No.001-Python-学习之路-Day1-编码|注释|变量|交互|流程
charater encoding

First of all
computer only know 0 and 1
then sientist use binary to express the number large than one
255 --- 1111 1111
then sientist make a correspondence between words and numbers,we call it character encoding
ASCII 255 1bytes
---> 1980 gb2312 7000+
---> 1995 GBK1.0 2W+
---> 2000 GB18030 27000+
---> unicode 2bytes
--->utf-8 en:1bytes zh:3bytes
Coding
Singe Line:
# single line coding by "#"
Multi Lines:
msg = ''' When you want to giveup tell yourself "every cloud has a silver lining" '''
print(msg)
Varable
变量名规则:
1.变量名内只能包含字符<英文字符及中文字符>,下划线及数字的组合;
2.变量名开头不可以为数字
3.变量名不可以是语言关键字,如:and as assert break class continue def del elif # else except finally for from global if import in is lambda not or pass print raise return # try with yield
变量的存储于调用:
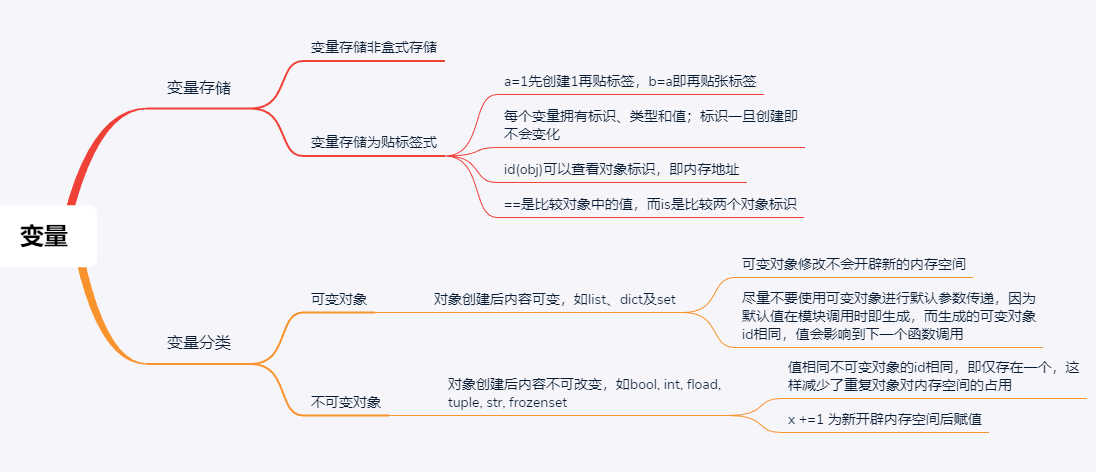
# 非盒式存储
list1 = [1, 2, 3] # [1,2,3]开辟内存空间, list1为标签
list2 = list1 # list2为标签2
print(id(list1), id(list2)) # 17223432 17223432
print(list1 is list2) # True
# 可变对象
list3 = [1, 2, 3]
print(id(list3)) # 12994184 于list1对比即使值相同id也不同,不同于不可变对象
list3.append(4)
print(id(list3), list3) # 12994184 [1, 2, 3, 4] id无变化,值变化,修改id不变
def fun(value, default = []): # 加载模块时即生成默认的[]
default.append(value)
return default
l1 = fun("a")
l2 = fun("b")
print(id(l1), id(l2), l1, l2) # 23607048 23607048 ['a', 'b'] ['a', 'b'] 值相同,id相同,值异常
# 不可变对象
name1 = "Bruce"
name2 = "Bruce"
print(id(name1), id(name2)) # 16841280 16841280 # 值相同的不可变变量只会创建一个,再次创建只是引用;
print(id(name1.replace("B", "b"))) # 6109248 非在原id上变更,而是直接生成了一片新内存用于存储新值
Interation
username = input("Input your username:") age = input("Input your age:") job = input("Input your job:") salary = input("Input your salay:") info = ''' --------------info of $---------------- Name: Age: Job: Salary: ''' # first method --- String splicing ---use multi block memory info1 = ''' --------------info of ''' + username + '''---------------- Name:''' + username + ''' Age:''' + age + ''' Job:''' + job + ''' Salary:''' + salary + ''' ''' # print(info1) # second method --- reference variables %s->string %d->integer %f->float # So default input is string ,we need change str to integer # [python is strong type definition] age = int(age) info2 = ''' --------------info of %s---------------- Name:%s Age:%d Job:%s Salary:%s ''' % (username, username, age, job, salary) print(info2) # Third method --- .format() --sometimes you can only use this method info3 = ''' --------------info of {_name} ---------------- Name:{_name} Age:{_age} Job:{_job} Salary:{_salary} '''.format( _name=username, _age=age, _job=job, _salary=salary) print(info3) # Fourth Method ---.format() with {0-N} variables in sequence info4 = ''' --------------info of {0} ---------------- Name:{1} Age:{2} Job:{3} Salary:{4} '''.format(username, username, age, job, salary) print(info4)
Python中的流程
程序中的三大流程:
