python 堆排序
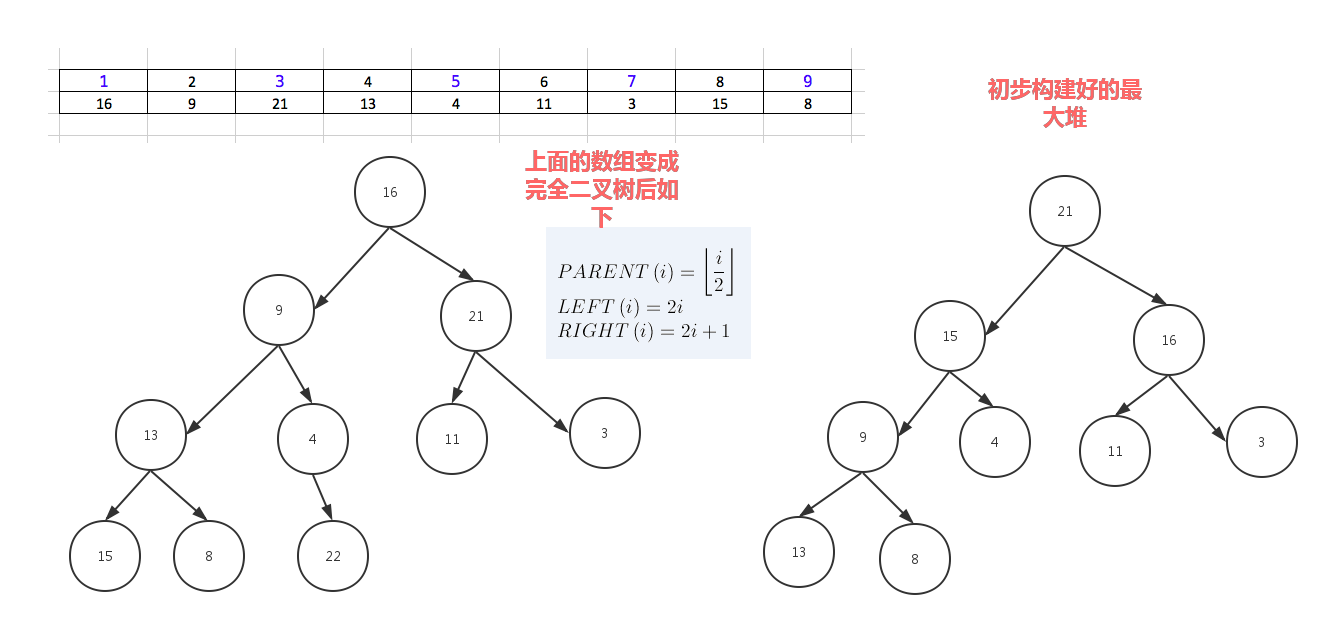
堆排序就是把堆顶的最大数取出,
将剩余的堆继续调整为最大堆,具体过程在第二块有介绍,以递归实现
剩余部分调整为最大堆后,再次将堆顶的最大数取出,再将剩余部分调整为最大堆,这个过程持续到剩余数只有一个时结束
dataset = [16,9,21,3,13,14,23,6,4,11,3,15,99,8,22] for i in range(len(dataset)-1,0,-1): print("-------",dataset[0:i+1],len(dataset),i) #for index in range(int(len(dataset)/2),0,-1): for index in range(int((i+1)/2),0,-1): print(index) p_index = index l_child_index = p_index *2 - 1 r_child_index = p_index *2 print("l index",l_child_index,'r index',r_child_index) p_node = dataset[p_index-1] left_child = dataset[l_child_index] if p_node < left_child: # switch p_node with left child dataset[p_index - 1], dataset[l_child_index] = left_child, p_node # redefine p_node after the switch ,need call this val below p_node = dataset[p_index - 1] if r_child_index < len(dataset[0:i+1]): #avoid right out of list index range right_child = dataset[r_child_index] print(p_index,p_node,left_child,right_child) if p_node < right_child: #swith p_node with right child dataset[p_index - 1] , dataset[r_child_index] = right_child,p_node # redefine p_node after the switch ,need call this val below p_node = dataset[p_index - 1] else: print("p node [%s] has no right child" % p_node) #最后这个列表的第一值就是最大堆的值,把这个最大值放到列表最后一个, 把神剩余的列表再调整为最大堆 print("switch i index", i, dataset[0], dataset[i] ) print("before switch",dataset[0:i+1]) dataset[0],dataset[i] = dataset[i],dataset[0] print(dataset)



