第一次个人编程作业
第一次个人编程作业
目录
目录
一.github链接与作业归属
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/CSGrade22-34/ |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/CSGrade22-34/homework/13229 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 通过开发个人项目,实现项目单元测试 |
二.psp表格
| *PSP2.1* | *Personal Software Process Stages* | *预估耗时(分钟)* | *实际耗时(分钟)* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 20 | 10 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 390 | 400 |
| Development | 开发 | 20 | 20 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 150 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 20 | 10 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 20 | 10 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 10 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 20 | 10 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 30 | 20 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 20 | 20 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 40 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 40 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 30 | 40 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 20 |
| · 合计 |
三.模块设计
函数设计
1.read
负责读入一个文件
2.OutputFile
负责在指定文件输出
3.work
负责对传入的本文进行分词并且计算每个词出现的频率
4.cul
用来计算每个词的向量模
5.getans
得到最后的余弦相似度
流程图
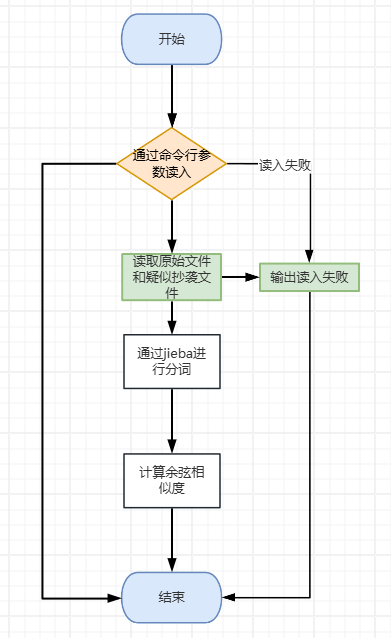
算法关键
1.使用了jieba库对于文本进行分词
//文件的读入
void read(string& text, string path) {
ifstream fstream;
fstream.open(path);
if (!fstream.is_open()) {
cout << "Failed to open the file:" << path << endl;
return;
}
string s;
cout << "cut " << path << " success" << endl;
while (getline(fstream, s))
text += s;
fstream.close();
}
2.对于相似度的计算是通过余弦相似度计算
void work(string text, map<string, int>& mp) {
cppjieba::Jieba jieba(DICT_PATH,
HMM_PATH,
USER_DICT_PATH,
IDF_PATH,
STOP_WORD_PATH);
vector<string> words;
jieba.Cut(text, words, true);
for (auto i : words)
mp[i]++;
}
//求向量模
double cul(map<string, int>& mp) {
double mo = 0.0;
for (auto [x, y] : mp) {
