Spring WebFlux 简介
本文基于 Spring Boot 2.6.0
基于之前提到的 Reactor 的出现,使得编写响应式程序成为可能。为此,Spring 的开发团队决定添加有关 Reactor 模型的网络层。这样做的话将会对 Spring MVC 作出许多重大的修改,因此 Spring 的研发团队决定开发一个单独的响应式处理框架,随之,Spring WeFlux 就这么诞生了。
Spring WebFlux 与 Spring MVC 的关系如下:
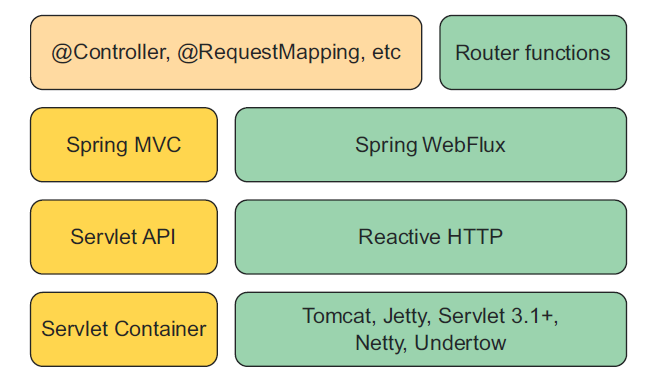
Spring WebFlux 的大部分内容都借鉴了 Spring MVC,许多在 Spring MVC 上使用的注解在 Spring WebFlux 上依旧是可用的,但是 Spring WebFlux 会为此作出特定于 Reactor 的实现
基本使用
注解
依旧可以使用在 Spring MVC 中存在的那些注解
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping(path = "") // MVC 相关
public String hello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", "xhliu2");
return "hello";
}
@GetMapping(path = "/test") // Rest。。。。
public @ResponseBody
Mono<String> test() {
return Mono.just("xhliu2"); // 每个请求都将创建一个 Mono 流,在对请求作出响应时将会将这些流组合到一起(flatMap),因此整个请求整体来讲将会是非阻塞的
}
}
RouteFunction
通过 RouteFunction 来定义请求处理:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunction;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RouterFunctions;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.ServerResponse;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Configuration
public class RouterController {
/*
通过 RouterFunction 来定义处理逻辑。。。。
*/
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route1() {
return RouterFunctions.route(
RequestPredicates.GET("/route1"), // 定义请求方法和路径
// 使用函数式的方式来处理请求,这是为了结合 Reactor 的最佳处理方式(非阻塞)
request -> ServerResponse.ok().body(Mono.just("This is a Mono Sample"), String.class)
);
}
}
如果需要定义多个请求路径,可以额外定义一个 RouterFunction 的 Bean,也可以在一个 RouterFunction Bean 中定义额外的处理路径和处理逻辑
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route2() {
return RouterFunctions.route( // 第一个处理逻辑。。。。
RequestPredicates.GET("/route2"),
request -> ServerResponse.ok().body(Mono.just("This is route2"), String.class)
).andRoute( // 定义的第二个处理。。。
RequestPredicates.GET("/route3"),
request -> ServerResponse.ok().body(Mono.just("This is route3"), String.class)
);
}
也可以通过预先定义的 Bean 的相关的方法,使用函数式编程的方式来处理对应的逻辑:
首先定义一个 Bean,用于定义一些逻辑处理:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.ServerRequest;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.ServerResponse;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Component(value = "handleA")
public class HandlerA {
private final static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HandlerA.class);
public Mono<ServerResponse> echo(ServerRequest request) {
log.info("Ready to echo......");
return ServerResponse.ok().body(Mono.just(request.queryParams().toString()), String.class);
}
}
再定义对应的路径的处理逻辑:
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route3(@Autowired HandlerA handlerA) {
return RouterFunctions.route(
RequestPredicates.GET("/route4"),
handlerA::echo
);
}
源码解析
WebFlux 的初始化
-
根据
classpath来判断当前的 web 应用所属的类型// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication。。。 public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); // 省略一部分不太相关的代码。。。。 }deduceFromClasspath()方法对应的源代码:// 该方法位于 org.springframework.boot.WebApplicationType 中 private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet"; private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler"; private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer"; static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { /* 如果当前加载的 Class 中,WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS 已经被加载并且 WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS 和 JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS 都没有被加载的情况下,才会认为当前的 Web 应用的类型是 Reactive 的 */ if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) { return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; } for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) { if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { return WebApplicationType.NONE; } } return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; } -
创建
Reactive应用上下文创建应用上下文对应的源代码:
// 该源代码位于 org.springframework.boot.ApplicationContextFactory 中。。。 // 注意这里的 Lamada 表达式。。。 ApplicationContextFactory DEFAULT = (webApplicationType) -> { try { switch (webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: return new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(); case REACTIVE: // 根据上一步推断出的 Web 应用类型为 Reactive,因此会走这 return new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext(); default: return new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); } } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext instance, " + "you may need a custom ApplicationContextFactory", ex); } };实例化
AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext对应的源代码:// 一些基本的 Spring IOC 的内容。。。。具体细节可以查看有关 Spring IOC 部分的内容 public AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext() { this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); } -
之后就是一般的 Spring IOC 容器的创建和
Bean的初始化了,与Reactor相关的比较重要的部分为onRefresh()方法调用的阶段,这个方法使用到了模板方法模式,在org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext类中得到了具体的实现onRefresh()在WebFlux中的实现的源代码如下:@Override protected void onRefresh() { // AbstractApplicationContext 中定义的 “模板方法”,就目前 Spring 5.3.13 的版本来讲,是一个空的方法 super.onRefresh(); createWebServer(); // 由 WebFlux 具体定义 // 省略有一部分异常捕获代码 }createWebServer()方法对应的源代码如下:// 该方法定义依旧位于 org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext 中 private void createWebServer() { WebServerManager serverManager = this.serverManager; // 默认为 null if (serverManager == null) { // 获取 BeanFactory。。。。。 StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create"); String webServerFactoryBeanName = getWebServerFactoryBeanName(); /* 默认情况下,WebFlux 会选择 Netty 作为服务器,这是因为 Netty 的处理模型十分适合 Reactor 编程,因此能够很好地契合 WebFlux 在这里的 webServerFactory 为 org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.netty.NettyReactiveWebServerFactory */ ReactiveWebServerFactory webServerFactory = getWebServerFactory(webServerFactoryBeanName); createWebServer.tag("factory", webServerFactory.getClass().toString()); // 获取 BeanFactory 结束。。。。 boolean lazyInit = getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(webServerFactoryBeanName).isLazyInit(); // 默认为 false /* 比较关键的部分,这里会创建一个 WebServerManager */ this.serverManager = new WebServerManager(this, webServerFactory, this::getHttpHandler, lazyInit); // 剩下的部分就是完成一些其它 Bean 的注册了。。。 getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown", new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.serverManager.getWebServer())); getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop", new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this.serverManager)); createWebServer.end(); } // 最后再初始化相关的属性资源,在当前的类中,这也是一个模板方法 initPropertySources(); } -
剩下的就是一般的 IOC 初始化流程,在此不做赘述
WebServerFactory 的实例化
具体对应上文描述的 createWebServer() 方法中
ReactiveWebServerFactory webServerFactory=getWebServerFactory(webServerFactoryBeanName);
的部分,其中 getWebServerFactory 对应的源代码如下:
protected ReactiveWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(String factoryBeanName) {
/*
当前环境下的 factoryBeanName 为 "nettyReactiveWebServerFactory",按照 Spring Bean 默认的命名方式,将会加载 NettyReactiveWebServerFactory 作为 ReactiveWebServerFactory 的实现
*/
return getBeanFactory().getBean(factoryBeanName, ReactiveWebServerFactory.class);
}
WebServerManager 的实例化对应的源代码如下:
WebServerManager(
ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext applicationContext,
ReactiveWebServerFactory factory,
Supplier<HttpHandler> handlerSupplier, boolean lazyInit
) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
Assert.notNull(factory, "Factory must not be null");
/*
比较重要的部分就是有关 HttpHandler 的处理,在这里定义了 HttpHandler Bean 的初始化方式
结合上文中默认传入的参数,在当前的上下文环境中不是以 lazy-init 的方式进行加载的
*/
this.handler = new DelayedInitializationHttpHandler(handlerSupplier, lazyInit);
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(this.handler);
}
具体 NettyReactiveWebServerFactory 中对 getWebServer(handler) 方法的实现如下:
// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.netty.NettyReactiveWebServerFactory
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(HttpHandler httpHandler) {
HttpServer httpServer = createHttpServer();
/*
这里是重点部分!HttpHandler 的作用相当于 Spring MVC 中的 DispatcherServlet,用于处理请求的分发,以及寻找 Handler 对请求进行处理。。。。
这里使用到了 "适配器模式", handlerAdapter 将 HttpHandler 适配到 Netty 的 Channel,使得原本不相干的两个对象能够协同工作
*/
ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter handlerAdapter = new ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(httpHandler);
// 创建 Netty 服务端。。。。。。。。
NettyWebServer webServer = createNettyWebServer(
httpServer, handlerAdapter, this.lifecycleTimeout, getShutdown()
);
webServer.setRouteProviders(this.routeProviders);
return webServer;
}
HttpHandler 的实例化
在 Reactive 中,对于 handlerSupplier 的定义如下:
// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext 中
protected HttpHandler getHttpHandler() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(HttpHandler.class);
// 省略一部分参数检测代码。。。。
// 一般的 BeanFactory 获取 Bean 的步骤
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], HttpHandler.class);
}
由于 Spring Boot 自动配置的存在,在创建应用时会把能够自动配置的类自动配置到 IOC 中,具体包括 spring.factories 文件中定义的 Bean、以及使用 @Configuration 注解修饰的配置类。
在 WebFlux 中 HttpHandler 的配置类的定义如下:
// 此静态类位于 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration 类中,这个类在 spring.factories 文件中定义为是可以自动配置的
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public static class AnnotationConfig {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public AnnotationConfig(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Bean
public HttpHandler httpHandler(ObjectProvider<WebFluxProperties> propsProvider) {
/*
这里使用到了构建者模式的方式来创建对象。。。。。
*/
HttpHandler httpHandler = WebHttpHandlerBuilder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext).build();
// 省略一部分不太重要的代码。。。。。
return httpHandler;
}
}
applicationContext(applicationContext) 对应的源代码如下:
public static WebHttpHandlerBuilder applicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
/*
获取 WebHandler Bean,由于 Spring Boot 的自动配置的存在,在将 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration 配置类加载到 IOC 容器中时,将会自动引入 DispatcherHandler 的 WebHandler Bean
HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration 在 spring.factories 中定义为是可以自动配置的
*/
WebHttpHandlerBuilder builder = new WebHttpHandlerBuilder(
context.getBean(WEB_HANDLER_BEAN_NAME, WebHandler.class), context);
// 添加 WebFliter。。。。
List<WebFilter> webFilters = context
.getBeanProvider(WebFilter.class)
.orderedStream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
builder.filters(filters -> filters.addAll(webFilters));
// 异常处理 Handler。。。
List<WebExceptionHandler> exceptionHandlers = context
.getBeanProvider(WebExceptionHandler.class)
.orderedStream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
builder.exceptionHandlers(handlers -> handlers.addAll(exceptionHandlers));
// 省略一部分不太重要的代码。。。。
return builder;
}
bulid() 方法的定义如下:
// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.web.server.adapter.WebHttpHandlerBuilder 中
public HttpHandler build() {
/*
这里是 WebFlux 用于处理请求的关键的地方,通过 “装饰者” 模式,将 FilterWebHandler 通过 ExceptionHandlingWebHandler 进行 “装饰”,使得在处理请求时先执行 ExceptionHandlingWebHandler 的 handle 的处理逻辑,从而增强了底层 FilterWebHandler 的功能
在设计时值得考虑使用这样的方式来优化自己的设计,从而尽可能地复用已有的对象和类
*/
WebHandler decorated = new FilteringWebHandler(this.webHandler, this.filters);
decorated = new ExceptionHandlingWebHandler(decorated, this.exceptionHandlers);
// 因此最终生成的 HttpHandler 的具体实例化类为 HttpWebHandlerAdapter
HttpWebHandlerAdapter adapted = new HttpWebHandlerAdapter(decorated);
// 省略一部分设置属性相关的代码。。。
return (this.httpHandlerDecorator != null ? this.httpHandlerDecorator.apply(adapted) : adapted);
}
组件的定义
这里又涉及到 Spring Boot 的自动配置,spring.factories 文件中定义了对于 WebFlux 的自动配置类 WebFluxAutoConfiguration:
// 该类定义于org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE)
