1. 对于下面的类声明:
class Cow
{
char name[20 ];
char * hobby;
double weight;
public :
Cow();
Cow(const char * nm, const char * ho, double wt);
Cow(const Cow & c);
~Cow();
Cow & operator =(const Cow & c);
void ShowCow () const
};
给这个类提供实现,并编写一个使用所有函数的小程序。
#ifndef COW_H_
#define COW_H_
class Cow
{
char name[20 ];
char * hobby;
double weight;
public :
Cow ();
Cow (const char * nm, const char * ho, double wt);
Cow (const Cow & c);
~Cow ();
Cow & operator =(const Cow & c);
void ShowCow () const
};
#endif
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "cow.h"
Cow::Cow ()
{
name[0 ] = '\0' ;
hobby = NULL ;
weight = 0.0 ;
}
Cow::Cow (const char * nm, const char * ho, double wt)
{
strcpy (name, nm);
hobby = new char [strlen (ho) + 1 ];
strcpy (hobby, ho);
weight = wt;
}
Cow::Cow (const Cow & c)
{
strcpy (name, c.name);
hobby = new char [strlen (c.hobby) + 1 ];
strcpy (hobby, c.hobby);
weight = c.weight;
}
Cow::~Cow ()
{
delete [] hobby;
}
Cow & Cow::operator =(const Cow & c)
{
strcpy (name, c.name);
hobby = new char [strlen (c.hobby) + 1 ];
strcpy (hobby, c.hobby);
weight = c.weight;
return *this ;
}
void Cow::ShowCow () const
{
std::cout << "Name: " << name << ", hobby: " << hobby << ", weight = " << weight << '\n' ;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "cow.h"
int main ()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int num;
char tname[20 ];
double wt;
char tho[20 ];
cout << "Enter the number of student: " ;
cin >> num;
cin.get ();
Cow cows[num];
int i;
for (i = 0 ; i < num; i++)
{
cout << "Student #" << i + 1 << ":\n" ;
cout << "Enter student's name<empty line to quit>: " ;
cin.getline (tname, 20 );
if (strcmp (tname, "" ) == 0 )
break ;
cout << "Enter the hobby of this student: " ;
cin.getline (tho,20 );
cout << "Enter this student's weight: " ;
cin >> wt;
cin.get ();
cows[i] = Cow (tname,tho,wt);
}
int total = i;
cout << "Student list:\n" ;
for (i = 0 ; i < total; i++)
cows[i].ShowCow ();
Cow last;
last = cows[total - 1 ];
cout << "Last student is \n" ;
last. ShowCow ();
return 0 ;
}
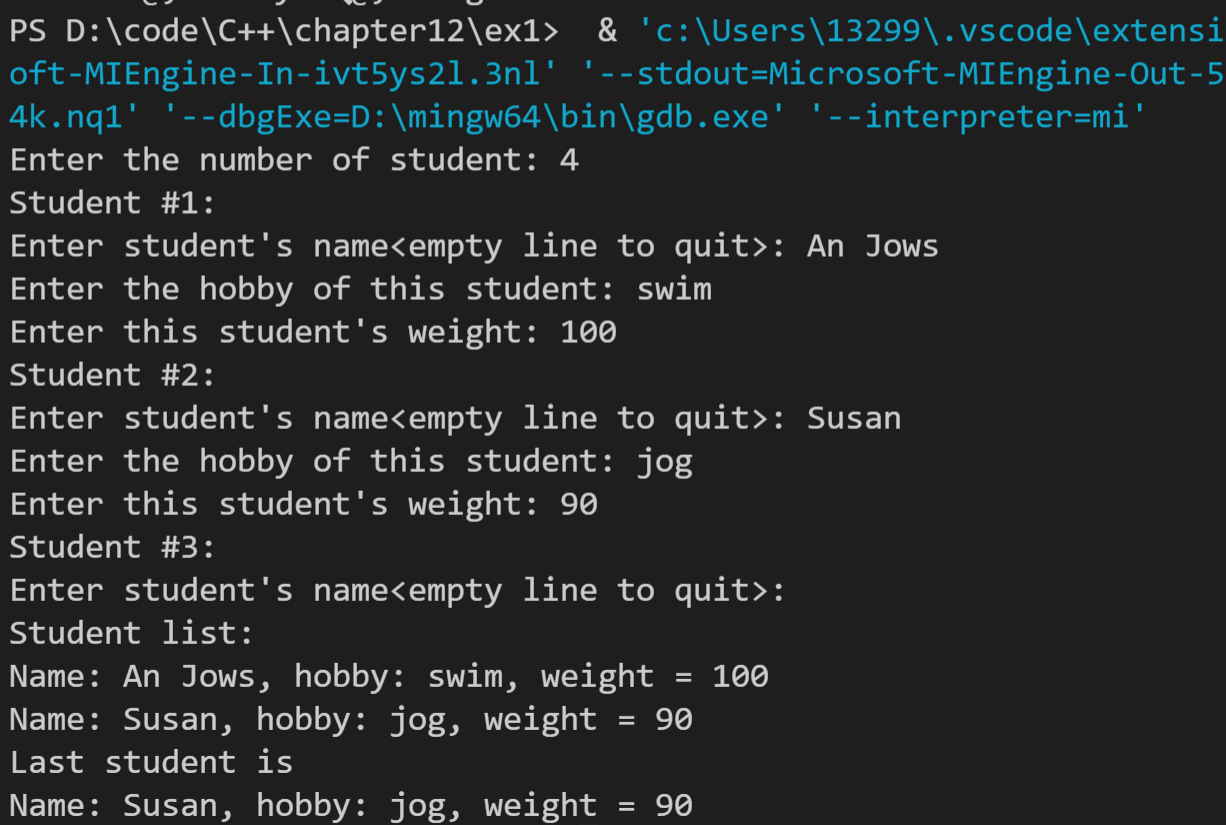
运行结果如下:
2. 通过完成下面的工作来改进String类声明(即将String1.h升级为String2.h)
a. 对+运算符进行重载, 使之可将两个字符串合并成1个。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "String2.h"
int main ()
{
String s1 (" and I am a C++ student." ) ;
String s2 = "Please enter your name: " ;
String s3;
cout << s2;
cin >> s3;
s2 = "My name is " + s3;
cout << s2 << ".\n" ;
s2 = s2 + s1;
s2.Stringup ();
cout << "The string\n" << s2 << "\ncontains " << s2.has ('A' )
<< " 'A' characters in it.\n" ;
s1 = "red" ;
String rgb[3 ] = { String (s1), String ("green" ), String ("blue" )};
cout << "Enter the name of a primary color for mixing light: " ;
String ans;
bool success = false ;
while (cin >> ans)
{
ans.Stringlow ();
for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)
{
if (ans == rgb[i])
{
cout << "That's right!\n" ;
success = true ;
break ;
}
}
if (success)
break ;
else
cout << "Try again!\n" ;
}
cout << "Bye\n" ;
return 0 ;
}
本题类实现方法不算难。本例的代码运行时没有问题,调试运行时,调用析构函数的delete str[]多次,笔者暂时没有找到原因,以后找到了会来修改。后发现原因时strcat()函数引起的,将该函数代码改成利用for循环依次给temp[]赋值;另一种方法是使用strcpy_s(temp,int size;const char *)函数,第一个函数是赋值字符串的起始点,第二个是复制字符串的长度,第三个是被复制的字符串。 样例代码如下:
#ifndef STRING2_H_
#define STRING2_H_
#include <iostream>
using std::istream;
using std::ostream;
class String
{
private :
char * str;
int len;
static int num_strings;
static const int CINLIM = 80 ;
public :
String (const char * s);
String ();
String (const String &);
~String ();
int length () const return len; }
void Stringlow ()
void Stringup ()
int has (char ch)
String & operator =(const String &);
String & operator =(const char *);
char & operator [](int i);
const char & operator [](int i) const ;
friend String operator +(const String & st1, const String & st2);
friend bool operator <(const String & st1, const String & st2);
friend bool operator >(const String & st1, const String & st2);
friend bool operator ==(const String & st1, const String & st2);
friend istream & operator >>(istream & is, String & st);
friend ostream & operator <<(ostream & os, const String & st);
static int HowMany ()
};
#endif
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include "String2.h"
int String::num_strings = 0 ;
String::String ()
{
len = 0 ;
str = new char [len + 1 ];
*str = '\0' ;
num_strings++;
}
String::String (const char * s)
{
len = strlen (s);
str = new char [len + 1 ];
strcpy (str, s);
num_strings++;
}
String::String (const String & s)
{
len = s.len;
str = new char [len + 1 ];
strcpy (str, s.str);
num_strings++;
}
String::~String ()
{
--num_strings;
delete [] str;
}
void String::Stringlow ()
{
for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++)
str[i]=tolower (str[i]);
}
void String::Stringup ()
{
for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++)
str[i]=toupper (str[i]);
}
int String::has (char ch)
{
int count = 0 ;
for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++)
if (str[i] == ch)
++count;
return count;
}
String & String::operator =(const String & s)
{
if (this == &s)
return *this ;
len = s.len;
delete [] str;
str = new char [len + 1 ];
strcpy (str, s.str);
return *this ;
}
String & String::operator =(const char * s)
{
len = strlen (s);
delete [] str;
str = new char [len + 1 ];
strcpy (str, s);
return * this ;
}
char & String::operator [](int i)
{
return str[i];
}
const char & String::operator [](int i) const
{
return str[i];
}
String operator +(const String & st1, const String & st2)
{
char * temp = new char [st1.len + st2.len + 1 ];
int i;
for (i = 0 ; i < st1.len; i++)
temp[i] = st1.str[i];
for (; i < st1.len + st2.len + 1 ; i++)
{
temp[i] = st2.str[i - st1.len];
}
temp[st1.len + st2.len + 1 ] = '\0' ;
return String (temp);
}
bool operator <(const String & st1, const String & st2)
{
return (strcmp (st1.str, st2.str) < 0 );
}
bool operator >(const String & st1, const String & st2)
{
return st2 < st1;
}
bool operator ==(const String & st1, const String & st2)
{
return (strcmp (st1.str, st2.str) == 0 );
}
istream & operator >>(istream & is, String & st)
{
char temp[String::CINLIM];
is.get (temp,String::CINLIM);
if (is)
st = temp;
while (is && is.get () != '\n' )
continue ;
return is;
}
ostream & operator <<(ostream & os, const String & st)
{
os << st.str;
return os;
}
int String::HowMany ()
{
