前后端分离djangorestframework——认证组件
authentication
认证是干嘛的已经不需要多说。而前后端未分离的认证基本是用cookie或者session,前后端分离的一般用token
全局认证
先创建一个django项目,项目名为drfversion,app名为DRF,设置简单的数据库表,并迁移:
model:

view:
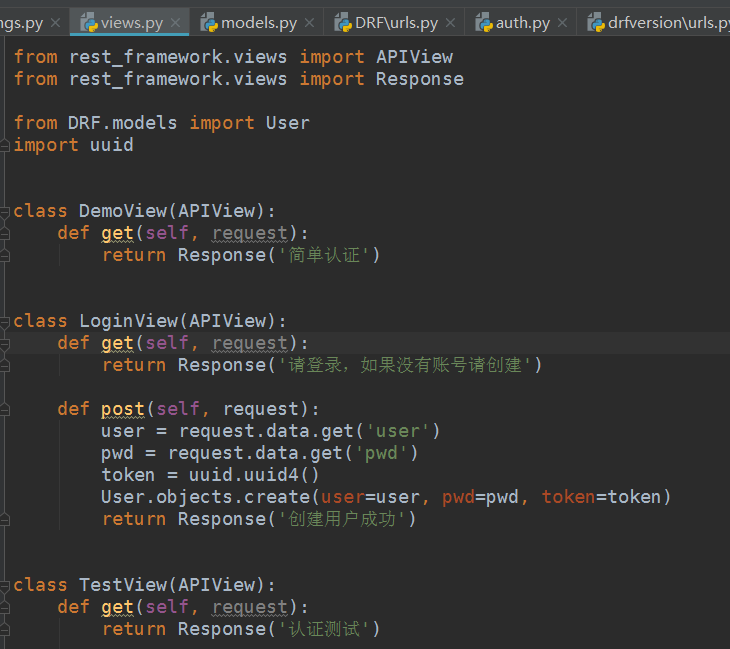
url:

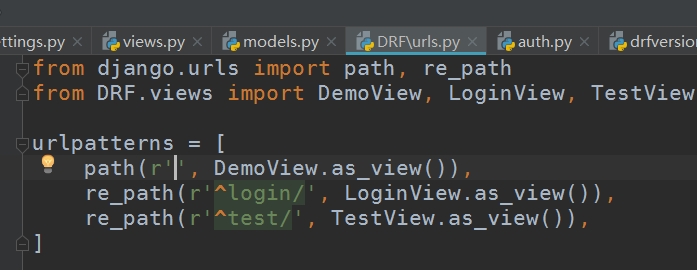
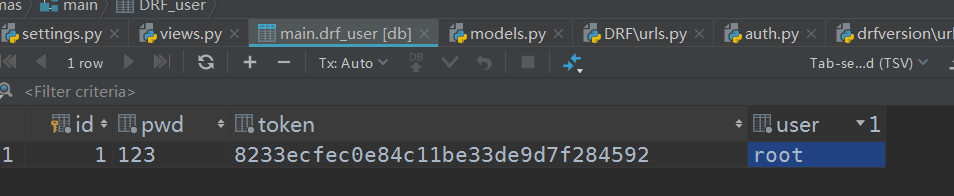
启动项目,访问测试,先创建一个用户root,密码123:
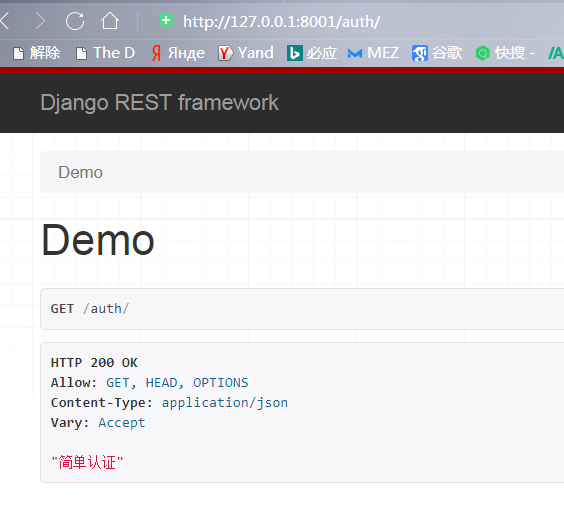

