << "Dear mat, please enter your friend's name <quit to quit>: ";
while (getline(cin, name) && name != "quit")
{
mat.insert(name);
cout << "enter next name <quit to quit>: ";
}
cout << "Mat's friend list:\n";
for_each(mat.begin(), mat.end(), show);
cout << endl;
// pat
set<string> pat;
cout << "Dear pat, please enter your friend's name <quit to quit>: ";
while (getline(cin, name) && name != "quit")
{
pat.insert(name);
cout << "enter next name <quit to quit>: ";
}
cout << "Pat's friend list:\n";
for_each(pat.begin(), pat.end(), show);
cout << endl;
// set_union
set<string> pm_union;
std::set_union(mat.begin(), mat.end(), pat.begin(), pat.end(),
std::insert_iterator< set<string> >(pm_union, pm_union.begin()));
cout << "Pat and Mat friend list:\n";
for_each(pm_union.begin(), pm_union.end(), show);
cout << endl;
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
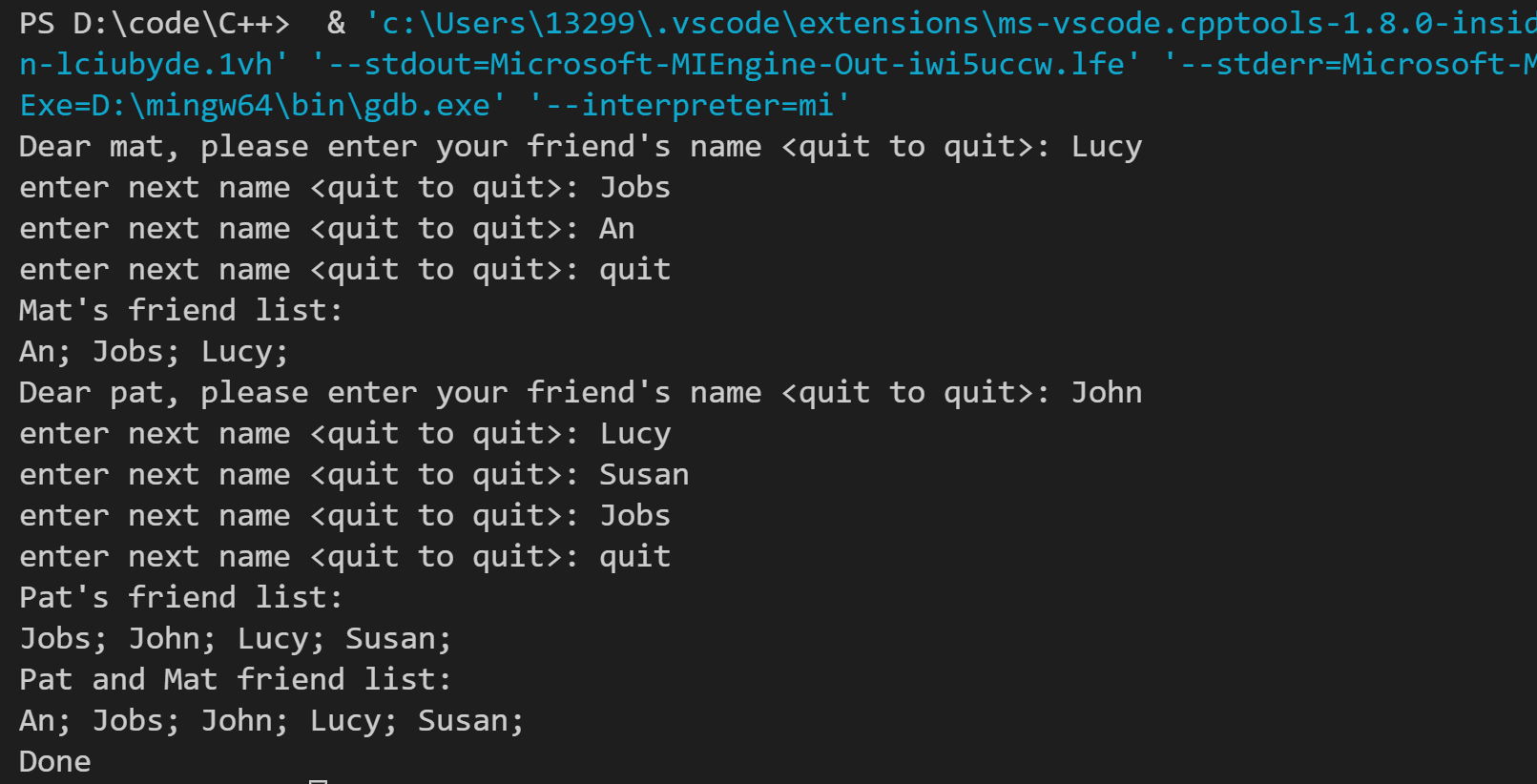
运行结果如下:
9. 相对于数组,在链表中添加和删除元素更容易,但排序速度更慢。这就引出了一种可能性:相对于使用链表算法进行排序,将链表复制到数组中,对数组进行排序,再将排序后的结果复制到链表中的速度可能更快;但这也可能占用更多的内存。请使用如下方法检验上述假设。
a. 创建大型vector<int>对象vi0,并使用rand()给它提供初始值。
b. 创建vector<int>对象vi和list<int>对象li,它们的长度都和初始值vi0相同。
c. 计算使用STL算法sort()对vi进行排序所需的时间,再计算使用list的方法与sort()进行排序所需的时间。
d. 将li重置为排序的v10的内容,并计算执行如下操作所需的时间:将li的内容复制到vi中,对vi进行排序,并将结果复制到li中。
要计算这些操作所需的时间,可使用ctime库中的clock()。正如程序清单5.14演示的,可使用下面的语句来获取开始时间:
clock_t start = clock();
再在操作结束后使用下面的语句获取经过了多长时间:
clock_t end = clock();