mo += pow((double)y, 2);
}
return sqrt(mo);
}
//计算余弦相似度
double getans(map<string, int>& mp1, map<string, int>& mp2) {
double dotProduct = 0.0;
for (auto it : mp1) {
auto it2 = mp2.find(it.first);
if (it2 != mp2.end())
dotProduct += ((double)it.second) * ((double)it2->second);
}
double mo1 = cul(mp1);
double mo2 = cul(mp2);
return dotProduct / (mo1 * mo2);
}
四.性能分析
代码的复杂度主要分为两大部分,一部分为计算每个词语的向量模,这里用了map的遍历,复杂度可以近似为O(nlogn),n为输入的文本字符数量,第二部分为调用jieba库的cut功能,由于不知道jieba库的具体实现如何,只知道大体为一个数据规模很大的字典树,在字典树上进行的匹配,所以很遗憾,代码的大部分时间都用来跑jieba库的分词功能了,在不改变jieba库的前提下,能做的并不多,可能只有把map优化为vector来存词语才可以优化掉一个log,但是我们在找词语的时候要用一个二分,因此可能实际并没有快多少
以下为vs的性能分析工具跑出的结果可以印证以上的jieba库占用大量时长的原因
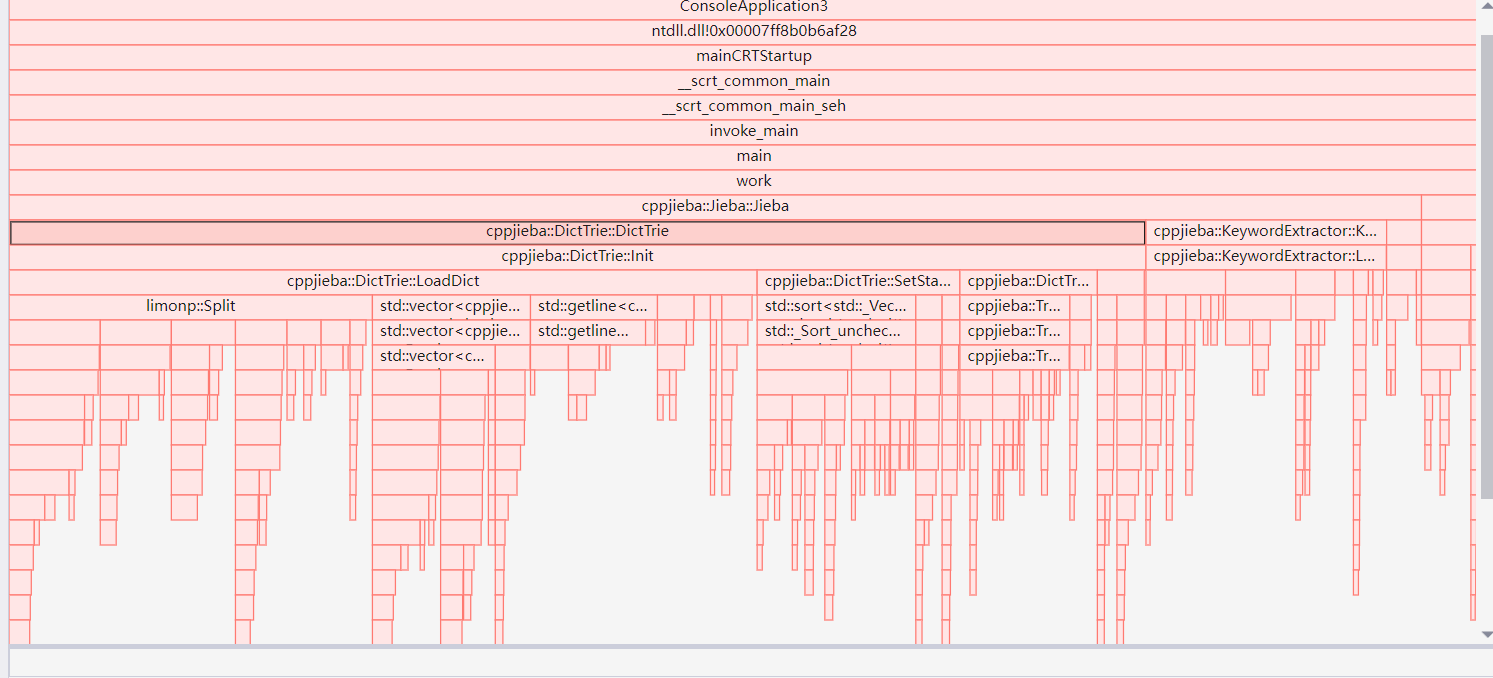
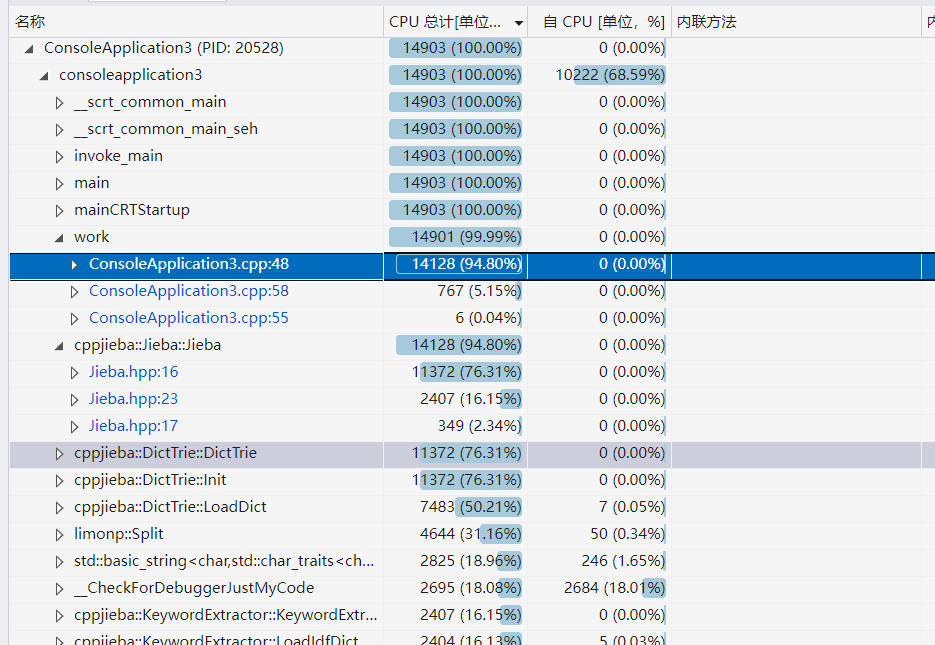
以下即消耗最大的函数代码
//调用jieba库进行分词,然后记录每个词出现的次数
void work(string text, map<string, int>& mp) {
cppjieba::Jieba jieba(DICT_PATH,
HMM_PATH,
USER_DICT_PATH,
IDF_PATH,
STOP_WORD_PATH);
vector<string> words;
jieba.Cut(text, words, true);
for (auto i : words)
mp[i]++;
}
五.测试部分
1.输入测试
void read(string& text, string path) {
ifstream fstream;
fstream.open(path);
if (!fstream.is_open()) {
cout << "Failed to open the file:" << path << endl;
return;
}
string s;
cout << "cut " << path << " success" << endl;
while (getline(fstream, s))
text += s;
fstream.close();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
string s,now="";
cin>>s;
read(s,now);
return 0;
}
2.输出测试
void OutputFile(string path, double ans) {
ofstream outputFile;
outputFile.open(path);
if (outputFile.is_open()) {
outputFile << ans;
} else {
outputFile.close();
cout << "failed to open the file:" << path << endl;
return;
}
cout << "output over" << endl;
outputFile.close();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
string s;
double now;
cin>>s>>now;
OutputFile(s,now);
return 0;
}
3.计算测试
double cul(map<string, int>& mp) {
double mo = 0.0;
for (auto [x, y] : mp) {
mo += pow((double)y, 2);
}
return sqrt(mo);
}
double getans(map<string, int>& mp1, map<string, int>& mp2) {
