【Qt 专栏】SQLite数据库操作示例
1. sqlite介绍
SQLite 是一种轻量级的嵌入式关系型数据库管理系统,它是一个开源的、零配置的、自包含的、事务性的 SQL 数据库引擎。SQLite 的设计目标是简单、高效、可靠,适用于各种大小的应用程序。
以下是SQLite的一些特点和优势:
1.轻量级: SQLite 非常小巧,数据库引擎的代码库非常紧凑,这使得它在资源受限的环境中表现出色,适合于嵌入式设备或移动应用程序。
2.无服务器架构: SQLite 是无服务器的数据库引擎,不需要独立的数据库服务器进程,数据库存储在单个文件中,方便管理和移植。
3.零配置: 使用 SQLite 时无需进行复杂的配置,只需要包含 SQLite 库并连接到数据库文件即可开始使用。
4.支持标准 SQL: SQLite 支持大部分标准的 SQL 语法,包括事务、索引、视图等功能,使其可以胜任许多应用场景。
5.跨平台性: SQLite 可以在各种操作系统上运行,包括 Windows、macOS、Linux 等,提供了广泛的平台支持。
2. sqlite 基础语法:创建库、插入记录操作
2-1 在SQLite中创建表的SQL语句通常遵循以下格式:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
...
);以下是一个具体的例子,创建一个名为students的表,包含三个字段:id(主键),name和age。
CREATE TABLE students (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
age INTEGER
);在这个例子中,id字段被设置为主键并自动增长,意味着每次插入新记录时不需要手动指定id值,SQLite会自动为其分配一个唯一的整数。name字段被设置为文本类型并且不允许为空,age字段是整数类型。
关键字列举如下:
- PRIMARY KEY:主键
- AUTOINCREMENT:自动增大,一般与主键ID使用
- NOT NULL:不为空
- DEFAULT: 可以设置默认值
- 类型可选: INTEGER(可简写为INT)、TEXT、VARCHAR(n)、TimeStamp
另一个例子:
CREATE TABLE Logs
([ID] INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
[IDCardNo] VARCHAR (50),
[CreatedTime] TimeStamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime('now','localtime')));2-2 在SQLite中插入记录表的SQL语句——INSERT INTO语句:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);这种方式需要指定要插入数据的表名和对应的列名,然后提供要插入的值。
以下是一个插入记录的基本示例:
假设你有一个名为students的表,它有三列:id(主键),name和age。
INSERT INTO students (id, name, age) VALUES (1, '张三', 20);如果你想插入多条记录,可以这样做:
INSERT INTO students (id, name, age) VALUES
(1, '张三', 20),
(2, '李四', 22),
(3, '王五', 23);
2. Qt操作sqlite数据库示例
pro文件:
QT += core gui sqlsqlitebasic.h
#ifndef SQLITEBASIC_H
#define SQLITEBASIC_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QSqlDatabase>
#include <QSqlQuery>
#include <QSqlError>
#include <QDebug>
typedef struct
{
int id;
QString name;
int age;
}w2dba;
class SqliteBasic : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit SqliteBasic(QObject *parent = nullptr);
// 打开数据库
bool openDb(void);
// 创建数据表
void createTable(void);
// 判断数据表是否存在
bool isTableExist(QString& tableName);
// 查询全部数据
void queryTable();
// 插入数据
void singleInsertData(w2dba &singleData); // 插入单条数据
void moreInsertData(QList<w2dba> &moreData); // 插入多条数据
// 修改数据
void modifyData(int id, QString name, int age);
// 删除数据
void deleteData(int id);
//删除数据表
void deleteTable(QString& tableName);
// 关闭数据库
void closeDb(void);
private:
QSqlDatabase database;
signals:
public slots:
};
#endif // SQLITEBASIC_Hsqlitebasic.cpp
#include "sqlitebasic.h"
SqliteBasic::SqliteBasic(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
if (QSqlDatabase::contains("qt_sql_default_connection"))
{
database = QSqlDatabase::database("qt_sql_default_connection");
}
else
{
// 建立和SQlite数据库的连接
database = QSqlDatabase::addDatabase("QSQLITE");
// 设置数据库文件的名字
database.setDatabaseName("MyDataBase.db");
}
}
bool SqliteBasic::openDb()
{
if (!database.open())
{
qDebug() << "Error: Failed to connect database." << database.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "Open database.";
}
return true;
}
void SqliteBasic::createTable()
{
// 用于执行sql语句的对象
QSqlQuery sqlQuery;
// 构建创建数据库的sql语句字符串
QString createSql = QString("CREATE TABLE student (\
id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\
name TEXT NOT NULL,\
age INT NOT NULL)");
sqlQuery.prepare(createSql);
// 执行sql语句
if(!sqlQuery.exec())
{
qDebug() << "Error: Fail to create table. " << sqlQuery.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "Table created!";
}
}
bool SqliteBasic::isTableExist(QString& tableName)
{
QSqlDatabase database = QSqlDatabase::database();
if(database.tables().contains(tableName))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void SqliteBasic::queryTable()
{
QSqlQuery sqlQuery;
sqlQuery.exec("SELECT * FROM student");
if(!sqlQuery.exec())
{
