DRF-基础知识回顾
一. REST规范
Representational State Transfer表现层状态转换,是一种用于创建Web服务的架构模式。而RESTfull服务则是实现该模式的服务-API;
1.1 REST的起源
Roy Fielding在2000年撰写的一篇论文中介绍了REST架构模式;该论文定义了客户端和服务器交换application数据的方法;一个关键特定是客服端不需要事先知道application的任何信息;Roy定义了个图案与约束和架构元素的REST;
1.2 REST的架构约束
客户端-服务器、分层系统和无状态约束相结合,形成了一个具有坚实边界和关注点之间明确分离的应用程序。在 REST 中,客户端和服务器共享有关数据和状态的知识。该架构不隐藏数据,它只隐藏实现。
客户端-服务器:REST 应用程序有一个管理应用程序数据和状态的服务器。服务器与处理用户交互的客户端进行通信。客户端与服务器完全分离-前后端分离;
无状态:服务器不维护任何客户端状态。客户端管理他们的应用程序状态。他们对服务器的请求包含处理它们所需的所有信息。
可缓存:服务器必须将其响应标记为可缓存或不可缓存。因此,基础设施和客户端可以在可能的情况下缓存它们以提高性能。它们可以处理不可缓存的信息,因此没有客户端使用陈旧数据。
统一接口:这个约束是 REST 最著名的特性或规则。Roy说过“将 REST 架构风格与其他基于网络的风格区分开来的核心特征是它强调组件之间的统一接口。”。
分层系统:系统中的组件无法“看到”超出其层的内容。因此,您可以轻松添加负载平衡器和代理以提高安全性或性能。
1.3 RESTfull API规范
-
协议:API与用户的通信协议,总是HTTPs协议。
-
域名:应尽量将API部署在专用域名之下。
# 专用域名,建议使用,但是会导致跨域问题 https://api.example.com # 如果确定API很简单,不会进一步扩展,可以考虑放在主域名下 https://www.example.com/api/ -
版本:Versioning将API的版本号放入URL。
# 版本信息放入URL https://api.example.com/v1/ # 版本信息也可以放入HEAD,但不够直观 Accept: vnd.example-com.foo+json; version=1.0 -
路径:即Endpoit,在REST架构中每个URI代表一种resource,所以网址中不能有动词,只能用名词;
# 这些名词往往与数据库的表格名对应 # 而数据库中的表都是同种记录的集合,所以API中的名词也应该使用复数; https://api.example.com/v1/zoos https://api.example.com/v1/animals https://api.example.com/v1/employees -
动词:HTTP动词,对于资源的操作类型
# 常用的共5种: GET - SELECT:从服务器取出资源,一项或多项; POST - CREATE:在服务器上新建一个资源; PUT - UPDATE:在服务器更新资源,客户端提供改变后的完成资源; PATCH - UPDATE:在服务器更新资源,客户端仅需提供资源改变的属性; DELETE - DELETE:从服务器删除资源; # 不常用的2种: HEAD:获取资源的元数据; OPTIONS:获取信息,关于资源的哪些属性是客户端可以改变的; # 一些例子: GET /zoos:列出所有的动物园 GET /zoos/ID:获取某个特定的动物园信息 GET /zoos/ID/animals:列出某个指定动物园的所有动物 POST /zoos:新建一个动物园 PUT /zoos/ID:更新某个动物园,提供这个动物园的所有信息 PATCH /zoos/ID:更新某个动物园,提供这个动物园的部分信息 DELETE /zoos/ID:删除某个动物园 DELETE /zoos/ID/animals/ID:删除某个动物园的指定动物 -
过滤:Filter限定放置在URL中,API应根据参数,返回过滤后的结果;
tips: 参数的设计语序存在冗余,即允许API路径和URL参数偶尔有重复,如:GET /zoos/ID/animals与GET /animals?zoo_id=ID的含义是相同的。
?limit=10:指定返回记录的数量 ?offset=10:指定返回记录的开始位置 ?page=2&page_size=100:指定第几页,以及每页的记录数 ?sortby=name&order=asc:指定返回结果按照哪个属性排序,以及排序顺序 ?animail_type_id=1:指定筛选条件 -
状态码:Status Codes,服务器向客户端返回状态码和提示信息
# 常见的状态码: 200 OK - GET 服务器成功返回请求数据,幂等-Idempotent 201 CREATED - POST/PUT/PATCH 用户新建或修改数据成功 202 Accepted - * 请求已进入后台排队-异步任务 204 NO CONTENT - DELETE 删除数据成功 400 INVALID REQUEST - POST/PUT/PATCH 客户端发送请求有错误,服务器没有做操作,幂等-Idempotent 401 Unauthorized - * 客户度未认证,token/用户名/密码错误 403 Forbidden - * 客户端认证,但是没有访问该资源的权限 404 NOT FOUND - * 客户端请求的资源,服务器上没有,幂等-Idempotent 406 NOT Acceptable - GET 客户端请求的数据封装格式不可得,比如请求json,而服务器只有xml 410 Gone - GET 客户端请求的资源已被永久删除,且不会再得到 422 Uprocesable entity - POST/PUT/PATCH 当创建对象时发生一个验证错误 500 INTERNAL SERVER ERROR - * 服务器发生错误,用户无法判断发出的请求是否陈宫 -
错误返回:Error handling,如果返回4XX状态码,就应该向客户端返回错误信息,一般以error为key
{ error: "invalid API key" } -
结果返回:针对不同的动作,服务器向客户端返回的结果应该符合一定规范
GET /collection:返回资源对象的列表/数组 - [{}..{}..[]] GET /collection/resource:返回单个资源对象 - {} POST /collection:返回新生成的资源对象 - {} PUT /collection/resource:返回完整的资源对象 - {} PATCH /collection/resource:返回完整的资源对象 - {} DELETE /collection/resource:返回一个空文档 - {} -
Hypermedia API:返回结果中提供链接,连向其他API方法,告诉客户端下一步怎么做
{ "link": { // 文档内带link属性,告知客户端下不易该调用什么API // rel表示这个API与网址的关系, 网址的collection "rel": "collection https://www.example.com/zoos", // hrep 表示API的链接 " href": "https://api.example.com/zoos", // title 说明或标题 "title": "List of zoos", // 支持什么样的封装格式,这里是json "type": "application/vnd.yourformat+json" } }
