Trie树-字典树
字典树
Trie树的本质,就是利用字符串之间的公共前缀,把重复的前缀合并在一起。
(图片来自于比《数据结构与算法之美》)
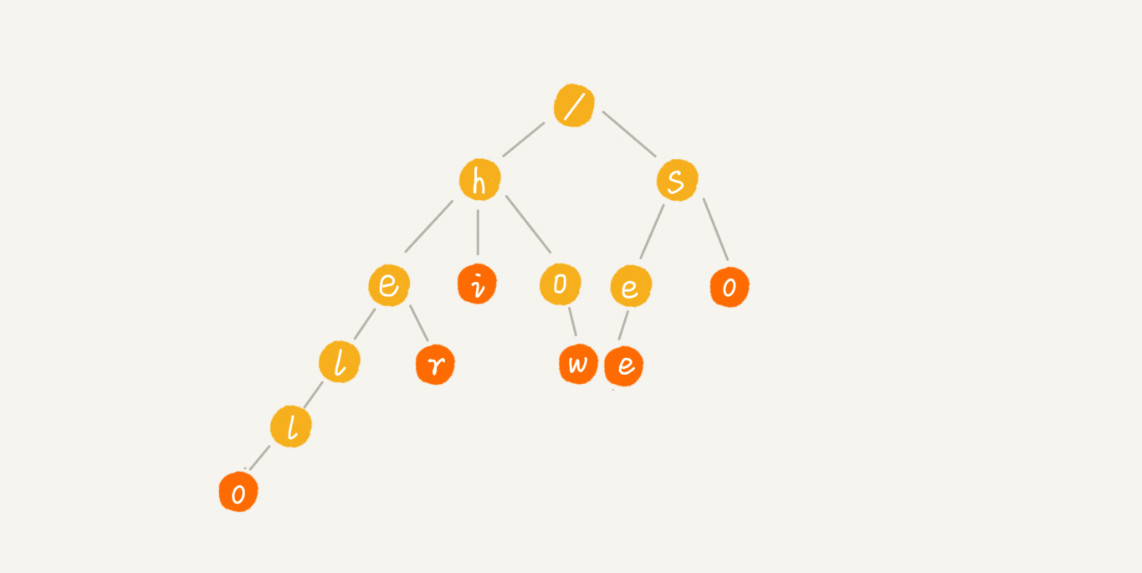
根节点不包含任何信息,每个节点表示一个字符串中的字符,从根节点到红色节点(并不一定都是叶子节点,红色节点表示到此为止是一个字符)的一条路径表示为字符串
代码实现
- 经典存储方式--散列表
下标0-25存储 a-z的指针,字符子节点不存在,下标位置存储null。
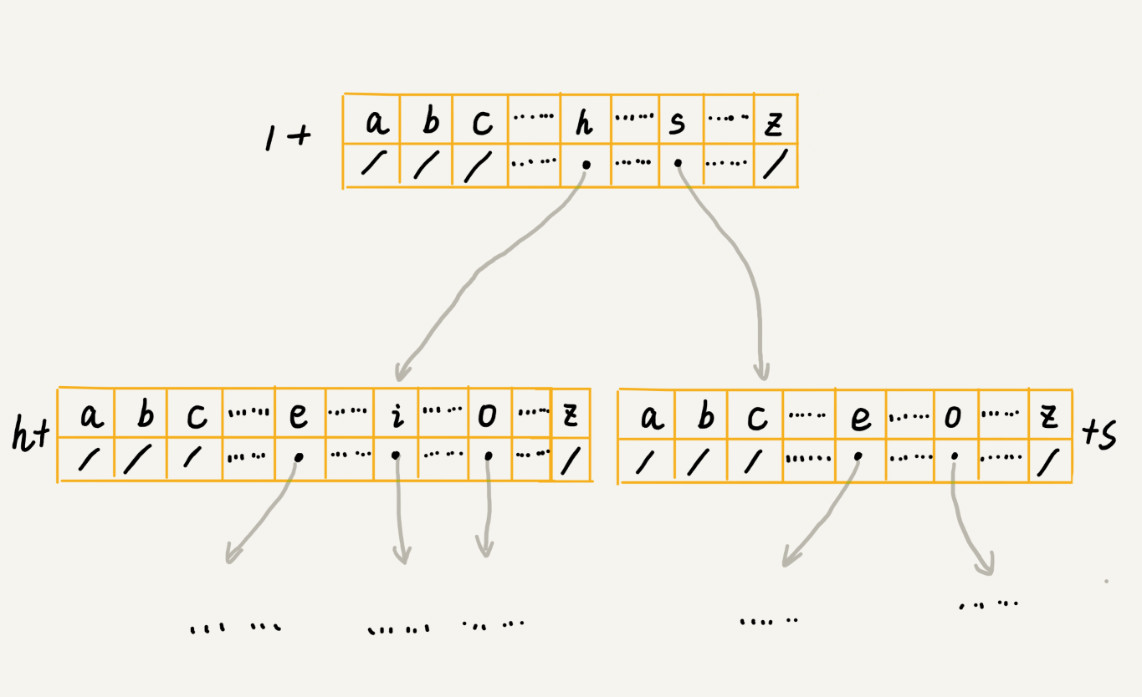
class TrieNode {
char data;
TrieNode children[26];
}
java代码
例题

电话号码归属地,字典序解法
public class Trie {
private TrieNode root = new TrieNode('/'); // 存储无意义字符
// 往Trie树中插入一个字符串
public void insert(char[] text) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (int i = 0; i < text.length; ++i) {
int index = text[i] - 'a';
if (p.children[index] == null) {
TrieNode newNode = new TrieNode(text[i]);
p.children[index] = newNode;
}
p = p.children[index];
}
p.isEndingChar = true;
}
// 在Trie树中查找一个字符串
public boolean find(char[] pattern) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length; ++i) {
int index = pattern[i] - 'a';
if (p.children[index] == null) {
return false; // 不存在pattern
}
p = p.children[index];
}
if (p.isEndingChar == false) return false; // 不能完全匹配,只是前缀
else return true; // 找到pattern
}
public class TrieNode {
public char data;
public TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
public boolean isEndingChar = false;
public TrieNode(char data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
}
构建Trie树的过程需要扫描所有的字符串,时间复杂度是O(n),一旦构建成功,后续的查询操作会非常高效。
Trie树有可能会很浪费内存,但确实非常高效。
//Trie树的例题。
