Linux就该这么学28期——Day03 2.4-2.7
2.4 系统状态检测命令

ifconfig 查询网卡配置和网络状态等信息 WIN系统——ipconfig ifconfig = interface config
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ifconfig ens160: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255 inet6 fe80::c8f8:f5c5:8251:aeaa prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20 ether 00:0c:29:7d:27:bf txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 304 bytes 33283 (32.5 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 91 bytes 11052 (10.7 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
不同版本中网卡的默认名称如下:
RHEL 5/6 eth0 eth1
RHEL 7 eth16777728
RHEL 8 ens160
uname 查看系统内核与系统版本等信息
[root@localhost ~]# uname -a Linux localhost.localdomain 4.18.0-80.el8.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Mar 13 12:02:46 UTC 2019 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
Linux 内核名称
localhost.localdomain 主机名
4.18.0-80.el8.x86_64 内核版本
#1 SMP Wed Mar 13 12:02:46 UTC 2019 系统打包时间
x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 硬件名称 硬件平台 处理器类型
GNU/Linux OS名称 GNU开源
查看当前系统版本的详细信息
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release Red Hat Enterprise Linux release 8.0 (Ootpa)
uptime 查看CPU负载 所显示的内容与top命令显示的第一行一致
[root@localhost ~]# uptime 12:36:37 up 18 min, 1 user, load average: 0.01, 0.04, 0.07
当前时间 已运行时间 启用终端数量 1分钟 5分钟 15分钟
RHEL8中 GUI不算终端,只统计用户的数量
负载值越低越好,建议是负载值保持在1左右,不要超过5就好
free 显示内存当前使用量
-h human-readable 以可读性最高的形式输出,更人性化 即易读模式 [root@localhost ~]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1.9Gi 1.2Gi 158Mi 13Mi 573Mi 558Mi Swap: 2.0Gi 3.0Mi 2.0Gi [root@localhost ~]# free -g total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1 1 0 0 0 0 Swap: 1 0 1 [root@localhost ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1966 1234 158 13 573 558 Swap: 2047 3 2044
who 看哪个用户登录着呢
[root@localhost ~]# who root tty2 2020-10-10 12:20 (tty2)
登陆的用户名 终端设备(远程的会显示IP) 登陆时间
last 用于调取登陆记录,仅供参考
[root@localhost ~]# last root tty2 tty2 Sat Oct 10 12:20 still logged in reboot system boot 4.18.0-80.el8.x8 Sat Oct 10 12:17 still running root tty2 tty2 Sat Oct 10 15:50 - 17:24 (-22:26) reboot system boot 4.18.0-80.el8.x8 Sat Oct 10 15:50 - 17:24 (-22:25) root tty2 tty2 Mon Oct 5 03:59 - down (18:26) reboot system boot 4.18.0-80.el8.x8 Mon Oct 5 03:35 - 22:25 (18:50) root tty2 tty2 Sun Oct 4 00:32 - crash (1+03:03) reboot system boot 4.18.0-80.el8.x8 Sun Oct 4 00:21 - 22:25 (1+22:03) wtmp begins Sun Oct 4 00:21:51 2020