qDebug() << "Error: Fail to query table. " << sqlQuery.lastError();
}
else
{
while(sqlQuery.next())
{
int id = sqlQuery.value(0).toInt();
QString name = sqlQuery.value(1).toString();
int age = sqlQuery.value(2).toInt();
qDebug()<<QString("id:%1 name:%2 age:%3").arg(id).arg(name).arg(age);
}
}
}
void SqliteBasic::singleInsertData(w2dba &singledb)
{
QSqlQuery sqlQuery;
sqlQuery.prepare("INSERT INTO student VALUES(:id,:name,:age)");
sqlQuery.bindValue(":id", singledb.id);
sqlQuery.bindValue(":name", singledb.name);
sqlQuery.bindValue(":age", singledb.age);
if(!sqlQuery.exec())
{
qDebug() << "Error: Fail to insert data. " << sqlQuery.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "singleInsert.";
}
}
void SqliteBasic::moreInsertData(QList<w2dba>& moredb)
{
// 进行多个数据的插入时,可以利用绑定进行批处理
QSqlQuery sqlQuery;
sqlQuery.prepare("INSERT INTO student VALUES(?,?,?)");
QVariantList idList,nameList,ageList;
for(int i=0; i< moredb.size(); i++)
{
idList << moredb.at(i).id;
nameList << moredb.at(i).name;
ageList << moredb.at(i).age;
}
sqlQuery.addBindValue(idList);
sqlQuery.addBindValue(nameList);
sqlQuery.addBindValue(ageList);
if (!sqlQuery.execBatch()) // 进行批处理,如果出错就输出错误
{
qDebug() << sqlQuery.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "moreInsert.";
}
}
void SqliteBasic::modifyData(int id, QString name, int age)
{
QSqlQuery sqlQuery;
sqlQuery.prepare("UPDATE student SET name=?,age=? WHERE id=?");
sqlQuery.addBindValue(name);
sqlQuery.addBindValue(age);
sqlQuery.addBindValue(id);
if(!sqlQuery.exec())
{
qDebug() << sqlQuery.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "updated data success!";
}
}
void SqliteBasic::deleteData(int id)
{
QSqlQuery sqlQuery;
sqlQuery.exec(QString("DELETE FROM student WHERE id = %1").arg(id));
if(!sqlQuery.exec())
{
qDebug()<<sqlQuery.lastError();
}
else
{
qDebug()<<"deleted data success!";
}
}
void SqliteBasic::deleteTable(QString& tableName)
{
QSqlQuery query;
QString deleteTableQuery = QString("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS %1").arg(tableName);
if (query.exec(deleteTableQuery)) {
qDebug() << "Table deleted successfully.";
} else {
qDebug() << "Error: Failed to delete table.";
}
}
void SqliteBasic::closeDb(void)
{
database.close();
qDebug() << "close success";
}mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include "sqlitebasic.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
this->setWindowTitle("sqlite基础");
SqliteBasic sqliteBasic;
sqliteBasic.openDb();
sqliteBasic.createTable();
// 判断数据表是否存在
QString str1 = QString("student");
qDebug() << "isTabelExist:" << sqliteBasic.isTableExist(str1);
// 插入单条数据
w2dba w2dbaTest1 = {1, "zhangsan", 24};
w2dba w2dbaTest2 = {2, "lisi", 28};
sqliteBasic.singleInsertData(w2dbaTest1);
sqliteBasic.singleInsertData(w2dbaTest2);
// 插入多条数据
QList<w2dba> list;
w2dba w2dbaTest3 = {3, "liwu", 26};
w2dba w2dbaTest4 = {4, "zhaoliu", 27};
list.append(w2dbaTest3);
list.append(w2dbaTest4);
sqliteBasic.moreInsertData(list);
// 查询全部数据
sqliteBasic.queryTable();
qDebug() << endl;
// 修改数据
sqliteBasic.modifyData(2, "modify", 10);
sqliteBasic.modifyData(3, "modify-2", 20);
// 查询全部数据
sqliteBasic.queryTable();
qDebug() << endl;
// 删除数据
sqliteBasic.deleteData(2);
// 查询全部数据
sqliteBasic.queryTable();
qDebug() << endl;
// 删除数据表
QString str2 = QString("student");
qDebug() << "isTabelExist:" << sqliteBasic.isTableExist(str2);
sqliteBasic.deleteTable(str2);
qDebug() << "isTabelExist:" << sqliteBasic.isTableExist(str2);
//关闭数据库
sqliteBasic.closeDb();
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}运行结果如下(目前只做了终端):
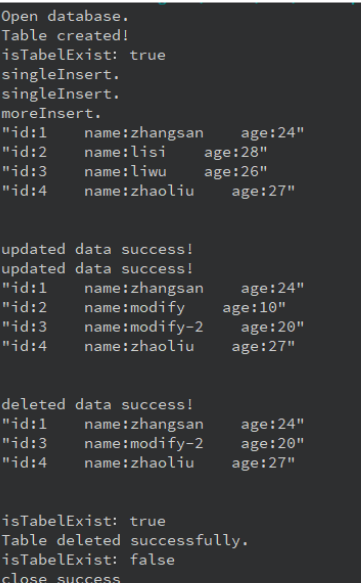
3. db数据库访问操作
数据库以db文件形式存在,可通过Navicat访问和操作数据库。
参考资料
1. sqlite语法:https://www.cnblogs.com/zpchya/p/11190738.html
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40344790/article/details/129521573
作者:DevFrank (CSDN C/C++ 优质创作者)