来源于这个博主的代码:https://blog.csdn.net/u011721440/article/details/81559189
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define N 20010
#define M 10 //child :0-9;
struct Trie
{
string s; //一般是空的,如果到了节点字符,就写地名。
int next; //去下一个节点,被使用的k,如果没有,则是-1,表示这个点没有用到。(插入)
}rt[N][M];
int cnt; //point to index which just used (被用到的k,做标记位置)
void Trie_clear(int k)
{
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i)
{
rt[k][i].next = -1;
rt[k][i].s.clear();
}
}
void Insert(string& s1, string& s2)
{
int k = 0; // point to root node
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); ++i)
{
int id = s1[i] - '0';
if (rt[k][id].next == -1)
{
rt[k][id].next = ++cnt;
Trie_clear(cnt);
}
if (s1[i + 1] == 'x')
{
rt[k][id].s = s2;
break;
}
k = rt[k][id].next;
}
}
string find_val(string& s1)
{
int k = 0; //point to root node
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); ++i)
{
int id = s1[i] - '0';
if (rt[k][id].next == -1)
return "";
if (rt[k][id].s != "")
{
return rt[k][id].s;
}
k = rt[k][id].next;
}
return "";
}
int main()
{
int T, n, m;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n;
string s1, s2;
cnt = 0;
Trie_clear(cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> s1 >> s2;
s1 += 'x'; //害怕输入数据没有x
Insert(s1, s2);
}
cin >> m;
while (m--)
{
cin >> s1;
s1 += 'x';
string ans = find_val(s1);
if (ans == "") cout << "unknown" << endl;
else cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号