写入一个认证类,读源码可知,自定义的认证类必须要定义这个方法:

在项目根目录创建一个utils文件夹,创建auth文件,定义一个认证类,必须继承BaseAuthentication,注意我的代码获取token是通过url的条件而得,通过request.query_params获取:

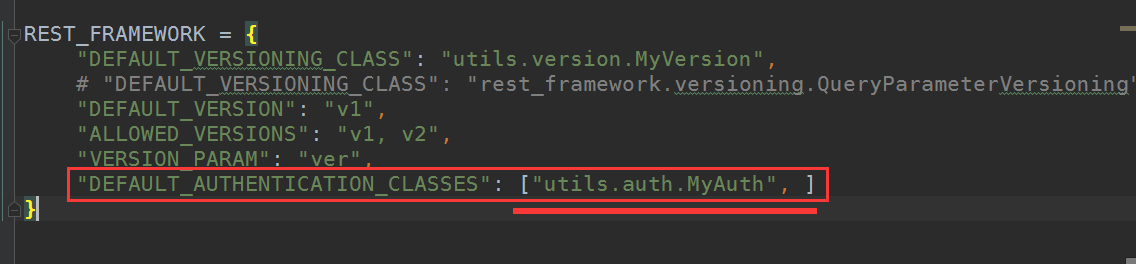
同样,要应用此认证类,读源码可知,需要在配置文件里作如下配置:
重启项目测试:
第一次,没有带值

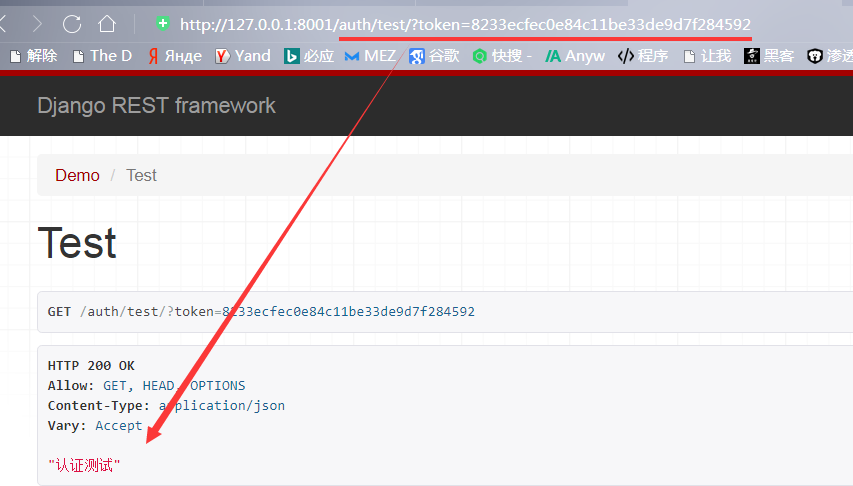
从数据库中复制该token值再次测试:

跳转到其他网页查看:
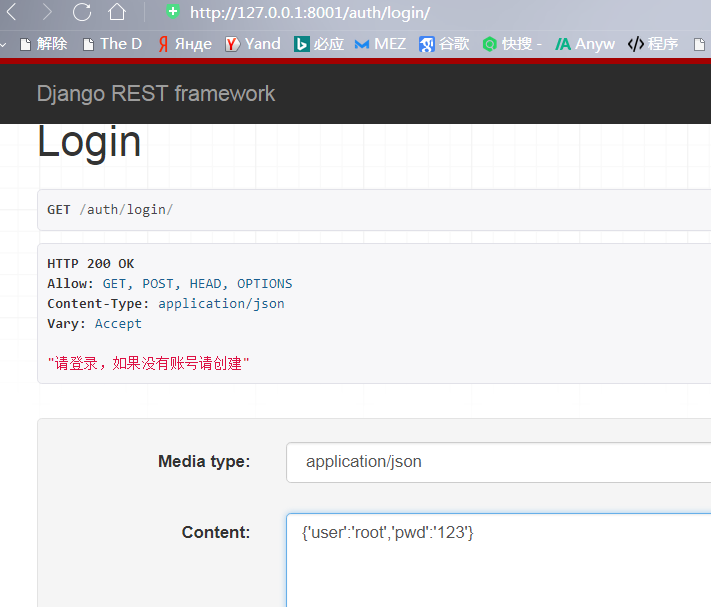
login登录页面也可以:

但是按开发逻辑,登录页面不应该验证token对吧?还没登录怎么能有token呢?是吧,所以不带token:

但是不带token此时又提示必须要带,所以这就是全局认证的弊端
局部认证
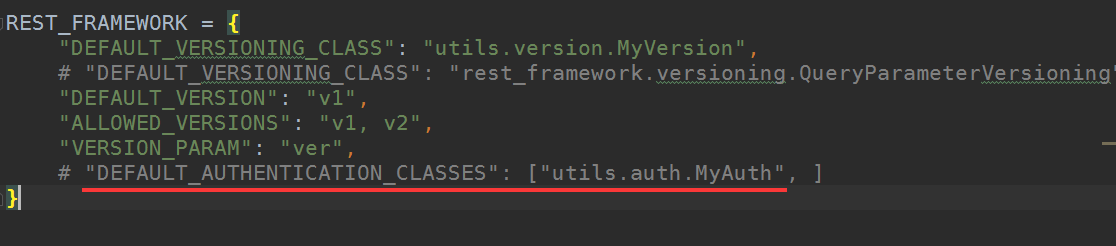
先在配置文件里注释掉全局认证:
在视图类里导入自定义的认证类,在需要认证的视图类添加一个类属性 :authentication_classes = [自定义认证类名,]
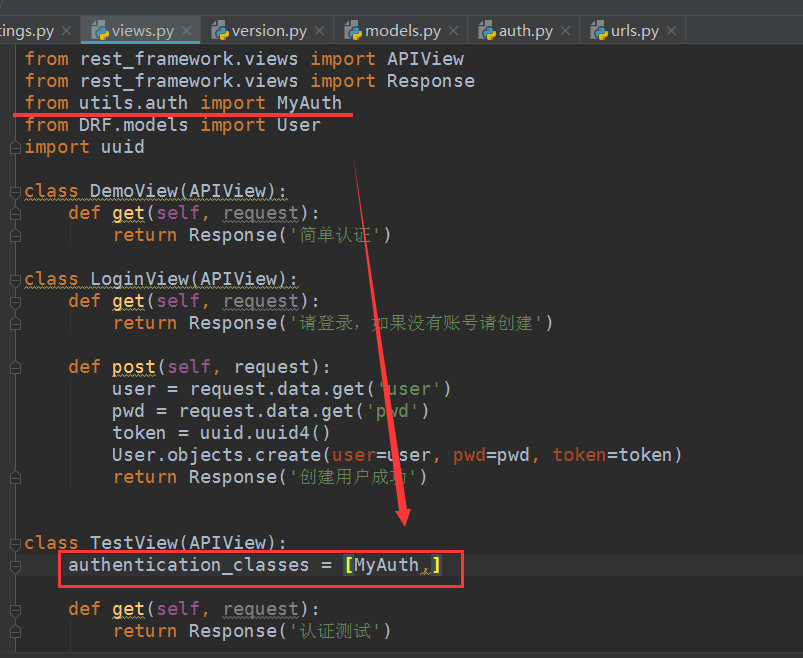
其他都不用修改,启动测试:
登录页面:
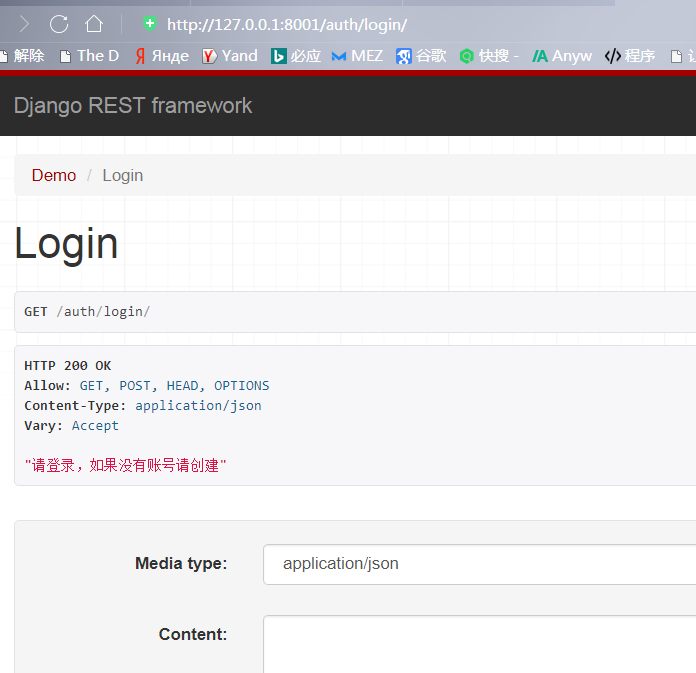
test页面,不带token:
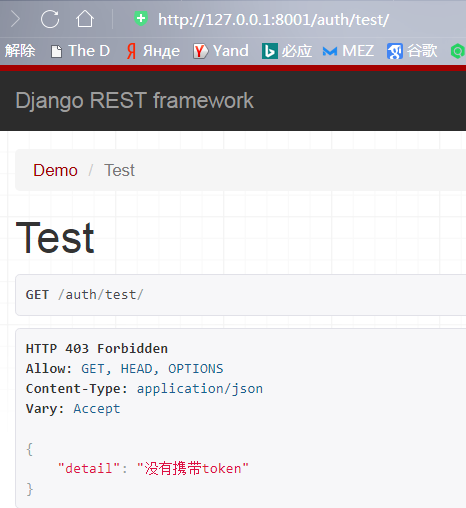
test页面,带上token:

