012 Linux_线程控制
前言
本文将会向你介绍线程控制(创建(请见上文),终止,等待,分离)
线程控制
线程终止
pthread_t pthread_self(void); 获取线程自身的ID

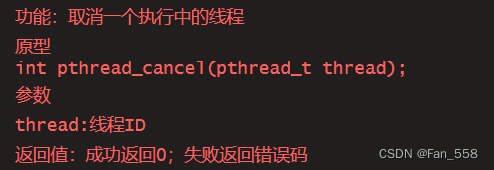
如果需要只终止某个线程而不终止整个进程,可以有三种方法:
1. 从线程函数return。这种方法对主线程不适用,从main函数return相当于调用exit。
2. 线程可以调用pthread_ exit终止自己。
3. 一个线程可以调用pthread_ cancel终止同一进程中的另一个线程 若是在线程中使用exit()退出,整个进程都会退出
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%x", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
int cnt = 3;
while(cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread is running, thread name: " << name << " ,thread id: " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
//return nullptr; //线程退出
//exit(13); //进程退出
pthread_exit(nullptr); //线程退出
std::cout << "The thread ended ago" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main: The new thread id is: " << ToHex(tid) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
return nullptr:
exit():
pthread_exit(nullptr):
pthread_ cancel:

线程等待
为什么需要线程等待?
已经退出的线程,其空间没有被释放,仍然在进程的地址空间内。
创建新的线程不会复用刚才退出线程的地址空间

1. 如果thread线程通过return返回,value_ ptr所指向的单元里存放的是thread线程函数的返回值。
2. 如果thread线程被别的线程调用pthread_ cancel异常终掉,value_ ptr所指向的单元里存放的是常数 (-1)PTHREAD_ CANCELED。
3. 如果thread线程是自己调用pthread_exit终止的,value_ptr所指向的单元存放的是传给pthread_exit的参数。
4. 如果对thread线程的终止状态不感兴趣,可以传NULL给value_ ptr参数
这里只证实后3、4两个结论
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
int cnt = 3;
while(cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread is running, thread name: " << name << " ,thread id: " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
//----------------------------------------------------------线程退出
pthread_exit((void*)"thread-1 over...");
std::cout << "The thread ended ago" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
void *ret = nullptr;
int n = pthread_join(tid, &ret);
std::cout << "main thread done" << " ,n: " << n << "info: " << "," << (char*)ret << std::endl;
return 0;
}
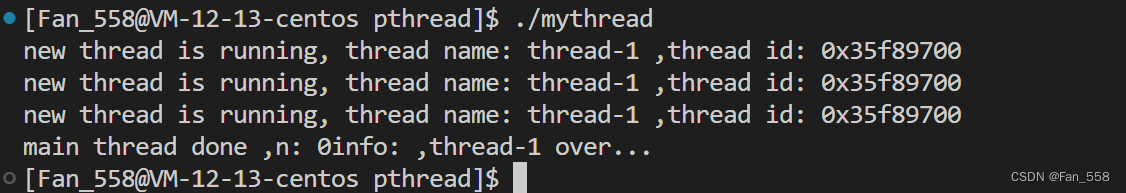
//等待新线程结束并获取新线程退出的信息(获取新线程退出时的ID、信息、以及退出码)
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
class ThreadReturn
{
public:
ThreadReturn(pthread_t id, const std::string &info, int code)
: _id(id)
, _info(info)
, _code(code)
{}
public:
pthread_t _id; //线程ID
std::string _info; //信息
int _code; //返回码
};
//十六进制转换
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%x", tid);
return id;
}
//线程任务
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
int cnt = 3;
while(cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread is running, thread name: " << name << " ,thread id: " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
//pthread_exit((void*)"thread-1 over...");
ThreadReturn *ret = new ThreadReturn(pthread_self(), "thread quit normal", 6);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
//创建线程
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
void *ret = nullptr;
//线程等待
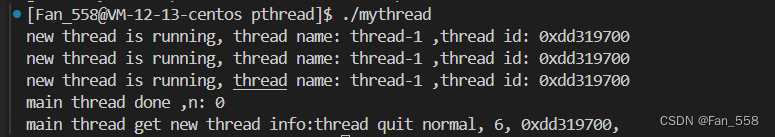
int n = pthread_join(tid, &ret);
std::cout << "main thread done" << " ,n: " << n << std::endl;
//安全类型转换
ThreadReturn *r = static_cast<ThreadReturn *>(ret);
//输出新线程退出时的参数信息
std::cout << "main thread get new thread info:" << r->_info << ", " << r->_code << ", " << ToHex(r->_id) << ", " << std::endl;
delete r;
return 0;
}
线程分离

#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int gcnt = 3;
void *ThreadRoutine(void *arg)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
const char *threadname = (const char *)arg;
while(true)
{
std::cout<< "I am a new thread" << std::endl;
gcnt--;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid1;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, ThreadRoutine, (void*)"thread 1");
sleep(1);
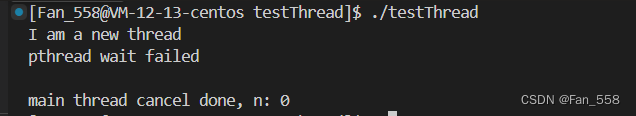
if ( pthread_join(tid1, NULL ) == 0 )
{
std::cout << "pthread wait success\n" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "pthread wait failed\n"<< std::endl;
}
int n = pthread_cancel(tid1);
std::cout << "main thread cancel done, " << "n: " << n << std::endl;
return 0;
}
现象:
线程如果是被分离的,该线程是可以被取消,但是不能被等待
小结
今日的分享就到这里啦,如果本文存在疏漏或错误的地方还请您能够指出!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架