double dotProduct = 0.0;
for (auto it : mp1) {
auto it2 = mp2.find(it.first);
if (it2 != mp2.end()) dotProduct += ((double)it.second) * ((double)it2->second);
}
double mo1 = cul(mp1);
double mo2 = cul(mp2);
return dotProduct / (mo1 * mo2);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
map<string, int> mp1, mp2;
auto work=[&](map<string, int>& mp) {
int n=rand();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int l = rand();
string s = "";
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++) s += rand() % 10 + '0';
mp[s]++;
}
};
work(mp1),work(mp2);
getans(mp1,mp2);
return 0;
}double cul(map<string, int>& mp) {
double mo = 0.0;
for (auto [x, y] : mp) {
mo += pow((double)y, 2);
}
return sqrt(mo);
}
double getans(map<string, int>& mp1, map<string, int>& mp2) {
double dotProduct = 0.0;
for (auto it : mp1) {
auto it2 = mp2.find(it.first);
if (it2 != mp2.end()) dotProduct += ((double)it.second) * ((double)it2->second);
}
double mo1 = cul(mp1);
double mo2 = cul(mp2);
return dotProduct / (mo1 * mo2);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
map<string, int> mp1, mp2;
auto work=[&](map<string, int>& mp) {
int n=rand();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int l = rand();
string s = "";
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++) s += rand() % 10 + '0';
mp[s]++;
}
};
work(mp1),work(mp2);
getans(mp1,mp2);
return 0;
}
4.分词测试
由于分词是调用外部库,所以没有测试
六.异常处理部分
1.命令行输入的命令数量不对
这时候会直接结束程序
if (argc != 4) {
cout << "input error" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.文件读取路径出错
会告诉你文件读取失败,然后返回
if (!fstream.is_open()) {
cout << "Failed to open the file" << endl;
return;
}
3.文件输出路径出错
会告诉你文件读取失败,然后返回
if (outputFile.is_open()) {
outputFile << ans;
}
else {
outputFile.close();
cout << "failed to open the file" << endl;
return;
}



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek V3 两周使用总结
· 回顾我的软件开发经历(1)
· C#使用yield关键字提升迭代性能与效率
· 低成本高可用方案!Linux系统下SQL Server数据库镜像配置全流程详解
· 4. 使用sql查询excel内容