C++实现类似python中list, dict的结构
前言
公司某段业务需要将python代码移植到c++, 其中多数情况下, 只需简单的更改词法和语法即可, 直到我遇到如下场景:
-
初始化时使用大量数据, 且会做多次数据拼接. 有时数据中还会混入不同的类型

在python中, 这一需求可使用
list轻松地实现, 但c++中就xx了.. -
大量使用dict, 且value中的数据类型不统一.
这些情况下, 如果不做些封装处理, 代码将变得非常难看. 经过查阅资料, 发现boost库中有一个类非常适合这种场景:boost::any, 遂开干.
实现
首先需要安装
boost,我使用vcpkg安装的, 亦可直接到[官网][https://www.boost.org/0]下载, 参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/235157113
-
安装
vcpkggit clone https://github.com/microsoft/vcpkg vcpkg\bootstrap-vcpkg.bat vcpkg\vcpkg integrate install -
安装
boost(比较慢,须耐心等待)vcpkg\vcpkg install boost -
实现
Elem.hpp#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include <boost/any.hpp> #include <typeinfo> #include <vector> using namespace std; using boost::any; union ListElement { unsigned char byte; unsigned short word; unsigned int dword; unsigned long long qword; float f; double d; }; class Elem { public: Elem() = default; template<typename ValueType> Elem(const ValueType& value) { this->data = value; } Elem(const Elem& other) { this->data = other.data; } bool operator==(bool value) { return ((bool)toByte()) == value; } bool operator==(char value) { return toByte() == value; } bool operator==(unsigned char value) { return toByte() == value; } bool operator==(short value) { return toInt16() == value; } bool operator==(unsigned short value) { return toInt16() == value; } bool operator==(int value) { return toInt32() == value; } bool operator==(unsigned int value) { return toInt32() == value; } Elem operator=(const Elem& e) { this->data = e.data; return this->data; } /*static Elem operator+(const Elem& left ,const Elem& right) { if (left.type() == typeid(int)) return this->data + e.toInt32(); }*/ unsigned char toByte() { ListElement e = this->convert(); return e.byte; } short toInt16() { ListElement e = this->convert(); return e.word; } int toInt32() { ListElement e = this->convert(); return e.dword; } long long toInt64() { ListElement e = this->convert(); return e.qword; } float toFloat() { ListElement e = this->convert(); return e.f; } double toDouble() { ListElement e = this->convert(); return e.d; } string toString() { if (this->isType<string>()) return "\""+this->cast<string>()+ "\""; else if (this->isType<const char*>()) return "\""+string(this->cast<const char*>())+ "\""; else if (this->isType<char*>()) return "\""+string(this->cast<char*>())+"\""; else if (this->isType<bool>()) return this->cast<bool>() ? "true" : "false"; else if (this->isType<char>() || this->isType<unsigned char>()) return to_string(this->toByte()); else if (this->isType<short>() || this->isType<unsigned short>()) return to_string(this->toInt16()); else if (this->isType<int>() || this->isType<unsigned int>()) return to_string(this->toInt32()); else if (this->isType<long>() || this->isType<unsigned long>()) return to_string(this->toInt32()); else if (this->isType<long long>() || this->isType<unsigned long long>()) return to_string(this->toInt64()); else if (this->isType<float>()) return to_string(this->toFloat()); else if (this->isType<double>()) return to_string(this->toDouble()); else return string("undefined"); } template<class T> T cast() { if (this->data.type() != typeid(T)) throw exception(("data type:"+string(this->data.type().name())+" is not "+string(typeid(T).name())).c_str()); T result = boost::any_cast<T>(this->data); return result; } const boost::typeindex::type_info& type() { return this->data.type(); } template<class T> bool isType() { if (this->empty()) return false; return this->data.type() == typeid(T); } bool empty() { return this->data.empty(); } private: ListElement convert() { ListElement e{ 0 }; if (this->data.type() == typeid(unsigned char)) e.byte = boost::any_cast<unsigned char>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(char)) e.byte = boost::any_cast<char>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(short)) e.word = boost::any_cast<short>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(unsigned short)) e.word = boost::any_cast<unsigned short>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(int)) e.dword = boost::any_cast<int>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(unsigned int)) e.dword = boost::any_cast<unsigned int>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(long)) e.dword = boost::any_cast<long>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(unsigned long)) e.dword = boost::any_cast<unsigned long>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(long long)) e.qword = boost::any_cast<long long>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(unsigned long long)) e.qword = boost::any_cast<unsigned long long>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(float)) e.f = boost::any_cast<float>(this->data); else if (this->data.type() == typeid(double)) e.d = boost::any_cast<double>(this->data); else { string name = this->data.type().name(); throw std::exception(("data type " + name + " is not supported").c_str()); } return e; } private: any data; }; -
实现
List.hpp#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include <vector> #include "Elem.hpp" using namespace std; class List { public: List() = default; List(const List& list, bool isRestruct = true) { if (isRestruct) { for (int i = 0; i < list.data.size(); i++) { this->data.push_back(list.data[i]); } return; } this->data.push_back(list); } List(const string& str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) { this->data.push_back((unsigned char)str[i]); } } /* 其实现必须在头文件,否则会找不到符号 */ template<typename... Arg> List(Arg... args) { append(args...); } template<typename T> void append(T value) { data.push_back(value); } template <typename Head, typename... Rail> void append(Head head, Rail... last) { data.push_back(head); append(last...); } List operator+(const int i) { this->data.push_back(i); return this; } List operator+(const List& list) { List tempList; for (int i = 0; i < this->data.size(); i++) { tempList.data.push_back(this->data[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < list.data.size(); i++) { tempList.data.push_back(list.data[i]); } return tempList; } List operator=(const List& list) { this->data.clear(); for (int i = 0; i < list.data.size(); i++) { this->data.push_back(list.data[i]); } return this; } List operator+=(const string& str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) { this->data.push_back(str[i]); } return this; } List operator+=(const List& list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.data.size(); i++) { this->data.push_back(list.data[i]); } return this; } List operator+=(unsigned char c) { this->data.push_back(c); return this; } Elem& operator[](int index) { return data[index]; } void set(int index, Elem a) { this->data[index] = a; } Elem get(int index) { return this->data[index]; } void foreach(void(*callback)(Elem&)) { for (int i = 0; i < this->data.size(); i++) { callback(this->data[i]); } } string toByteString() { string str; for (int i = 0; i < this->data.size(); i++) { str += this->data[i].toByte(); } if (str.size() != this->data.size()) throw exception(("List to string failed,"+to_string(this->data.size() - str.size())+" byte(s) are missing").c_str()); return str; } int size() { return this->data.size(); } bool empty() { return this->data.size() == 0; } bool exist(int index) { if (this->data.size() >= index && !this->data[index].empty()) { return true; } return false; } static void fromJson(string jsonValue) { } string toIntArray() { string intArray; for (auto i = 0; i < this->data.size() - 1; i++) { intArray += to_string((unsigned int)data[i].toByte()) + ", "; } intArray += to_string((unsigned int)data[this->data.size() - 1].toByte()); return intArray; } string toStringArray() { string array = "["; for (auto i = 0; i < this->data.size(); i++) { array += data[i].toString()+ (i==(this->data.size()-1)? "":","); } array += "]"; return array; } private: vector<Elem> data; }; -
实现
Dict.hpp#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include <map> #include "Elem.hpp" using namespace std; class Dict { public: Dict() = default; Dict(const Dict& dict) { this->update(const_cast<Dict&>(dict)); } Dict(pair<Elem, Elem>) { } Elem& operator[](const Elem& key) { string strKey; Elem& e = const_cast<Elem&>(key); string name = e.type().name(); if (e.isType<string>()) { strKey = e.cast<string>(); } else if (e.isType<int>()) { strKey = to_string(e.cast<int>()); } else if (e.isType<char*>()) { strKey = e.cast<char*>(); } else if (e.isType<const char*>()) { strKey = e.cast<const char*>(); } else { throw exception(("unsupport type "+ name).c_str()); } if (!this->exist(strKey)) { this->data[strKey] = Elem(); } return this->data[strKey]; } Dict& operator+(Dict& dict) { this->update(dict); return *this; } void operator=(const Dict& dict) { this->data.clear(); this->update(dict); } void operator+=(Dict dict) { this->update(dict); } map<string,Elem>::iterator begin() { return this->data.begin(); } map<string, Elem>::iterator end() { return this->data.end(); } void foreach(void callback(string& key, Elem& value)) { for (auto i = this->data.begin(); i != this->data.end(); i++) { callback((string&)i->first, (Elem&)i->second); } } int size() { return this->data.size(); } bool empty() { return this->data.empty(); } bool exist(int key) { return this->data.find(to_string(key)) != this->data.end(); } bool exist(string key) { return this->data.find(key) != this->data.end(); } void update(const Dict& dict) { int a = 0; for (auto i = dict.data.begin(); i != dict.data.end(); i++) { this->data[i->first] = i->second; } } vector<string> keys() { vector<string> keys; for (auto i = this->data.begin(); i != this->data.end(); i++) { keys.push_back(i->first); } return keys; } string toStringArray() { string array="{"; int count = 0; for (auto i = this->begin(); i != this->end(); i++) { array = array + i->first + ":" + i->second.toString() + (count == this->size()-1? "":","); count++; } array += "}"; return array; } private: map<string, Elem> data; }; -
测试案例
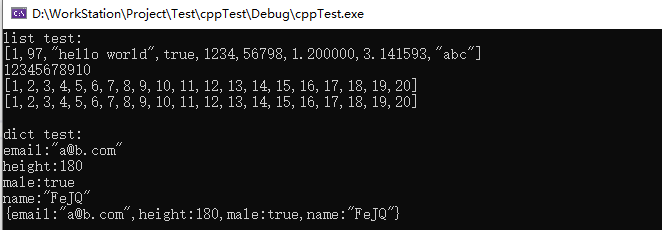
// cppTest.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。 // #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include "List.hpp" #include "Dict.hpp" using namespace std; void listTest() { char c[] = { 'a','b','c','\0' }; List list1(1, 'a', "hello world", true, (short)1234, (long long)56798, 1.2f, 3.14159264); List list2(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10); List list3(11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20); // 往list1结尾追加元素(或 list1+=c;) list1.append(c); cout << list1.toStringArray() << endl; // 遍历list2 for (auto i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) { cout << list2[i].toString(); } cout << endl; // 拼接list2和list3 List listA = list2 + list3; cout << listA.toStringArray() << endl; // 当List中数据只有C语言基本类型时,List和string可以互相转换 string byteStr = listA.toByteString(); List strList = List(byteStr); cout << strList.toStringArray() << endl; // 默认情况下,构造List时传入List类型,会将ListA中的元素转移过去,如果第二个参数为falst,则会产生List嵌套 List(listA,true); } void dictTest() { Dict dict1; dict1["name"] = "FeJQ"; dict1["height"] = 180; dict1["male"] = true; if (!dict1.exist("email")) { dict1["email"] = "a@b.com"; } for (auto i=dict1.begin();i!=dict1.end();i++) { cout << i->first << ":" << i->second.toString() << endl; } cout << dict1.toStringArray() << endl; } int main() { cout << "list test:" << endl; listTest(); cout <<endl<< "dict test:" <<endl; dictTest(); getchar(); }效果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号