Python-进程与线程
1 import time 2 from multiprocessing import Process 3 import os 4 5 6 def dance(num, name): 7 print('Process of basketball is %s.' % os.getpid()) 8 for i in range(num): 9 print(name+' is playing basketball right now.') 10 time.sleep(0.5) 11 12 13 def sing(num, name): 14 print('Process of the guitar is %s.' % os.getpid()) 15 for i in range(num): 16 print(name+' is playing the guitar next door.') 17 time.sleep(0.5) 18 19 20 if __name__ == '__main__': 21 print('Parent process: %s.' % os.getpid()) 22 # 下面这两个是在创建子进程对象并指定执行的任务名 23 # target就是指定函数名,args就是参数 24 # 若使用元组,参数位置必须按照定义的函数的顺序来写 25 p = Process(target=dance, args=(2, 'Bob')) # 只传一个参数时,加个逗号,否则解释器会认为这不是一个元祖而是一个数字 26 f = Process(target=sing, kwargs={'num': 2, 'name': 'Eric'}) # 使用字典时,甚至可以不按顺序,只要参数名称对就可以 27 # 启动子进程并执行任务 28 p.start() 29 f.start() 30 p.join() 31 f.join() 32 print('Boys love these things.')

再来看看进程间的通信:
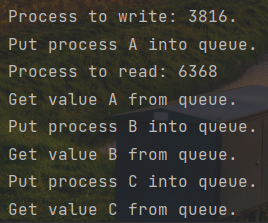
1 import os 2 import time 3 import random 4 from multiprocessing import Process, Queue 5 6 7 def write(p): 8 print('Process to write: %s.' % os.getpid()) 9 for value in ['A', 'B', 'C']: 10 print('Put process %s into queue.' % value) 11 p.put(value) 12 time.sleep(random.random()) 13 14 15 def read(q): 16 print('Process to read: %s' % os.getpid()) 17 while True: 18 value = q.get(True) 19 print('Get value %s from queue.' % value) 20 21 22 if __name__ == '__main__': 23 queue = Queue() 24 pw = Process(target=write, args=(queue, )) 25 pr = Process(target=read, args=(queue, )) 26 pw.start() 27 pr.start() 28 pw.join() 29 pr.terminate()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号