@ConditionalOnClass(WebFluxConfigurer.class) // 有关 WebFlux 的相关配置。。。。
// 这里引入的类是和 WebFlux 相关的主要类
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ WebFluxConfigurationSupport.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter({ ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class, CodecsAutoConfiguration.class,
ReactiveMultipartAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class,
WebSessionIdResolverAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
public class WebFluxAutoConfiguration {
// 省略类中的内容
}
主要需要关注的是 WebFluxConfigurationSupport 的引入,在这个类中定义了有关请求分发和处理的逻辑的类。
WebFluxConfigurationSupport 中定义的 Bean 如下:
// 此类定义于 org.springframework.web.reactive.config.WebFluxConfigurationSupport
public class WebFluxConfigurationSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
/*
这个 Bean 类似于 Spring MVC 中的 DiaptcherServlet,用于处理请求的分发以及查找对应的 handler 去处理对应的请求(“外观模式” 的使用)
*/
@Bean
public DispatcherHandler webHandler() {
return new DispatcherHandler();
}
/*
由于篇幅问题,在此省略了一些其它必需的 Bean 的定义
*/
}
简单起见,在此仅仅只是描述一下 WebFluxConfigurationSupport 中定义的必需的 Bean:
-
DispatcherHandler用于处理请求的分发、为当前请求寻找对应的处理 Handler,类似于 Spring MVC 中的 DispatcherServlet
-
RouterFunctionMapping和RequestMappingHandlerMapping定义了请求和处理方法之间的对应关系,Spring WebFlux 支持使用传统的 Spring MVC 的注解方式来定义 Handler,也支持使用
RouterFunction通过函数式的方式来定义对应的请求的 Handler -
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter和HandlerFunctionAdapter同样地,两者是都是为了处理实际的请求而做的适配,和 Spring MVC 中对 Handler 的适配是一样的。由于 Spring WebFlux 支持使用
@RequestMapping的方式来定义请求,因此也必须对这种类型的方式定义对应的适配器。 -
WebSocketHandlerAdapter对于
WebSocket的支持。。。。 -
ResponseEntityResultHandler、ResponseBodyResultHandler、ViewResolutionResultHandler以及ServerResponseResultHandlerResponseEntityResultHandler、ResponseBodyResultHandler和ServerResponseResultHandler都是针对 Rest 的响应结果(Http);ViewResolutionResultHandler则是相当于返回的是一个View(MVC 中的View)即 “视图”
整合 Handler
有了这些组件之后,值得关心的地方就是 .*Adapter 和对应的 Handler 之间的连接,即 Adapter 是如何调用 Handler的
首先,经过一系列的 debug 操作,得到 WebFlux 对于一个一般的 Http 请求的处理链如下:

有关 WebHandler 的类层次结构如下:

对请求的具体分析:
-
服务的启动
以
NettyWebServer为例,查看服务启动的源代码// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.netty.NettyWebServer DisposableServer startHttpServer() { HttpServer server = this.httpServer; // HttpServerBind 为当上下文的具体实现 if (this.routeProviders.isEmpty()) { // 在这里定义了对于请求的处理逻辑。。。。 server = server.handle(this.handler); } else { server = server.route(this::applyRouteProviders); } if (this.lifecycleTimeout != null) { return server.bindNow(this.lifecycleTimeout); } return server.bindNow(); }handle(handler)对应的源代码如下:// 该方法定义于 reactor.netty.http.server.HttpServer /* 该方法的主要目的是捕获来自客户端的请求,附加一个 IO 处理程序以对连接的客户端作出响应 */ public final HttpServer handle( BiFunction<? super HttpServerRequest, ? super HttpServerResponse, ? extends Publisher<Void>> handler) { Objects.requireNonNull(handler, "handler"); // 重点在于具体的 handler,它定义了处理请求的逻辑 return childObserve(new HttpServerHandle(handler)); }继续查看
HttpServerHandle的源代码,具体如下:static final class HttpServerHandle implements ConnectionObserver { final BiFunction<? super HttpServerRequest, ? super HttpServerResponse, ? extends Publisher<Void>> handler; HttpServerHandle(BiFunction<? super HttpServerRequest, ? super HttpServerResponse, ? extends Publisher<Void>> handler) { this.handler = handler; } /* 重点部分在这里,这里设置一个观察者来监听请求,当请求状态发生改变时,则作出对应的响应 */ @Override @SuppressWarnings("FutureReturnValueIgnored") public void onStateChange(Connection connection, State newState) { if (newState == HttpServerState.REQUEST_RECEIVED) { try { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(format(connection.channel(), "Handler is being applied: {}"), handler); } HttpServerOperations ops = (HttpServerOperations) connection; /* 重点部分就在这里了,在当前的上下问环境中当前的 handler 为 ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter 具体细节可以查看 org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext 在 refresh() 阶段创建 WebManager 的源代码,在那里定义了当前 webServer 的具体实现过程 */ Mono<Void> mono = Mono.fromDirect(handler.apply(ops, ops)); if (ops.mapHandle != null) { mono = ops.mapHandle.apply(mono, connection); } mono.subscribe(ops.disposeSubscriber()); } catch (Throwable t) { log.error(format(connection.channel(), ""), t); //"FutureReturnValueIgnored" this is deliberate connection.channel() .close(); } } } } -
ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter具体处理请求的源代码如下:
// 此方法定义于 org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter @Override public Mono<Void> apply(HttpServerRequest reactorRequest, HttpServerResponse reactorResponse) { // 用于创建对应的 ByteBuf,具体可以查看有关 Netty 的 ByteBuf NettyDataBufferFactory bufferFactory = new NettyDataBufferFactory(reactorResponse.alloc()); /* 为 request 和 response 创建对应的 ByteBuf。。。。。 但是就目前步骤来讲并不会真正创建 ByteBuf,而是只是设置创建 ByteBuf 的工厂对象 */ ReactorServerHttpRequest request = new ReactorServerHttpRequest(reactorRequest, bufferFactory); ServerHttpResponse response = new ReactorServerHttpResponse(reactorResponse, bufferFactory); // Rest 风格的请求,“Head”,不常用。。。 if (request.getMethod() == HttpMethod.HEAD) { response = new HttpHeadResponseDecorator(response); } /* 这里是重点部分!在这里定义了实际的处理逻辑 (handle 方法) */ return this.httpHandler.handle(request, response) .doOnError(ex -> logger.trace(request.getLogPrefix() + "Failed to complete: " + ex.getMessage())) .doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logger.trace(request.getLogPrefix() + "Handling completed")); // 省略部分异常检测代码。。。。 } -
HttpWebHandlerAdapter经过上文的相关分析,在当前的运行条件下唯一存在于 Spring IOC 的
HttpHandler的实际 Bean 为HttpWebHandlerAdapter,即具体执行的handle()方法为HttpWebHandlerAdapter的具体实现对应的源代码如下:
// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.web.server.adapter.HttpWebHandlerAdapter @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) { if (this.forwardedHeaderTransformer != null) { request = this.forwardedHeaderTransformer.apply(request); // 省略一部分异常检测代码。。。。 } ServerWebExchange exchange = createExchange(request, response); // 省略一部分日志打印的代码。。。。 /* 通过对 HttpHandler 实例化的分析,现在调用的是最外层的 ExceptionHandlingWebHandler 的 handle() 方法 */ return getDelegate().handle(exchange) .doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logResponse(exchange)) .onErrorResume(ex -> handleUnresolvedError(exchange, ex)) .then(Mono.defer(response::setComplete)); } -
ExceptionHandlingWebHandler其中具体的源代码如下:
// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.web.server.handler.ExceptionHandlingWebHandler。。。 @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { Mono<Void> completion; try { // 首先会执行父类的 handle 方法 completion = super.handle(exchange); } catch (Throwable ex) { // 处理过程中存在异常则返回一个 error 到上层 completion = Mono.error(ex); } /* 遍历当前上下文中存在的 WebExceptionHandler,如果处理结果存在对应的 Handler 预定义的异常,那么将会处理对应的异常。。。 */ for (WebExceptionHandler handler : this.exceptionHandlers) { completion = completion.onErrorResume(ex -> handler.handle(exchange, ex)); } return completion; }根据上文中的
WebHandler的类结构图,ExceptionHandlingWebHandler继承自WebHandlerDecorator,其中中的handle()方法的定义如下:// 该具体实现定义于 org.springframework.web.server.handler.WebHandlerDecorator @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { /* 结合之前使用 “构建者模式” 来构造 HttpHandler 的过程,在构建时通过 “装饰器模式” 来增强 FilterWebHandler 功能的逻辑,对于当前的执行上下文 ExceptionHandlingWebHandler, 其中的 delegate 为 FilterWebHandler */ return this.delegate.handle(exchange); }也就是说,WebFlux 在接收到一个请求时,首先将请求发送到
ExceptionHandlingWebHandler进行进一步的处理,而在ExceptionHandlingWebHandler在调用handle()方法进行处理时,首先会再讲请求发送到下一层的handle()方法,最后通过处理结果再执行当前上下文对应的逻辑在
ExceptionHandlingWebHandler中,当处理结果出现异常时将会进行捕获,并返回一个带有 error 的Mono -
FilteringWebHandler具体的源代码如下:
// 该方法定义于 org.springframework.web.server.handler.FilteringWebHandler 中 /* 在使用 “构建者模式” 构建 HttpHandler Bean 时,会创建一个 FilteringWebHandler 的实例 传入的参数为 DispatcherHandler, filters */ public FilteringWebHandler(WebHandler handler, List<WebFilter> filters) { super(handler); // 设置当前的 delegate,将请求发送到下一层 this.chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(handler, filters); } @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { // 在这里定义了对应的过滤处理 return this.chain.filter(exchange); }结合构造
