saltstack 基本操作
一、常用操作
①、模块查看
#查看全部模块 [root@k8s_master ~]# salt '*' sys.list_modules # "*"为所有node节点 (此处可以写通过salt-key -L 命令获取的node节点的名称) k8s_master: - acl - aliases - alternatives - archive
查看模块对应的api
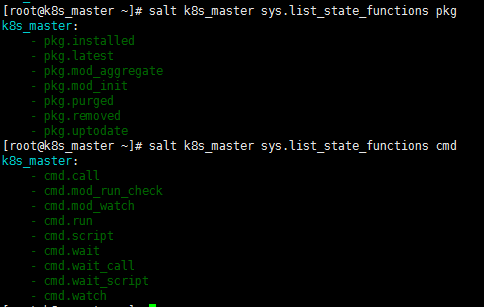
salt k8s_master sys.list_state_functions
[root@k8s_master ~]# salt k8s_master sys.list_state_functions pkg ##查看pkg对应的api k8s_master: - pkg.installed - pkg.latest - pkg.mod_aggregate - pkg.mod_init - pkg.purged - pkg.removed - pkg.uptodate [root@k8s_master ~]# salt k8s_master sys.list_state_functions cmd ##查看cmd模块对应的api k8s_master: - cmd.call - cmd.mod_run_check - cmd.mod_watch - cmd.run - cmd.script - cmd.wait - cmd.wait_call - cmd.wait_script - cmd.watch
②、模块使用
查看模块使用说明
salt '*' sys.doc 模块名称(模块api) ## state.apply/cmd.run/...
实例说明:

[root@k8s_master ~]# salt k8s_master sys.doc cmd.run 'cmd.run:' Execute the passed command and return the output as a string Note that ``env`` represents the environment variables for the command, and should be formatted as a dict, or a YAML string which resolves to a dict. Warning: This function does not process commands through a shell unless the python_shell flag is set to True. This means that any shell-specific functionality such as 'echo' or the use of pipes, redirection or &&, should either be migrated to cmd.shell or have the python_shell=True flag set here. The use of python_shell=True means that the shell will accept _any_ input including potentially malicious commands such as 'good_command;rm -rf /'. Be absolutely certain that you have sanitized your input prior to using python_shell=True CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" Specify an alternate shell with the shell parameter: salt '*' cmd.run "Get-ChildItem C:\ " shell='powershell' A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input.: salt '*' cmd.run "grep f" stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' If an equal sign (``=``) appears in an argument to a Salt command it is interpreted as a keyword argument in the format ``key=val``. That processing can be bypassed in order to pass an equal sign through to the remote shell command by manually specifying the kwarg: salt '*' cmd.run cmd='sed -e s/=/:/g'
查看帮助文档都有那些方法(api):
[root@k8s_master ~]# salt k8s_master sys.list_functions sys
k8s_master:
- sys.argspec
- sys.doc
- sys.list_functions
- sys.list_modules
- sys.list_renderers
- sys.list_returner_functions
- sys.list_returners
- sys.list_runner_functions
- sys.list_runners
- sys.list_state_functions
- sys.list_state_modules
- sys.reload_modules
- sys.renderer_doc
- sys.returner_argspec
- sys.returner_doc
- sys.runner_argspec
- sys.runner_doc
- sys.state_argspec
- sys.state_doc
③、执行命令
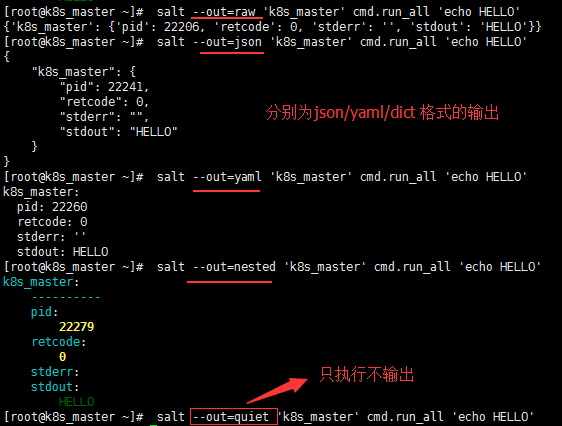
[root@k8s_master ~]# salt --out=raw 'k8s_master' cmd.run_all 'echo HELLO' #raw格式 {'k8s_master': {'pid': 22206, 'retcode': 0, 'stderr': '', 'stdout': 'HELLO'}} [root@k8s_master ~]# salt --out=json 'k8s_master' cmd.run_all 'echo HELLO' #json格式 { "k8s_master": { "pid": 22241, "retcode": 0, "stderr": "", "stdout": "HELLO" } } [root@k8s_master ~]# salt --out=yaml 'k8s_master' cmd.run_all 'echo HELLO' #yml格式 k8s_master: pid: 22260 retcode: 0 stderr: '' stdout: HELLO [root@k8s_master ~]# salt --out=nested 'k8s_master' cmd.run_all 'echo HELLO' #nested格式 k8s_master: ---------- pid: 22279 retcode: 0 stderr: stdout: HELLO [root@k8s_master ~]# salt --out=quiet 'k8s_master' cmd.run_all 'echo HELLO' #只执行,不输出
例:检测网络连接情况:
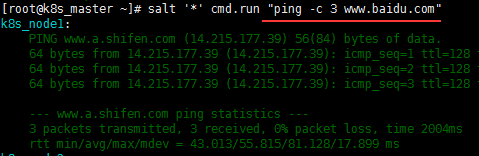
命令执行常用参数
对主机进行过滤参数:
-E,--pcre,通过正则表达式进行匹配:
salt -E 'k8s.*' test.ping #探测k8s开头的主机id名是否连通
-L,--list,以主机id名列表的形式进行过滤,格式与Python的列表相似,即不同主机id名称使用逗号分离。
salt -L 'k8s_master,k8s_node1' grains.item osfullname #获取主机id为:k8s_master,k8s_node1完整操作系统发行版名称
-G,--grain,根据被控主机的grains信息进行匹配过滤,格式为:<grain value>:<grain expression>
salt -G 'osrelease:7.3.1611' cmd.run 'python -V' #获取发行版本号为7.3.1611的python版本号
-I,--pillar,根据被控主机的pillar信息进行匹配过滤,格式为:"对象名称":"对象值"
salt -I 'nginx:root:/data' test.ping #探测具有'nginx:root:/data'信息的连通性。 #pillar属性配置文件如下: nginx: root: /data
-N,--nodegroup,根据主控端master配置文件中的分组名称进行过滤。
#分组配置:【/etc/salt/master】 nodegroups: master: 'k8s_master' agent: 'L@k8s_node1,k8s_node2' #其中L@表示后面的主机id格式为列表,即主机id以逗号分隔:G@表示以grain格式描述:S@表示以IP子网或地址格式描述 salt -N agent test.ping #探测agent被控主机的连通性
-C,--compound,根据条件运算符not、and、or去匹配不同规则的主机信息
salt -C 'E@^k8s_node.* and G@os:Centos' test.ping #探测k8s_node开头并且操作系统版本为CentOS的主机的连通性
-S,--ipcidr,根据被控主机的IP地址或IP子网进行匹配
salt -S 192.168.0.0/16 test.ping salt -S 192.168.1.10 test.ping



