Spring MVC源码——Root WebApplicationContext
Spring MVC源码——Root WebApplicationContext
打算开始读一些框架的源码,先拿 Spring MVC 练练手,欢迎点击这里访问我的源码注释.
Spring MVC 的文档一开始就给出了这样的两段示例:
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletCxt) {
// Load Spring web application configuration
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ac.register(AppConfig.class);
ac.refresh();
// Create and register the DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(ac);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletCxt.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/app/*");
}
}
web.xml :
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/app-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value></param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
我们按照 web.xml 中的实例来看一下 Spring MVC 初始化过程.
上下文层次结构
Spring MVC 的上下文有如下这样的层级:
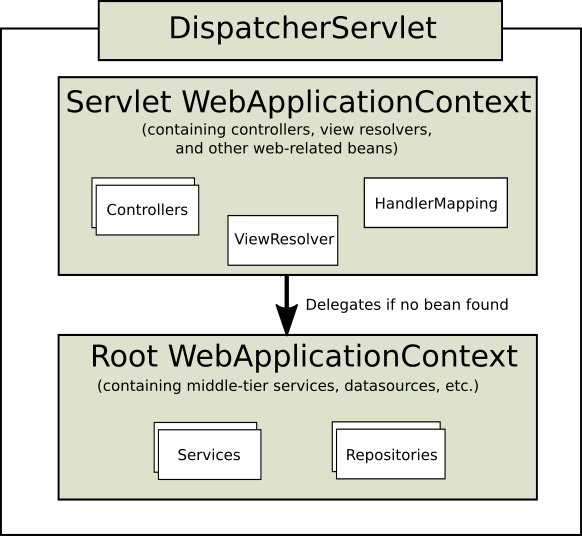
图中的 Servlet WebApplicationContext 是与 DispatcherServlet 绑定的上下文, 其中还有 controllers、ViewResolver、HandlerMapping 等组件.
Root WebApplicationContext 不是必须的上下文, 在需要时,可以用来在多个 DispatcherServlet 间共享一些 bean.
Root WebApplicationContext 初始化和销毁
ContextLoaderListener
web.xml 中配置的 ContextLoaderListener 用于启动和终止 Spring 的 root WebApplicationContext.
ContextLoaderListener 本身的代码十分简单:
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
* Servlet 上下文初始化,调用父类的方法初始化 WebApplicationContext
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
* Servlet 上下文被销毁,调用父类的方法销毁 WebApplicationContext
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
// 销毁 ServletContext 上实现了 DisposableBean 的属性并移除他们
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
ContextLoader
ContextLoaderListener 直接调用了父类 ContextLoader 的方法来初始化和销毁上下文.
ContextLoaderListener 在创建上下文时,会尝试读取 contextClass context-param 来指定上下文的类型,被指定的类需要实现 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 接口. 如果没有获取到,默认会使用 WebApplicationContext.
初始化上下文时,会尝试读取 contextConfigLocation context-param, 作为 xml 文件的路径.
初始化上下文
initWebApplicationContext() 方法如下:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 检查有没有绑定上下文
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
// 初始化开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
// 保存上下文到本地实例变量中,保证上细纹能在 ServletContext 关闭时访问到
if (this.context == null) {
// 创建上下文
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
// 如果上下文实现了 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// 上下文还没有刷新,设置 父上下文(如果能找到),并且刷新
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 设置和刷新上下文
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// 将上下文绑定到 servletContext 的属性上
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
// 获取当前线程的上下文类加载器
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
// 如果有线程上下文类加载器,而且不是 ContextLoader 本身的类加载器,放入到 currentContextPerThread 中。这是一个 static 的域
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// 发生异常, 把异常绑定到上下文对应的属性上,之后不会再进行初始化
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
initWebApplicationContext() 方法调用了 createWebApplicationContext() 方法来创建上下文;调用了 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext() 来对实现了 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 接口的上下文做初始化.
createWebApplicationContext() 会调用 determineContextClass() 来获取上下文类型的 Class 对象.
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// 获取上下文类型
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
// 检查是否实现了 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
// 实例化
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 获取 serveltContext 的 'contextClass' 初始化参数。
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
// 指定过上下文类型,加载类
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// 去默认策略里获取默认的上下文类型名称
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
// 加载类
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext() 方法
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
// 用可以获取到的信息,获取一个更有意义的上下文
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
// 获取 ServletContext 的 'contextId' 初始化参数。
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
// 生成默认 id
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
// 设置 servletContext 属性
wac.setServletContext(sc);
// 设置配置文件路径
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
// 初始化属性源, 确保 servlet 属性源到位并能够在任何 refresh 之前的后期处理和初始化中使用
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
// 在设置了配置文件之后上下文刷新之前,自定义上下文
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
protected void customizeContext(ServletContext sc, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
// 根据 ServletContext 的 'contextInitializerClasses' 和 'globalInitializerClasses' 初始化参数 加载 ApplicationContextInitializer 的 class
List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>> initializerClasses =
determineContextInitializerClasses(sc);
for (Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> initializerClass : initializerClasses) {
// 获取范型参数类型
Class<?> initializerContextClass =
GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
// 检查 Initializer 是否适用于当前上下文对象
if (initializerContextClass != null && !initializerContextClass.isInstance(wac)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format(
"Could not apply context initializer [%s] since its generic parameter [%s] " +
"is not assignable from the type of application context used by this " +
"context loader: [%s]", initializerClass.getName(), initializerContextClass.getName(),
wac.getClass().getName()));
}
// 创建 Initializer 实例,并添加到 contextInitializers
this.contextInitializers.add(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(initializerClass));
}
// 根据 org.springframework.core.Ordered 和 org.springframework.core.annotation.Order 排序,如果没有实现或注解,会被排到最后
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.contextInitializers);
// 执行每个 initializer 的 initialize() 方法
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> initializer : this.contextInitializers) {
initializer.initialize(wac);
}
}
销毁上下文
closeWebApplicationContext() 方法如下:
public void closeWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
servletContext.log("Closing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
try {
// 如果 context 是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 调用 close() 方法
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
((ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context).close();
}
}
finally {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = null;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.remove(ccl);
}
// 移除 servletContext 中的 context 属性
servletContext.removeAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
}
Servlet 3.0+ 中初始化
Servlet 3.0+ 中可以通过 ServletContext 的 addlistener() 方法来添加监听器.因此可以先把 Spring 容器先创建好,再传给 ContextLoaderListener 的构造器.这里就不自己写例子了,选了单元测试中的 ContextLoaderTests.testContextLoaderListenerWithDefaultContext() 方法:
public void testContextLoaderListenerWithDefaultContext() {
MockServletContext sc = new MockServletContext("");
sc.addInitParameter(ContextLoader.CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM,
"/org/springframework/web/context/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml " +
"/org/springframework/web/context/WEB-INF/context-addition.xml");
ServletContextListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener();
ServletContextEvent event = new ServletContextEvent(sc);
listener.contextInitialized(event);
String contextAttr = WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE;
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) sc.getAttribute(contextAttr);
assertTrue("Correct WebApplicationContext exposed in ServletContext", context instanceof XmlWebApplicationContext);
assertTrue(WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext(sc) instanceof XmlWebApplicationContext);
LifecycleBean lb = (LifecycleBean) context.getBean("lifecycle");
assertTrue("Has father", context.containsBean("father"));
assertTrue("Has rod", context.containsBean("rod"));
assertTrue("Has kerry", context.containsBean("kerry"));
assertTrue("Not destroyed", !lb.isDestroyed());
assertFalse(context.containsBean("beans1.bean1"));
assertFalse(context.containsBean("beans1.bean2"));
listener.contextDestroyed(event);
assertTrue("Destroyed", lb.isDestroyed());
assertNull(sc.getAttribute(contextAttr));
assertNull(WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sc));
}
参考资料
芋道源码




