Elasticsearch Search your data
Search your data 章节主要介绍ES的整体性search的设计,对具体的语法、API如何则需要参考相关章节
Collapse search results 对查询结果进行collapse,可以理解为去重、分组等行为
假设index中有如下文档(为了方便以行表示):
user.id message http.response.bytes @timestamp
1 ... 100 2021-10-28 12:00:00
1 ... 200 2021-10-28 11:00:00
1 ... 250 2021-10-28 10:00:00
2 ... 120 2021-10-28 12:00:00
2 ... 150 2021-10-28 11:00:00
现在要找出每个用户的http.response.bytes最大的文档,可以用以下的collapse查询
GET my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"message": "GET /search"
}
},
"collapse": {
"field": "user.id"
},
"sort": [
{
"http.response.bytes": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"from": 0
}
该查询按user.id去重,按http.response.bytes倒排,查询结果将是:
user.id message http.response.bytes
1 ... 250
2 ... 150
collapse还不至于此,继续上面的需求,追加需求 并且找出每个用户的最近发生的5条文档
GET /my-index-000001/_search { "query": { "match": { "message": "GET /search" } }, "collapse": { "field": "user.id", "inner_hits": { "name": "most_recent", "size": 5, "sort": [ { "@timestamp": "desc" } ] }, "max_concurrent_group_searches": 4 }, "sort": [ { "http.response.bytes": { "order": "desc" } } ] }
注意这里的inner_hits,就可以按user.id分组的内部数据,这个数据按@timestamp desc,size 5。支持多个同级inner_hits,也就是多个维度数据;也支持二级collapse。
如果要对collapse使用search_after,则要求search_after和collapse、sort的字段相同。
Filter search results 查询过滤。
这里特别要提到的是 post_filter ,这个过滤器只对搜索结果 即hits 起作用,而不对agg起作用,他的触发时机是在search出结果后。
例如下面这个post_filter,只影响query的hits结果,而不会影响agg的结果,相当于只对query部分附加了匹配条件:
GET /shirts/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": { "brand": "gucci" }
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"colors": {
"terms": { "field": "color" }
},
"color_red": {
"filter": {
"term": { "color": "red" }
},
"aggs": {
"models": {
"terms": { "field": "model" }
}
}
}
},
"post_filter": {
"term": { "color": "red" }
}
}
Highlighting 对一个或多个字段中获取高亮显示的代码段,以便向用户显示查询匹配的位置。
Long-running searches 慢搜索任务的应对方法。
通常情况下ES在大量的数据集上查询都非常快,在某些情况下如果有慢搜索需求,对冻结的索引并跨越多个远程集群,对于这些碎片,搜索结果预计不会在毫秒内返回。
当需要执行长时间运行的搜索时,同步等待其结果返回并不理想。相反,异步搜索允许提交异步执行的搜索请求,监视请求的进度,并在稍后阶段检索结果。
还可以在部分结果可用时但在整个搜索完成之前检索它们。
要使用异步搜索,可使用 submit async search 。
Near real-time search 近实时的搜索。
默认情况下,ES的文档被索引和可被搜索是近实时的,大约需要1s。
Luence中的index是 "a collection of segments plus a commit point" (segment的集合加上提交点),commit后,一个新的segment会添加到提交点,并且清空buffer。
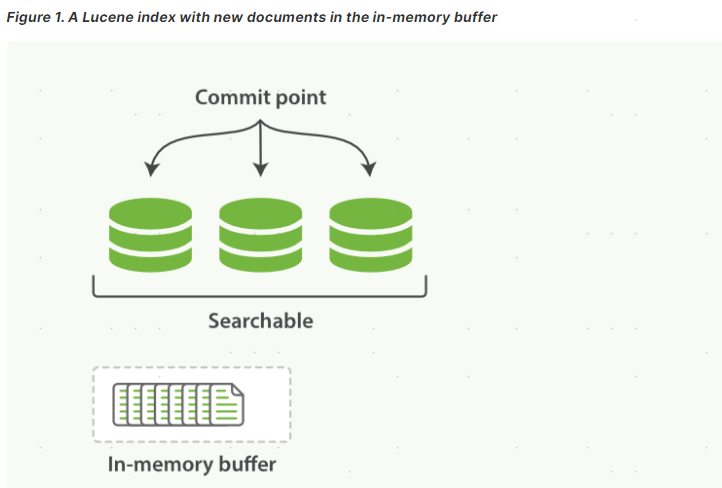
在ES和磁盘之间有一层 系统文件缓存,文档数据先进入in-memory buffer,然后提交到一个新的segment,这个新的segment首先就是写到 系统文件缓存(消耗低),然后再刷入磁盘(消耗高)。
当文档数据进入segment后就可以被搜索了,即使这个数据还没有被刷入磁盘,因此这个动作是可以较频繁的进行的(默认1s),这个动作叫做refresh。
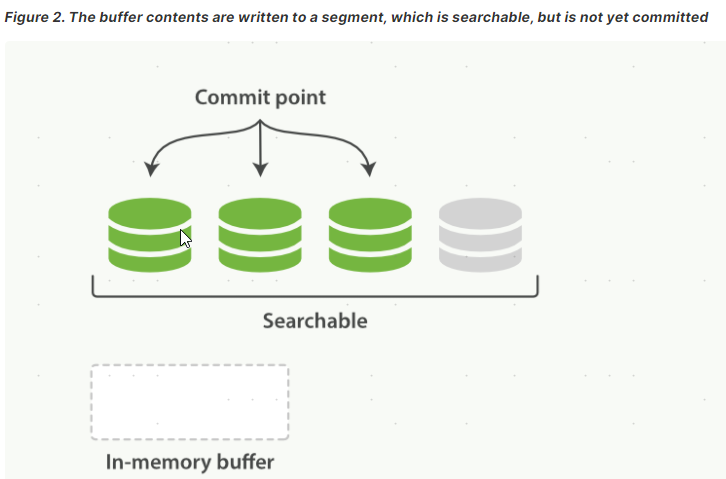
有以下方式控制refresh的触发:
- 等待自动刷新
- 使用 ?refresh 参数
- 使用 Refresh API
