2022.7DASCTF re wp
RE
完全忘记这个比赛 和同学玩的很开心)
所有全是赛后做的)
隐秘的角落
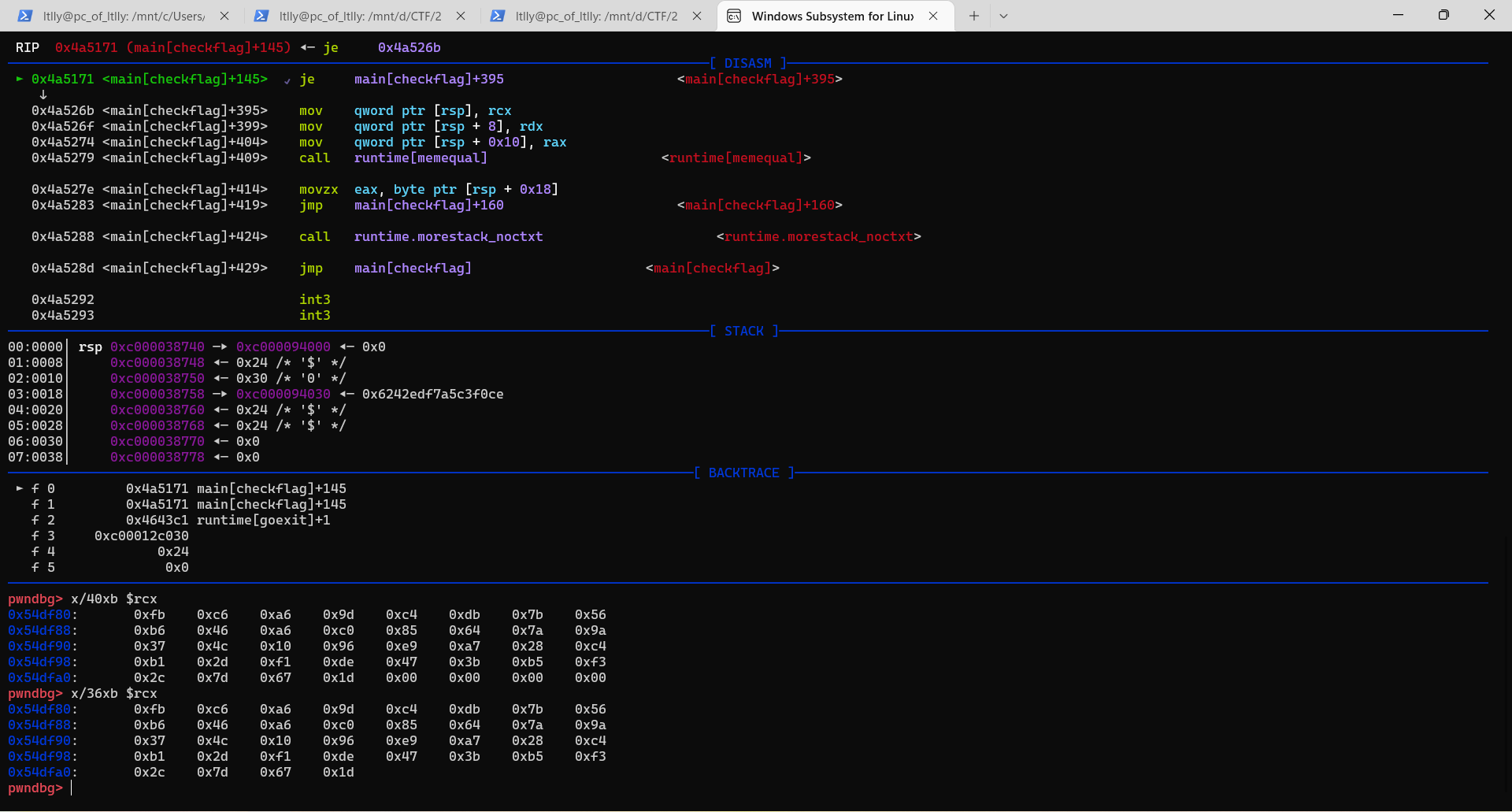
非常简单的签到题 如果我不发病的话
动调拿到enc
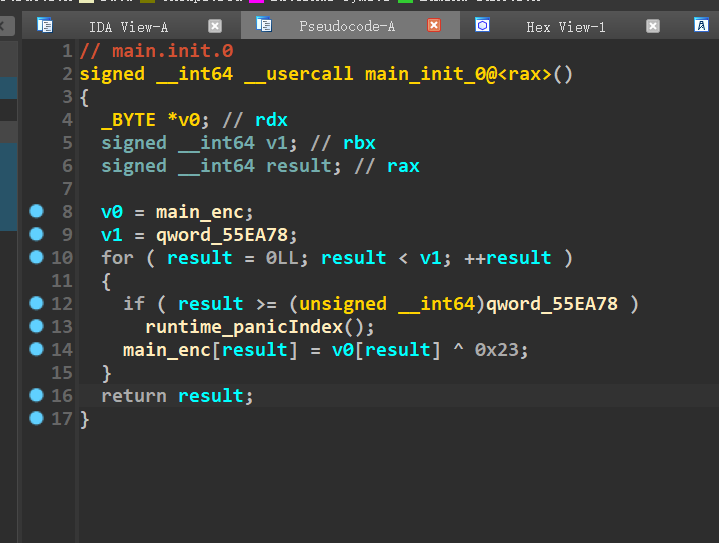
或者静态拿enc 记得有^0x23
看函数名看出来是rc4算法 别管啥玩意key了
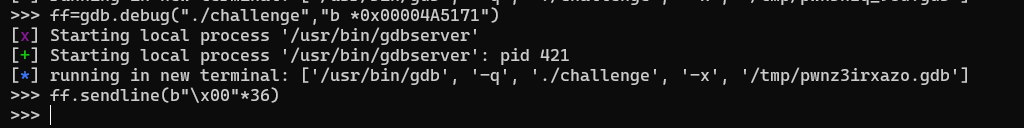
传进去"\x00"*36
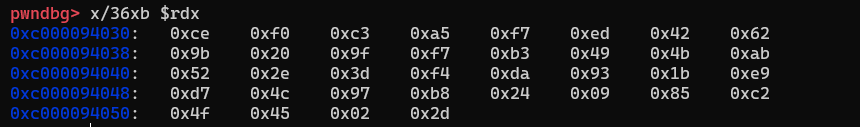
拿到加密后结果 由于rc4是异或算法 0^key==key
所以现在的值就是key 直接异或即可
enc = [251, 198, 166, 157, 196, 219, 123, 86, 182, 70, 166, 192, 133, 100, 122, 154, 55, 76, 16, 150, 233, 167, 40, 196,
177, 45, 241, 222, 71, 59, 181, 243, 44, 125, 103, 29]
key = [0xce, 0xf0, 0xc3, 0xa5, 0xf7, 0xed, 0x42, 0x62,
0x9b, 0x20, 0x9f, 0xf7, 0xb3, 0x49, 0x4b, 0xab,
0x52, 0x2e, 0x3d, 0xf4, 0xda, 0x93, 0x1b, 0xe9,
0xd7, 0x4c, 0x97, 0xb8, 0x24, 0x09, 0x85, 0xc2,
0x4f, 0x45, 0x02, 0x2d, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, ]
for i in range(36):
print(chr(enc[i] ^ key[i]), end="")
56e83694-f976-11eb-b343-faffc201c8e0
输入程序后 记得按提示md5一下
DASCTF{9e1963bbbb1285b993c862a5a6f12604}
fatanstic_maze
和上次stargate好像) 不过这次用另一种方式做
连上靶机后先爆破sha256
用了个go语言的)(
./test.exe sha256尾 值
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"runtime"
"sync"
"os"
)
var (
chars = []byte("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz1234567890")
tail = []byte("SUex0zeSOI7DilNj")
result, _ = hex.DecodeString("b5bbdab6b117ece3e45ca60ecf2c666e7a5ee1bcbb9596c1e06c7e7995c1ee8d")
wg sync.WaitGroup
)
func sha(s []byte) {