return num_strings;
}
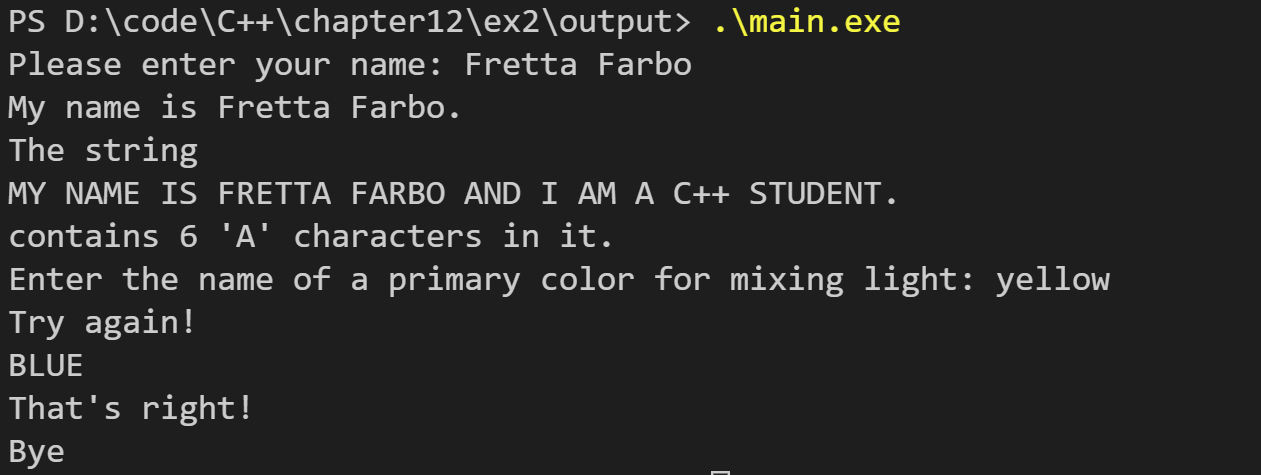
运行结果如下:
3. 新编写程序清单10.7和程序清单10.8描述的Stock类,使之使用动态分配的内存,而不是string类对象来存储股票名称。另外重载的operator<<()定义代替show()成员函数。再使用程序清单10.9测试新的定义程序。
本题修改动态分配的内存要改变的不多,修改完私有成员后,修改构造函数默认构造函数和析构函数以及返回company值函数的代码,修改完之后就实现了company的动态内存分配,由于本题没有使用复制构造函数,因此不需要编写深度复制构造函数,重载的operator<<()函数,注意需要返回os,本题代码如下:
#ifndef STOCK20_H_
#define STOCK20_H_
#include <iostream>
class Stock
{
char * company;
long shares;
double share_val;
double total_val;
void set_tot ()
public :
Stock ();
Stock (const char * str, long n = 0.0 , double pr = 0.0 );
~Stock ();
void buy (long num, double price)
void sell (long num, double price)
void update (double price)
void show () const
const Stock & topval (const Stock & s) const
const char * getcompany () const return company;}
long getshares () const return shares;}
double getshares_val () const return share_val;}
double gettotal_val () const return total_val;}
friend std::ostream & operator <<(std::ostream & os, const Stock & s);
};
#endif
#include <cstring>
#include "stock20.h"
Stock::Stock ()
{
company = new char [1 ];
company[0 ] = '\0' ;
shares = 0 ;
share_val = 0.0 ;
total_val = 0.0 ;
}
Stock::Stock (const char * str, long n, double pr)
{
company = new char [strlen (str) + 1 ];
strcpy (company, str);
if (n < 0 )
{
std::cout << "Number of shares can't be negative; "
<< company << " shares will be set to 0.\n" ;
}
else
shares = n;
share_val = pr;
set_tot ();
}
Stock::~Stock ()
{
delete [] company;
}
void Stock::buy (long num, double price)
{
if (num < 0 )
{
std::cout << "Number of shares purchased can't be negative. "
<< "Transaction is aborted.\n" ;
}
else
shares += num;
share_val = price;
set_tot ();
}
void Stock::sell (long num, double price)
{
if (num < 0 )
{
std::cout << "Number of shares sold can't be negative. "
<< "Transaction is aborted.\n" ;
}
else if (num > shares)
{
std::cout << "You can't sell more than you have! "
<< "Transaction is aborted.\n" ;
}
else
shares -= num;
share_val = price;
set_tot ();
}
void Stock::update (double price)
{
share_val = price;
}
void Stock::show () const
{
using std::cout;
using std::ios_base;
ios_base::fmtflags orig =
cout.setf (ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
std::streamsize prec = cout.precision (3 );
cout << "Company: " << company
<< "Shares: " << shares << '\n' ;
cout << " Share Price: $" << share_val;
cout.precision (2 );
cout << " Total Worth: $" << total_val << '\n' ;
cout.setf (orig,ios_base::floatfield);
cout.precision (prec);
}
const Stock & Stock::topval (const Stock & s) const
{
return s.total_val > total_val ? s : *this ;
}
std::ostream & operator <<(std::ostream & os, const Stock & s)
{
using std::ios_base;
ios_base::fmtflags orig =
os.setf (ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
std::streamsize prec = os.precision (3 );
os << "Company: " << s.getcompany ()
<< "Shares: " << s.shares << '\n' ;
os << " Share Price: $" << s.share_val;
os.precision (2 );
os << " Total Worth: $" << s.total_val << '\n' ;
os.setf (orig,ios_base::floatfield);
os.precision (prec);
return os;
}
#include <iostream>
#include "stock20.h"
const int STKS = 4 ;