cout << (double)(end - start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
这种测试并非绝对可靠,因为结果取决于很多因素,如可用内存量、是都支持多处理以及数组(列表)的长度(对着要排序的元素数增加,数组相对于列表的效率将更明显)。另外,如果编译器提供了默认生成的方式和发布生成方式,请使用发布生成方式。鉴于当今计算机的速度非常快,要获得有意义的结果,可能需要使用尽可能大的数组。例如,可尝试包含100000、1000000和10000000个元素。
本题不算难,但是有几个需要注意的地方。首先使用copy时第三个迭代器应该时插入类型的迭代器,即insert_iterator类型的类型的时间。完成b、c之后,在复制vi0到li之前应该先将li和vi擦除。程序如下:
// pe9.cpp -- compare the speed list.sort and copy list to vector, sort, and copy to list
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <iterator>
const int LIM = 10000000; // numbers of elements
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::sort;
using std::list;
using std::vector;
using std::copy;
using std::endl;
using std::insert_iterator;
cout << "Number of elements: " << LIM << endl;
// generate elements of vector<int> vi0
srand(time(0)); // generate random seeds
vector<int> vi0;
for (int i = 0; i < LIM; i++)
vi0.push_back(rand() % LIM);
// copy vi0 to ci and li
vector<int> vi;
list<int> li;
copy(vi0.begin(), vi0.end(), insert_iterator<vector<int>>(vi, vi.begin()));
copy(vi0.begin(), vi0.end(), insert_iterator<list<int>>(li, li.begin()));
/**** calculate the time of sort(vi) and li.sort() ****/
// calculate the time of sort(vi.begin(), vi.end());
clock_t start = clock();
sort(vi.begin(), vi.end());
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "The time of sort(vi.begin(), vi.end()):\n";