1.自上至下的代码执行------------------顺序
2.根据条件判断执行相应代码---------分支
# if....elif....else...
3.根据一定特征循环执行某块代码---循环
# while (someting is true) ....
# for .... in ......
Loop
for....in......:可以遍历任何序列中的项目,如列表字符串
string = "every cloud has a silver lining" for letter in string: print(letter) # [] is a list list = ["every", "cloud", "has", "a", "silver", "lining"] for string in list: print(string) # range() can make a inter list range(begin, end, step) for string in range(1, 10, 3): print(string) # () is a tuple , if only on parameter tuple is ("parameter",) not ("parameter") LIST = ("silver1", "lining1") for string in LIST: print(string) # {} is dict LIST = {"AA": "BB", "c": "dd"} # enumerate() can get both index and value of a string,list,dict and tuple .etc for index, key in enumerate(LIST): print("%d-%s:%s" % (index, key, LIST["%s" % key]))
while (somthing is true):当条件成立是执行循环
# "True" mean forever true # continue mean end cycle of this time # break mean end the whole loop count = 0 while True: count += 1 if count % 2 == 0: continue if count > 100: break print(count) # len() can get the num of element in a tuple,list,dict,string TUPLE = ("every", "cloud", "has", "silver", "lining") index = 0 while index < len(TUPLE): print("index: %d value: %s" % (index, TUPLE[index])) index += 1
Judgement
if.....elif....elif.....else....:按照从上到下顺序,条件成立执行相应程序块并结束judgement,如果条件不成立,则继续向下判断elif,如果都不成立则执行else下面程序块
import numpy as np age = np.random.randint(0, 100, size=1) chance = 3 times = 0 while chance > 0: guess_age = input("你猜的年龄是:") if len(guess_age) == 0: print("请输入你猜测的年龄") continue try: guess_age = int(guess_age) times += 1 if guess_age == age: print("Congratulation!! {times}次猜对".format(times=times)) break elif guess_age < age: print("Too Young") else: print("Too old") chance -= 1 if chance <= 0: yes_no = input("3 chance is over!! continue(yes/no):") if yes_no == "yes": chance += 3 else: print("Bye Bye") break except ValueError: print("你的输入不是0-100间的整数") continue
task-1
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Author : Bruce Lee import re # define a class class Aaa(object): def __init__(self, username, password, data_file): self.username = username self.password = password self.data_file = data_file # read file self.fp = open(self.data_file, "r") self.context = self.fp.readlines() self.fp.close() # status mark self.line = "" self.line_list = [] self.result = 0 self.index = 0 def login(self): # If not true ,then the result's value is 0 self.result = 0 # use For...in.. to get value in list() for self.line in self.context: self.line_list = re.split(",", self.line.strip()) if self.username == self.line_list[0]: if self.line_list[2] != "1": if self.password == self.line_list[1]: self.result = 1 break else: self.result = 3 break else: self.result = 2 break else: self.result = 4 return self.result def lock(self): for self.line in self.context: self.index = self.context.index(self.line) self.line_list = re.split(",", self.line.strip()) if self.username == self.line_list[0]: self.line_list[2] = "1" self.line = ",".join(self.line_list) + "\n" self.context[self.index] = self.line self.fp = open(self.data_file, "w") self.fp.write("".join(self.context) + "\n") self.fp.close() self.result = 2 break if self.result != 2: self.fp = open(self.data_file, "a") self.fp.write("%s,NULL,%s%s" % (self.username, "1", "\n")) self.fp.close() # Main program file = "User_name_and_password.txt" step = 0 footprint = [["user", 1]] find_true = 0 while step < 3: username1 = input("请输入用户名:") if username1 == "": print("Please input username!!!") continue password1 = input("请输入密 码:") lg = Aaa(username1, password1, file) login_result = lg.login() if login_result == 2: print("Username has been locked!!!") break elif login_result == 1: print("Welcome to login in my program!!!") break elif login_result == 4: print("Wrong Username!!!!") for used_info in footprint: if username1 == used_info[0]: used_info[1] += 1 step = used_info[1] find_true = 1 break if find_true != 1: footprint.append([username1, 1]) step = 1 if step < 3: continue print("Locked") lg.lock() elif login_result == 3: print("Wrong Password!!!!") if step < 3: continue print("Locked") lg.lock() task-2 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Author : Bruce Lee menu = { "吃": { "火锅": { "海底捞": {11}, "川锅一号": {11}, "辣庄重庆老火锅": {22} }, "炒菜": { "骆马湖活鱼馆": {}, "味府": {}, "项家庄": {} }, "自助": { "欢乐牧场": {}, "金釜山自助烤肉": {}, "多伦多海鲜自助": {} } }, "喝": { "矿泉水": { "娃哈哈": {}, "康帅傅": {}, "百岁山": {} }, "碳酸饮料": { "可口可乐": {}, "雪碧": {}, "芬达": {} }, "果汁": { "农夫果园": {}, "特种兵": {} } }, "玩": { "看电影": { "万达影城": {}, "幸福蓝海": {}, "万象": {} }, "玩游戏": { "网咖": {}, "游戏厅": {}, "手机": {} }, "游乐园": { "夜市": {}, "千鸟园": {}, "向阳城": {} } } } current_layer = menu parent_layers = [] while True: for key in current_layer: print(key) choice = input("你的选择:") if choice in current_layer: parent_layers.append(current_layer) current_layer = current_layer[choice] elif choice == "b": if parent_layers: current_layer = parent_layers.pop() elif choice == "q": print("谢谢光临,下次再见!") break else: print("无此项")
end
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/marton/p/10668003.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangkun122/p/9082088.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号