int main ()
{
Stock stocks[STKS] =
{
Stock ("NanaSmart" , 12 , 20.0 ),
Stock ("Boffo Objects" , 200 , 2.0 ),
Stock ("Monolithic Obelisks" , 130 , 3.25 ),
Stock ("Fleep Enterprises" , 60 , 6.5 )
};
std::cout << "Stock holding:\n" ;
int st;
for (st = 0 ; st < STKS; st++)
std::cout << stocks[st];
const Stock * top = & stocks[0 ];
for (st = 1 ; st < STKS; st++)
top = &top->topval (stocks[st]);
std::cout << "\nMost valuable holding:\n" ;
std::cout << * top;
return 0 ;
}
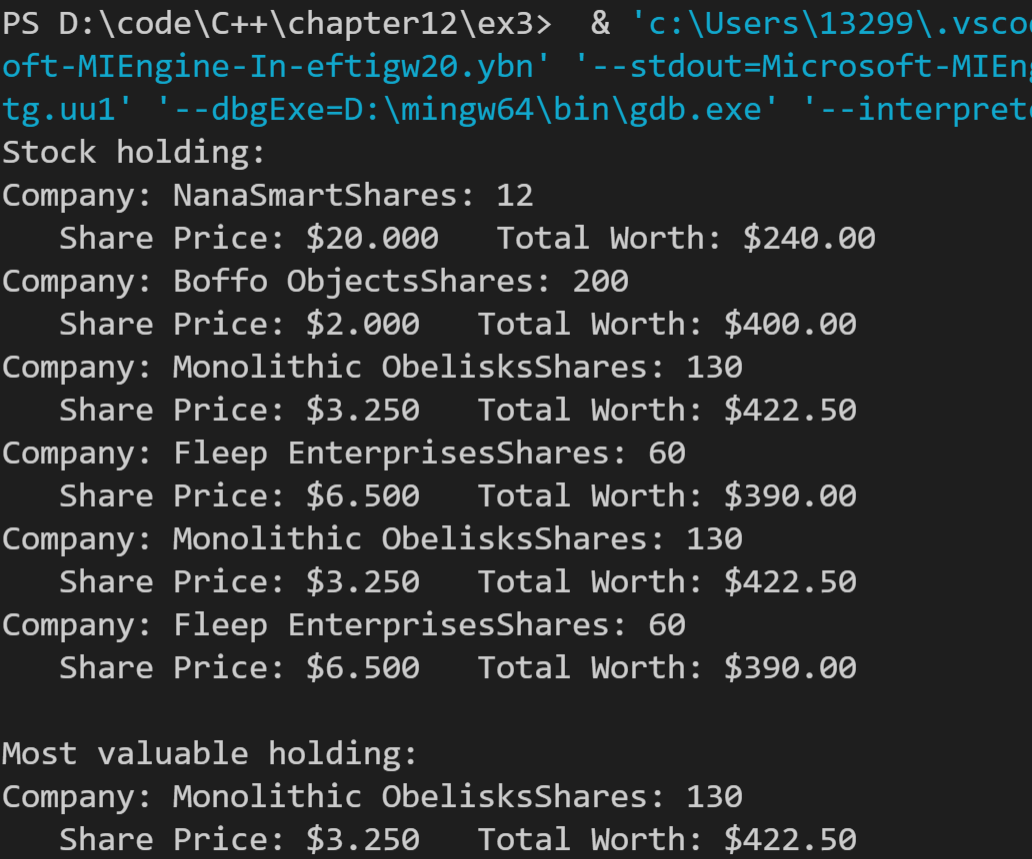
运行结果如下:
4. 请看下面程序清单10.10定义的Stack类的变量:
#ifndef STACK_H_
#define STACK_H_
typedef unsigned long Item;
class Stack
{
private :
enum {MAX = 10 };
Item * pitems;
int top;
int size;
public :
Stack (int n = MAX);
Stack (const Stack & st);
~Stack ();
bool isempty () const
bool isfull () const
bool push (const Item & item)
bool pop (Item & item)
Stack & operator =(const Stack & st);
};
#endif
正如私有成员表明的,这个类使用动态分配的数组来保存栈项。请重新编写方法,以适应这种新的表示法,并编写一个程序来演示所有的方法,包括复制构造函数和赋值运算符。
#ifndef STACK_H_
#define STACK_H_
typedef unsigned long Item;
class Stack
{
private :
enum {MAX = 10 };
Item * pitems;
int top;
int size;
public :
Stack (int n = MAX);
Stack (const Stack & st);
~Stack ();
bool isempty () const
bool isfull () const
bool push (const Item & item)
bool pop (Item & item)
Stack & operator =(const Stack & st);
};
#endif
#include "stack.h"
Stack::Stack (int n)
{
size = n;
pitems = new Item[n];
top = 0 ;
}
Stack::Stack (const Stack & st)
{
size = st.size;
pitems = new Item[st.size];
for (top = 0 ; top < st.top; top++)
pitems[top] = st.pitems[top];
top = st.top;
}
Stack::~Stack ()
{
size = 0 ;
delete [] pitems;
}
bool Stack::isempty () const
{
return top == 0 ;
}
bool Stack::isfull () const
{
return top == size;
}
bool Stack::push (const Item & item)
{
if (top == size)
return false ;
pitems[top++] = item;
return true ;
}
bool Stack::pop (Item & item)
{
if (top == 0 )
return false ;
item = pitems[--top];
return true ;
}
Stack & Stack::operator =(const Stack & st)
{
if (this == &st)
return *this ;
size = st.size;
pitems = new Item[st.size];
for (top = 0 ; top < st.top; top++)
pitems[top] = st.pitems[top];
top = st.top;
return *this ;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
#include "stack.h"
Item findmax (Stack st) ;
int main ()
{
using namespace std;
Item num;
Stack st1 (6 ) ;
Stack st2;
int count = 0 ;
cout << "Enter a seires of number, I'll show them and find the maximum.\n" ;
cout << "Enter q to quit\n" ;
while (!st1.isfull ())
{
cout << "Value #" << count + 1 << ": " ;
cin >> num;
if (!cin)
break ;
st1.push (num);
count++;
}
cout << "The list of you input number:\n" ;
st2 = st1;
while (!st2.isempty ())
{
st2.pop (num);
cout << num << '\t' ;
}
cout << endl;
Item max = findmax (st1);
cout << "The maximun of these numbers is " << max << endl;
cout << "Pop st1:\n" ;
while (!st1.isempty ())
{
st1.pop (num);
cout << num << '\t' ;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Done\n" ;
return 0 ;
}
Item findmax (Stack st)
{
Item max,temp;
st.pop (max);
while (!st.isempty ())
{
st.pop (temp);
max = max > temp ? max : temp;
}
return max;
}
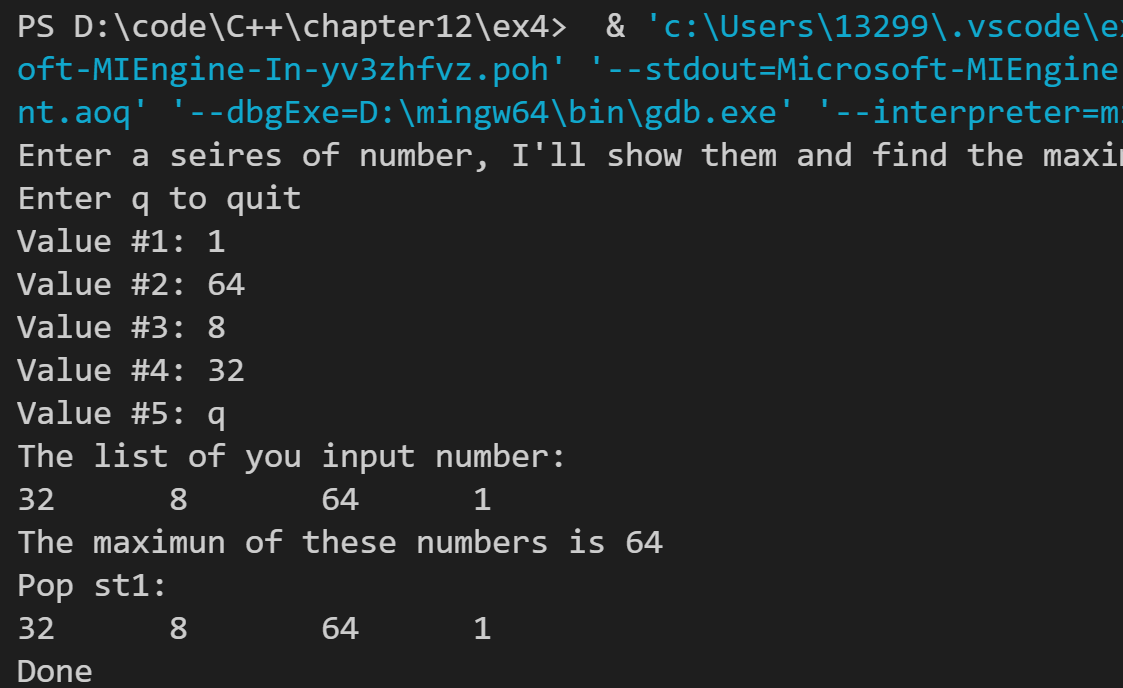
运行结果如下:
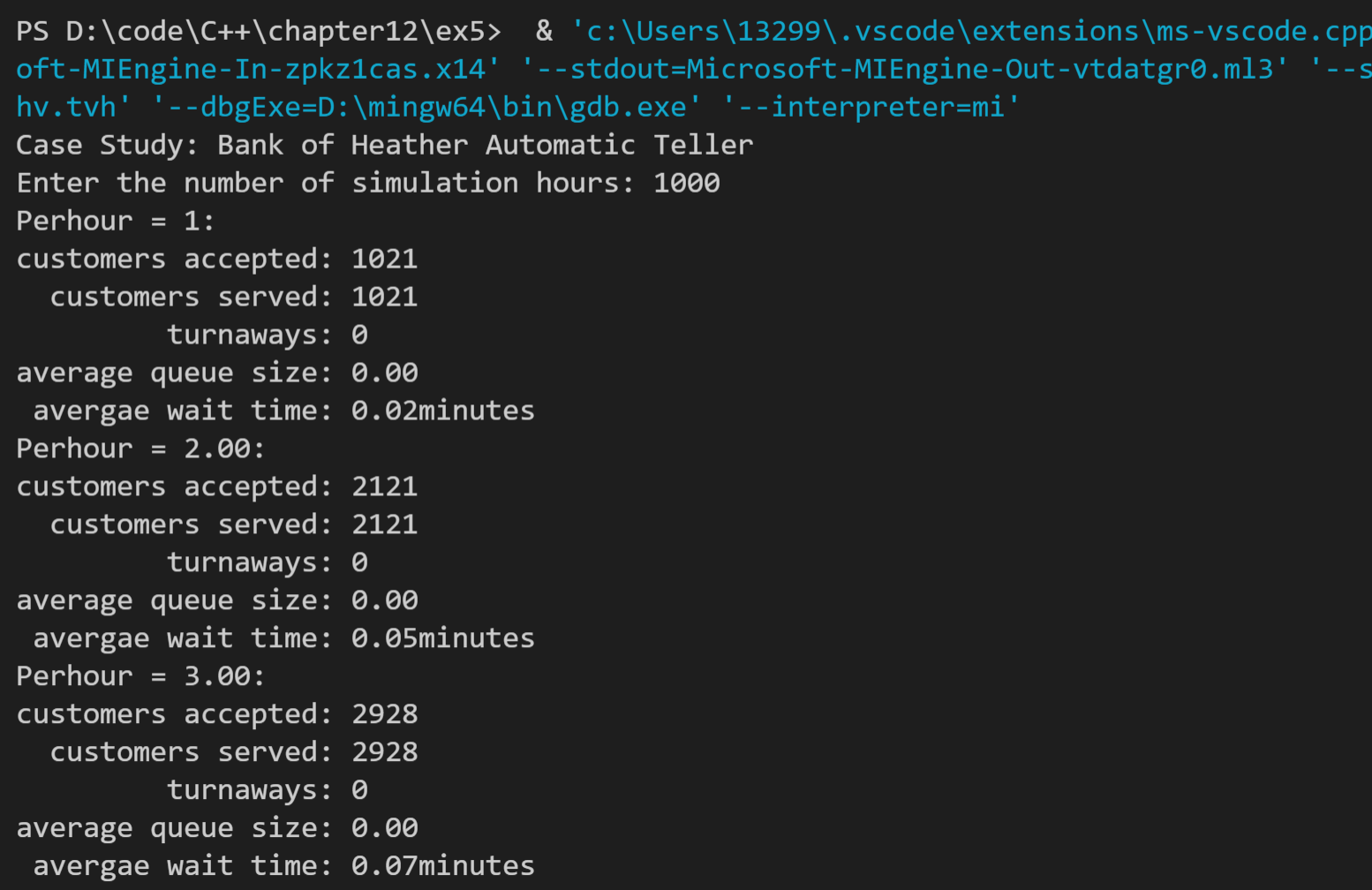
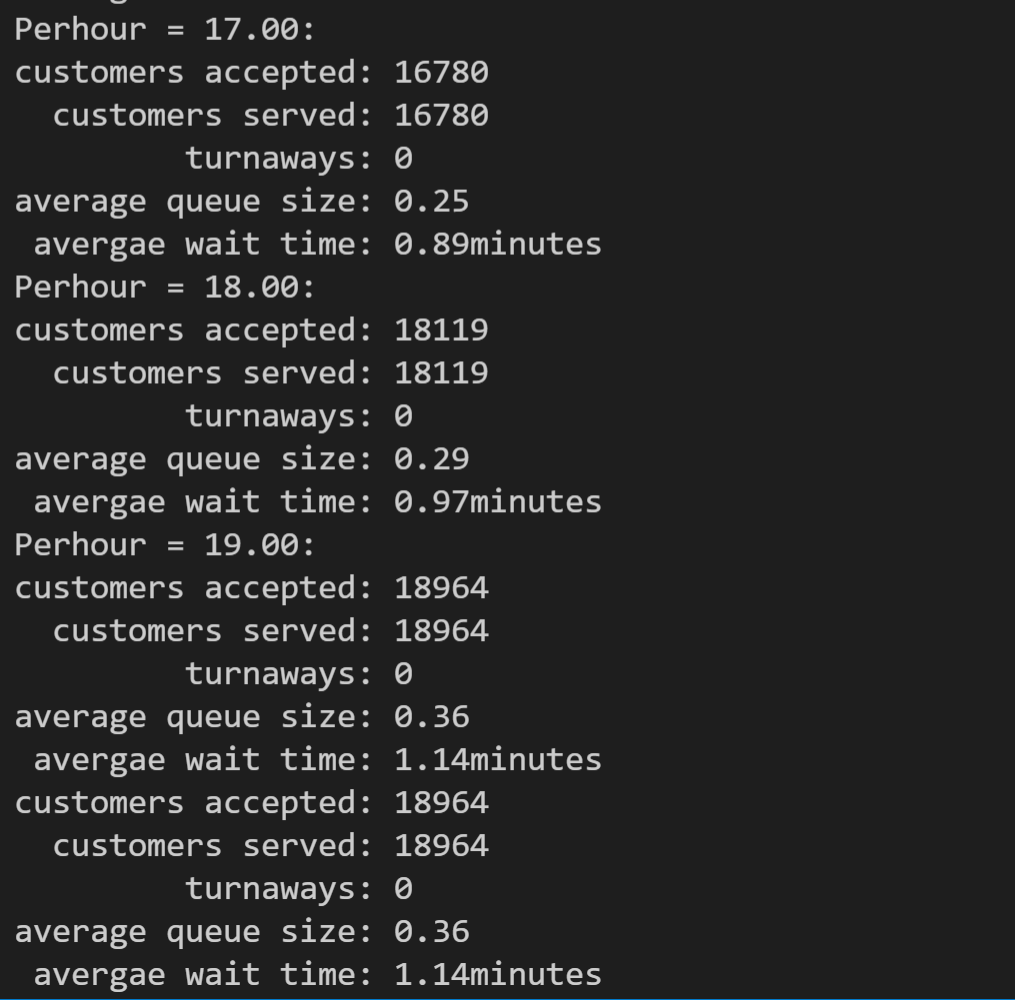
5. Heather银行进行的研究表明,ATM客户不希望排队时间不超过1分钟。使用程序清单12.10中的模拟,找出平均等候时间为1分钟,每小时到达的客户数应为多少(试验时间不短于100个小时)?
本题主要修改的是主函数的程序,由于比较需要计算一轮循环的结果获取数据后才可以比较,因此选择了dowhile循环,本题的关键是循环中需要改变的变量都要放在循环里,刚开始笔者没有将每小时几人转换成每小时几分钟的循环放入循环体中,导致程序无法跳出循环,加入后解决。代码如下:
#ifndef QUEUE_H_
#define QUEUE_H_
class Customer
{
private :
long arrive;
int processtime;
public :
Customer (){ arrive = processtime = 0 ;}
void set (long when)
long When () const return arrive;}
long Ptime () const return processtime;}
};
typedef Customer Item;
class Queue
{
private :
struct Node
{
Item item;
struct Node * next;
};
enum {Q_SZIE = 10 };
Node * front;
Node * rear;
int items;
const int qsize;
Queue (const Queue & q):qsize (0 ){}
Queue & operator =(const Queue & q){return * this ;}
public :
Queue (int qs = Queue::Q_SZIE);
~Queue ();
bool isempty () const
bool isfull () const
int queuecount () const
bool enqueue (const Item & item)
bool dequeue (Item & item)
};
#endif
#include "queue.h"
#include <cstdlib>
Queue::Queue (int q):qsize (q)
{
items = 0 ;
front = rear = nullptr ;
}
Queue::~Queue ()
{
while (!isempty ())
{
Node * temp;
temp = front;
front = front->next;
items--;
delete temp;
}
}
bool Queue::isempty () const
{
return items == 0 ;
}
bool Queue::isfull () const
{
return items == qsize;
}
int Queue::queuecount () const
{
return items;
}
bool Queue::enqueue (const Item & item)
{
if (items < qsize)
{
Node * add = new Node;
add->item = item;
if (isempty ())
{
front = rear =add;
}
else
{
rear->next = add;
rear = add;
}
rear->next = nullptr ;
items++;
return true ;
}
return false ;
}
bool Queue::dequeue (Item & item)
{
if (items > 0 )
{
Node * temp;
item = front->item;
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
items--;
return true ;
}
return false ;
}
void Customer::set (long when)
{
arrive = when;
processtime = rand () % 3 + 1 ;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include "queue.h"
const int MIN_PER_HR = 60 ;
bool newcustomer (double x)
int main ()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::ios_base;
std::srand (std::time (0 ));