cout << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout << endl;
// calculate the time of list.sort();
start = clock();
li.sort();
end = clock();
cout << "The time of li.sort():\n";
cout << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout << endl;
/**** calculate the time of copy() + sort(vi.begin(),vi.end()) + copy() ****/
// clear list and vi
li.erase(li.begin(), li.end());
vi.erase(vi.begin(), vi.end());
// calculate time
copy(vi0.begin(), vi0.end(), insert_iterator<list<int>>(li, li.begin()));
start = clock();
copy(li.begin(), li.end(), insert_iterator<vector<int>>(vi, vi.begin()));
sort(vi.begin(), vi.end());
copy(vi.begin(), vi.end(), insert_iterator<list<int>>(li, li.begin()));
end = clock();
cout << "The time of combination:\n";
cout << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
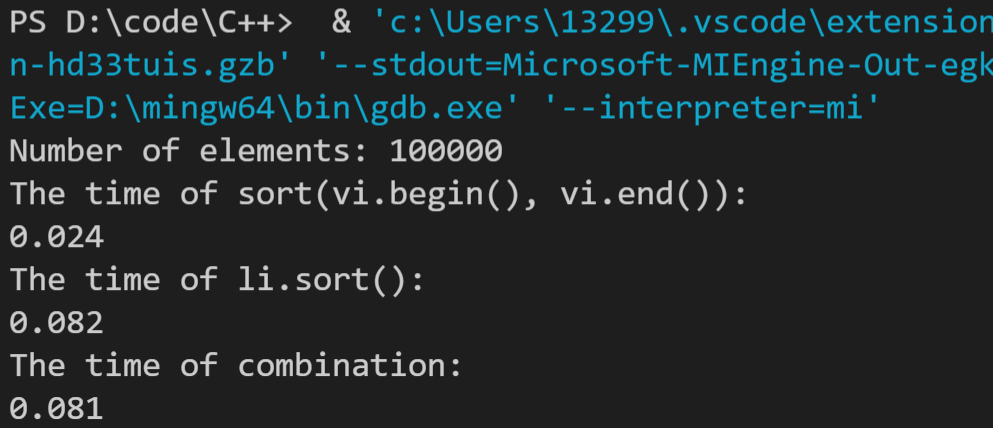
分别设置元素数为100000、1000000、10000000,运行结果如下:
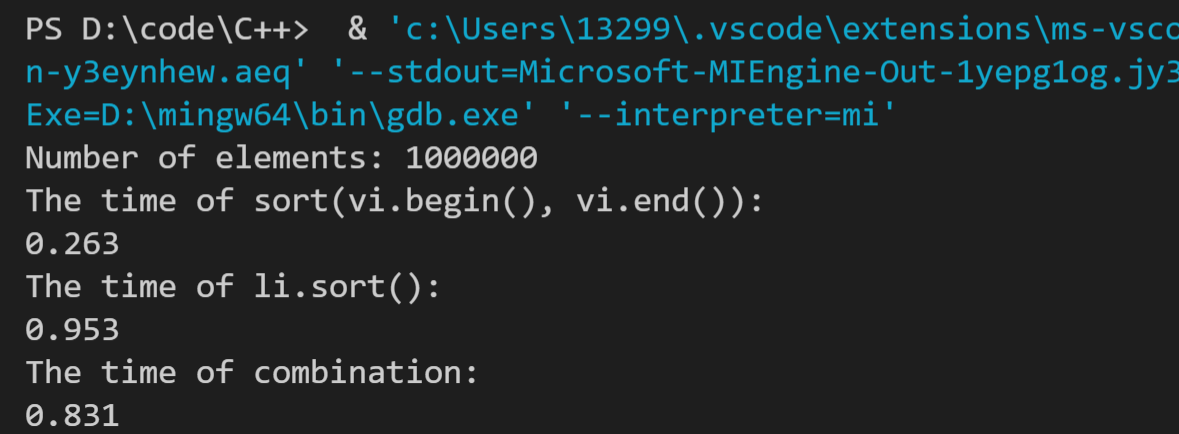
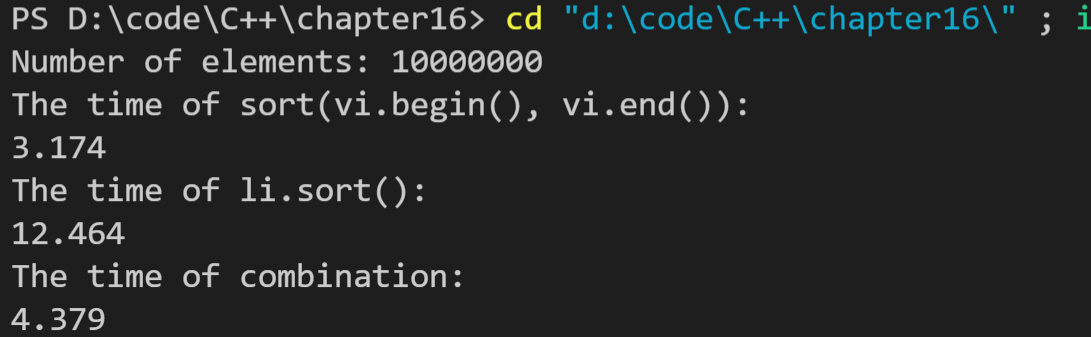
最后一个没有使用vscode自带的调试工具,猜测该工具可能限制了内存,最后一个结果计算不出来,使用了命令行运行,可以计算出结果。
10. 请按如下方式修改程序清单16.9(vect3.cpp)。
a. 在结构Review中添加成员price。
b. 不要使用vector<Review>来存储输入,而使用vector<shared_ptr<Review>>。别忘了必须使用new的返回指针来初始化shared_ptr。
c. 在输入阶段结束后,使用一个循环让用户选择如下方式之一显示书籍:按原始顺序显示、按字母表顺序显示、按评级升序显示、按评级降序显示、按价格升序显示,按价格降序显示、退出。