{ "current_user_url": "https://api.github.com/user", "current_user_authorizations_html_url": "https://github.com/settings/connections/applications{/client_id}", "authorizations_url": "https://api.github.com/authorizations", "code_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/code?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}", "commit_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/commits?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}", "emails_url": "https://api.github.com/user/emails", "emojis_url": "https://api.github.com/emojis", "events_url": "https://api.github.com/events", "feeds_url": "https://api.github.com/feeds", "followers_url": "https://api.github.com/user/followers", "following_url": "https://api.github.com/user/following{/target}", "gists_url": "https://api.github.com/gists{/gist_id}", "hub_url": "https://api.github.com/hub", "issue_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/issues?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}", "issues_url": "https://api.github.com/issues", "keys_url": "https://api.github.com/user/keys", "label_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/labels?q={query}&repository_id={repository_id}{&page,per_page}", "notifications_url": "https://api.github.com/notifications", "organization_url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/{org}", "organization_repositories_url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/{org}/repos{?type,page,per_page,sort}", "organization_teams_url": "https://api.github.com/orgs/{org}/teams", "public_gists_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/public", "rate_limit_url": "https://api.github.com/rate_limit", "repository_url": "https://api.github.com/repos/{owner}/{repo}", "repository_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}", "current_user_repositories_url": "https://api.github.com/user/repos{?type,page,per_page,sort}", "starred_url": "https://api.github.com/user/starred{/owner}{/repo}", "starred_gists_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/starred", "user_url": "https://api.github.com/users/{user}", "user_organizations_url": "https://api.github.com/user/orgs", "user_repositories_url": "https://api.github.com/users/{user}/repos{?type,page,per_page,sort}", "user_search_url": "https://api.github.com/search/users?q={query}{&page,per_page,sort,order}" }-
其他
API的身份认证应该使用OAuth 2.0框架;
服务器返回的数据格式,应该尽量使用JSON,避免使用XML;
返回信息中有code和data两个key,code存放额外约定的信息,data中存放返回的对象或列表;
{ "code":0, "data":[ {"message": "hello api01"}, {"message": "hello api02"}, {"message": "hello api03"}, {"message": "hello api04"}, ] }
-
二. FBV与CBV
Django同时支持FBC(Function base view)和CBV(Class base view)这两种关系;
2.1 FBV
在url映射的view中使用函数的方式来handle请求
def home(request):
if request.method == "GET":
pass
elif request.method == "POST":
USER_LIST.append({'user': request.POST.get('user1'),
'pwd': request.POST.get('pwd'),
'mail': request.POST.get('mail')})
# 通过dict将USER_LIST映射给模板中的user_list
# 模板中的user_list接到数据后,会执行循环语句遍历并替换
return render(request, 'home.html', {"user_list": USER_LIST})
2.1.1 装饰FBV
在装饰FBV时,为防止出错,需要使用functools.wraps对装饰器的inner装饰,防止原始函数信息改变;
from functools import wraps
# 普通装饰器会覆盖被装饰函数的inner信息,比如fun._name__, fun.__info__等;
# 使用wraps可以将fun的相关信息保留并完成装饰
def time_cost(func):
@wraps(func)
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
print("spend time", time.time() - start)
return res
return inner
# View视图函数
@time_cost
def some_view_fun(request):
...
