python 操作MongoDB
安装MongoDB
启动数据库:安装完成指定数据库存放路径 mongod.exe --dbpath c:\data\db
进入目录后运行mongo.exe 成功
创建数据库
> use mydb switched to db mydb > db mydb
> book = {"title":"from beginner to master", "author":"qiwsir", "lang":"python"}
{
"title" : "from beginner to master",
"author" : "qiwsir",
"lang" : "python"
}
> db.books.insert(book)
> db.books.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("554f0e3cf579bc0767db9edf"), "title" : "from beginner to master", "author" : "qiwsir", "lang" : "Python" }
db 指向了数据库 mydb,books 是这个数据库里面的一个集合(类似 mysql 里面的表),向集合 books 里面插入了一个文档(文档对应 mysql 里面的记录)。“数据库、集合、文档”构成了 mongodb 数据库。
用到数据库,就通过 use xxx,如果不存在就建立;用到集合,就通过 db.xxx 来使用,如果没有就建立。可以总结为“随用随取随建立”。
投影
- 在查询到的返回结果中,只选择必要的字段,而不是选择一个文档的整个字段
- 如:一个文档有5个字段,需要显示只有3个,投影其中3个字段即可
- 语法:
- 参数为字段与值,值为1表示显示,值为0不显示
db.集合名称.find({},{字段名称:1,...})
- 对于需要显示的字段,设置为1即可,不设置即为不显示
- 特殊:对于_id列默认是显示的,如果不显示需要明确设置为0
- 例1
db.stu.find({},{name:1,gender:1})
- 例2
db.stu.find({},{_id:0,name:1,gender:1})
排序
- 方法sort(),用于对结果集进行排序
- 语法
db.集合名称.find().sort({字段:1,...})
- 参数1为升序排列
- 参数-1为降序排列
- 例1:根据性别降序,再根据年龄升序
db.stu.find().sort({gender:-1,age:1})
消除重复
- 方法distinct()对数据进行去重
- 语法
db.集合名称.distinct('去重字段',{条件})
- 例1:查找年龄大于18的性别(去重)
db.stu.distinct('gender',{age:{$gt:18}}) 安装 Pymongo
pip install Pymongo
>>> import Pymongo >>> client = pymongo.MongoClient("localhost", 27017)
刚才已经建立了一个数据库 mydb,并且在这个库里面有一个集合 books,于是:
>>> db = client.mydb
或者
>>> db = client['mydb']
获得数据库 mydb,并赋值给变量 db(这个变量不是 mongodb 的 shell 中的那个 db,此处的 db 就是 Python 中一个寻常的变量)。
>>> db.collection_names() [u'system.indexes', u'books']
查看集合,发现了我们已经建立好的那个 books,于是在获取这个集合,并赋值给一个变量 books:
>>> books = db["books"] 或者 >>> books = db.books
增删改查
>>> books.find_one() {u'lang': u'Python', u'_id': ObjectId('554f0e3cf579bc0767db9edf'), u'author': u'qiwsir', u'title': u'from beginner to master'}
在 mongodb 的 shell 中是这样子的:
> db.books.findOne() { "_id" : ObjectId("554f0e3cf579bc0767db9edf"), "title" : "from beginner to master", "author" : "qiwsir", "lang" : "python" }
新增和查询
>>> b2 = {"title":"physics", "author":"Newton", "lang":"english"}
>>> books.insert(b2)
ObjectId('554f28f465db941152e6df8b')
>>> books.find().count()
2
>>> for i in books.find(): ... print i ... {u'lang': u'Python', u'_id': ObjectId('554f0e3cf579bc0767db9edf'), u'author': u'qiwsir', u'title': u'from beginner to master'} {u'lang': u'english', u'title': u'physics', u'_id': ObjectId('554f28f465db941152e6df8b'), u'author': u'Newton'}
批量插入
>>> n1 = {"title":"java", "name":"Bush"}
>>> n2 = {"title":"fortran", "name":"John Warner Backus"}
>>> n3 = {"title":"lisp", "name":"John McCarthy"}
>>> n = [n1, n2, n3]
>>> n
[{'name': 'Bush', 'title': 'java'}, {'name': 'John Warner Backus', 'title': 'fortran'}, {'name': 'John McCarthy', 'title': 'lisp'}]
>>> books.insert(n)
[ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8d'), ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8e'), ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8f')]
按条件查询
>>> books.find_one({"name":"Bush"})
{u'_id': ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8d'), u'name': u'Bush', u'title': u'java'}
对于查询结果,还可以进行排序:
>>> for i in books.find().sort("title", pymongo.ASCENDING): ... print i ... {u'_id': ObjectId('554f2b4565db941152e6df8c'), u'name': u'Hertz'} {u'_id': ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8e'), u'name': u'John Warner Backus', u'title': u'fortran'} {u'lang': u'python', u'_id': ObjectId('554f0e3cf579bc0767db9edf'), u'author': u'qiwsir', u'title': u'from beginner to master'} {u'_id': ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8d'), u'name': u'Bush', u'title': u'java'} {u'_id': ObjectId('554f30be65db941152e6df8f'), u'name': u'John McCarthy', u'title': u'lisp'} {u'lang': u'english', u'title': u'physics', u'_id': ObjectId('554f28f465db941152e6df8b'), u'author': u'Newton'}
这是按照"title"的值的升序排列的,注意 sort() 中的第二个参数,意思是升序排列。如果按照降序,就需要将参数修改为Pymongo.DESCEDING,也可以指定多个排序键。
更新数据
对于已有数据,进行更新,是数据库中常用的操作。比如,要更新 name 为 Hertz 那个文档:
在更新的时候,用了一个 $set 修改器,它可以用来指定键值,如果键不存在,就会创建。
>>> books.update({"name":"Hertz"}, {"$set": {"title":"new physics", "author":"Hertz"}})
{u'updatedExisting': True, u'connectionId': 4, u'ok': 1.0, u'err': None, u'n': 1}
>>> books.find_one({"author":"Hertz"})
{u'title': u'new physics', u'_id': ObjectId('554f2b4565db941152e6df8c'), u'name': u'Hertz', u'author': u'Hertz'}
关于修改器,不仅仅是这一个,还有别的呢。
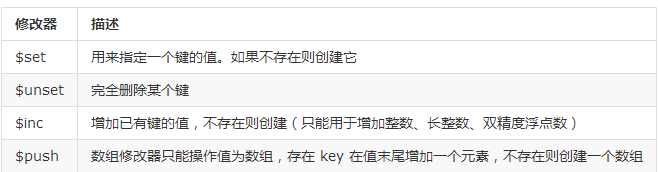
删除
删除可以用 remove() 方法:
>>> books.remove({"name":"Bush"})
{u'connectionId': 4, u'ok': 1.0, u'err': None, u'n': 1}
>>> books.find_one({"name":"Bush"})
>>>
也可以根据 mongodb 的语法规则,写个条件,按照条件删除。
索引
索引的目的是为了让查询速度更快,当然,在具体的项目开发中,要视情况而定是否建立索引。因为建立索引也是有代价的。
>>> books.create_index([("title", pymongo.DESCENDING),]) u'title_-1'
数据导出CSV

在用mongoexport导出csv文件时,发现数据库中的中文在excel中都显示为乱码,用notepad打开则正常。
解决办法: 在notepad中,将编码格式改为UTF-8,保存,再用excel打开,则中文可正常显示。