history 显示执行过的历史命令
[root@localhost ~]# history 1 man echo 2 date 3 date "+%Y-%m-%d" 4 date "+%Y-%m-%d %H-%M-%S" 5 timedatectl set-time 21:20 6 date 7 echo Linuxprobe.com 可以使用 !编码数字 的方式重复执行某一次的命令 [root@localhost ~]# !48 who root tty2 2020-10-10 12:20 (tty2)
历史命令会被保存到用户家目录中的.bash_history文件中
[root@linuxprobe ~]# cat ~/.bash_history
history -c 清空当前用户在本机上执行过的命令记录
sosreport 收集系统配置及架构信息并输出诊断文档 可以理解为体检报告
2.5 查找定位文件命令

pwd命令 print working directory 查看用户当前所在工作目录
[root@linuxprobe ~]# pwd
/root
cd命令 用来切换工作路径
[root@linuxprobe ~]# cd /etc/ssh #切换到/etc/ssh 目录 [root@linuxprobe ssh]# pwd /etc/ssh [root@linuxprobe ssh]# cd ~ #切换到当前用户家目录 [root@linuxprobe ~]# pwd /root [root@linuxprobe ~]# cd - #返回上一次所在目录 相当于后退 /etc/ssh [root@linuxprobe ssh]# cd .. #切换到上一级所在目录 [root@linuxprobe etc]# pwd /etc
cd ~username 切换到其他用户家目录
cd / 切换到根目录
ls 命令 显示当前目录中的文件信息 Linux中一切皆文件
ls -a 显示所有文件,包括隐藏文件。 隐藏文件:以“.”开始的文件 ls -l 显示文件详细信息 缩写为 ll ls -al 显示所有文件详细信息
如果想查看目录的属性信息,需要额外添加 -d 参数
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -ld /etc
drwxr-xr-x. 136 root root 8192 Oct 13 09:54 /etc
tree 命令 以树状图形式 列出目录内容及结构
find 按照指定条件来查找文件所对应的位置 “find [查找范围] 寻找条件” -exec参数 把find命令搜索到的结果交由紧随其后的命令作进一步处理 由于find命令对参数的特殊要求,因此虽然exec是长格式形式,但依然只需要一个减号(-) [root@linuxprobe ~]# find / -user linuxprobe -exec cp -a {} /root/findresults/ \; 其中的{}表示find命令搜索出的每一个文件,并且命令的结尾必须是“\;”。
locate命令用于按照名称快速搜索文件所对应的位置,语法格式为:“locate 文件名称”
但是该命令在使用前需要先执行 updatedb 生成索引数据库
find 实时,全盘;locate 基于数据库
2.6文本文件编辑
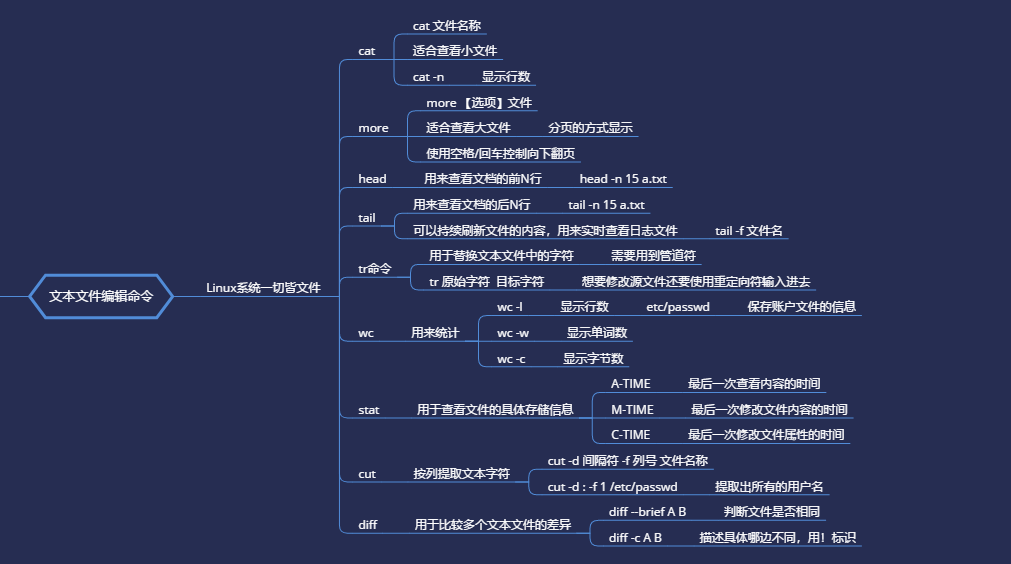
cat 适用于内容较少的 -n 显示行号 more 适用于内容较多的,通过空格或者回车向下翻页 无论长短,推荐使用more命令
有头有尾
head 用于查看前N行 head -n 10
tail 用于查看后N行 或 持续刷新内容 tail -n 10
tail -f 文件名 持续刷新一个文件的内容,适合实时查看最新日志文件等。
tr 用来替换文本文件中的字符 translate tr 原始字符 目标字符
tr [a-z] [A-Z] 把某个文本内容中的英文全部替换为大写
wc 命令 用来进行统计 -l 行数 -w 单词数 -c 字节数
[root@linuxprobe ~]# wc -l /etc/passwd 45 /etc/passwd #/etc/passwd 保存系统账户信息 #用来统计当前系统中多少个用户
stat 查看文件的具体存储信息和时间等信息 三种时间状态: [root@linuxprobe ~]# stat anaconda-ks.cfg File: anaconda-ks.cfg Size: 1407 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 35321091 Links: 1 Access: (0600/-rw-------) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root) Context: system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 Access: 2020-07-21 05:16:52.347279499 +0800 ATIME 最后一次访问文件内容的时间 Modify: 2020-07-21 05:09:16.421009316 +0800 Mtime 修改文件内容的时间 Change: 2020-07-21 05:09:16.421009316 +0800 Ctime 更改文件属性的时间 Birth: -