for _, ch1 := range s {
for _, ch2 := range chars {
for _, ch3 := range chars {
for _, ch4 := range chars {
head := []byte{ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4}
h := sha256.New()
h.Write(head)
h.Write(tail)
if bytes.Equal(h.Sum(nil), result) {
fmt.Println(string(head))
}
}
}
}
}
wg.Done()
}
func main() {
args := os.Args
tail = []byte(args[1])
result, _ = hex.DecodeString(args[2])
// fmt.Println(string(tail))
// fmt.Println(string(result))
threads := runtime.NumCPU() // 获取cpu逻辑核心数(包括超线程)
snum := len(chars) / threads
sthreads := threads*(1+snum) - len(chars)
wg.Add(threads)
for i := 0; i < threads; i++ {
if i < sthreads {
go sha(chars[snum*i : snum*(i+1)])
} else {
base := snum * sthreads
go sha(chars[base+(snum+1)*(i-sthreads) : base+(snum+1)*(i-sthreads+1)])
}
}
wg.Wait()
}
然后是pwntools脚本编写
import os
import time
from pwn import *
# context(log_level="DEBUG")
ppp=remote('node4.buuoj.cn',27564)
tem=ppp.recvuntil(b'[+] Plz Tell Me XXXX :')
tail=tem.decode()[18:].split(")")[0]
sha256=tem.decode()[18:].split("== ")[1].replace("\'","")
#这是个go写个sha256爆破
ccc=r".\test.exe "+tail+" "+sha256
eee=os.popen(ccc).read()
ppp.send(str(eee).encode())
ppp.recvuntil(b"a map :")
map=ppp.recvuntil(b"That's all")
with open("mappp",'wb') as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(map))
把文件写入mappp中
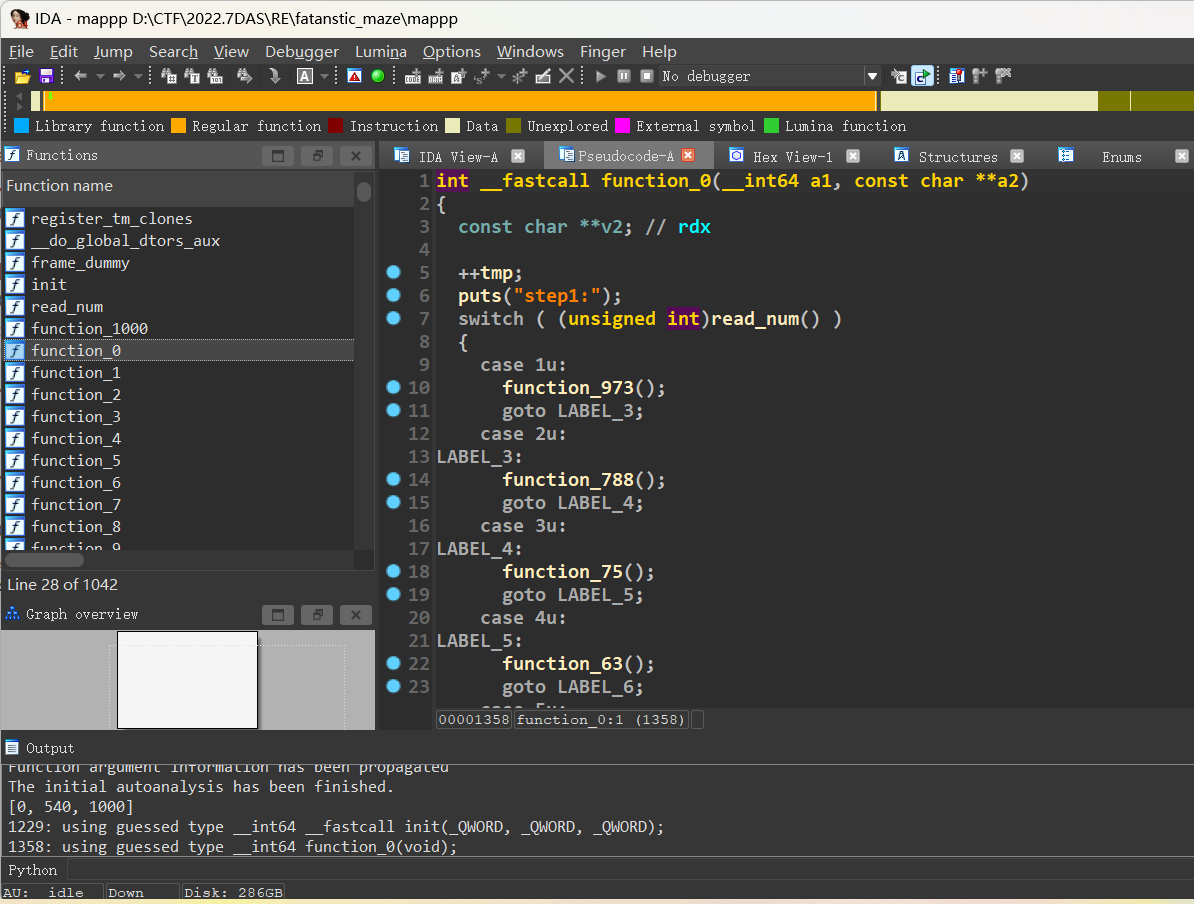
IDA小分析一下
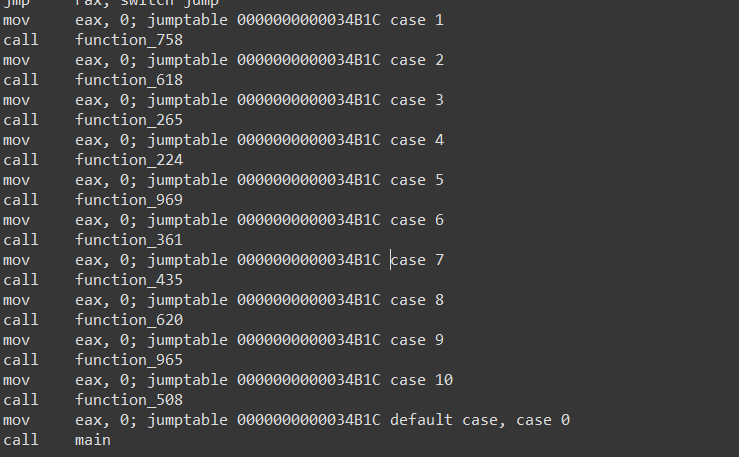