默认情况下,Elasticsearch每秒定期刷新索引,但仅针对在过去30秒内收到一个或多个搜索请求的索引。文档更改对于搜索来说不是立即可见的,而是在这个时间范围内可见的。
Paginate search results 分页处理。
分页处理有以下方式:
使用from
使用search_after
使用scroll
其中search_after 和 scroll都可以处理深度分页
Retrieve inner hits 提取inner_hits,可以对Nested、嵌套Nested、Parent/Child join 精确的提取 inner_hits 命中的数据
PUT test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"comments": {
"type": "nested"
}
}
}
}
PUT test/_doc/1?refresh
{
"title": "Test title",
"comments": [
{
"author": "kimchy",
"number": 1
},
{
"author": "nik9000",
"number": 2
}
]
}
POST test/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "comments",
"query": {
"match": { "comments.number": 2 }
},
"inner_hits": {}
}
}
}
结果
{
...,
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": ...,
"inner_hits": {
"comments": {
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_nested": {
"field": "comments",
"offset": 1
},
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"author": "nik9000",
"number": 2
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
Retrieve selected fields 提取查询的字段。
默认返回_source ,可以使用以下方式控制返回的字段
fieldsoption 精确字段_sourceoption 原始文档
使用fields
POST my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user.id": "kimchy"
}
},
"fields": [
"user.id",
"http.response.*",
{
"field": "@timestamp",
"format": "epoch_millis"
}
],
"_source": false
}
使用_source
GET /_search
{
"_source": [ "obj1.*", "obj2.*" ],
"query": {
"match": {
"user.id": "kimchy"
}
}
}
GET /_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": [ "obj1.*", "obj2.*" ],
"excludes": [ "*.description" ]
},
"query": {
"term": {
"user.id": "kimchy"
}
}
}
Search across clusters 跨集群搜索。允许对一个或多个远程集群发起search。
先设置远程集群
PUT _cluster/settings
{
"persistent": {
"cluster": {
"remote": {
"cluster_one": {
"seeds": [
"127.0.0.1:9300"
]
},
"cluster_two": {
"seeds": [
"127.0.0.1:9301"
]
},
"cluster_three": {
"seeds": [
"127.0.0.1:9302"
]
}
}
}
}
}
对一个或多个集群发起search
GET /my-index-000001,cluster_one:my-index-000001,cluster_two:my-index-000001/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user.id": "kimchy"
}
},
"_source": ["user.id", "message", "http.response.status_code"]
}
Search multiple data streams and indices 允许对多个data stream或index发起search
GET /my-index-000001,my-index-000002/_search
GET /my-index-*/_search
GET/_search GET/_all/_search GET/*/_search 这3种都对集群种的所有data stream和index发起search
Search shard routing search时的路由。
默认情况下,Elasticsearch使用自适应副本选择来路由搜索请求。他的规则如下
- Response time of prior requests between the coordinating node and the eligible node 协调节点和合格节点之间先前请求的响应时间,越低的越优先
- How long the eligible node took to run previous searches 合格节点运行以前的搜索所用的时间,平均值,越低的越优先
- Queue size of the eligible node’s