cut 按“列”提取文本字符 cut -d间隔符 -f列号 文件名称 cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd
#提取出passwd文件中的用户名信息 [root@linuxprobe ~]# cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd root bin daemon adm lp sync shutdown ………………省略部分输出信息……………… grep 按“行”提取文本内容 用途最广泛的文本搜索匹配工具 grep -n 显示搜索到信息的行号 grep -v 用于反选信息,即查找没有包含关键词的所有信息行 [root@linuxprobe ~]# grep /sbin/nologin /etc/passwd bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin ………………省略部分输出过程信息………………
diff 比较多个文件之间的差异 different diff --brief A B diff --brief命令显示比较后的结果,判断文件是否相同 使用带有-c参数的diff命令来描述文件内容具体的不同 [root@linuxprobe ~]# diff -c diff_A.txt diff_B.txt *** diff_A.txt 2020-08-30 18:07:45.230864626 +0800 --- diff_B.txt 2020-08-30 18:08:52.203860389 +0800 *************** *** 1,5 **** ! Welcome to linuxprobe.com Red Hat certified ! Free Linux Lessons Professional guidance Linux Course --- 1,7 ---- ! Welcome tooo linuxprobe.com ! Red Hat certified ! Free Linux LeSSonS ! ////////.....//////// Professional guidance Linux Course
uniq命令,用于去除文本中连续的重复行,英文全称为:“unique”,语法格式为:“uniq [参数] 文件名称”。 sort命令,用于对文本内容进行再排序,语法格式为:“sort [参数] 文件名称”。
2.7文件目录管理命令

touch 创建空白文件或修改时间
-a 修改读取时间
-m 修改修改时间
-d 同时修改a m
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-------. 1 root root 1213 May 4 15:44 anaconda-ks.cfg [root@linuxprobe ~]# echo "Visit the LinuxProbe.com to learn linux skills" >> anaconda-ks.cfg [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-------. 1 root root 1260 Aug 2 01:26 anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@linuxprobe ~]# touch -d "2020-05-04 15:44" anaconda-ks.cfg [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-------. 1 root root 1260 May 4 15:44 anaconda-ks.cfg
mkdir 创建空白的目录
mkdir -p /a/s/d/f 递归创建具有嵌套关系的文件目录
cp
-p 保留原始文件的属性 -d 若对象为“链接文件”,则保留该“链接文件”的属性 -r 递归持续复制(用于目录) -i 若目标文件存在则询问是否覆盖 -a 相当于-pdr(p、d、r为上述参数)
mv
rm
-f 强制执行 -i 删除前询问 -r 删除目录 -v 显示过程 rm -rf / 清空系统
dd
按照指定大小的数据块个数来复制文件或转换文件 语法格式为:“dd if=参数值 of=参数值 count=参数值 bs=参数值”。 if 输入的文件名称 input file of 输出的文件名称 output file bs 设置每个“块”的大小 数据大小 count 设置要复制“块”的个数 次数
file
查看文件的类型
[root@linuxprobe ~]# file anaconda-ks.cfg anaconda-ks.cfg: ASCII text [root@linuxprobe ~]# file /dev/sda /dev/sda: block special
tar
tar -czvf -c 创建压缩文件 -z 用Gzip压缩或解压 -v 显示压缩或解压的过程 -f 目标文件名 z = Gzip >backup.tar.gz j = bzip2 > backup.tar.bz2 -C 指定解压目录