下面是一种可能的解决方案:获取输入后,在创建一个shared_ptr矢量,并用原始数组初始化它。定义一个对指向结构的指针进行比较的operator<()函数,并使用它对第二个矢量进行排序,让其中的shared_ptr按其指向对象中的书名排序。重复上述过程,创建按rating和price排序的shared_ptr矢量。请注意,通过使用rbegin()和rend(),可避免创建相反的顺序排列的shared_ptr矢量。
本题比较复杂,考查了shared_ptr智能指针的使用,排序函数的程序编写,由于名称都比较长,因此可以采用typedef简化编码。程序如下:
// pe10.cpp -- using STL functions and shared_ptr
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
#include <iterator>
struct Review{
std::string title;
int rating;
double price;
};
// using name
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::vector;
using std::for_each;
using std::shared_ptr;
using std::sort;
using std::copy;
using std::insert_iterator;
// simplify the name
typedef shared_ptr<Review> SpR;
typedef vector<SpR> VSpR;
typedef insert_iterator<VSpR> insert_ir_VSpR;
bool FillReview(Review & rr); // input a book
SpR make_Review(Review & rr); // return a shared_ptr of a book
void ShowMenu(); // display the menu
void ShowReview(const SpR spr); // show a book
// compare the book of title
bool operator<(const SpR spr1, const SpR spr2);
// compare the book of rating
bool compare_rating(const SpR spr1, const SpR spr2);
// compare the book of price
bool compare_price(const SpR spr1, const SpR spr2);
void ShowBooks(const VSpR & vspr);
int main()
{
// input the book to books_spr
VSpR books_ptr;
vector<Review> books;
Review temp;
while (FillReview(temp))
books_ptr.push_back(make_Review(temp));
VSpR temp_books_ptr; // prototype a temp_books_ptr to restore result
// output menu
ShowMenu();