2.2 CBV
CBV方式中view中的url对应的是一个类<此类事views类的子类>。
2.2.1 处理请求前
- 调用as-view方法,返回view方法;
- as-view中对view方法的处理:
- 使用获取的相关init参数实例化cls;
- 使用setup方法初始化一些属性;
- 定义dispatch方法的调用,并返回结果;
@classonlymethod
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs):
"""Main entry point for a request-response process."""
# initkwargs传入一些初始化参数
# 参数的key不可以为http_method的名字,如get, post之类
# 传入的参数的key必须在当前类中可以找到,也就说本身就存在的,可以改值,本身不存在的不可以新增
for key in initkwargs:
if key in cls.http_method_names:
raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a "
"keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that."
% (key, cls.__name__))
if not hasattr(cls, key):
raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r. as_view "
"only accepts arguments that are already "
"attributes of the class." % (cls.__name__, key))
# 内部的view函数,用于as_view的返回
def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
# 1. 使用initkwargs实例化一个当前View类/子类的对象
self = cls(**initkwargs)
# 2. 如果没有head方法,那么head方法按照get方法来处理
if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'):
self.head = self.get
# 3.1 将request封装进self.request中
# 3.2 将args封装进self.args
# 3.3 将kwargs封装进self.kwargs
self.setup(request, *args, **kwargs)
# 4. 如果没有request对象,则报错
if not hasattr(self, 'request'):
raise AttributeError(
"%s instance has no 'request' attribute. Did you override "
"setup() and forget to call super()?" % cls.__name__
)
# 5. view返回的是self的dispatch方法,所以dispatch方法必须返回一个HTTPResponse类的对象
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
# 为view添加属性viewclas为当前的view类/子类
# 为view添加view_initkwargs属性,值为initkwargs
view.view_class = cls
view.view_initkwargs = initkwargs
# 从类中获取名称和文档字符串
# take name and docstring from class
update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=())
# 获取一些可能的参数,比如装饰器
# and possible attributes set by decorators
# like csrf_exempt from dispatch
update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=())
# 返回view函数
return view
2.2.2 处理请求
- django会根据ur来找到指定的function或者class;
- 根据request.method属性通过对view示例的反射查找到对应的方法并执行;
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Try to dispatch to the right method; if a method doesn't exist,
# defer to the error handler. Also defer to the error handler if the
# request method isn't on the approved list.
# 1. 判断当前的method是否是一个允许的请求
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
# 如果不在,则为非法请求,使用预定义的方式返回异常响应
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
# 使用view内对应的函数作为handler
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
# 2. 使用handler处理request请求并返回处理结果
return handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
2.2.3 装饰CBV
在装饰CBV时,需要额外调用一个django.utils.decorators中的method_decorator方法;
from django.views import View
# 需要导入method_decorator
# 作用是让传入的第一个参数为request,与FBV方式相同,而非self即当前对象;
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
方式一:直接装饰CBV中的某个函数
class Home(View):
@method_decorator(time_cost) # 为所有的方法添加装饰器
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
result = super(Home, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)dispatch
return result
@method_decorator(time_cost) # 为单独的某个方法添加装饰器
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse("get..")
方式二:装饰CBV,并指定某个参数
@method_decorator(time_cost, name='post') # 可以写在类上面,并指定被装饰方法
@method_decorator(time_cost, name='dispatch') # 可以写在类上面,并指定被装饰方法
class Home(View):
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse("get..")
三. CSRF
CSRF(Cross-site request forgery),中文名称:跨站请求伪造,也被称为:one click attack/session riding,缩写为:CSRF/XSRF
如图中所示,B利用了A在浏览器中的cookie信息,模拟合法用户在A上完成了一个用户完全不知得到操作,从而达成一定的目的;

3.1 django中CSRF的防御流程
django中使用csrf-token验证的方式来防御CSRF攻击:
-
当用户GET请求,django会在HTML中内生成一个隐藏标签并设置cookies;
# HTML的隐藏标签 <input type="hidden" name="csrfmiddlewaretoken" value=64位字符串> -
当用户发起POST/PUT/PATCH类的请求时,data需要同时携带隐藏input的value值(CSRF-TOKEN);
-
django收到后,会在CSRF中间件中完成data内的token与cookies中的token的比较,相同则通过;
class CsrfViewMiddleware(MiddlewareMixin): # 在request中获取cookie中的csrf_token def process_request(self, request): csrf_token = self._get_token(request) if csrf_token is not None: # Use same token next time. request.META['CSRF_COOKIE'] = csrf_token def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs): if getattr(request, 'csrf_processing_done', False): return None # 如果设置了豁免,则不执行 if getattr(callback, 'csrf_exempt', False): return None # Assume that anything not defined as 'safe' by RFC7231 needs protection if request.method not in ('GET', 'HEAD', 'OPTIONS', 'TRACE'): # 如果request中没有强制认证则直接返回 if getattr(request, '_dont_enforce_csrf_checks', False): return self._accept(request) if request.is_secure(): #如果是HTTPS请求,则验证下token,过程忽略吧,获取请求不主要 pass # 从META中获取cookie中的token csrf_token = request.META.get('CSRF_COOKIE') # 获取非cookie中的csrf-token request_csrf_token = "" # 如果是POST请求,从data中获取 if request.method == "POST": request_csrf_token = request.POST.get('csrfmiddlewaretoken', '') # 如果未获取到,去头部中预定义的CSRF_HEADER_NAME中查找 if request_csrf_token == "": request_csrf_token = request.META.get(settings.CSRF_HEADER_NAME, '') # 一个token长64为,其中前32位位salt后32位加密后的secret; # 分别使用salt对密文解密得到secret,并对比是否相同; request_csrf_token = _sanitize_token(request_csrf_token) if not _compare_salted_tokens(request_csrf_token, csrf_token): return self._reject(request, REASON_BAD_TOKEN) # 默认返回通过 return self._accept(request) def process_response(self, request, response): # 根据cookies中的异常是行之来维护csrf-token if not getattr(request, 'csrf_cookie_needs_reset', False): if getattr(response, 'csrf_cookie_set', False): return response if not request.META.get("CSRF_COOKIE_USED", False): return response # 刷新csrf-token self._set_token(request, response) response.csrf_cookie_set = True return response
四. 中间件
中间件是一个用来处理Django的请求和响应的框架级别的钩子。它是一个轻量、低级别的插件系统,用于在全局范围内改变Django的输入和输出。每个中间件组件都负责做一些特定的功能。本质是一个自定义类,类中定义了几个方法,Django框架会在处理请求的特定的时间去执行这些方法。
4.1 配置方式
# 新建类-需要使用MiddlewareMixin
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
class MID01(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request): # 处理request对象,在url匹配之前
return None # 正常流程
return HttpResponse # 直接跳转至同cls下的Response方法,然后向上返回
def process_view(self, request, view_func, view_args, view_kwargs): # 在路由之后,View函数之前
return None # 正常流程
return HttpResponse # 跳过view函数的执行,直接进入最后一个中间件的response函数,开始返回;
def process_response(self, request, response): # view执行之后,处理response
return response # 返回处理后的HttpResponse对象
def process_exception(self, request, exception): # 当view函数执行异常时,执行
return None # 当前中间件没有处理异常的方法,交予下一级处理
return HttpResponse # 当前中间件处理异常,跳过之后的exception,开始返回;
def process_template_response(self, request, response): # 在render之前
return response # 修改TemplateResponse对象,如TR.template.name, TR.response.context.data
# 在setting中调用
MIDDLEWARE = [
'app.middlewares.mid01.MID01',
]
4.2 中间件执行流程
非触发式流程如下

包含触发式流程如下

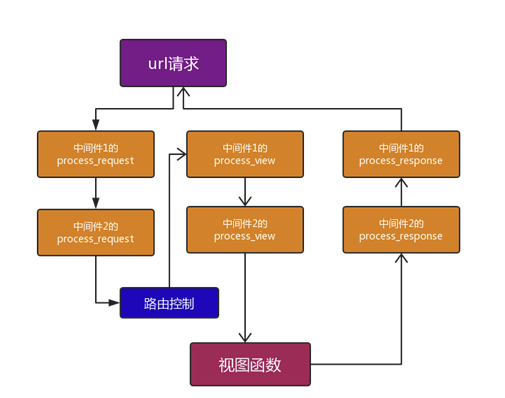
参考:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号