C++正则
头文件<regex>
先贴正则规则:
链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hesse-summer/p/10875487.html
\:\字符能够改变字符原本的含义
^:^字符指示字符串的头,且要求字符串以字符开头,不占位。\^表示一个真正的^符号。
$:$字符指示字符串的尾,且要求字符串以字符结尾,不占位。\$表示一个真正的$符号。
():分组,大正则中包含小正则。可以改变默认的优先级。在模式中可以使用\1来表示第一组已然捕获到的东西。
\b:指示字符串的边界(头/尾/空格左/空格右),字符\b要求边界的左边是字符,\b字符要求边界的右边是字符。
.:表示一个除了\n以外的任意一个字符。\.表示一个真正的.符号。
|:字符串1|字符串2表示一个字符串,该字符串是字符串1、字符串2中的一个。|在正则中的优先级比较混乱,所以建议加上足够多的括号来分组。
[]:[字符1字符2字符3...]表示一个字符,该字符是字符1、字符2、字符3……中的某一个。中括号中出现的所有字符都是代表本身意思的字符(没有特殊含义),如[.]只能匹配.符号,而不能匹配任意符号。
[^字符1字符2字符3...]表示一个字符,该字符不是字符1、字符2、字符3……中的任何一个
[a-z]表示一个字符,该字符是a、b、c……z中的某一个
[^a-z]表示一个字符,该字符不是a、b、c……z中的任何一个
\w:表示一个字符,该字符是数字、字母、下划线中的某一个。等价于[(0-9)(a-z)(A-Z)(_)]
\W:表示一个字符,该字符不是数字、字母、下划线中的任何一个。等价于[]
\d表示一个字符,该字符是0、1、2……9中的某一个
\D表示一个字符,该字符不是0、1、2……9中的任何一个
\s表示一个字符,该字符是空白符(空格、制表符、换页符)2、代表出现次数的
量词元字符
*:字符*要求字符出现0到多次
+:字符+要求字符出现1到多次
?:字符?要求字符出现0次或1次
{n}:字符{n}要求字符出现n次
{n,}:字符{n,}要求字符出现n到多次
{n,m}:字符{n,m}要求字符出现n到m次、
regex为正则对象,用来声明正则匹配的模式,比如:
regex pattern("(fuck)*");
匹配 空串、fuck 、fuckfuck、fuckfuck。。。
三个函数:
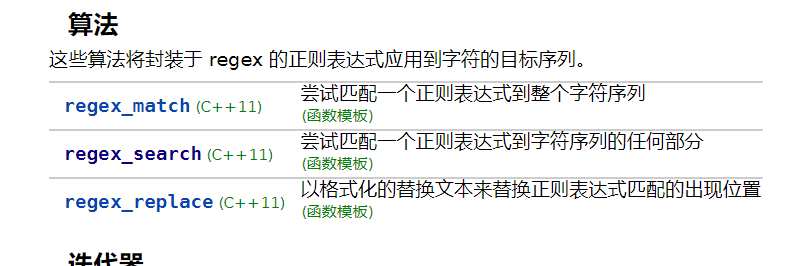
regex_match和regex_search用法基本相同,栗子:
int main() { string s = "{1}432523523rewwf{ff32d23f2},{42323}{3}"; string pattern = "(\\{)(\\w*)(\\})"; regex ss(pattern); smatch x; auto iter = s.cbegin(); while (regex_search(iter, s.cend(), x, ss)) { cout << x[0] << endl; for (auto& str : x) { cout << "---"<<str; }cout << endl; iter = x[0].second; } getchar(); }
分析一下匹配模式:(\\{)(\\w*)(\\})
由于{x,y}在正则中有特殊意义,所以{}是特殊字符,如需要使用得转义,用\\{表示{字符。(正常一个转义字符即:\{ 应该就够了,但C++好像不行)
()括起来的称为一个分组,相当于一个大正则表达式里面的每个括号括起来的都是小正则表达式。
\\w也是转义,实际是\w,意义在上面表里。
*是修饰\w的,意思是可以有0或多个\w。
regex_search是模板函数,有多个重载版本,比如:
bool regex_search( BidirIt first, BidirIt last,
std::match_results<BidirIt,Alloc>& m,
const std::basic_regex<CharT,Traits>& e,
std::regex_constants::match_flag_type flags =
std::regex_constants::match_default );
其中flags不用管,前面参数依次是起始迭代器、终止迭代器、匹配结果容器、匹配模式串。
template< class CharT, class Alloc, class Traits >
bool regex_search( const CharT* str,
std::match_results<const CharT*,Alloc>& m,
const std::basic_regex<CharT,Traits>& e,
std::regex_constants::match_flag_type flags =
std::regex_constants::match_default );
参数依次:c字符串、匹配结果容器、匹配模式
template< class STraits, class SAlloc,
class Alloc, class CharT, class Traits >
bool regex_search( const std::basic_string<CharT,STraits,SAlloc>& s,
std::match_results<
typename std::basic_string<CharT,STraits,SAlloc>::const_iterator,
Alloc
>& m,
const std::basic_regex<CharT, Traits>& e,
std::regex_constants::match_flag_type flags =
std::regex_constants::match_default );
参数依次:string、匹配结果容器、匹配模式串。
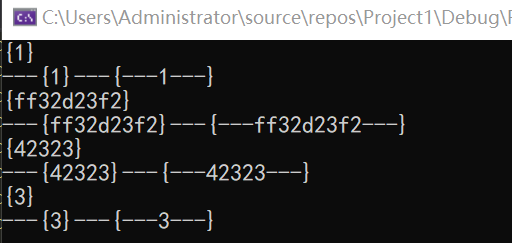
regex_replace:把匹配的子串都替换为相应的新串,当然也有各种重载版本,比如带迭代器的、c字符串的、string的。这里举一个string版本的栗子:
int main() { string s = "{1}432523523rewwf{ff32d23f2},{42323}{3}"; string pattern = "(\\{)(\\w*)(\\})"; regex ss(pattern); smatch x; auto iter = s.cbegin(); string out=regex_replace(s, ss,"fuck"); cout << out; getchar(); }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号