main进入function_0中 然后通过case数字来回在各个函数中跳 每走一个函数tmp++
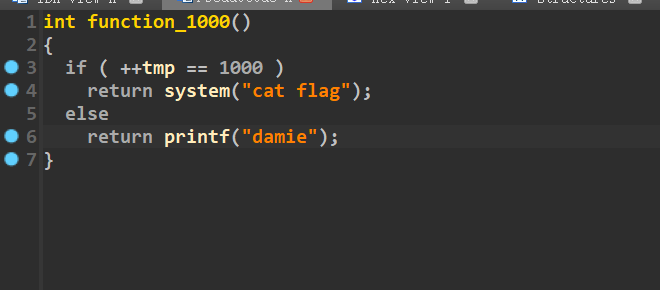
最后到达function_1000时tmp要为1000
我们先找到路径 使用idapython!
这里是ida7.7 内置python3.8 记得给内置的python装一下numpy什么的库
用idapython的各个api得到asm,简单匹配一下得到可达关系
import idaapi
import idautils
import idc
def fuckfuncnew():
all_funcs = idautils.Functions()
indexdddd = {}
dddd={}
for fn in all_funcs:
#fn是个int 就是这个函数的地址
func_name = idc.get_func_name(fn)
if (not func_name.startswith("function_")):
continue
if func_name.startswith("function_1000"):
continue
#获得当前函数的起始与结束
start = idc.get_func_attr(fn, FUNCATTR_START)
end = idc.get_func_attr(fn, FUNCATTR_END)
curr_addr = start
func_index=int(func_name.split("_")[-1])
#我用indexdddd字典表示函数间的可达关系 下标为0的表示case 1进入
indexdddd[func_index]=[]
#dddd没用到
dddd[func_name] = []
#逐句遍历当前函数asm
while curr_addr <= end:
# print(hex(curr_addr),idc.GetDisasm(curr_addr))
#当前地址的汇编
asmmm = idc.GetDisasm(curr_addr)
#print(asmmm)
import re
casein = re.match(".*case [0-9]{1,5}", asmmm)
if casein and ("case 0" not in asmmm):
index = asmmm.split()[-1]
nextfunc = idc.GetDisasm(idc.next_head(curr_addr, end)).split()[1]
nextindex=int(nextfunc.split("_")[-1])
indexdddd[func_index].append(nextindex)
dddd[func_name].append(nextfunc)
# print(index, nextfunc)
curr_addr = idc.next_head(curr_addr, end)
# return dddd
return indexdddd
a=fuckfuncnew()
# b=fuckfuncori()
#求有向无权图最短路径 networkx
