BST的中序后继
二叉搜索树中的顺序后继:从BST中找到指定节点的下一个节点。
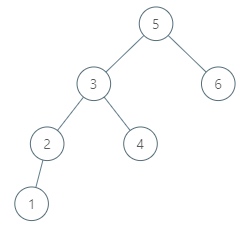
比如1的下一个是2,2的下一个是3,4的下一个是5.
思路:
方法1:递归执行中序遍历,获取list,得到p的下一个。时间O(N),空间O(N)
方法2:
递归执行中序遍历,在递归过程中获取x的下一个。如果当前值是<=x的,那么根据BST的特性只需要在右子树中找。如果当前值>x,则当前值有可能,它的左子树也有可能有更小的但是也>x的,对左子递归后,选择更接近的(更小的).
时间O(logN),空间O(logN)调用栈的深度。
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
if(p==null||root==null){
return null;
}
if(root.val<=p.val){//当前和左边都不可能>p
return inorderSuccessor(root.right,p);
}
//root>p
TreeNode res1=inorderSuccessor(root.left,p);
if(res1!=null&&res1.val<root.val){
return res1;
}else{
return root;
}
}
方法3:循环实现
如果当前值是<=x的,那么根据BST的特性只需要在右子树中找:cur=cur.right。
如果当前值>x,则当前值有可能,它的左子树也有可能有更小的但是也>x的。则每次走入这个分支时,当前点是一个候选点,记录该节点的值和历史最小节点的值。
时间O(logN),空间O(1)
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
if(p==null||root==null){
return null;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode res=null;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<=p.val){
cur=cur.right;
}else{
if(res==null||res.val>cur.val){
res=cur;
}
cur=cur.left;
}
}
return res;
}
二叉搜索树中的中序后继 II,这道题和上面一道题是一样的,唯一的区别是节点并非普通的二叉树节点,还带有父节点指针。
循环实现:分析得出:
- 如果有右子树:则后继节点是右子的最左值。
- 否则,向上找。cur作为左子时,对于的父节点是第一个>x的值。
public Node inorderSuccessor(Node x) {
if(x==null){
return null;
}
if(x.right!=null){
Node tmp=x.right;
while(tmp.left!=null){
tmp=tmp.left;
}
return tmp;
}else{
Node cur=x;
while(cur.parent!=null&&cur!=cur.parent.left){
cur=cur.parent;
}
//cur为null、cur的parent为null
return cur.parent;
}
}