// display books_list
char choice;
while (cin >> choice && choice != 'q')
{
// if input other char
if(!strchr("abcdef",choice))
{
cout << "Please enter a a, b, c, d, e, f, q <q to quit>: ";
continue;
}
switch (choice)
{
case 'a': cout << "Orignal order:\nRating\tBook\tprice\n";
for_each(books_ptr.begin(), books_ptr.end(), ShowReview);
break;
case 'b': temp_books_ptr.erase(temp_books_ptr.begin(),
temp_books_ptr.end());
copy(books_ptr.begin(), books_ptr.end(),
insert_ir_VSpR(temp_books_ptr, temp_books_ptr.begin()));
cout << "Letter order:\nRating\tBook\tprice\n";
sort(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end());
for_each(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(), ShowReview);
break;
case 'c': temp_books_ptr.erase(temp_books_ptr.begin(),
temp_books_ptr.end());
copy(books_ptr.begin(), books_ptr.end(),
insert_ir_VSpR(temp_books_ptr, temp_books_ptr.begin()));
cout << "Rating ascending order:\nRating\tBook\tprice\n";
sort(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(),compare_rating);
for_each(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(), ShowReview);
break;
case 'd': temp_books_ptr.erase(temp_books_ptr.begin(),
temp_books_ptr.end());
copy(books_ptr.begin(), books_ptr.end(),
insert_ir_VSpR(temp_books_ptr, temp_books_ptr.begin()));
cout << "Rating decending order:\nRating\tBook\tprice\n";
sort(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(),compare_rating);