DRF自带的认证类
看了源码,其实还有很多DRF自带的认证类,都在rest_framework.authentication里面,也可以根据需求直接选用DRF自带的认证类

以上项目主要的代码:
根url:
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, re_path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), re_path(r'auth/', include(('DRF.urls'))), ]
app下url:
from django.urls import path, re_path from DRF.views import DemoView, LoginView, TestView urlpatterns = [ path(r'', DemoView.as_view()), re_path(r'^login/', LoginView.as_view()), re_path(r'^test/', TestView.as_view()), ]
view:

from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.views import Response from utils.auth import MyAuth from DRF.models import User import uuid class DemoView(APIView): def get(self, request): return Response('简单认证') class LoginView(APIView): def get(self, request): return Response('请登录,如果没有账号请创建') def post(self, request): user = request.data.get('user') pwd = request.data.get('pwd') token = uuid.uuid4() User.objects.create(user=user, pwd=pwd, token=token) return Response('创建用户成功') class TestView(APIView): authentication_classes = [MyAuth,] def get(self, request): return Response('认证测试')
model:
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(models.Model): user = models.CharField(max_length=32, verbose_name='用户名', null=True, blank=True) pwd = models.CharField(max_length=32, verbose_name='密码', null=True, blank=True) token = models.UUIDField()
auth:
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed from DRF.models import User class MyAuth(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): # 认证token token = request.query_params.get('token') if not token: raise AuthenticationFailed('没有携带token') user_obj = User.objects.filter(token=token) if not user_obj: raise AuthenticationFailed('非法用户') return (user_obj, token)
settings:
REST_FRAMEWORK = { "DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS": "utils.version.MyVersion", "DEFAULT_VERSION": "v1", "ALLOWED_VERSIONS": "v1, v2", "VERSION_PARAM": "ver", # "DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": ["utils.auth.MyAuth", ] }
总结
- 自定义类,必须继承DRF定义好的认证类,需要用什么就继承什么,且根据继承的类不同,必须要定义该基类里明确规定需要的方法或者属性
- 全局认证直接在配置文件里的REST_FRAMEWORK里配置字段"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": ["自定义认证类", ],配置全局认证即表示每个页面都要验证
- 局部认证直接在需要认证的视图类添加属性authentication_classes = [自定义认证类名,]
- 认证可以再url添加条件参数,可以再请求头,可以再请求体,根据认证类的认证类型,在认证时做不同的处理






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】