import networkx as nx
G = nx.DiGraph()
for i in range(0,1001):
G.add_node(i)
for x in a.keys():
for t in a[x]:
G.add_edge(x,t)
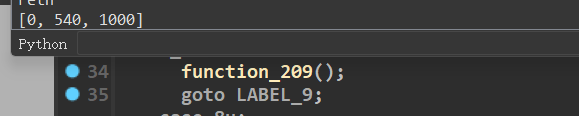
p=nx.shortest_path(G,source=0,target=1000)
#p就是最短路径 但是题目要求步数为1000步 观察程序发现输入不在case表中的话 会回到function_0 利用这一点刷步数
f=[666666]*(1000-len(p))
for index in range(len(p)-1):
f.append(a[p[index]].index(p[index+1])+1)
#这个为了当回车用
f.append("")
#这个文件名只要和下面的一样就行)
with open(r"D:\CTF\2022.7DAS\RE\fatanstic_maze\ffff.txt","w")as filee:
filee.write("\n".join(list(map(str,f))))
print(p)
计算出来的最短路径
接下来回到pwntools的脚本中
import os
import time
from pwn import *
# context(log_level="DEBUG")
ppp=remote('node4.buuoj.cn',27564)
tem=ppp.recvuntil(b'[+] Plz Tell Me XXXX :')
tail=tem.decode()[18:].split(")")[0]
sha256=tem.decode()[18:].split("== ")[1].replace("\'","")
#这是个go写个sha256爆破
ccc=r".\test.exe "+tail+" "+sha256
eee=os.popen(ccc).read()
ppp.send(str(eee).encode())
ppp.recvuntil(b"a map :")
map=ppp.recvuntil(b"That's all")
with open("mappp",'wb') as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(map))
#暂停
print("请去idapython里面跑一下脚本,跑完按回车")
input()
with open(r"D:\CTF\2022.7DAS\RE\fatanstic_maze\ffff.txt","r")as fileee:
t=fileee.read()
ppp.send(t)
ppp.interactive()
操作流是先打开ida64备好
先跑pwntools脚本 出现提示信息后 ida分析mappp文件 等分析完后alt+f7 选择idapython脚本 run 然后去pwntools脚本里按回车
得到flag!
ezGO
rsa题目 移步别的师傅wp 请(
)
e4sy_mix
VM题 还是调用so
先点开主函数 小修一下变量类型
__int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
int i; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-98h]
int j; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-94h]
int k; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-90h]
int V[2]; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-88h] BYREF
int key[4]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-80h] BYREF
int tem[8]; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-70h] BYREF
char input_[65]; // [rsp+50h] [rbp-50h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v11; // [rsp+98h] [rbp-8h]
v11 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
memset(input_, 0, sizeof(input_));
memset(tem, 0, sizeof(tem));
*V = 0LL;
key[0] = 0x21728857;
key[1] = 0xB5077292;
key[2] = 0xE737DC2B;
key[3] = 0x4CC17426;
__isoc99_scanf("%s", input_);
if ( strlen(input_) != 64 )
return 0LL;
for ( i = 0; i <= 7; ++i )
{
for ( j = 0; j <= 7; ++j )
tem[i] |= (input_[8 * i + j] - '0') << (4 * j);
}
for ( k = 0; k <= 3; ++k )
{
V[0] = tem[2 * k];
V[1] = tem[2 * k + 1];
TEA(0x20u, V, key);
tem[2 * k] = V[0];
tem[2 * k + 1] = V[1];
}
if ( vm(tem, 8LL) )
output_flag(input_);
return 0LL;
}
简单来说就是输入flag 经过一个小变换 然后跑一圈TEA加密 将加密后结果送入vm函数中
所以重点看vm 打开so
看一下函数内容 写opcode解析器即可
作者:FW-ltlly
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/FW-ltlly/p/16524961.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?