for_each(temp_books_ptr.rbegin(), temp_books_ptr.rend(), ShowReview);
break;
case 'e': temp_books_ptr.erase(temp_books_ptr.begin(),
temp_books_ptr.end());
copy(books_ptr.begin(), books_ptr.end(),
insert_ir_VSpR(temp_books_ptr, temp_books_ptr.begin()));
cout << "Price ascending order:\nRating\tBook\tprice\n";
sort(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(),compare_price);
for_each(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(), ShowReview);
break;
case 'f': temp_books_ptr.erase(temp_books_ptr.begin(),
temp_books_ptr.end());
copy(books_ptr.begin(), books_ptr.end(),
insert_ir_VSpR(temp_books_ptr, temp_books_ptr.begin()));
cout << "Price decending order:\nRating\tBook\tprice\n";
sort(temp_books_ptr.begin(), temp_books_ptr.end(),compare_price);
for_each(temp_books_ptr.rbegin(), temp_books_ptr.rend(), ShowReview);
break;
}
ShowMenu();
}
cout << "Done";
return 0;
}
bool FillReview(Review & rr)
{
std::cout << "Enter the book title (quit to quit): ";
std::getline(std::cin, rr.title);
if (rr.title == "quit")
return false;
std::cout << "Enter book rating: ";
std::cin >> rr.rating;
std::cout << "Enter book price: ";
std::cin >> rr.price;
while (std::cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
return true;
}
SpR make_Review(Review & rr)
{
return SpR(new Review(rr));
}
void ShowMenu()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