cout << "Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\n" ;
cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: " ;
int hours;
cin >> hours;
long cyclelimit = hours * MIN_PER_HR;
double perhour = 1 ;
int qs = int (4 *perhour);
Queue line (qs) ;
Item temp;
long turnaways = 0 ;
long customers = 0 ;
long served = 0 ;
long sum_line = 0 ;
long wait_time = 0 ;
long line_wait = 0 ;
do
{
int qs = int (4 *perhour);
double min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour;
Queue line (qs) ;
turnaways = 0 ;
customers = 0 ;
served = 0 ;
sum_line = 0 ;
wait_time = 0 ;
line_wait = 0 ;
for (int cycle = 0 ; cycle < cyclelimit; cycle++)
{
if (newcustomer (min_per_cust))
{
if (line.isfull ())
turnaways++;
else
{
customers++;
temp.set (cycle);
line.enqueue (temp);
}
}
if (wait_time <= 0 && !line.isempty ())
{
line.dequeue (temp);
wait_time = temp.Ptime ();
line_wait += cycle - temp.When ();
served++;
}
if (wait_time > 0 )
{
wait_time--;
}
sum_line += line.queuecount ();
}
cout << "Perhour = " << perhour << ":\n" ;
if (customers > 0 )
{
cout << "customers accepted: " << customers << endl;
cout << " customers served: " << served << endl;
cout << " turnaways: " << turnaways << endl;
cout << "average queue size: " ;
cout.precision (2 );
cout.setf (ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
cout << (double ) sum_line / cyclelimit << endl;
cout << " avergae wait time: "
<< (double ) line_wait / served << "minutes\n" ;
}
else
{
cout << "No customerr!\n" ;
}
perhour+=1 ;
line.~Queue ();
}while ((double ) line_wait / served < 1 );
if (customers > 0 )
{
cout << "customers accepted: " << customers << endl;
cout << " customers served: " << served << endl;
cout << " turnaways: " << turnaways << endl;
cout << "average queue size: " ;
cout.precision (2 );
cout.setf (ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
cout << (double ) sum_line / cyclelimit << endl;
cout << " avergae wait time: "
<< (double ) line_wait / served << "minutes\n" ;
}
else
cout << "No customerr!\n" ;
cout << "Done!\n" ;
return 0 ;
}
bool newcustomer (double x)
{
return (std::rand () * x / RAND_MAX < 1 );
}
本题由于从每小时接待1个人开始运行,因此结果比较长,截取了前三个和最后三个运行结果,如下: 可以看出应该是18人。
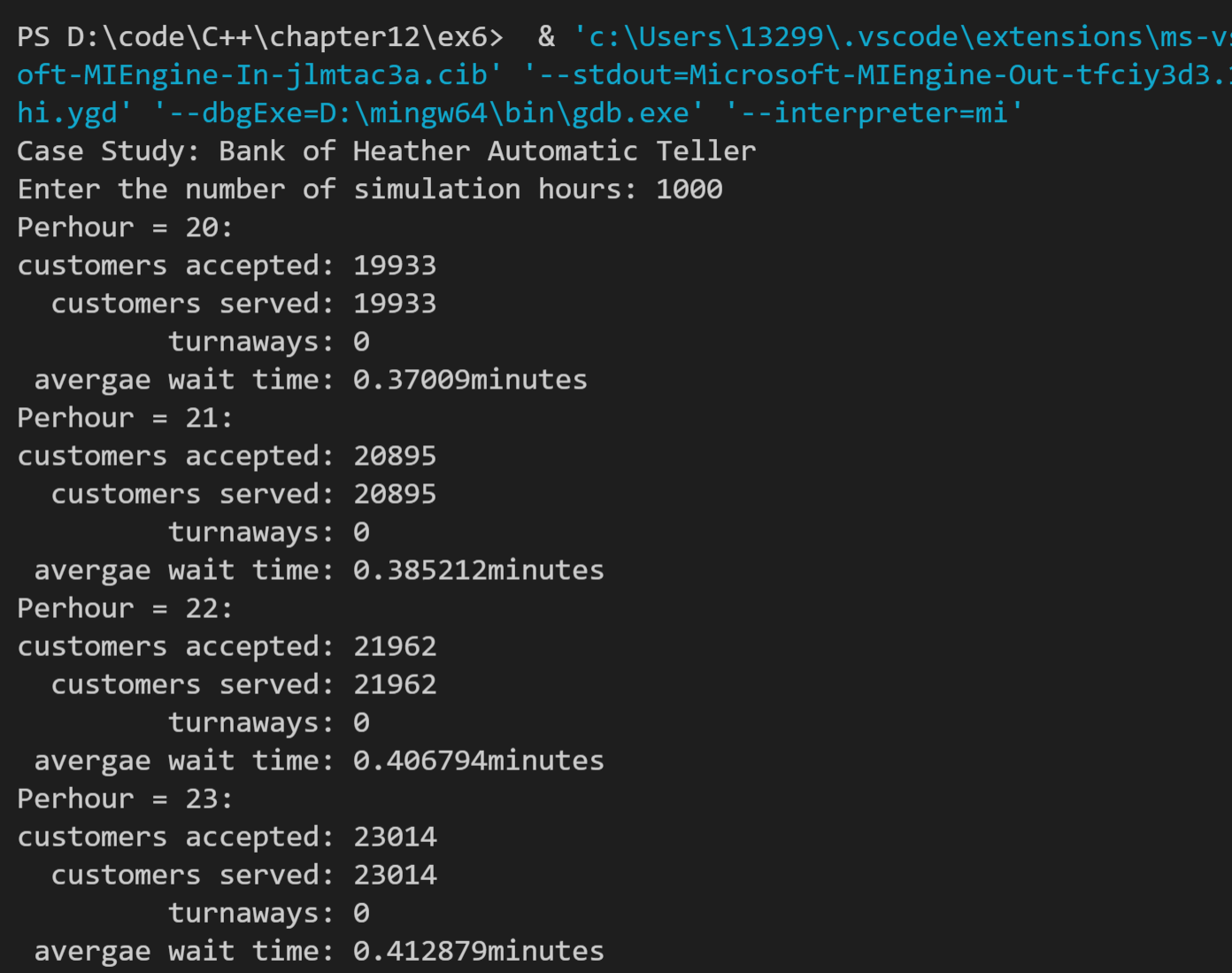
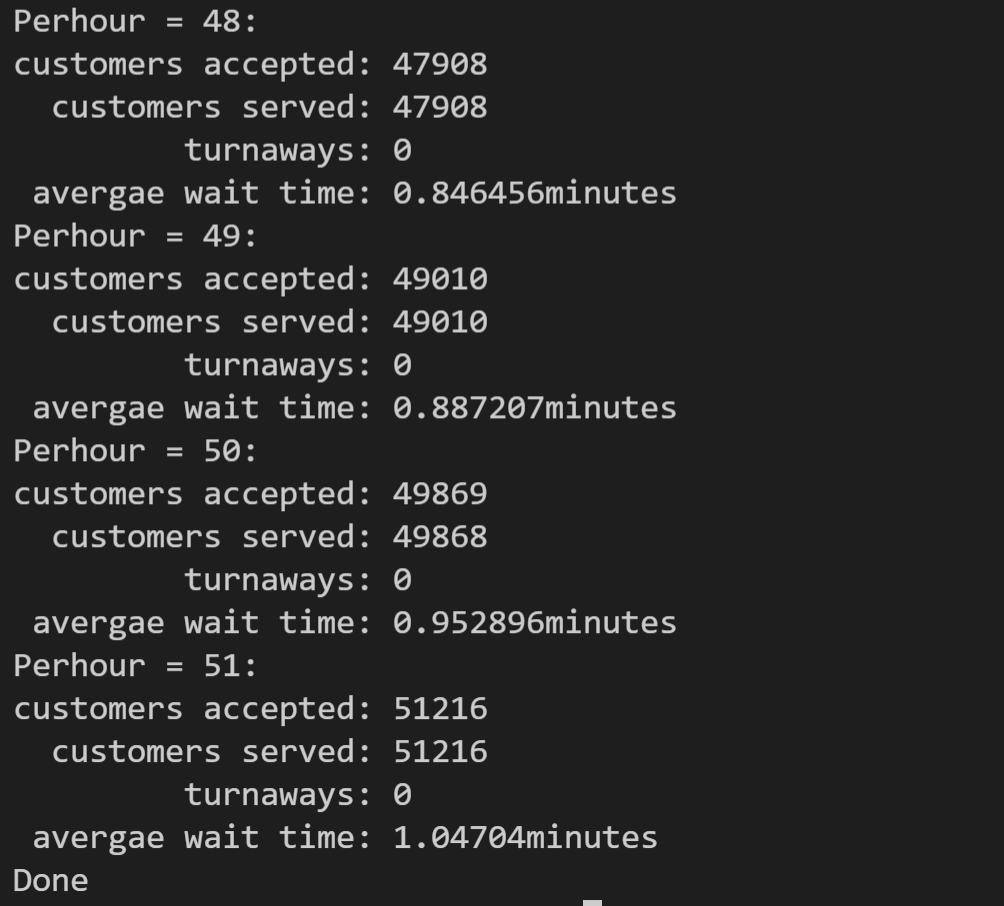
6. Heather银行想知道,如果在开设一台ATM,情况将如何。请对模拟做出修改,以包含两个队列。假设当第一台ATM前的排队人数少于第二台时,客户将排在第一队,否则将排在第二队。然后再找出要使平均等候时间为1分钟,每小时到达的客户数应该为多少(注意,这是一个非线性问题,即将ATM数量加倍,并不能保证每小时处理的客户数量也翻倍,并确保客户等候的时间少于1分钟)
本题与上一题类似,不同的时采用了两台ATM机,因此类的接口及实现文件不变,需要修改的是主函数,两台ATM机,因此需要两个队列,分别标记为line1,line2;接着修改有顾客来时的程序,当两个队列都满时,离开;否则入队,比较两个队列的人数,line1少,进line1否则line2。接下来判断出队的程序,由于是两个队列,因此有两个等待时间,分别记为waittime1和waittime2;分别进行离队操作和减时间操作。代码如下:
#ifndef QUEUE_H_
#define QUEUE_H_
class Customer
{
private :
long arrive;
int processtime;
public :
Customer (){ arrive = processtime = 0 ;}
void set (long when)
long When () const return arrive;}
long Ptime () const return processtime;}
};
typedef Customer Item;
class Queue
{
private :
struct Node
{
Item item;
struct Node * next;
};
enum {Q_SZIE = 10 };
Node * front;
Node * rear;
int items;
const int qsize;
Queue (const Queue & q):qsize (0 ){}
Queue & operator =(const Queue & q){return * this ;}
public :
Queue (int qs = Queue::Q_SZIE);
~Queue ();
bool isempty () const
bool isfull () const
int queuecount () const
bool enqueue (const Item & item)
bool dequeue (Item & item)
};
#endif
#include "queue.h"
#include <cstdlib>
Queue::Queue (int q):qsize (q)
{
items = 0 ;
front = rear = nullptr ;
}
Queue::~Queue ()
{
while (!isempty ())
{
Node * temp;
temp = front;
front = front->next;
items--;
delete temp;
}
}
bool Queue::isempty () const
{
return items == 0 ;
}
bool Queue::isfull () const
{
return items == qsize;
}
int Queue::queuecount () const
{
return items;
}
bool Queue::enqueue (const Item & item)
{
if (items < qsize)
{
Node * add = new Node;
add->item = item;
if (isempty ())
{
front = rear =add;
}
else
{
rear->next = add;
rear = add;
}
rear->next = nullptr ;
items++;
return true ;
}
return false ;
}
bool Queue::dequeue (Item & item)
{
if (items > 0 )
{
Node * temp;
item = front->item;
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
items--;
return true ;
}
return false ;
}
void Customer::set (long when)
{
arrive = when;
processtime = rand () % 3 + 1 ;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include "queue.h"
const int MIN_PER_HR = 60 ;
bool newcustomer (double x)
int main ()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::ios_base;
std::srand (std::time (0 ));
cout << "Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\n" ;
cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: " ;
int hours;
cin >> hours;
long cyclelimit = hours * MIN_PER_HR;
double perhour = 20 ;
int qs = int (4 *perhour);
Item temp;
long turnaways = 0 ;
long customers = 0 ;
long served = 0 ;
long wait_time1 = 0 ;
long wait_time2 = 0 ;
long line_wait = 0 ;
do
{
int qs = int (4 *perhour);
double min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour;
Queue line1 (qs) ,line2 (qs) ;
turnaways = 0 ;
customers = 0 ;
served = 0 ;
wait_time1 = 0 ;
wait_time2 = 0 ;
line_wait = 0 ;
for (int cycle = 0 ; cycle < cyclelimit; cycle++)
{
if (newcustomer (min_per_cust))
{
if (line1.isfull ()&&line2.isfull ())
turnaways++;
else
{
customers++;
temp.set (cycle);
if (line1.queuecount ()<line2.queuecount ())
line1.enqueue (temp);
else
line2.enqueue (temp);
}
}
if (wait_time1 <= 0 && !line1.isempty ())
{
line1.dequeue (temp);
wait_time1 = temp.Ptime ();
line_wait += cycle - temp.When ();
served++;
}
if (wait_time2 <= 0 && !line2.isempty ())
{
line2.dequeue (temp);
wait_time2 = temp.Ptime ();
line_wait += cycle - temp.When ();
served++;
}
if (wait_time1 > 0 )
{
wait_time1--;
}
if (wait_time2 > 0 )
{
wait_time2--;
}
}
cout << "Perhour = " << perhour << ":\n" ;
if (customers > 0 )
{
cout << "customers accepted: " << customers << endl;
cout << " customers served: " << served << endl;
cout << " turnaways: " << turnaways << endl;
cout << " avergae wait time: "
<< (double ) line_wait / served << "minutes\n" ;
}
else
{
cout << "No customerr!\n" ;
}
perhour+=1 ;
}while ((double ) line_wait / served < 1 );
cout << "Done\n" ;
return 0 ;
}
bool newcustomer (double x)
{
return (std::rand () * x / RAND_MAX < 1 );
}
由于20个人的时间肯定小于1分钟,因此从20开始运行,运行结果部分如下(前四组和后四组结果): 从结果可以看出,2台ATM机可以接收50人,没人等待时间小于1min,与第五题的结果相比,增加了接近三倍,因此这不是一个线性问题。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· Vue3状态管理终极指南:Pinia保姆级教程