searchthreadpool 合格节点的搜索线程池的队列大小,队列越小的说明等待中的任务越少,越低的越优先
ES提供了preference让我们自己选择路由优先级。
例如 GET /my-index-000001/_search?preference=_local 就会优先看本节点是否合格节点,不是再fallback使用默认方式
preference支持自定义参数(不能以_开头),例如可以使用user的id,user的web session,业务模块名等,目的是让相似的search路由到相同的节点,为频繁使用和资源密集型搜索提供缓存。
routing则允许文档按指定的路由进行索引 POST /my-index-000001/_doc?routing=my-routing-value
像Parent/Child是必须使用routing路由到相同的分片的
get的时候也必须指定routing
防止节点搜索请求过载:
默认情况下,ES的节点不会因为命中了过多的shard而拒绝请求。但是,命中大量碎片会显著增加CPU和内存使用率。
为了防止过载,可以使用max_concurrent_shard_requests参数控制每个节点搜索请求可以命中的最大并发shard数,该参数默认最大值为5。
GET /my-index-000001/_search?max_concurrent_shard_requests=3
还可以通过cluster settings 的 action.search.shard_count.limit 控制。
Search templates 搜索模板。
允许预定义search的模板,使用search时只需传递变量。
创建模板使用 create stored script API.
PUT _scripts/my-search-template
{
"script": {
"lang": "mustache",
"source": {
"query": {
"match": {
"message": "{{query_string}}"
}
},
"from": "{{from}}",
"size": "{{size}}"
},
"params": {
"query_string": "My query string"
}
}
}
使用模板
GET my-index/_search/template
{
"id": "my-search-template",
"params": {
"query_string": "hello world",
"from": 0,
"size": 10
}
}
Sort search results 结果排序。这里提一些ES sort的特别之处。
mode 例如 "price": [20, 4] ,想要对price的平均值排序,可以使用
POST /_search
{
"query" : {
"term" : { "product" : "chocolate" }
},
"sort" : [
{"price" : {"order" : "asc", "mode" : "avg"}}
]
}
mode的取值类型如下
|
|
Pick the lowest value. |
|
|
Pick the highest value. |
|
|
Use the sum of all values as sort value. Only applicable for number based array fields. |
|
|
Use the average of all values as sort value. Only applicable for number based array fields. |
|
|
Use the median of all values as sort value. Only applicable for number based array fields. |
numeric_type 允许在排序时转换字段的数据类型,支持转换类型 ["double", "long", "date", "date_nanos"]
例如有2个index,有相同名称的字段“field”但类型一个是long,一个是double,这种情况默认是不支持排序的,但可以通过numeric_type进行转换
POST /index_long,index_double/_search
{
"sort" : [
{
"field" : {
"numeric_type" : "double"
}
}
]
}
Nested sort 支持对nested使用顶层一样的sort规则
Missing Values 当某些文档不存在sort的字段时怎么处理?默认是排到最后,支持_last, _first
GET /_search
{
"sort" : [
{ "price" : {"missing" : "_last"} }
],
"query" : {
"term" : { "product" : "chocolate" }
}
}
unmapped_type 默认如果字段没有mapping会失败,unmapped_type允许处理这种情况。
GET /_search
{
"sort" : [
{ "price" : {"unmapped_type" : "long"} }
],
"query" : {
"term" : { "product" : "chocolate" }
}
}
script 使用script排序。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"term": { "user": "kimchy" }
},
"sort": {
"_script": {
"type": "number",
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['field_name'].value * params.factor",
"params": {
"factor": 1.1
}
},
"order": "asc"
}
}
}