cout << "Choice the display order <q to quit>:\n";
cout << "a: orignal order b: letter order\n";
cout << "c: rating ascending d: rating decending\n";
cout << "e: price ascendding f: price decending\n";
cout << "q: quit\n";
}
void ShowReview(const SpR spr)
{
std::cout << spr->rating << "\t" << spr->title << "\t$" << spr->price << std::endl;
}
bool operator<(const SpR spr1, const SpR spr2)
{
if (spr1->title < spr2->title)
return true;
else if (spr1->title == spr2->title && spr1->rating < spr2->rating)
return true;
else if (spr1->title == spr2->title && spr1->rating == spr2->rating
&& spr1->price < spr2->price)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool compare_rating(const SpR spr1, const SpR spr2)
{
if (spr1->rating < spr2->rating)
return true;
else if (spr1->rating == spr2->rating && spr1->title < spr2->title)
return true;
else if (spr1->title == spr2->title && spr1->rating == spr2->rating
&& spr1->price < spr2->price)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool compare_price(const SpR spr1, const SpR spr2)
{
if (spr1->price < spr2->price)
return true;
else if (spr1->price == spr2->price && spr1->title < spr2->title)
return true;
else if (spr1->title == spr2->title && spr1->price == spr2->price
&& spr1->rating < spr2->rating)
return true;
else
return false;
}
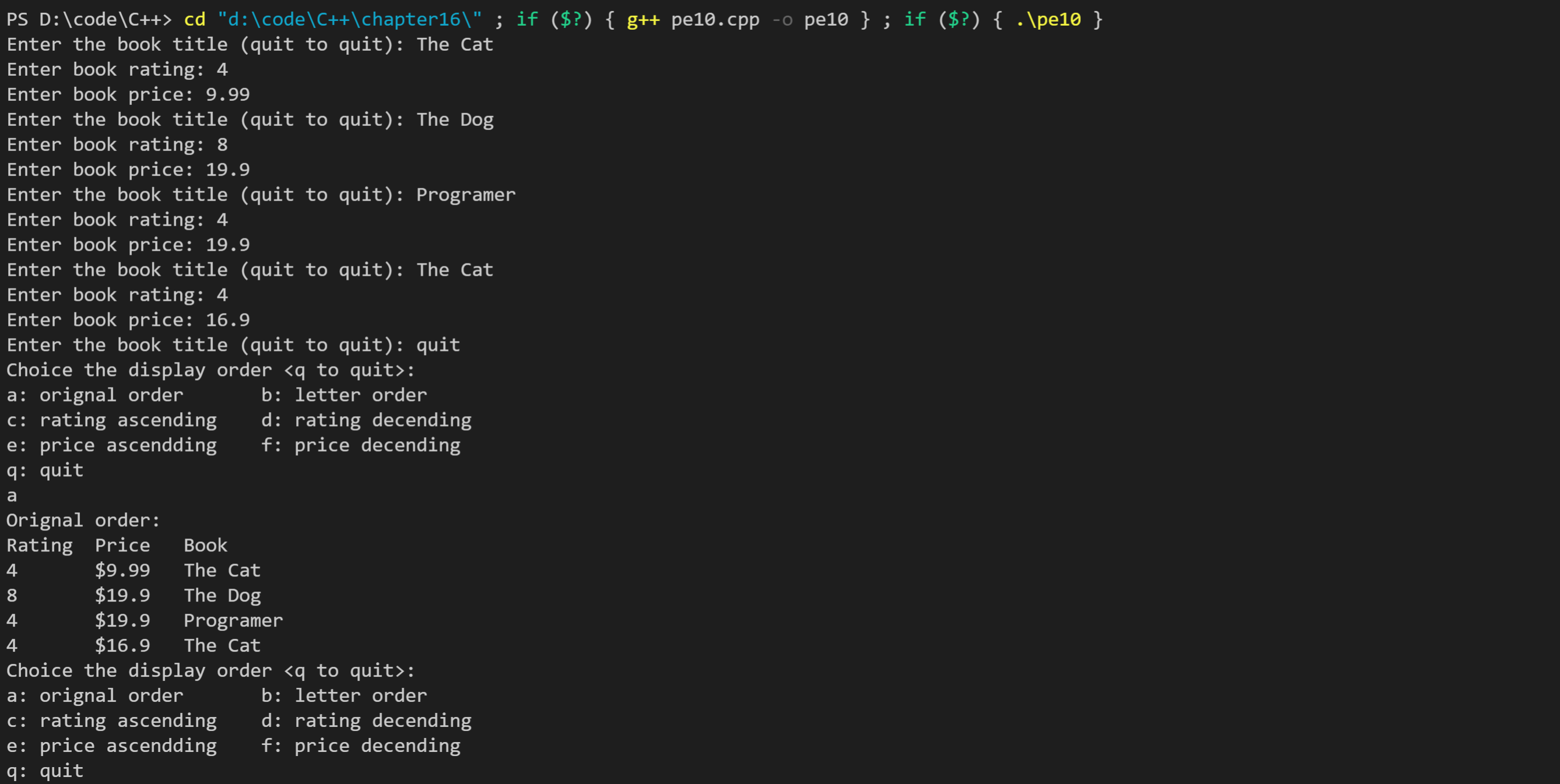
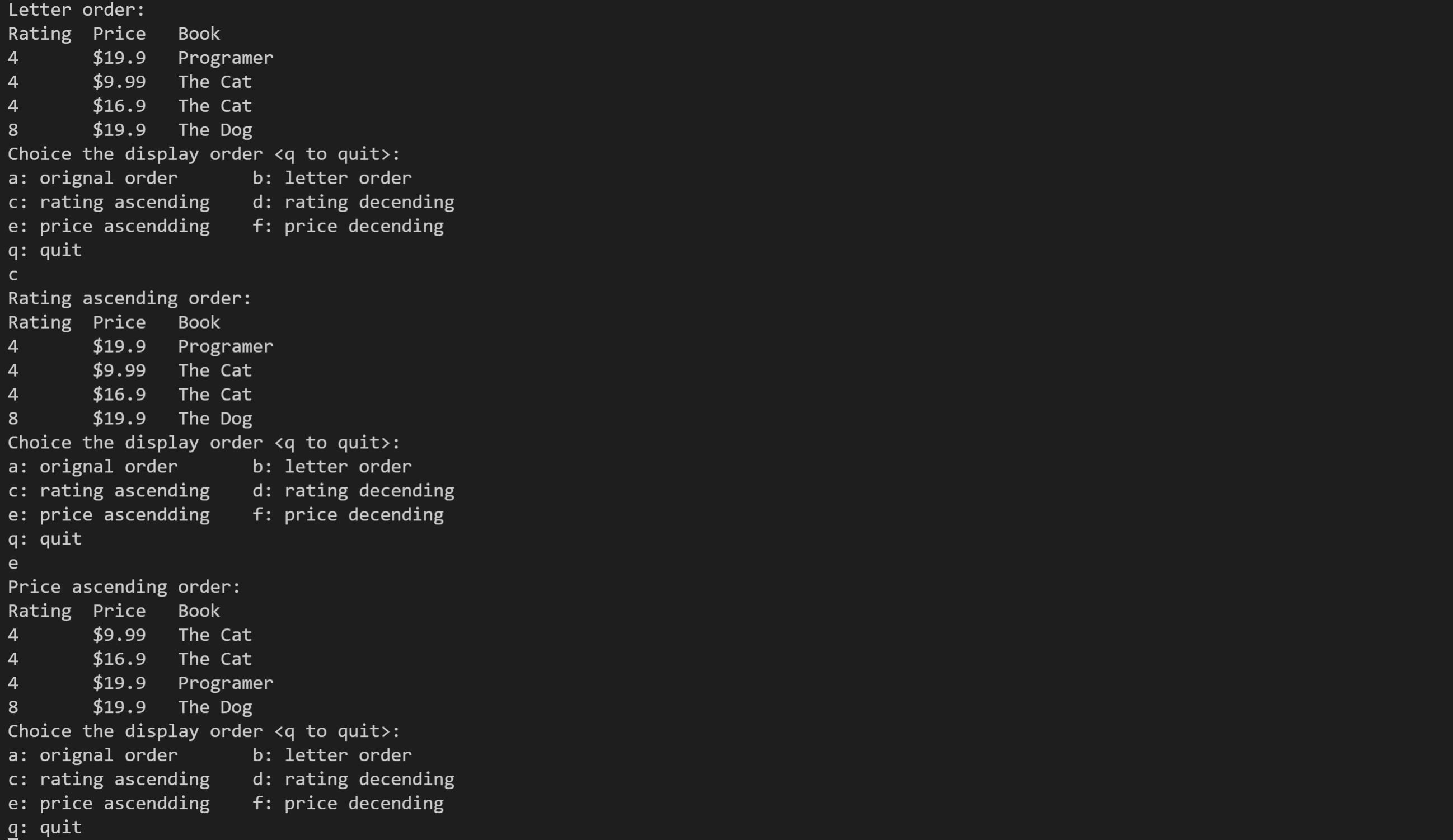
运行结果如下: