C++ Primier Plus(第六版) 第十章 对象和类 编程练习答案
本题考查的是类的声明定义以及简单的使用,没有什么难度,样例代码如下:
// account.h -- class defination for Account
#ifndef ACCOUNT_H_
#define ACCOUNT_H_
#include<string>
class BankAccount
{
private:
std::string name_;
std::string acc_num_;
double deposit_;
public:
BankAccount();
BankAccount(const std::string & name, const std::string & acc_num, double cash);
~BankAccount();
void show_account();
void deposit_in(double cash);
void deposit_out(double cash);
};
#endif
// account.cpp -- Account member function
#include <iostream>
#include "account.h"
BankAccount::BankAccount()
{
}
BankAccount::BankAccount(const std::string & name, const std::string & acc_num, double cash)
{
name_ = name;
acc_num_ = acc_num;
deposit_ = cash;
}
BankAccount::~BankAccount()
{
}
void BankAccount::show_account()
{
using std::cout;
cout << "Name: " << name_ << ", account number: "
<< acc_num_ << ", deposit: " << deposit_ << '\n';
}
void BankAccount::deposit_in(double cash)
{
using std::cout;
if(cash < 0)
{
cout << "The number of cash you deposit is negative; "
<< "transcation is aborted.\n";
}
else
deposit_ += cash;
}
void BankAccount::deposit_out(double cash)
{
using std::cout;
if(cash < 0)
{
cout << "The number of cash you deposit is negative; "
<< "transcation is aborted.\n";
}
else if(cash > deposit_)
{
cout << "You can't take the cash morn than you have!"
<< "Transcation is aborted.\n";
}
else
deposit_ -= cash;
}
// accounter.cpp -- test the class account
#include <iostream>
#include "account.h"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
BankAccount account;
std::string name;
std::string acc_num;
double cash;
cout << "Enter your name: ";
getline(cin,name);
cout << "Enter your account number: ";
getline(cin,acc_num);
cout << "Enter the cash: ";
cin >> cash;
account = BankAccount(name,acc_num,cash);
account.show_account();
cout << "Enter the cash you want to take in: ";
cin >> cash;
account.deposit_in(cash);
account.show_account();
cout << "Enter the cash you want to take out: ";
cin >> cash;
account.deposit_out(cash);
account.show_account();
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
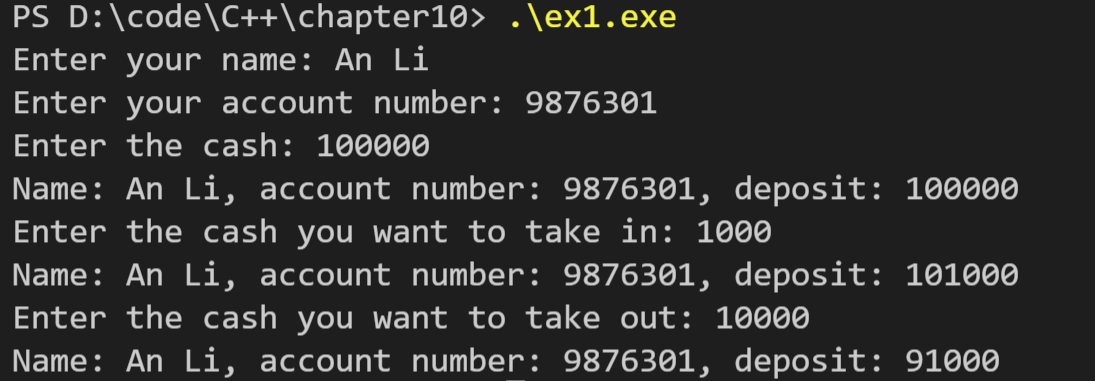
2. 下面是一个非常简单的类定义:
class Person
{
private:
static const LIMIT = 25;
std::string lname;
char fname[LIMIT];
public:
Person(){lname = "";fname[0] = '\0';};
Person(const std::string & ln, const char * fn = "Heyyou");
// the following methods display lname and fname
void Show()const; // firstname lastname format
void FormalShow() const; // lastname, firstname format
};
它使用了一个string对象和一个字符数组,让您能够比较他们的用法。请提供未定义的方法的代码,已完成这个类的实现。再编写一个使用这个类的程序,它使用了三种可能的构造函数调用(没有参数、一个参数和两个参数)以及两种显示方法。下面是一个使用这些构造函数和方法的例子。
Person one; // use default constructor
Person two("Smythecraft"); // use #2 with one default argument
Person three("Dimwiddy", "Sam"); // use #2, no defaults
one.Show();
cout << endl;
one.FormalShow();
// etc. for two and three
本题主要考查的是类方法的实现,实现的函数也很简单。比较string与char字符串数组,赋值时一个用=赋值,另一个用strcpy赋值。样例代码如下:
// person.h -- protype class Person
#ifndef PERSON_H_
#define PRESON_H_
#include <string>
class Person
{
private:
static const int LIMIT = 25;
std::string lname;
char fname[LIMIT];
public:
Person(){lname = "";fname[0] = '\0';}; // #1
Person(const std::string & ln, const char * fn = "Heyyou"); // #2
// the following methods display lname and fname
void Show()const; // firstname lastname format
void FormalShow() const; // lastname, firstname format
};
#endif
// person.cpp -- Person member function
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "person.h"
Person::Person(const std::string & ln, const char * fn)
{
lname = ln;
strcpy(fname, fn);
}
void Person::Show() const
{
using std::cout;
cout << fname << " " << lname;
}
void Person::FormalShow() const
{
std::cout << lname << ", " << fname << "\n";
}
// ex2_person.cpp -- test the class Person
#include <iostream>
#include "person.h"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Person one; // use default constructor
Person two("Smythecraft"); // use #2 with one default argument
Person three("Dimwiddy", "Sam"); // use #2, no defaults
one.Show();
cout << endl;
one.FormalShow();
// etc. for two and three
two.Show();
cout << endl;
two.FormalShow();
three.Show();
cout << endl;
three.FormalShow();
}
运行结果如下:
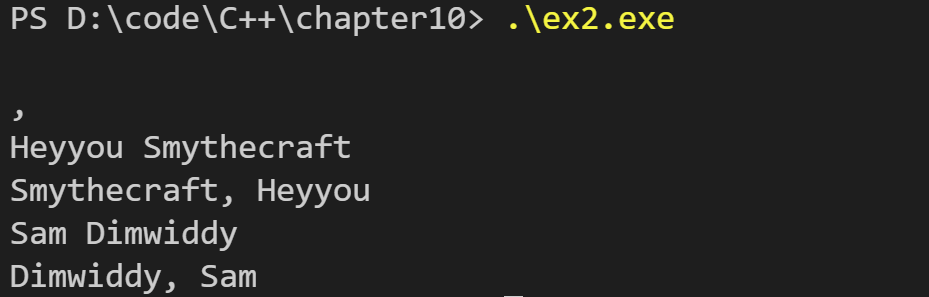
3. 完成第9章的编程练习1,但要使用正确的golf类声明替换哪里的代码,用带合适参数的构造函数替换setgolf(golf&,const char *,int),以提供初始值。保留setgolf()的交互版本,但要用构造函数来实现它(例如,setgolf()的代码应该获得数据,将数据传递给构造函数来创建一个临时对象,并将其赋给调用对象,即*this)。
本题的主要内容是将结构修改成类,操作结构的函数改成类的方法。通过修改发现原本函数的参数是结构,改成了对象使用方法。样例代码如下:
// golf.h -- definate Golf class
# ifndef GOLF_H_
# define GOLF_H_
class Golf
{
private:
static const int Len = 40;
char fullname[Len];
int handicap;
public:
Golf();
Golf(const char * name, int hc);
~Golf();
int setgolf();
void set_handicap(int hc);
void Show() const;
};
# endif
// golf.cpp -- member function of class Golf
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "golf.h"
Golf::Golf()
{
}
Golf::Golf(const char * name, int hc)
{
strcpy(fullname, name);
handicap = hc;
}
Golf::~Golf()
{
}
int Golf::setgolf()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
Golf temp;
cout << "Enter the users'name: ";
cin.getline(temp.fullname, Len);
if(!strcmp(temp.fullname,""))
return 0;
cout << "Enter the users'level: ";
while(!(cin>>temp.handicap))
{
cin.clear();
while(cin.get()!='\n')
continue;
cout << "Bad input, please enter a integer: ";
}
cin.get();
*this = temp;
return 1;
}
void Golf::set_handicap(int hc)
{
handicap = hc;
}
void Golf::Show() const
{
using std::cout;
cout << "Name: " << fullname << ", level: " << handicap << "\n" ;
}
// ex3_usegolf.cpp -- test class Golf
// compile with golf.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "golf.h"
const int Arsize = 5;
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int hd, number;
int count = 0;
Golf gar[Arsize];
cout << "Enter the Users' name and level(enter empty string to name to quit):\n";
for(int i = 0; i < Arsize; i++)
{
cout << "User #" << i + 1 << ":\n";
int end_flag = gar[i].setgolf();
if (end_flag == 0)
break;
count++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
cout << "User #" << i + 1 << ":\t";
gar[i].Show();
}
// using handicap
cout << "Enter the number of user you need to change level(q to quit): ";
while(cin >> number)
{
cout << "The new Level: ";
cin >> hd;
gar[number - 1].set_handicap(hd);
cout << "Enter next number(q to quit): ";
}
cout << "The new golf users list:\n";
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
cout << "User #" << i + 1 << ":\t";
gar[i].Show();
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
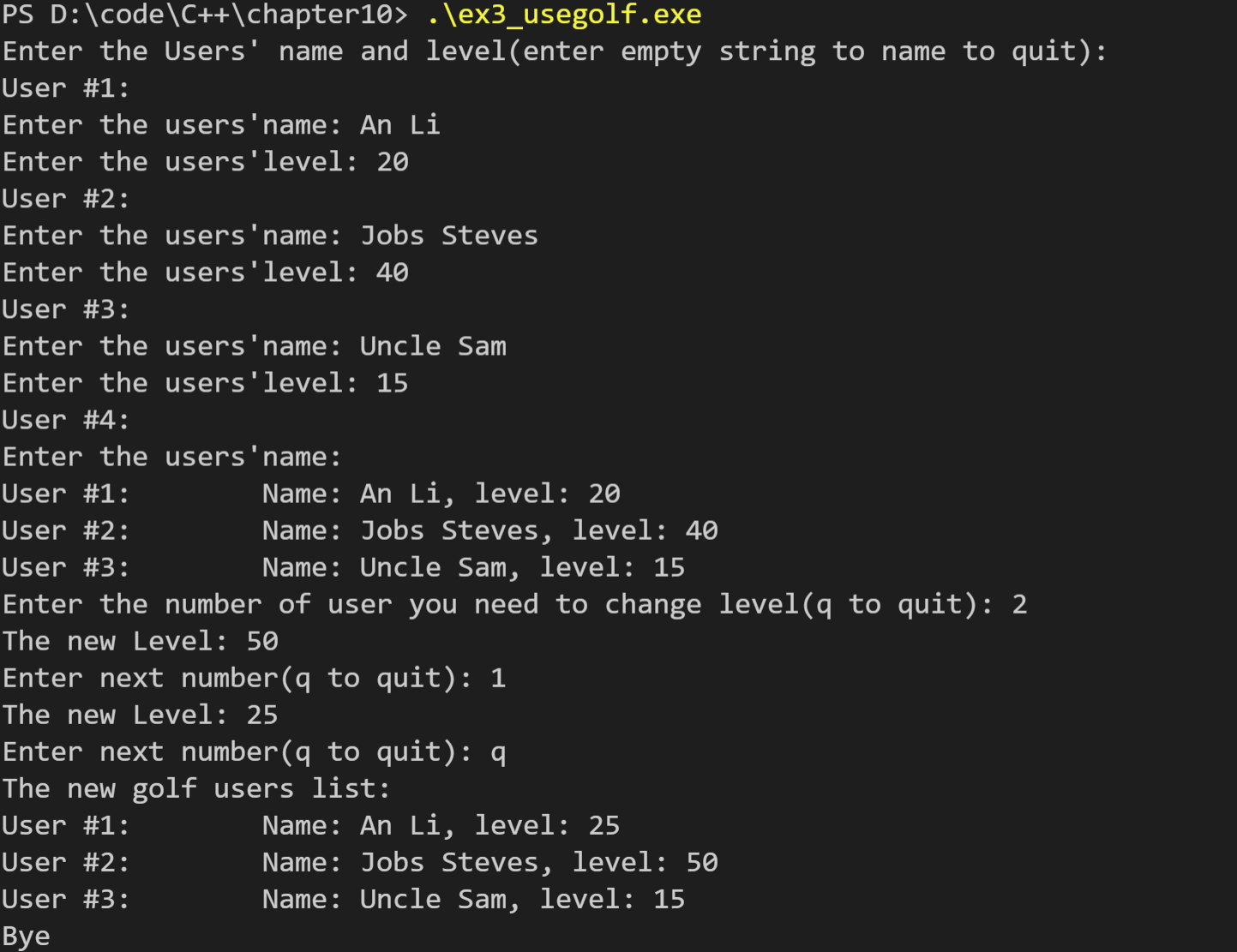
4. 完成第9章的编程练习4,但将Sales结构及相关的函数转换成一个类及其方法。用构造函数替换set(sales &, double[], int)函数。用构造函数实现setSales(Sales &)方法的交互版本。将类保留在名称空间SALES中。
本题考查的是在命名空间里定义类和类方法,要改的代码也不是很多。注意在命名空间里定义类方法也需要指名类,确定作用域。样例代码如下:
// sale.h store namespace for sale.cpp
// version class
namespace SALES
{
const int QUARTERS = 4;
class Sales
{
private:
double sales[QUARTERS];
double average;
double max;
double min;
public:
Sales();
Sales(const double ar[], int n);
void ShowSales() const;
};
}
// sale.cpp -- membet function for Sales in namespace SALES
// compile with ex4_useSales.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "sale.h"
static double find_min(const double ar[], int n);
static double find_max(const double ar[], int n);
static double getaverage(const double ar[], int n);
static double * find_4less(const double ar[], int n);
namespace SALES
{
Sales::Sales()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
cout << "Enter four sales:\n";
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cout << "Sales #" << i + 1 << ": ";
cin >> sales[i];
}
min = find_min(sales, 4);
max = find_max(sales, 4);
average = getaverage(sales, 4);
}
Sales::Sales(const double ar[], int n)
{
min = find_min(ar, n);
max = find_max(ar, n);
average = getaverage(ar,n);
if(n <= 4)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sales[i] = ar[i];
for(;i < 4; i++)
sales[i] = 0;
}
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
sales[i] = find_4less(ar, n)[i];
}
}
void Sales::ShowSales() const
{
using std::cout;
cout << "Sales list:\n";
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cout << "Sales #" << i + 1 << ": ";
cout << sales[i] << "\t";
}
cout << "\n";
cout << "Average = " << average << ", max = " << max;
cout << ", min = " << min << "\n";
}
}
double find_min(const double ar[], int n)
{
double min = ar[0];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
min = min < ar[i] ? min : ar[i];
return min;
}
double find_max(const double ar[], int n)
{
double max = ar[0];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
max = max < ar[i] ? ar[i] : max;
return max;
}
double getaverage(const double ar[], int n)
{
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += ar[i];
return sum / n;
}
static double * find_4less(const double ar[], int n)
{
double * lesser4 = new double[4];
double lesser;
lesser4[0] = find_min(ar, n);
for(int i = 1; i < 4; i++)
{
lesser = find_max(ar, n);
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(ar[j] > lesser4[i-1])
lesser = lesser < ar[j] ? lesser : ar[j];
}
lesser4[i] = lesser;
}
return lesser4;
}
// ex4_useSales.cpp -- using namespace and class
// compile with sale.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "sale.h"
int main()
{
using namespace SALES;
using std::cout;
Sales s1;
double arr[6] = {1111.1, 666.6, 999.9, 333.3, 2222.2, 1234.5};
Sales s2 = Sales(arr, 6);
s1.ShowSales();
s2.ShowSales();
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
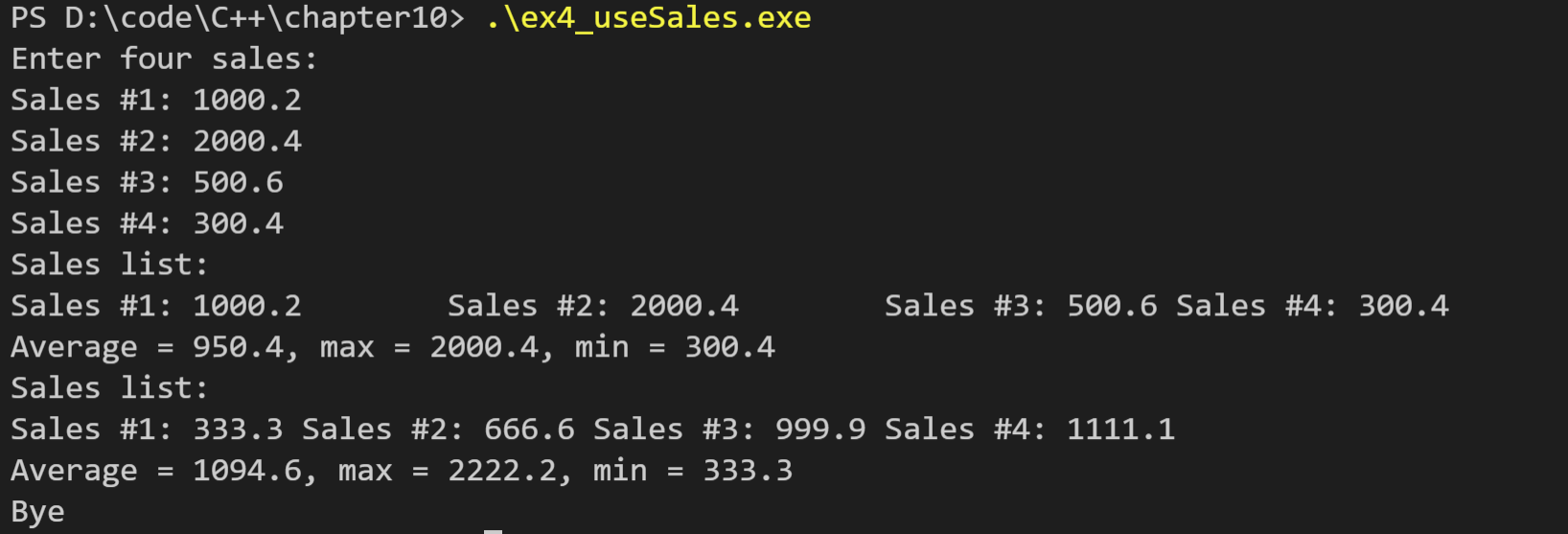
5. 考虑下面的结构声明:
struct customer{
char fullname[35];
double payment;
}
编写一个程序,它从栈中添加和删除custome结构(栈用Stack类声明表示)。每次customer结构被删除时,其payment的值都将被加入到总数中,并报告总数。注意:应该可以直接使用Stack类而不作修改;只需修改typedef声明,使Item的类型为customer,而不是unsigned long即可。
本题在编写过程中遇到了不少问题,首先是不理解stack的pop与push程序,栈顶元素是空着的,压入栈时将元素赋给栈顶元素,然后指针top++。弹出时,首先--top,然后将top指向元素的值弹出。
使用数组实现时:
push stack[top++] = value;该程序等价于stack[top] = value;top++;
pop value = stack[--top];该程序等价于--top;value = stack[top];
样例代码如下:
// stack.h -- Class Stack protype and member function protype
#ifndef STACK_H_
#define STACK_H_
const int NSIZE = 35;
struct customer
{
char fullname[NSIZE];
double payment;
};
typedef struct customer Item;
class Stack
{
private:
static const int MAX = 10; // also enum{MAX = 10};
Item items[MAX];
int top;
public:
Stack();
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull() const;
bool push(const Item & item);
bool pop(Item & item);
};
#endif
// stack.cpp -- member function for stack class
// compile with ex4.cpp
#include <cstring>
#include "stack.h"
Stack::Stack()
{
top = 0;
}
bool Stack::isempty() const
{
return top == 0;
}
bool Stack::isfull() const
{
return top == MAX;
}
bool Stack::push(const Item & item)
{
if(isfull())
return false;
strcpy(items[top].fullname,item.fullname);
items[top++].payment = item.payment;
return true;
}
bool Stack::pop(Item & item)
{
if(top > 0)
{
item = items[--top];
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
// ex4_usestack.cpp -- use stack class to store the custormer
// compile with stack.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "stack.h"
int main()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Stack st;
customer ct;
double sum_pm = 0;
int count = 0;
cout << "Enter the customer name(enter empty string to quit): ";
cin.getline(ct.fullname,NSIZE);
while (strcmp(ct.fullname, ""))
{
cout << "Enter the payment: ";
while(!(cin >> ct.payment))
{
cin.clear();
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
cout << "Bad input, please input a number: ";
}
cin.get();
st.push(ct);
if(st.isfull())
break;
cout << "Enter next customer name(enter empty string to quit): ";
cin.getline(ct.fullname,NSIZE);
}
while(!st.isempty())
{
++count;
st.pop(ct);
sum_pm += ct.payment;
cout << count << " customers' total payment is " << sum_pm << endl;
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
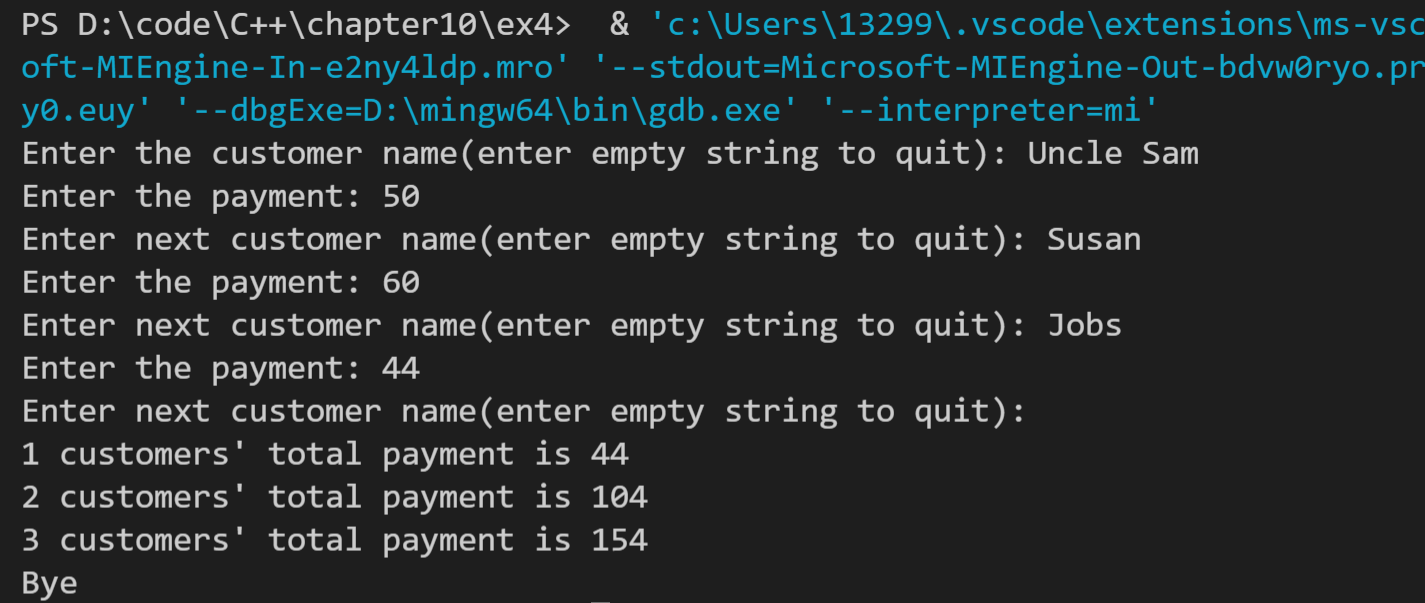
运行结果如下:
6. 下面是一个类声明:
class Move
{
private:
double x;
double y;
public:
Move(double a = 0.0,double b = 0.0); // sets x, y to a, b
void showmove() const; // shows current x, y values
Move add(const Move & m) const;
// this function adds x of m to x of invoking object to get new x,
// adds y to y of invokeing object to get new y, create a new
// move object initialized to new x, y values and returns it
void reset(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0); // resets x,t to a,b
};
请提供成员函数的定义和测试这个类的程序
本题比较简单,就是声明类和测试类,样例代码如下:
// move.h -- defination of Move class for move.cpp
// version
#ifndef MOVE_H_
#define MOVE_H_
class Move
{
private:
double x;
double y;
public:
Move(double a = 0.0,double b = 0.0); // sets x, y to a, b
void showmove() const; // shows current x, y values
Move add(const Move & m) const;
// this function adds x of m to x of invoking object to get new x,
// adds y to y of invokeing object to get new y, create a new
// move object initialized to new x, y values and returns it
void reset(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0); // resets x,t to a,b
};
#endif
// move.cpp -- member function of class Move
// compile with ex6_usemove.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "move.h"
Move::Move(double a, double b)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
void Move::showmove() const
{
std::cout << "x = " << x << ", y = " << y << '\n';
}
Move Move::add(const Move & m) const
{
Move temp;
temp.x = x + m.x;
temp.y = y + m.y;
return temp;
}
void Move::reset(double a , double b)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
// ex6_usemove.cpp -- test class Move
// compile with move.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "move.h"
int main()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
Move point;
double a, b;
Move mv;
Move result;
cout << "Enter the point of x,y position: ";
cin >> a >> b;
point.reset(a,b);
point.showmove();
cout << "Enter the move x y: ";
cin >> a >> b;
mv.reset(a,b);
result = point.add(mv);
cout << "After move, the point of position is ";
result.showmove();
return 0;
}
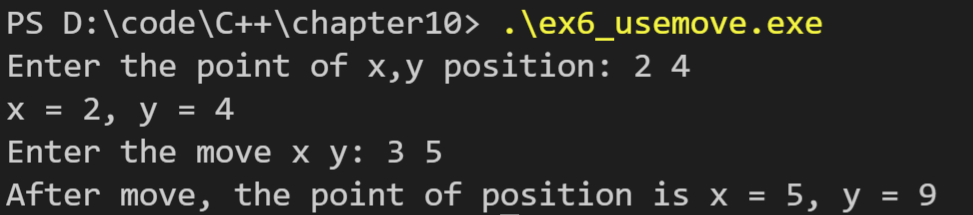
运行结果如下:
7. Betelgeusean plorg 有这些特征。
数据:
- plorg的名称不超过19个字符;
- plorg有满意指数(CI),这是一个整数。
操作:
- 新的plorg将有名称,其CI值为50;
- plorg的CI可以修改;
- plorg可以报告其名称和CI;
- plorg的默认名称为"Plorga"。
请编写一个Plorg类声明(包括成员函数和成员函数原型)来表示plorg,并编写成员函数的函数定义。然后编写一个小程序,以演示Plorg类的所有特性。
本题比较简单,首先将题目中的文字转换成代码实现,这些没有问题,在写测试主函数的时候,遇到了问题,由于cin >> CI 的优先级比!低,因此又该有括号!(cin >> CI),样例代码如下:
// plorg.h -- defination of class Plorg
// version 00
#ifndef PLORG_H_
#define PLORG_H_
const int NSIZE = 20;
class Plorg
{
private:
char name_[NSIZE];
int CI_;
public:
Plorg();
Plorg(const char * name, int CI = 50);
void setCI(int CI);
void ShowPlorg() const;
void setname(const char * name = "Plorga");
};
#endif
// plorg.cpp -- member funciton of class Plorg
// compile with ex7_useplorg.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "plorg.h"
Plorg::Plorg()
{
}
Plorg::Plorg(const char * name, int CI)
{
strcpy(name_, name);
CI_ = CI;
}
void Plorg::setCI(int CI)
{
CI_ = CI;
}
void Plorg::ShowPlorg() const
{
std::cout << "Plorg name: " << name_ << ", CI = " << CI_ << '\n';
}
void Plorg::setname(const char * name)
{
strcpy(name_,name);
}
// ex7_useplorg.cpp -- test class Plorg
// compile with plorg.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "plorg.h"
const int PSize = 10;
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
Plorg plorg[PSize];
Plorg pl = Plorg("Jobs Sam",60);
pl.ShowPlorg();
char name[NSIZE];
int CI;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < PSize; i++)
{
cout << "The plorg #" << i + 1 << ":\n";
cout << "Enter the name(enter empty string to quit): ";
cin.getline(name, NSIZE);
if(!strcmp(name,""))
break;
count++;
cout << "Enter the CI: ";
while(!(cin >> CI)) // () is must
{
cin.clear();
while(cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
cout << "Bad input, please input a integer: ";
}
cin.get();
plorg[i].setname(name);
plorg[i].setCI(CI);
}
cout << "Plorg List:\n" ;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
plorg[i].ShowPlorg();
cout << "Bye\n";
}
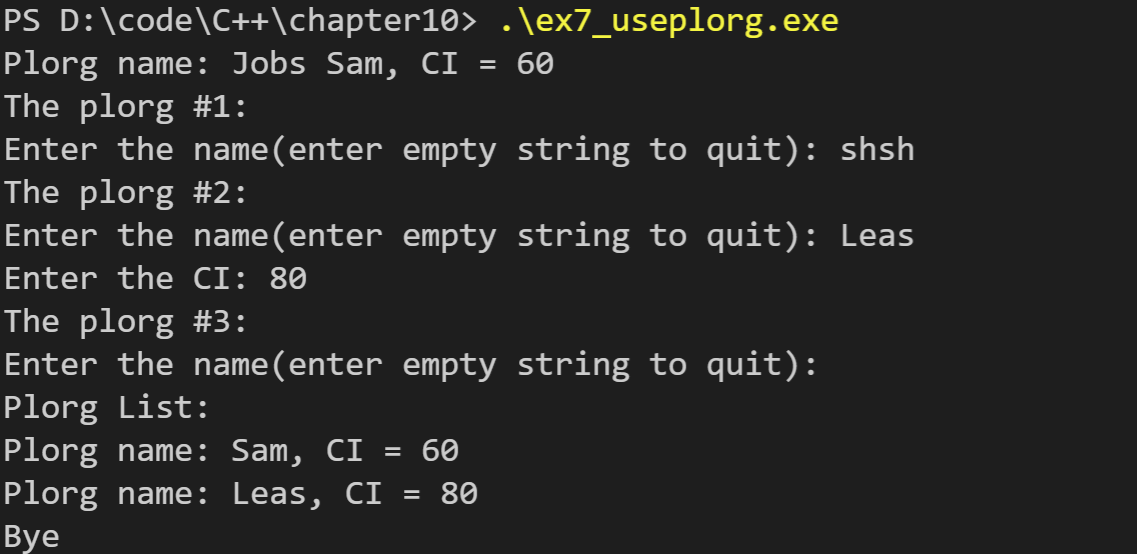
运行结果如下:
8. 可以将简单列表描述成下面这样:
- 可以存储0或多个某种类型的列表;
- 可创建空列表;
- 可在列表中添加数据项;
- 可确定列表是否为空;
- 可确定列表是否为满;
- 可以访问列表中每一个数据项,并对他执行某种操作。
可以看到,这个列表确实简单,例如它不允许插入或删除数据项。您应该提供头文件list.h和实现文件list.cpp,前者包含类定义,后者包含类方法的实现。您还应该创建一个简单的程序来使用这个类。
该列表的规范很简单,这主要旨在简化这个编程练习。可以选择使用数组或链表来实现该列表,但公有接口不应依赖于所做的选择,也就是说,公有接口不应有数组索引、节点指针等。应使用通用概念来表达创建列表、在列表中添加数据项等操作。对于访问数据项以及执行操作,通常应使用将函数指针作为参数的函数来处理:
void visit(void (*pf) (Item &))
其中,pf指向一个将Item引用作为参数的函数(不是成员函数),Item是列表中数据项的类型。visit()函数将该函数用于列表中的每个数据项。
本题由于笔者目前没有学过链表,因此没有使用链表,使用了数组来存储,编写程序时存在问题,visit函数,有问题,后面理解了函数作为参数之后,将程序写出来了,测试程序比较简陋,以后学了链表再来改进这个程序,也体会到了面向对象编程的好处。代码如下:
// list.h -- protype class list
// version 00
#ifndef LIST_H_
#define LIST_H_
typedef double Item;
class List
{
private:
enum{MAX = 10};
Item items[MAX];
int header;
public:
List();
List(const Item * aritem, int n);
bool add_data(const Item & item);
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull() const;
void visit(void (*pf) (Item & item));
};
#endif
// list.cpp -- member function of class List
// compile with ex8_uselist.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "list.h"
List::List()
{
header = 0;
}
List::List(const Item * aritem, int n)
{
for(header = 0; header < n; header++)
{
items[header] = aritem[header];
}
}
bool List::add_data(const Item & item)
{
if(header < MAX)
{
items[header++] = item;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool List::isempty() const
{
return header == 0;
}
bool List::isfull() const
{
return header == MAX;
}
void List::visit(void (*pf) (Item & item))
{
for(int i = 0; i < header; i++)
(*pf)(items[i]);
}
// ex8_uselist.cpp -- test class List
// compile with list.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "list.h"
void Show(Item & item);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
Item num;
List ld1;
double arr[10] = {1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.9, 2.0};
if(ld1.isempty())
cout << "List of double is empty\n";
List ld2 = List(arr,10);
if(ld2.isfull())
cout << "List of double is full\n";
ld2.visit(Show);
cout << '\n';
cout << "Before add data:\n";
ld1.visit(Show);
cout << '\n';
cout << "Enter the number you want to add: ";
std::cin >> num;
ld1.add_data(num);
cout << "After add data:\n";
ld1.visit(Show);
cout << '\n';
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
void Show(Item & item)
{
std::cout << item << " ";
}
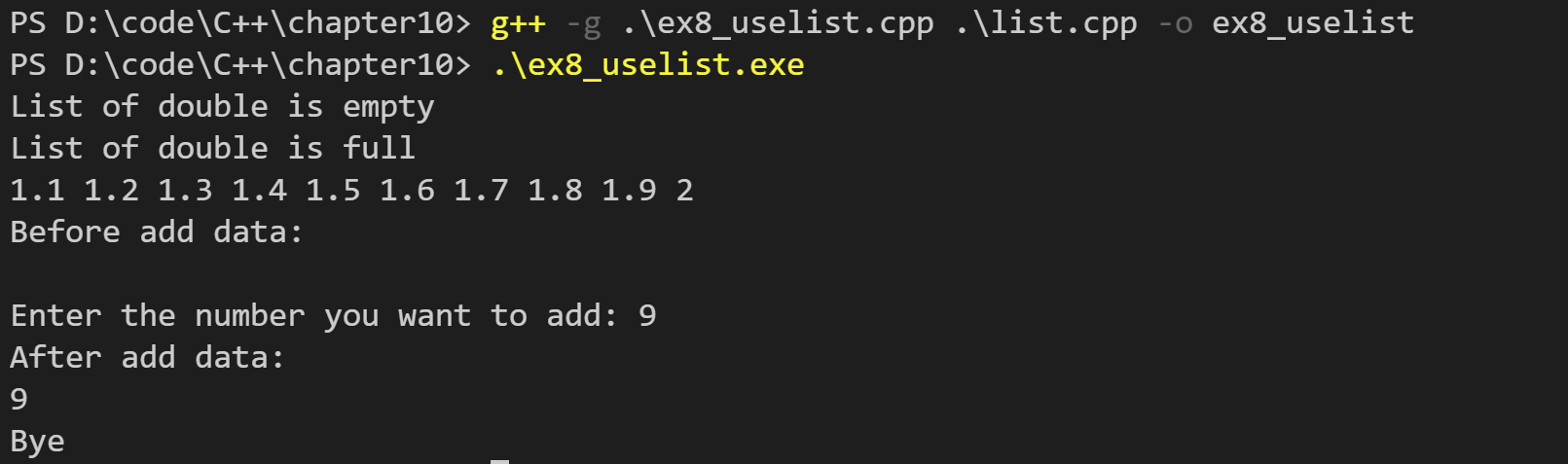
运行结果如下:
学习完链表之后,把之前提的坑补上,使用列表做题,除了接口内的实现不一样,其他代码基本上是一样的:
// list.h -- definition of List class
#ifndef LIST_H_
#define LIST_H_
typedef double Item;
class List
{
private:
// struct Node dedintion
struct Node
{
Item item;;
struct Node * next;
};
enum {L_SIZE = 10};
// private meber
Node * front;
Node * rear;
int items;
const int lsize;
// member methods
List(const List & lt):lsize(0){}
List & operator=(const List & lt){return *this;}
public:
List(int ls = L_SIZE);
~List();
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull() const;
bool enlist(const Item & item);
bool delist(Item & item);
void visit(void (* pf) (Item & item));
};
#endif
// list.cpp -- methods for List class
#include "list.h"
List::List(int n):lsize(n)
{
front = rear = nullptr;
items = 0;
}
List::~List()
{
while(!isempty())
{
Node * temp;
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
items--;
}
}
bool List::isempty() const
{
return items == 0;
}
bool List::isfull() const
{
return items == lsize;
}
bool List::enlist(const Item & item)
{
if(items < lsize)
{
Node * add = new Node;
add->item = item;
if(isempty())
{
front = rear = add;
rear->next = nullptr;
items++;
return true;
}
else
{
rear->next = add;
rear = add;
rear->next = nullptr;
items++;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool List::delist(Item & item)
{
if(items > 0)
{
Node * temp;
item = front->item;
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
items--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
void List::visit(void (* pf) (Item & item))
{
Node * temp;
temp = front;
for(int i = 0; i < items; i++)
{
(* pf) (front->item);
front = front->next;
}
front = temp;
}
// ex8_uselist.cpp -- test class List
// compile with list.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "list.h"
void Show(Item & item);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
Item num;
List ld1;
double arr[10] = {1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.9, 2.0};
if(ld1.isempty())
cout << "List of double is empty\n";
List ld2;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
ld2.enlist(arr[i]);
if(ld2.isfull())
cout << "List of double is full\n";
ld2.visit(Show);
cout << '\n';
cout << "Before add data:\n";
ld1.visit(Show);
cout << '\n';
cout << "Enter the number you want to add: ";
std::cin >> num;
ld1.enlist(num);
cout << "After add data:\n";
ld1.visit(Show);
cout << '\n';
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
void Show(Item & item)
{
std::cout << item << " ";
}
运行结果如下:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号