快速排序
最近学校在讲数据结构,个人觉得排序这一块的算法都挺重要的,不管怎么说,比较常见的几个排序算法一定要能够在短时间内写出来,这就是所谓基本功。---来自于班导师
哈哈哈,废话不多说,这里先记录一下快速排序的笔记,免得以后自己忘了。
快速排序的主要思想就是选取数组里面的一个数(这里主要是作数组元素的排序,这个数一般我们选第一个,所以极端情况下快排的时间复杂度其实也达到了O(n²)),把它赋给pivot。然后遍历这个数组,比这个数大的就放在数组的右边,比它小的就放在左边,然后这个过程再递归完成。下面来看看代码:
1 package com.hw.sorts0512; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 class Quicksort{ 6 public int length; 7 private int pivot,index; 8 public int[] data = null; 9 10 private int partition(int[] arr,int low,int high) 11 { 12 pivot = arr[low]; 13 while(low < high) 14 { 15 while(low<high && pivot<=arr[high]) 16 { 17 high--; 18 } 19 arr[low] = arr[high]; 20 21 while(low<high && pivot>=arr[low]) 22 { 23 low++; 24 } 25 arr[high] = arr[low]; 26 } 27 arr[low] = pivot; 28 return low; 29 } 30 31 public void quicksort(int[] arr,int low,int high) 32 { 33 if(low < high){ 34 index = partition(arr,low,high); 35 quicksort(arr,low,index-1); 36 quicksort(arr,index+1,high); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 public class Solution { 42 public void run() 43 { 44 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 45 Quicksort q = new Quicksort(); 46 System.out.println("请输入数组长度:"); 47 q.length = s.nextInt(); 48 q.data = new int[q.length]; 49 System.out.println("请输入待排序的所有数据:"); 50 for(int i = 0;i < q.length;i++){ 51 q.data[i] = s.nextInt(); 52 } 53 q.quicksort(q.data, 0, q.length-1); 54 for(int i = 0;i < q.length;i++){ 55 System.out.print(q.data[i]+" "); 56 } 57 } 58 59 public static void main(String[] args){ 60 Solution solution = new Solution(); 61 solution.run(); 62 } 63 }
核心部分就是Quicksort里面的那两个方法。我怎么才能做到把这个数组全部扫一遍,并判断那些数比pivot大哪些数比pivot小呢?这个时候我们就需要弄一个循环,通过循环控制这个过程不断地进行,以达到第一轮筛选的目的,即,把数组里面比pivot大的数全部放到右边,小的全放到左边,然后左右两边再重复这个过程。
那么这个循环设置的条件其实就是low<high,low就是数组的第一个元素,high就是数组的最后一个元素。在循环内部,只要是比pivot大的数,我就不动,放那放着就是,我动什么呢?动high这个值,也就是数组元素的索引。怎么动?我让它减减。然后继续判断下一个数。等到循环结束的时候,那么就找到了这个比pivot小的数了,这个时候呢,我把这个地方的这个元素赋给low这个位置。那么这样其实就完成了,把这个比pivot小的数放到了数组的左边。然后我再动low,过程与上面类似。这样一来,一旦循环结束,就是low=high.这个时候呢,我就已经把这个数组分成两部分了,左边部分的数都比pivot小,右边部分的数都比pivot大。这个时候呢,我就只需要把此时数组中low这个位置弄为pivot,整个过程就完成了,最后返回这个位置,以这个位置把数组分为两部分,两部分再分别递归。
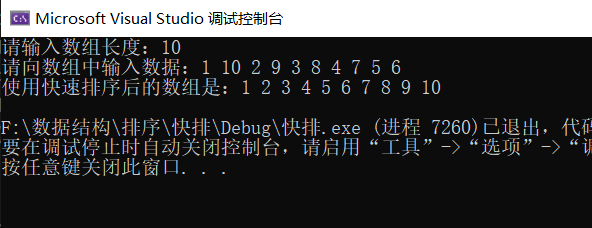
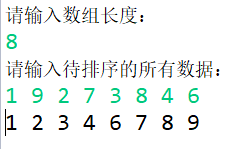
来看看运行效果:
接下来看看C++版本的:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #define N 300 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Quicksort 6 { 7 public: 8 int data[N]; 9 int length; 10 void quicksort(int arr[], int low, int high) 11 { 12 if (low < high) { 13 index = partition(arr, low, high); 14 quicksort(arr, index + 1, high); 15 quicksort(arr, low, index - 1); 16 } 17 } 18 19 private: 20 int index, pivot; 21 int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) 22 { 23 pivot = arr[low]; 24 while (low < high) 25 { 26 while (low < high && pivot <= arr[high]) 27 { 28 high--; 29 } 30 arr[low] = arr[high]; 31 while (low < high && pivot >= arr[low]) 32 { 33 low++; 34 } 35 arr[high] = arr[low]; 36 } 37 arr[low] = pivot; 38 return low; 39 } 40 }; 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 Quicksort q; 45 cout << "请输入数组长度:"; 46 cin >> q.length; 47 cout << "请向数组中输入数据:"; 48 for (int i = 0; i < q.length; i++) { 49 cin >> q.data[i]; 50 } 51 q.quicksort(q.data, 0, q.length - 1); 52 cout << "使用快速排序后的数组是:"; 53 for (int i = 0; i < q.length; i++) { 54 cout << q.data[i] << " "; 55 } 56 cout << endl; 57 return 0; 58 }