FilteringWebHandler对象时的构造函数,chain的具体实例对象为DefaultWebFilterChain,具体的filter(exchange)方法的定义如下:// org.springframework.web.server.handler.DefaultWebFilterChain @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return Mono.defer(() -> this.currentFilter != null && this.chain != null ? // 如果没有定义 Filter,那么就会将 request 发送到下一层的 WebHandler,在当前环境下下一层的 WebHandler 为 DispatcherHandler invokeFilter(this.currentFilter, this.chain, exchange) : this.handler.handle(exchange) ); } -
DispatcherHandler对应的源代码如下:
// org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { // 省略一部分不太重要的代码。。。 return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) /* 遍历对应的处理的 Mapping,将它们组合为一个 Flux,这么做的目的是为了使得 @RequestMapping 注解能够和 RouterFunction 能够协同工作 经过这一轮处理之后将会得到所有的 request 对应的 handler */ .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) .next() // 为每个处理创建一个单独的 Mono,以达到完全异步的效果 .switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError()) // 调用对应的 handler 方法处理请求 .flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) // 将处理后的结果进行一定的封装之后再组合成一个 Flux .flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result)); }invokeHandler(exchange, handler)对应的源代码如下:// org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler private Mono<HandlerResult> invokeHandler( ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler ) { // 省略一部分 CORS 检测。。。 if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { // 通过合适的 HandlerAdapter 适配所有的 handler,使得 handler 能够正常地处理请求 for (HandlerAdapter handlerAdapter : this.handlerAdapters) { if (handlerAdapter.supports(handler)) { // “适配器模式” 的使用 :) return handlerAdapter.handle(exchange, handler); } } } return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException("No HandlerAdapter: " + handler)); }具体的
HandlerAdapter的类结构图如下:
-
HandlerFunctionAdapter最后一步的
handle(exchange)方法,对应的源代码如下:// 在这里以 HandlerFunctionAdapter 的 handle() 方法为例 @Override public Mono<HandlerResult> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) { HandlerFunction<?> handlerFunction = (HandlerFunction<?>) handler; ServerRequest request = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(RouterFunctions.REQUEST_ATTRIBUTE); // 调用对应的 handle(request) 函数进行对应的处理 return handlerFunction.handle(request) .map(response -> new HandlerResult(handlerFunction, response, HANDLER_FUNCTION_RETURN_TYPE)); }最后对相应结果进行封装:
// org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler .... private Mono<Void> handleResult(ServerWebExchange exchange, HandlerResult result) { // 就当前上下文来讲,对应的 HandlerResultHandler 为 ServerResponseResultHandler return getResultHandler(result).handleResult(exchange, result) .checkpoint("Handler " + result.getHandler() + " [DispatcherHandler]") .onErrorResume(ex -> result.applyExceptionHandler(ex).flatMap(exResult -> { String text = "Exception handler " + exResult.getHandler() + ", error=\"" + ex.getMessage() + "\" [DispatcherHandler]"; return getResultHandler(exResult).handleResult(exchange, exResult).checkpoint(text); })); }ServerResponseResultHandler处理结果对应的源代码如下:/* org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.support.ServerResponseResultHandler */ @Override public Mono<Void> handleResult(ServerWebExchange exchange, HandlerResult result) { ServerResponse response = (ServerResponse) result.getReturnValue(); Assert.state(response != null, "No ServerResponse"); // 将响应结果写入到 response 中。。。 return response.writeTo(exchange, new ServerResponse.Context() { @Override public List<HttpMessageWriter<?>> messageWriters() { return messageWriters; } @Override public List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers() { return viewResolvers; } }); }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号